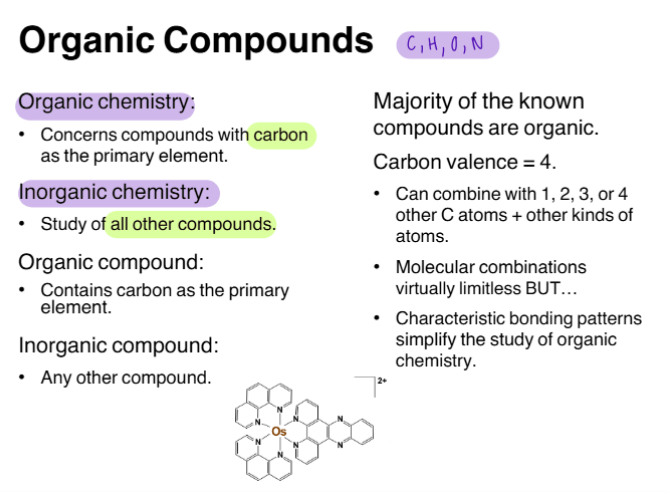
CH. 12 | Organic Compounds
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Organic Compounds
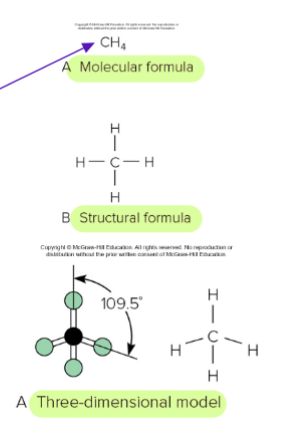
Hydrocarbons
Organic compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen
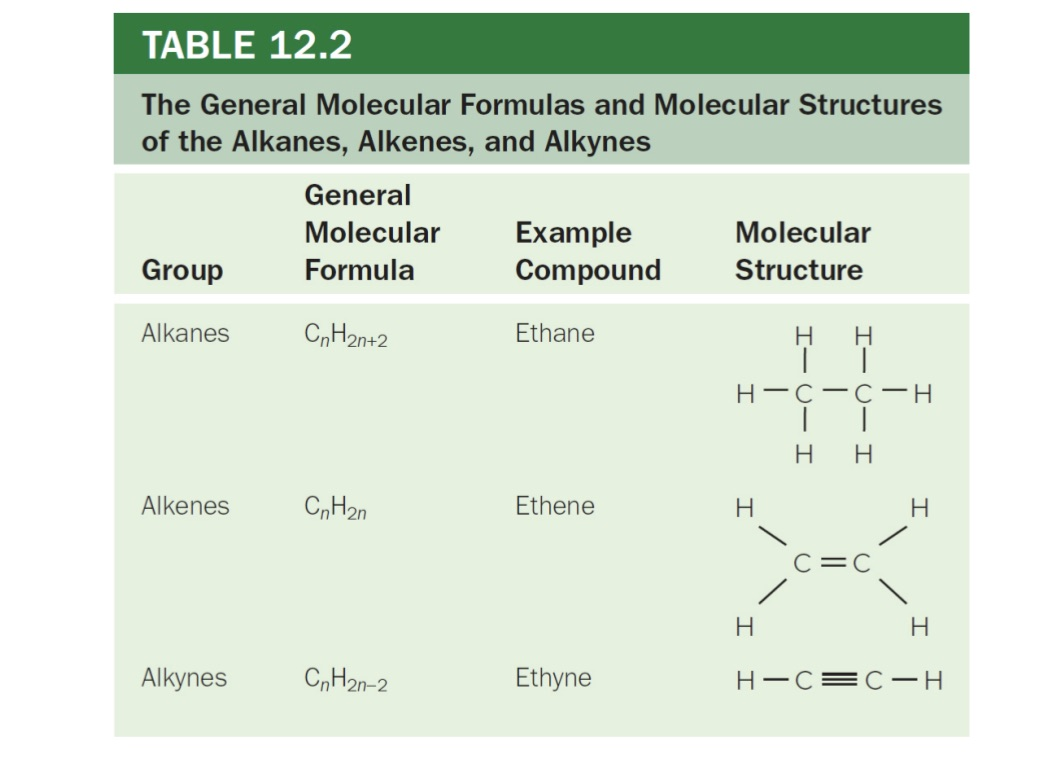
3 Types of Hydrocarbons
Alkanes (single bond)
Alkenes (double bond)
Alkynes (triple bond)
Saturated vs. Unsaturated
Saturated
Single bonds
All carbons are bonded to a max of 4 atoms
Unsaturated
Double or Triple bonds
Carbons are bonded to 2 or 3 atoms
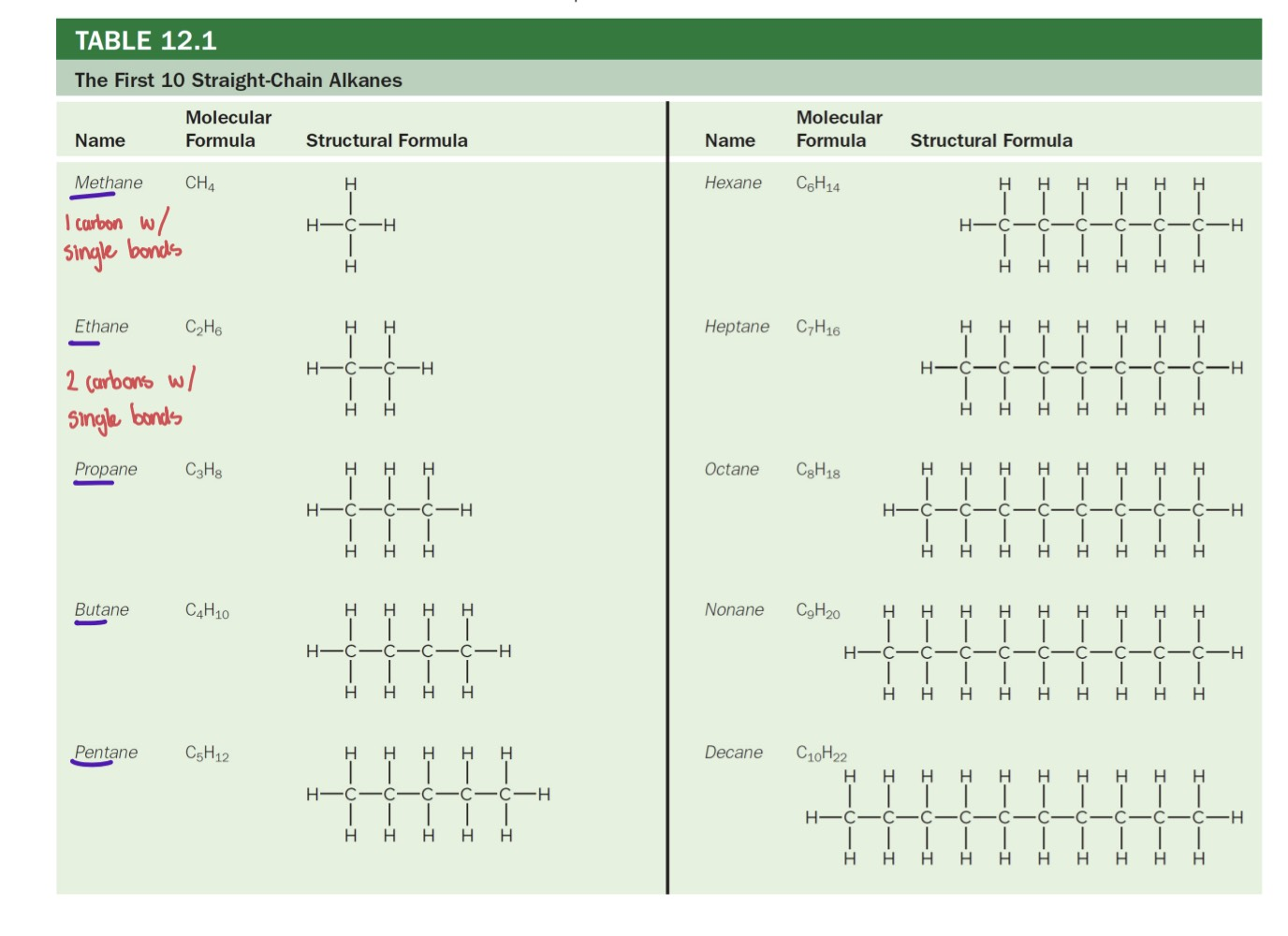
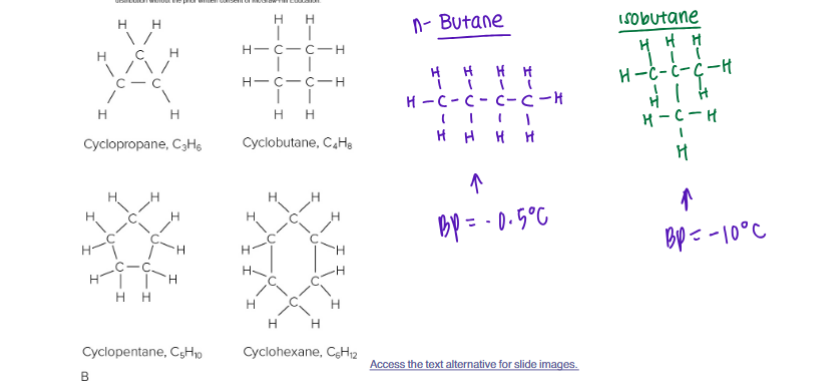
Alkanes
CnH2n+2
Hydrocarbons with all single carbon-carbon bonds
Can form straight, branched, or ring structures
Saturated
Picture
Alkenes
CnH2n
Hydrocarbons with a double carbon-carbon bond
Unsaturated
Alkynes
CnH2n-2
Hydrocarbons with a triple carbon-carbon bond
Unsaturated
Picture
Isomers
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures
Straight chains
Branches and rings
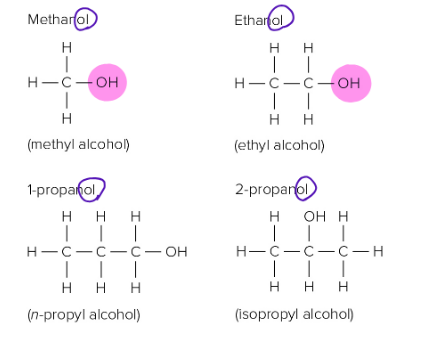
Alcohols
One or more hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups
Can be mixed with 6 carbons or under
Gasohol , solution of ethanol and gasoline
Functional Groups
Responsible for chemical properties of organic compound
Usually has multiple bonds or lone pairs of electrons that cause them to be sites of reactions
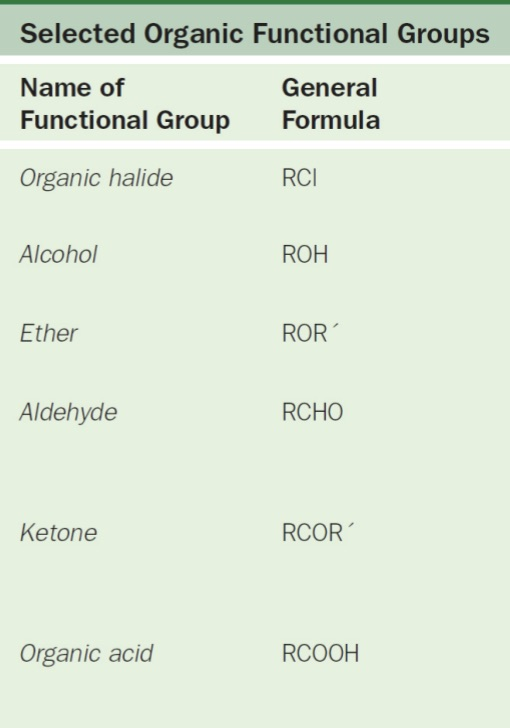
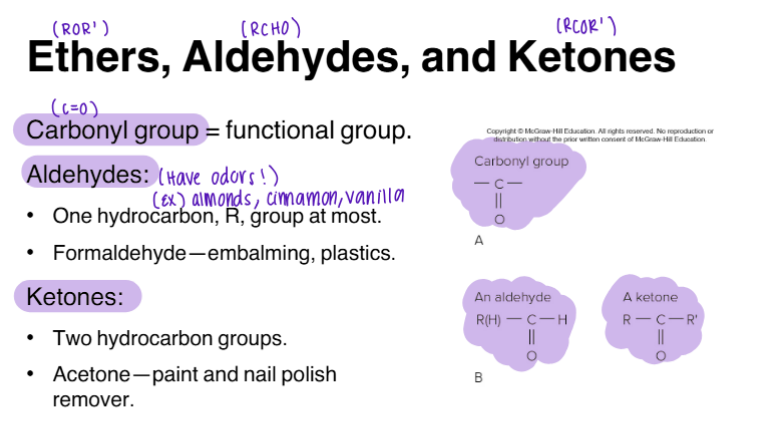
Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
R = Hydrocarbon
R1 = 2nd group of Hydrocarbon
Types of macromolecules
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Fats and oils
Nucleic acids
Proteins
Macromolecular polymers of smaller amino acids (20)
Polypeptides
Sequence of amino acids in chain determines biochemical properties
Carbohydrates
Watered carbon

Fats and Oils
Esters formed from glycerol and three long-chain carboxylic acid