Chemistry Kinetics
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for 3.1.5 Kinetics Chemistry (A Level)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Collision theory
AQ reactionwill occur only if the particles collide with sufficient energy (i.e. more than the activation energy, Ea)
Transition state
A very unstable state where bonds are broken and made
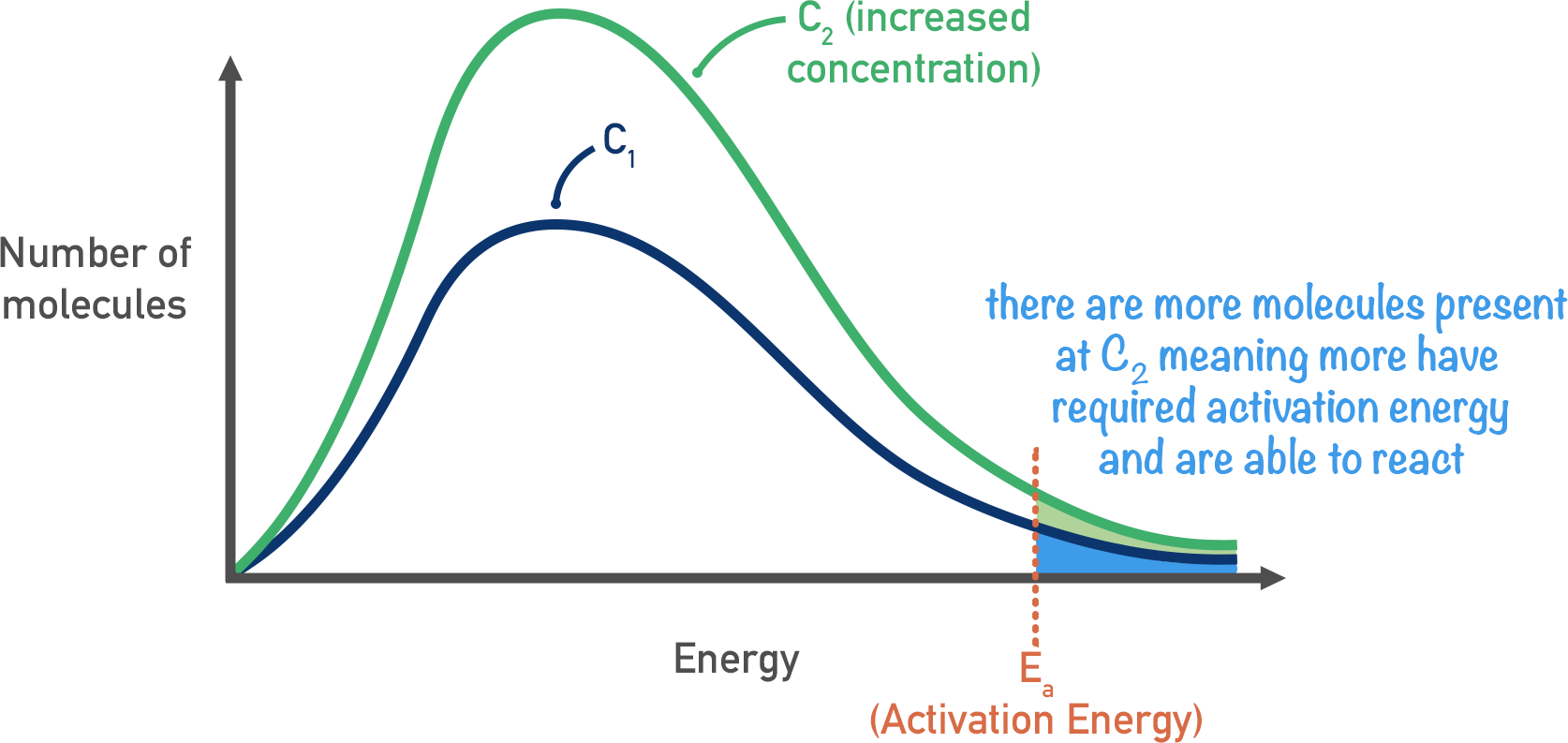
What is the affect on increasing concentration
Twice as many reactant particles H+ in same volume. Double collision frequency. DOuble the number of successful collisions with energy > activation energy so rate doubles
Average rate of reaction equation
Total volume of product/ time take to form
activation energy
Enthalpy difference between reactants and the transition station state or the minimum energy required for a reaction to occur when particles collide.
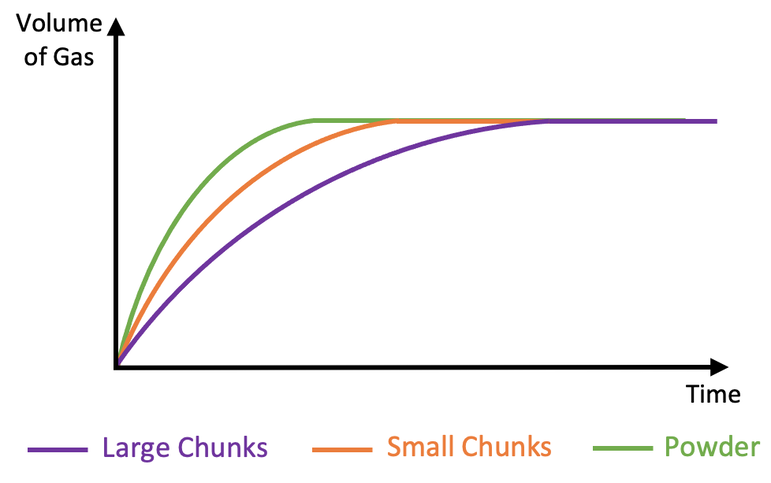
Effect of surface area on reaction (How quick;y gas is produced)
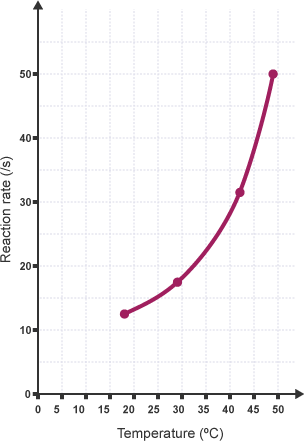
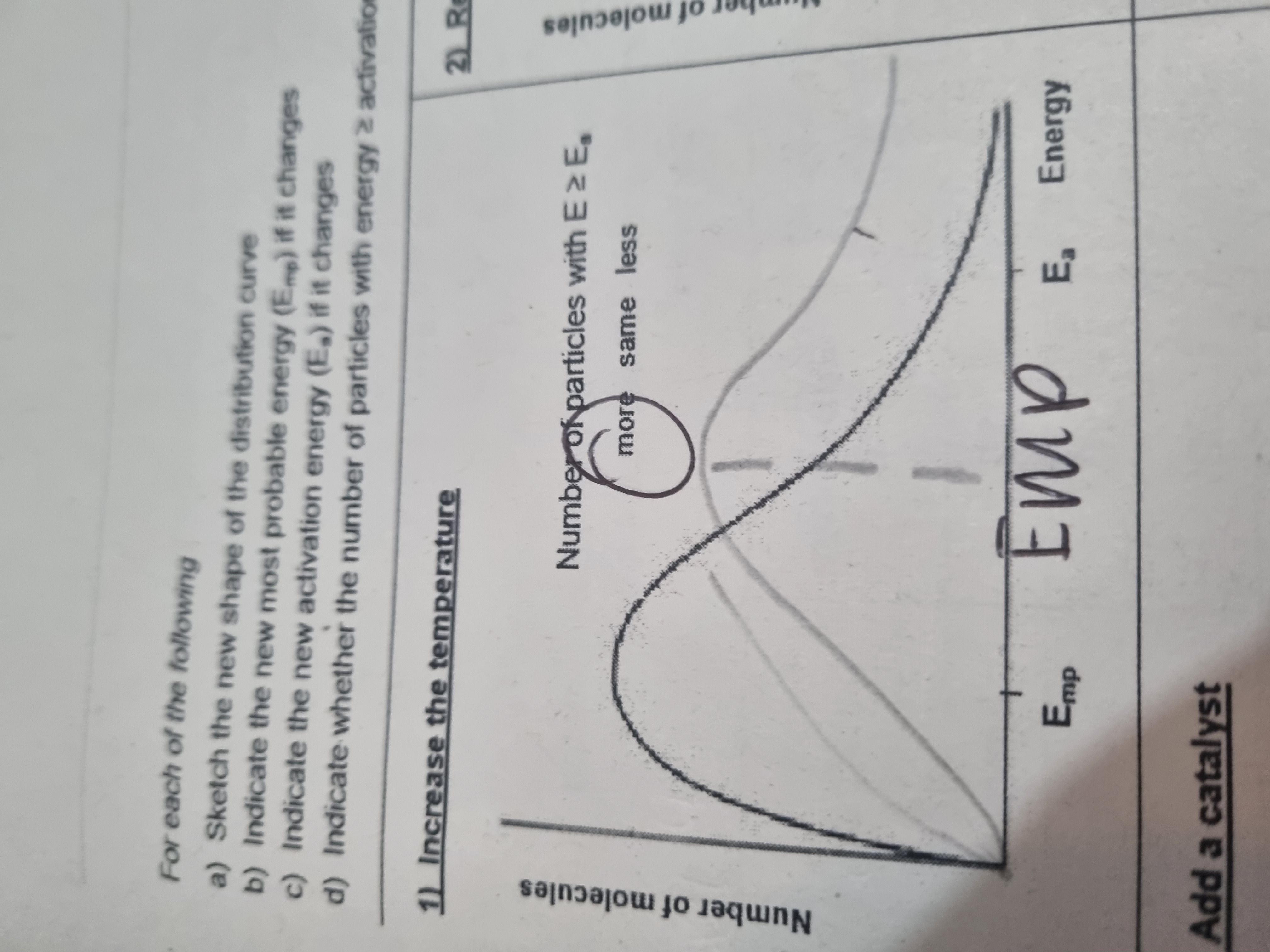
What actually is the effect of increasing temperature on the rate of reaction
Increasing the temperature increases the mean kinetic energy of the particles so they move faster. There is a greater collisions frequency and many more particles have energy> activation energy
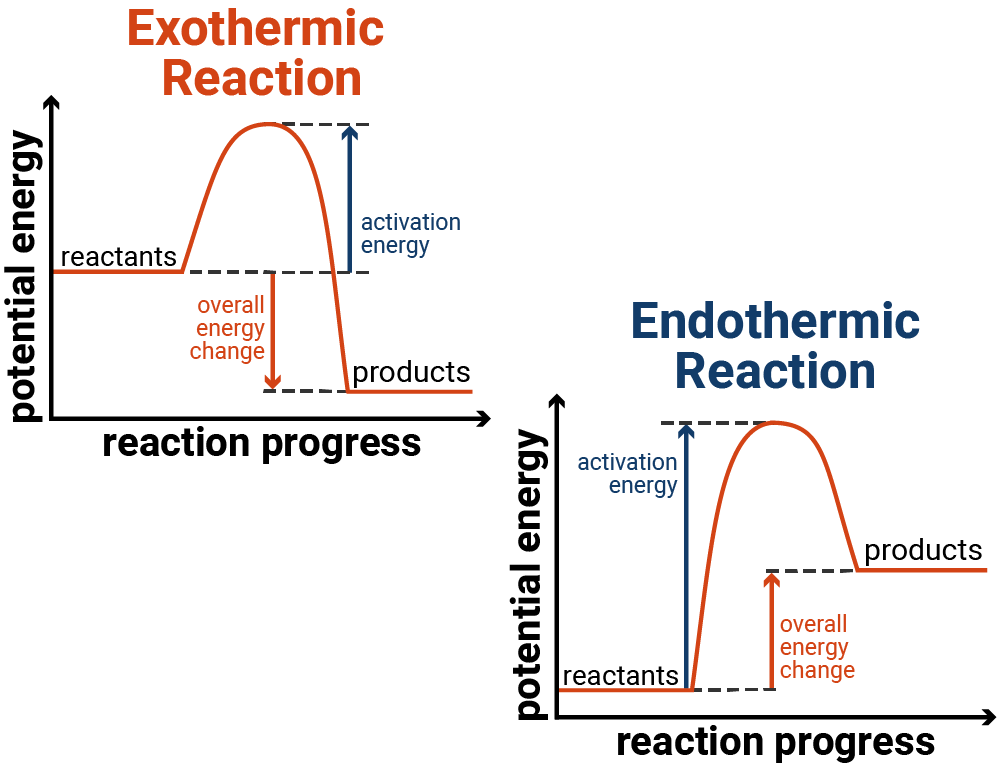
Energy profile for endothermic and exothermic reactions
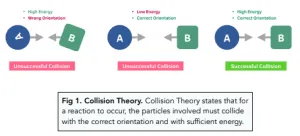
Collision orientation
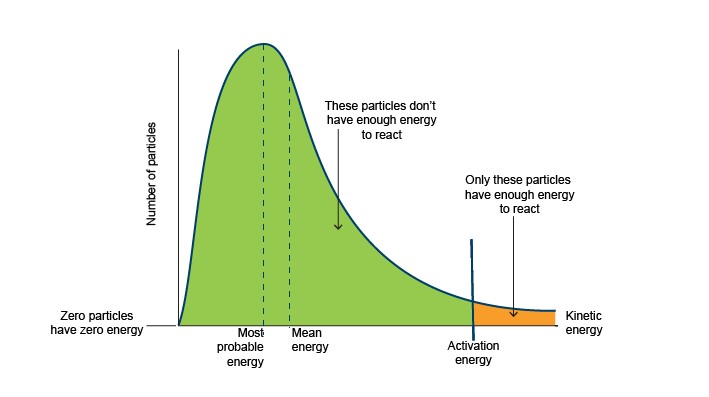
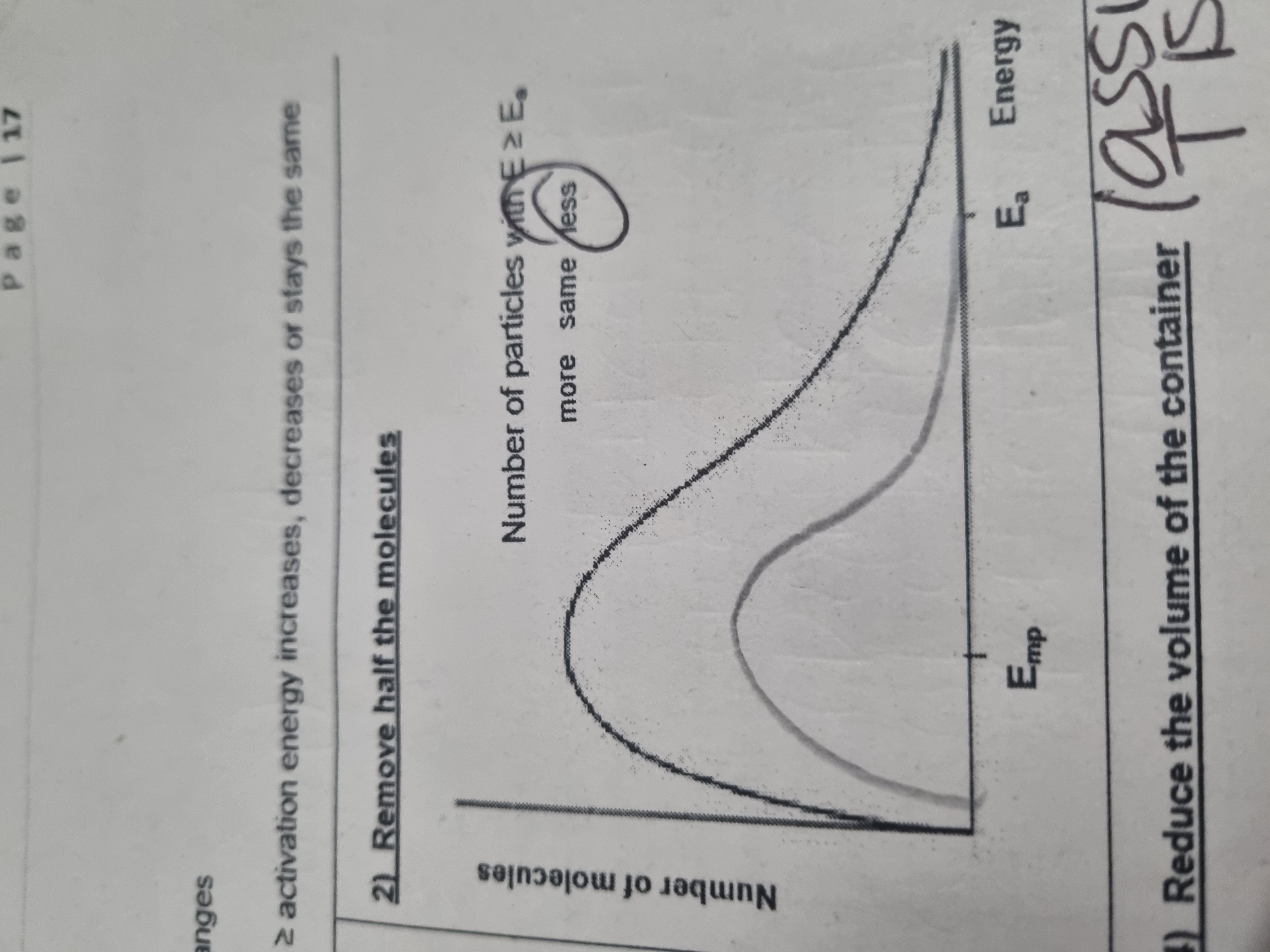
What exactly is the Maxwell Boltzmann curve?
Shows the distribution of molecular energies in a gas at a constant temperature
Maxwell Boltzmannn curve image
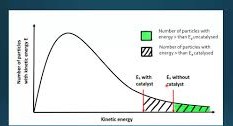
How does a catalyst effect the distribution in molecular energies?
It does not
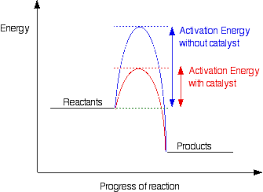
What happens when a catalyst is added during a reaction
More molecules in the system have an energy in excess of the new lower activation energy. More successful collisions occur in a given length of time (the rate of reaction increases.)
What does the Maxwell boltzman distribution show in terms of the particles
total rea under the curve represents number of molecules
The curve starts at origin as it is impossible for a molecule to possess 0 energy unless at 0 kelvin (in terms of temperature)
Asymptotic graph (graph does not touch x axis) therefore theoretically, infinite number of molecular energies
The curve shows most particles contain intermediate energy

What does the Ea section mean in the Maxwell Boltzman distribution curve
Only molecules with energy greater than or equal to activation energy can react by collision (little number of particles)
Where is most probable energy on a maxwell boltzman curve
Highest peak of the curve
Where is the mean energy on a maxwell boltzmann curve
Lies to the right of the most probable energy
Maxwell boltmann curve (increased concentration)
Catalysis diagram (reaction profile with and without a catalyst)
Maxwell Boltzmann curve with catalyst
Homogeneous catalysis:
the catalyst and reactants are in the same phase

Heterogeneous catalysis
The catalysts and reactants are in different phases
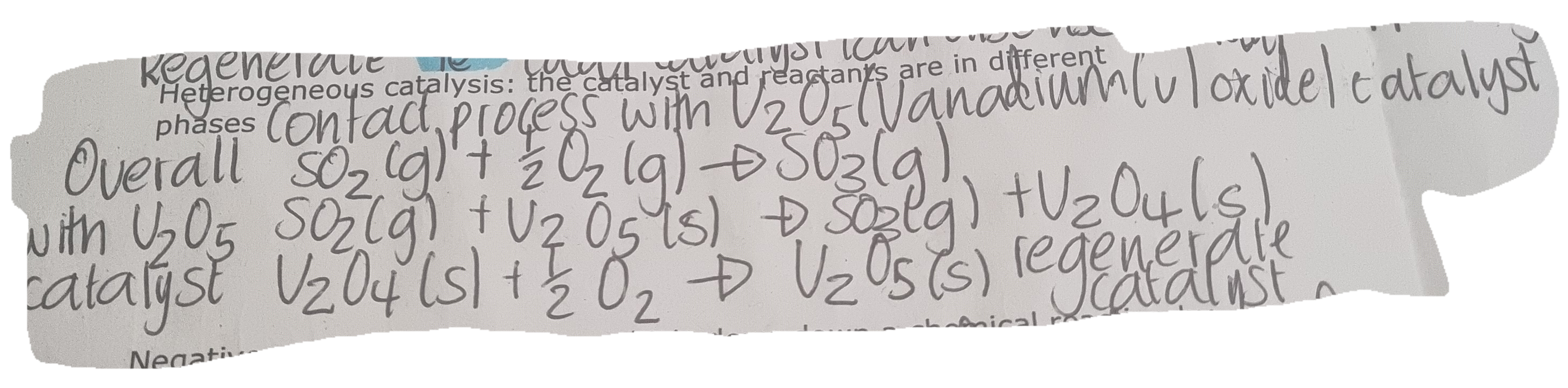
Negative catalyst
A substance whuch slows down a chemical reaction by blocking the pathway to reaction. E.g antimony oxide is used as a flame retardant in plastics.
Graph of rate against concentration for sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid
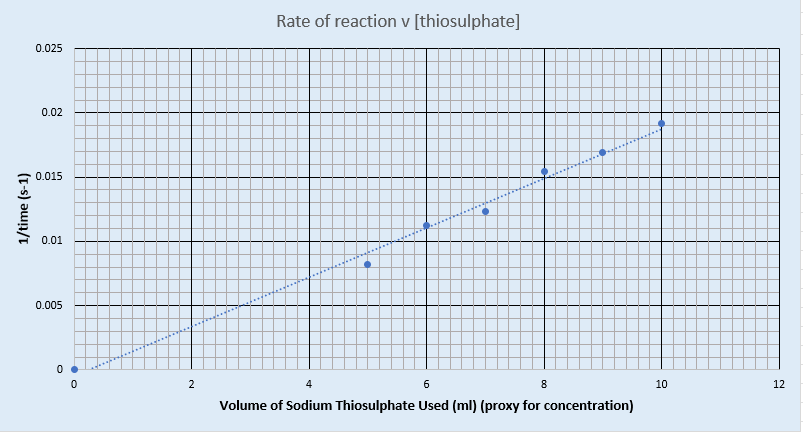
Graphs of rate against concentration for sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid (temperature)
Graph looks like this
How can collision frequency be changed in a chemical system
Increase of concentration = increased collision freq, increase pressure = increase collision freq, increased temperature = increase collision freq, addition of catalyst = constant collision freq
How can number of reactant particles be changed in a chemical system
Increase of concentration =increase number of reactant particles , increase pressure = increase number of reactant particles ,increased temperature = constant number of reactant particles , addition of catalyst =constant number of reactant particles ,
How can activation energy be changed in a chemical system
Increase of concentration = constant activation energy , increase pressure =constant activation energy ,increased temperature = constant activation energy , addition of catalyst =lower activation energy ,
How can number of particles with energy above activation energy be changed in a chemical system
Increase of concentration = increased number of particles (constant proportion) , increase pressure =increased number of particles (cosntant porportion) ,increased temperature = increased number of particles (increased proportion) , addition of catalyst = Increased number of particles (increased proportion) ,
How can most probable energy be changed in a chemical system
Increase of concentration = consant , increase pressure = constant ,increased temperature = increase , addition of catalyst = constant ,
How can the number of particles with most probable energy be changed in a chemical system?
Increase of concentration = increase , increase pressure = increase ,increased temperature = decrease , addition of catalyst = constant ,
What does increasing temeperature do to the distribution curve?
What does adding a catalyst do to the distribution curve
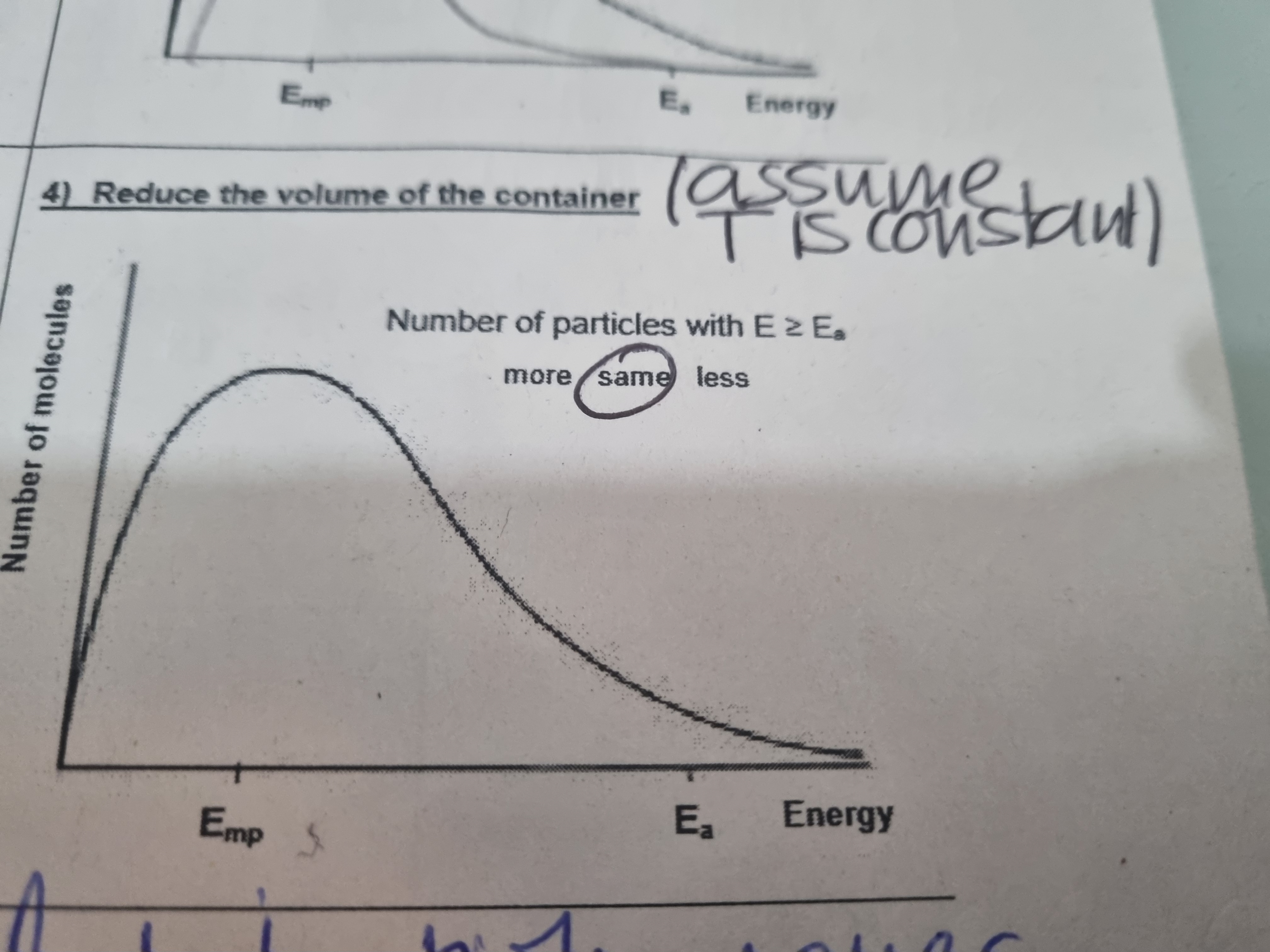
What does reducing the volume of the container do to the distribution curve
What does removing half the molecules do to the distibution curve
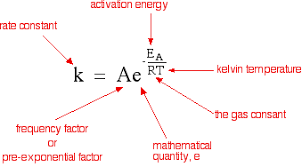
The Arrhenius Equation
Negative Catalyst
A substance which shows down a chemical reaction by blocking the pathway to reaction.
Why are ionic precipitation reactions almost instantaneous
When an ionic solid is dissolved in water the ions become completely seperated. The free ions in the solution can collide and react easily