Science Physics
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Force
A push or a pull or twist
Buoyancy
The ability of a fluid to exert an upward force on an object placed in it
Achimedes' Principle
when an object is placed in a fluid, the fluid pushes up on it with a force equal to the weight of the fluid the object displaces. If this upward force is greater than the object's weight, it floats; if it's less, the object sinks.
static friction
The object does not move, when a applied force is not big enough to over come the frictional force
kinetic energy
the friction between two or more moving surfaces. This could be sliding or rolling
Friction
A force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact
How to increase friction
Make surface rougher or bumpier e.g. sand on icy roads to stop cars from skidding
Newton's Frist Law of Motion
"An object at rest, or in motion, will stay at rest, or in motion, unless acted upon by an outside, unbalanced force."
Newton's Second Law
F = m x a
Force = mass x acceleration
Newton's Third Law
"For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction"
Velocity
the speed of an object with direction
Acceleration
a change in velocity (speeding up or slowing down)
Inertia
The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion
Mechanical Advantage
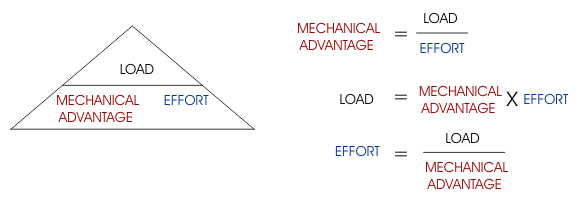
Contact Forces
are those types of forces that result when the two interacting objects are perceived to be physically contacting each other.
Non contact forces
the types of forces that result even when the two interacting objects are not in physical contact with each other yet are able to exert a push or pull despite their physical separation.
Constant Force
is speed maintained over time. To achieve a constant speed an object has to cover the for equal intervals over time
Energy
Energy is the ability to do work
Effort
is an applied force to bring desired change to the position
Wedge
variations of an inclined plane
and is a simple machine that changes either the size of a direction of a force
A wedge uses
cut. Knife
split/axe
lever
a simple machine that consists of a rigid bar or plank that pivots around a fixed point called a fulcrum. It is used to move or lift loads with less effort. Levers work on the principle of mechanical advantage, allowing a smaller force to move a larger load by increasing the distance over which the force is applied.
1st class lever
The fulcrum is positioned between the effort (force applied) and the load. An example is a seesaw.
2nd class lever
The load is between the fulcrum and the effort. An example is a wheelbarrow.
3rd class lever
The effort is applied between the fulcrum and the load. An example is a pair of tweezers.
Gravity
is the invisible force that attracts objects toward each other, especially pulling smaller objects toward larger ones like Earth. It keeps planets in orbit, gives weight to objects, and influences the structure of the universe.
The formula for work
W=FxD
Force times distance