Hypothesis Testing
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is the Null Hypothesis?
The Null Hypothesis, denoted by H₀, is a statement about a population parameter that we test using data from a random sample.
What is the Alternative Hypothesis?
The Alternative Hypothesis, denoted by H₁, is the hypothesis we accept if the null hypothesis (H₀) is rejected.
How is the null hypothesis usually written?
The null hypothesis is usually simple, meaning it specifies an exact value of the parameter, such as:H₀: θ = θ₀
When is the alternative hypothesis composite?
The alternative hypothesis is composite when it specifies a range of values, such as:
H₁: θ > θ₀
H₁: θ < θ₀
H₁: θ ≠ θ₀
What is a Type I error?
A Type I error occurs when we reject the null hypothesis (H₀) even though it is actually true.
How is the probability of a Type I error denoted?
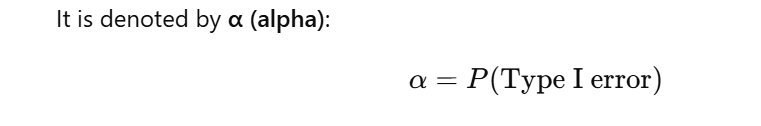
What is the significance level of a test?
The significance level is α, which is also called the size of the test.
What is a Type II error?
A Type II error occurs when we accept the null hypothesis (H₀) even though it is actually false.
How is the probability of a Type II error denoted?
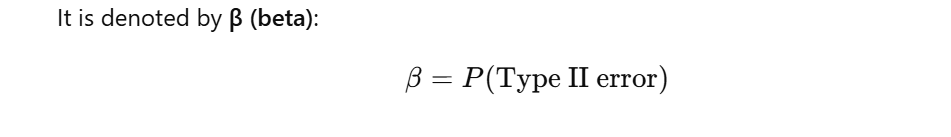
What is the power of a test?
The power of a test is the probability that we correctly reject H₀ when it is false.
How is power written mathematically?
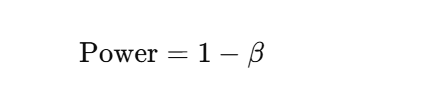
What defines a hypothesis test?
A hypothesis test is defined by its critical region.
What is the critical region?
The critical region is the set of values of the test statistic for which we reject the null hypothesis (H₀).
What determines the critical value k

What does the size of the test mean?

What does the power of a test depend on?
