Java CountDownLatch
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is CountDownLatch in Java?
A synchronization aid that allows one or more threads to wait until a set of operations being performed in other threads completes.
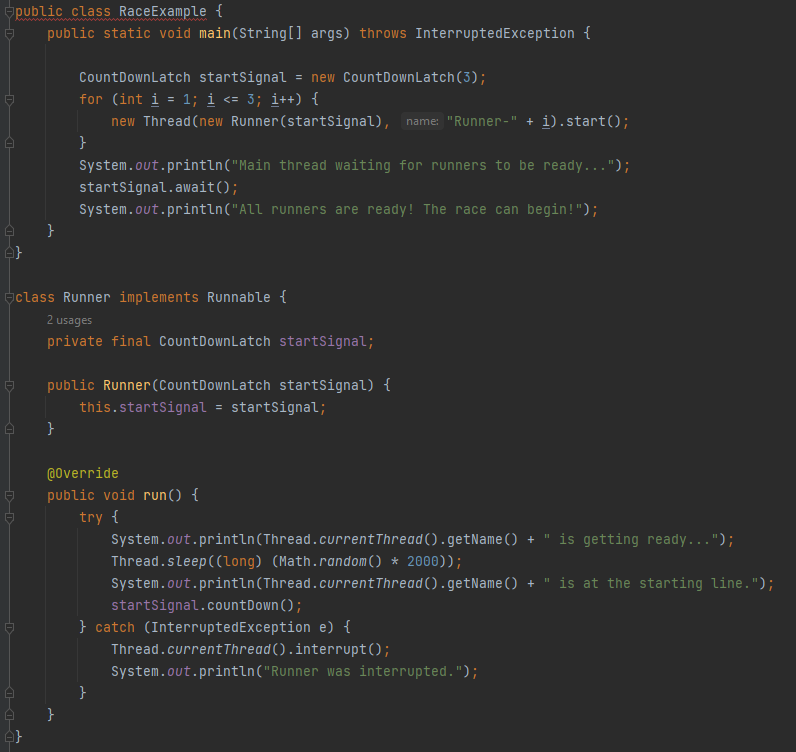
Which package contains CountDownLatch?
java.util.concurrent
What is the main use of CountDownLatch?
To block a thread until a set of tasks have been completed.
How do you initialize a CountDownLatch?
By specifying the number of times countDown() must be called before threads can proceed, e.g., new CountDownLatch(3).
What does await() do in CountDownLatch?
Causes the current thread to wait until the latch has counted down to zero.
What does countDown() do?
Decrements the count of the latch by one.
What happens if the count is already zero and await() is called?
The thread does not block and proceeds immediately.
Is CountDownLatch reusable?
No, once the count reaches zero, it cannot be reset.
What exception does await() throw?
InterruptedException if the waiting thread is interrupted.
How can you use CountDownLatch for starting multiple threads at the same time?
Use one latch to block all worker threads until the main thread calls countDown(), then they proceed together.
Can await() be timed?
Yes, using await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit).
What happens if the timeout expires in await(long, TimeUnit)?
Returns false and the thread continues execution without waiting for count to reach zero.
How do you check current count of a latch?
Using getCount().
What is a common use case of CountDownLatch?
Waiting for multiple threads to finish their tasks before proceeding (e.g., in test setup or shutdown sequences).
What is the default behavior of await()?
It blocks the thread until the latch count reaches zero or it's interrupted.
Can multiple threads call await() on the same CountDownLatch?
Yes, all waiting threads will proceed once the count reaches zero.
What happens if countDown() is called more times than the initial count?
Extra calls have no effect once count reaches zero.
What is the alternative if you want a reusable latch?
Use CyclicBarrier or Semaphore.
Is CountDownLatch thread-safe?
Yes, all methods are atomic and thread-safe.
Can CountDownLatch be used for testing concurrency code?
Yes, it's often used to coordinate test setup or verify execution order in concurrent unit tests.