BIOL 251 Microbiology Week 11 Lecture Notes
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microbiology: An Introduction 13th Edition - Ch. 8 - 9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Genetics
The study of how traits and characteristics are passed from one generation to the next through DNA.
Focuses on how microbes inherit, express, and mutate genes.
Chromosomes
Structures made of DNA and proteins (mostly histones in eukaryotes) that carry genetic information.
Bacteria typically have a single circular chromosome, while eukaryotic cells have multiple linear chromosomes.
Genes
Specific segments of DNA that code for proteins or functional RNA. Each gene is a unit of heredity and determines particular traits or functions
Genome
The entire set of genetic material in an organism.
Includes chromosomes, plasmids (in bacteria), and any other genetic elements.
Genetic Code
The set of rules by which the sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA is translated into the amino acid sequence of proteins.
DNA
AKA Genetic blueprint
2 functions
Double helix backbone
Antiparallel strands
Sugar phosphate backbone
Two strands held by hydrogen bond
Central Dogma
The theory that genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to protein
Single circular
Short tandem
_____ _____ Chromosome: Composed of DNA and protein
_____ _____ Repeats: Repeating sequences of non-coding DNA
Vertical
Horizontal
_____ Gene Transfer: Flow of genetic information from one generation to the next
_____ Gene Transfer: Transfer of genes between cells of the same generation
DNA Polymerase
Okazaki
ligase
Adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand during DNA replication. Goes in the 5’ → 3’ direction
Initiated by RNA primer
Leading strand is synthesized continuously
Lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously, creating _____ fragments
DNA Polymerase removes RNA primers, Okazaki fragments are joined by DNA _____
bidirectional
In prokaryotes, DNA replication is _____: occurs in two opposite directions from a single origin of replication
rRNA
tRNA
mRNA
_____: Integral part of ribosomes
_____: Transports amino acids during protein synthesis
_____: Carries coded information from DNA to ribosomes
Terminator
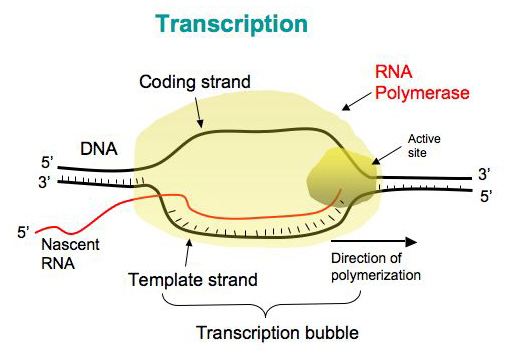
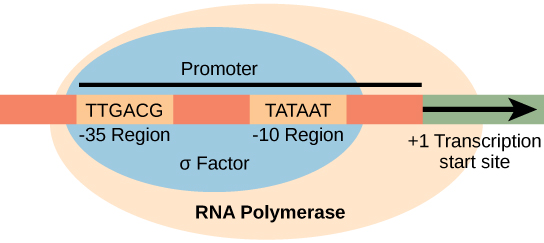
Transcription in Prokaryotes
Synthesis of complementary mRNA strands
RNA polymerase
Promotor
_____
Proceeds in the 5’ → 3’ direction
Translation
When mRNA is translated into the “language” of proteins
Codons
61 sense codons - 20 amino acids
1 start codon - AUG
3 nonsense codons - UAA, UAG, UGA
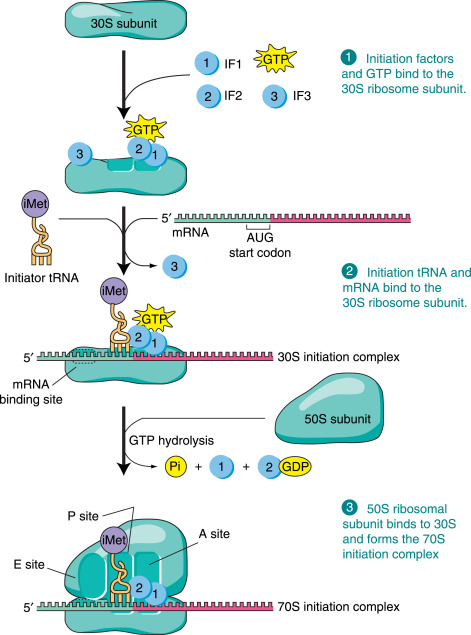
Ribosomes
Initiation, Elongation, Termination
What is the site of translation?
tRNA
anticodon
What are the 3 steps involved?
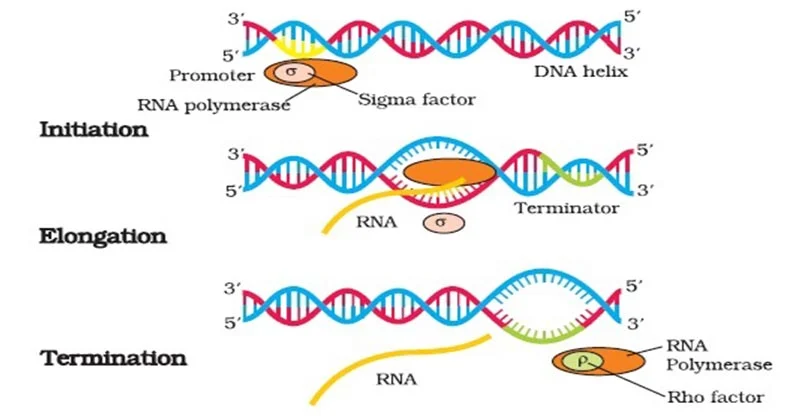
A
P
E
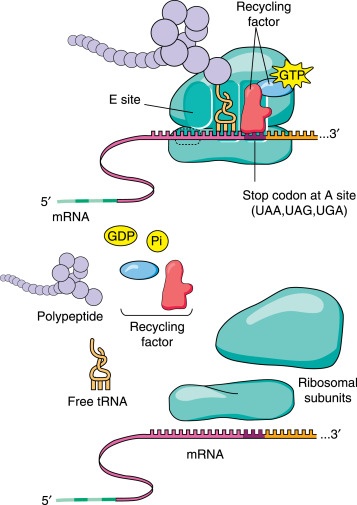
Ribosomes have 3 binding sites for tRNA;
___ Site: The entry point on the ribosome for a new tRNA carrying an amino acid.
It matches the anticodon of the tRNA with the codon on the mRNA strand.
___ Site: Holds the tRNA with the growing polypeptide chain.
The amino acid from the A site is joined to the chain here by a peptide bond.
___ Site: Where the empty tRNA (after it has donated its amino acid) is moved before it exits the ribosome.
fixed
inducible, repressible
Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression
Constitutive genes are expressed at a fixed rate
Not under control
Enzymes involved in glycolysis
Other genes are expressed as needed
_____ genes and _____ genes
Control mechanism: Induction and Repression
Regulates transcription of mRNA
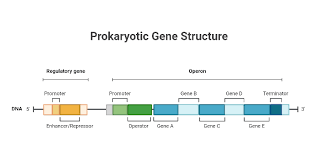
Promoter
Segment of DNA where RNA polymerase initiates transcription of structural genes
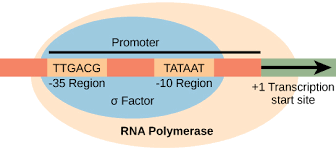
Operator
Segment of DNA that controls transcription of structural genes
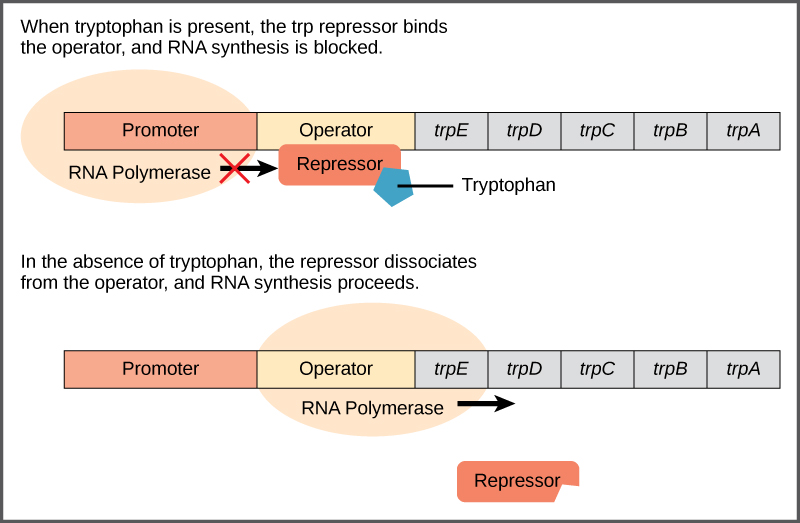
Structural Genes
Region of DNA that codes for specific protein
Mutation
Mutagen
Spontaneous
A permanent change in the base of sequence DNA
May be neutral, beneficial, or harmful
_____: Agent that causes mutations
_____ mutation: Occur in absence of mutagens
Point
Frameshift
_____ mutation: Change only one base pair
Base substitions
Silent, Missense, Nonsense mutations
_____ mutation: Insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotide pairs
Shifts the translational “reading frame”
Silent
Missense
Nonsense
_____ mutation: Normal protein
Does not change amino acid sequence
_____ mutation: Faulty protein
Amino acid is changed
_____ mutation: Incomplete protein
Results in stop codon
Chemicals
Radiation
What are some examples of mutagens?
Nucleotide
Direct
DNA Repair
Proofreading
DNA Polymerase
Mismatch pair
Exonuclease
DNA Polymerase
Ligase
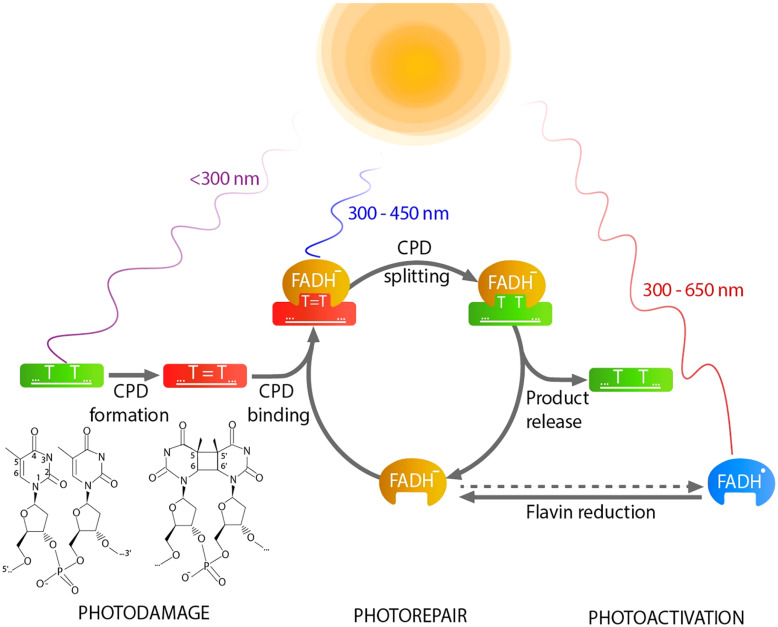
Repair of thymine dimers
_____ Excision repair: DNA polymerase, ligase
_____ Repair: Visible light photolyase
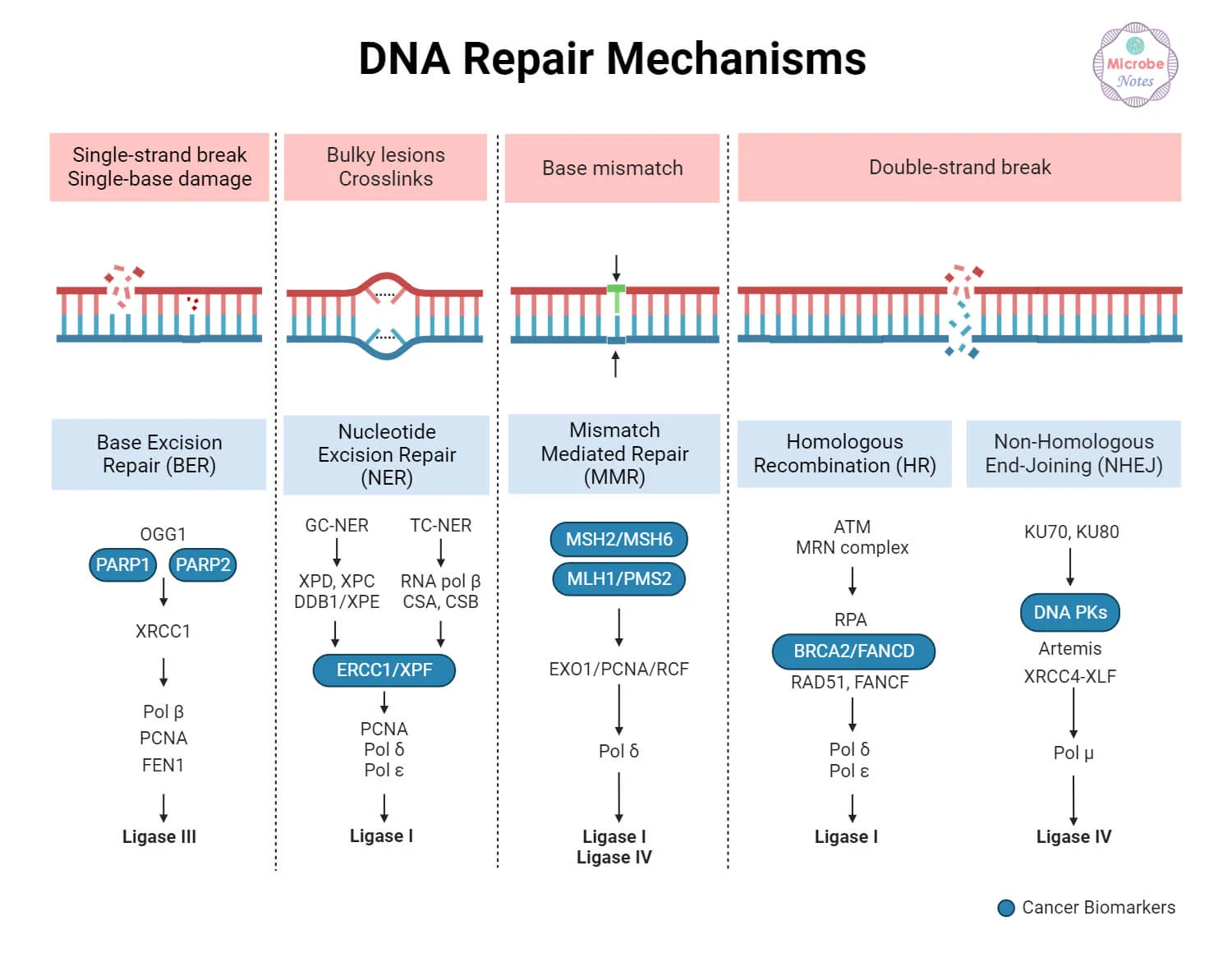
Genetic
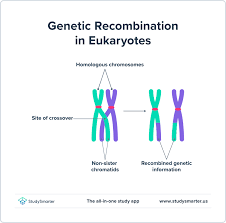
Crossing over
_____ Recombination: Exchange of genes between two DNA molecules
_____ _____: Two chromosomes break apart and rejoin
Insertion of foreign DNA into chromosome
RecA Protein
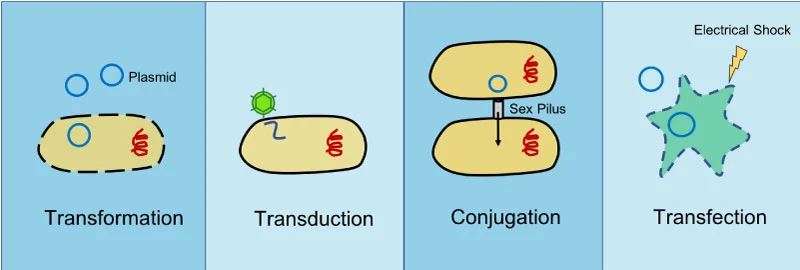
Transformation
Conjugation
Transduction
Types of Horizontal Gene Transfer
_____: Genes transferred from one bacterium to another as “naked” DNA
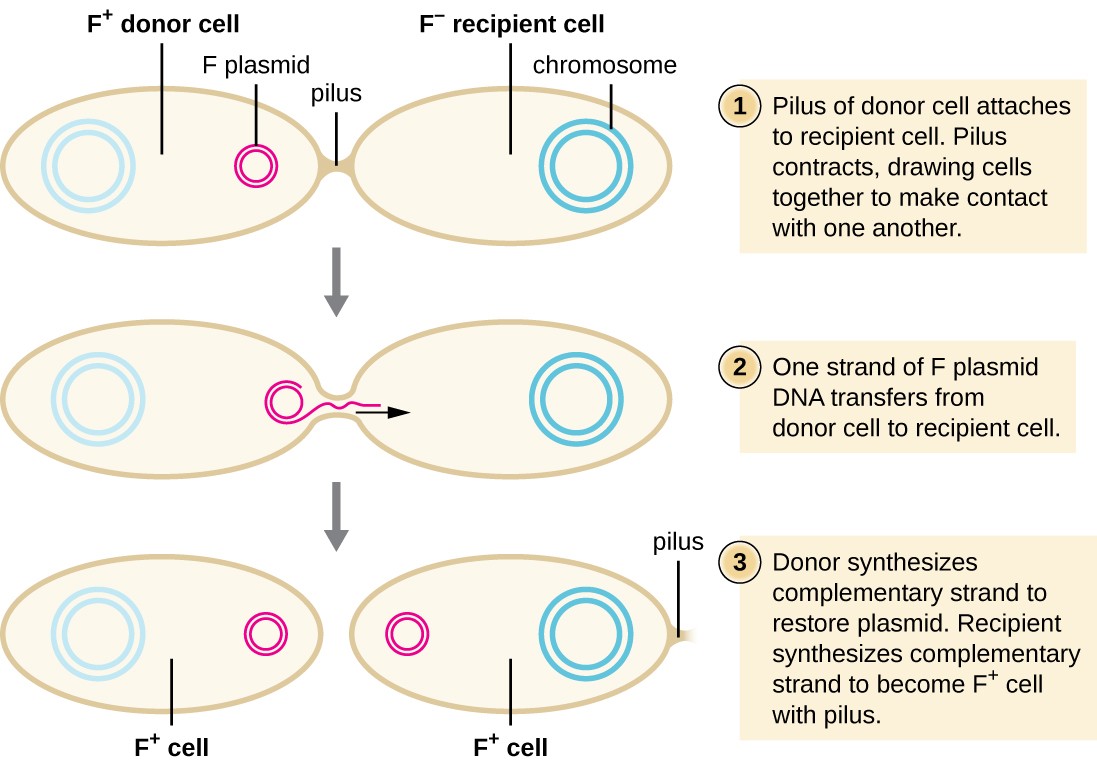
_____: Plasmids transferred from one bacterium to another
Requires cell to cell contact - sex pili
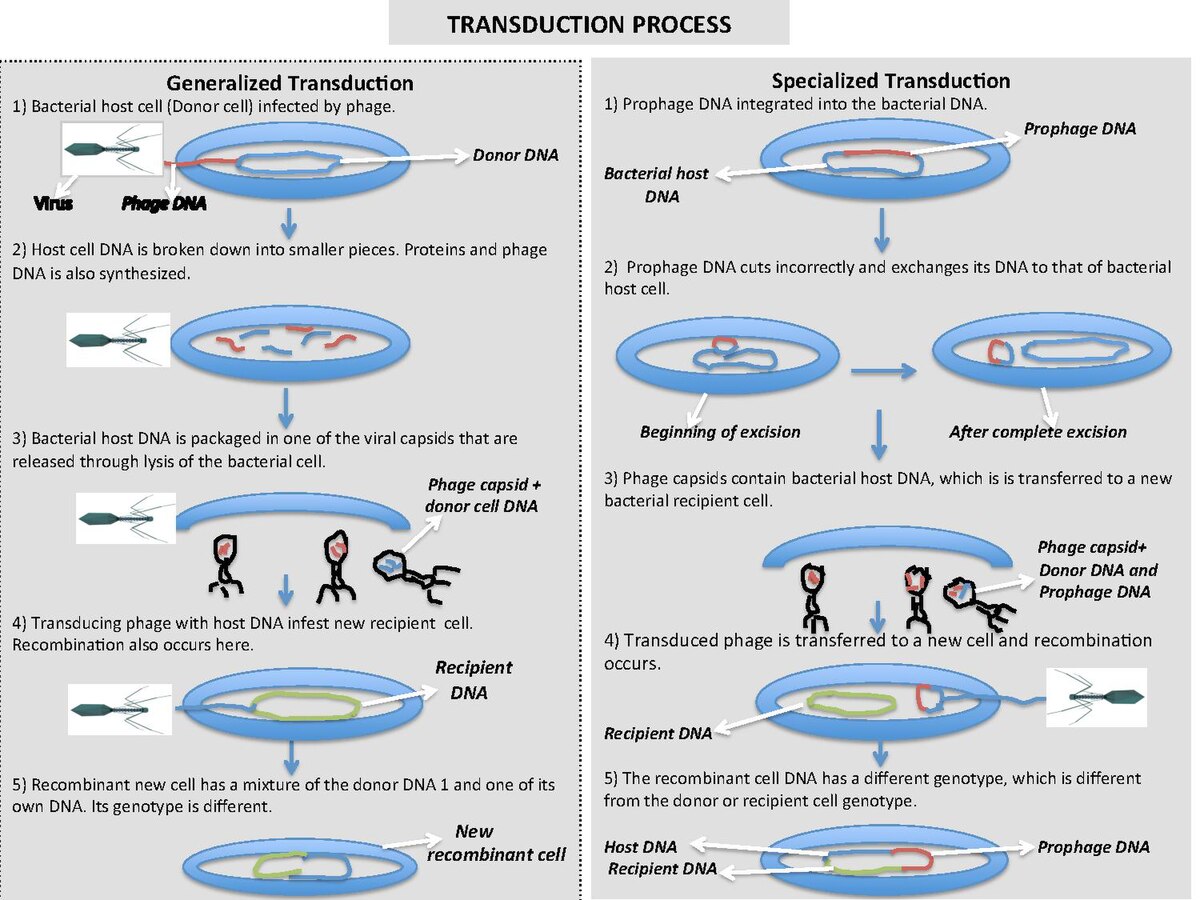
_____: DNA transferred from a donor cell to a recipient cell via bacteriophage (or phage)
Generalized or Specialized
Generalized
Specialized
_____ Transduction: Random DNA packaged into the phage and transferred
_____ Transduction: Specific bacterial genes are packaged inside the phage and transferred
Plasmids
Self-replicating circular pieces of DNA
1-5% size of bacterial chromosome
Often code for proteins that enhance the pathogenicity of a bacterium
Conjugative or Dissimilation, Resistance Factors
Exist independently of chromosomal DNA
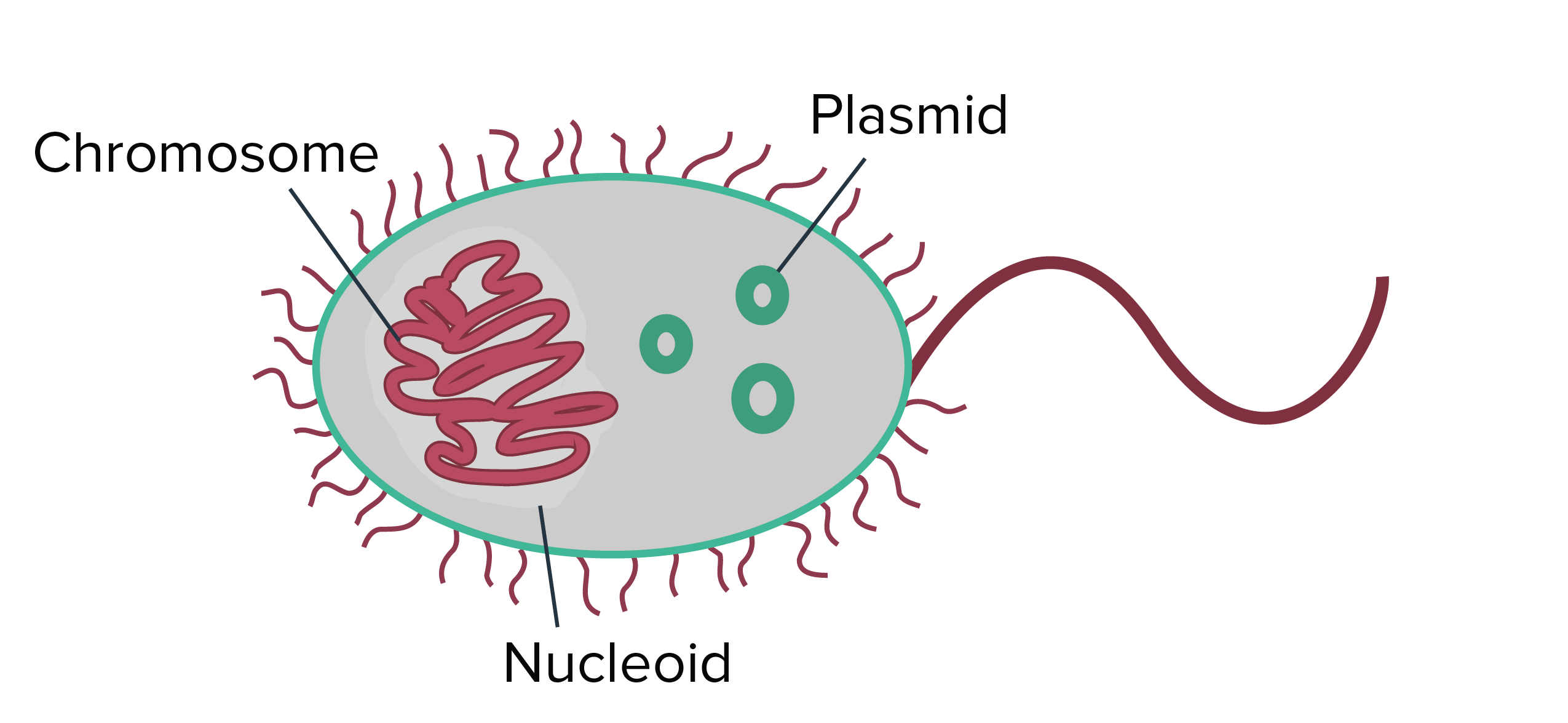
Conjugative
Dissimilation
_____ Plasmids: Carries genes for sex pili and transfer of plasmid
_____ Plasmids: Encode enzymes for the catabolism of unusual compounds
Resistance
_____ Factors: Encode antibiotic resistance
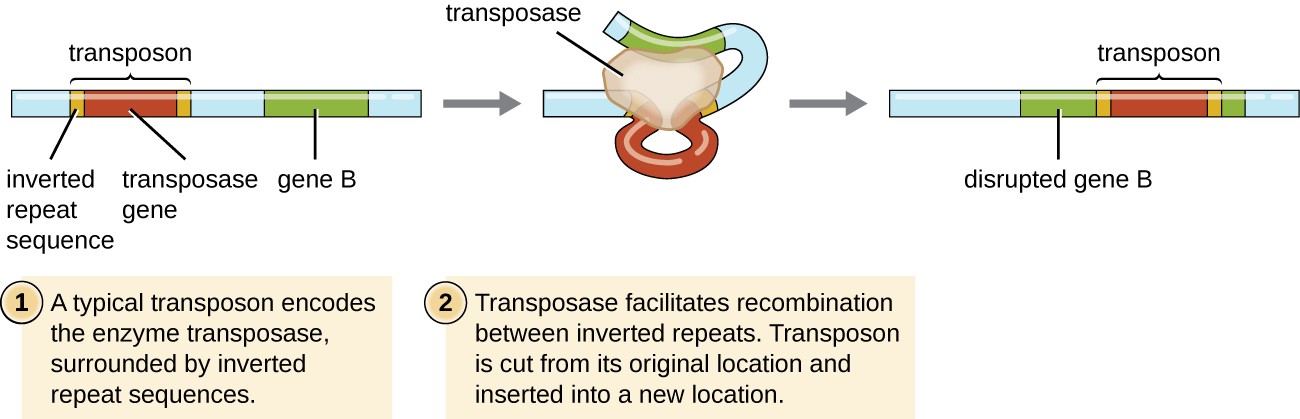
Transposons
Small segments of DNA (Chromosomes or plasmids)
Can move from one region of DNA to another
Contain insertion sequences (IS) - code for transposase
Cuts and reseals DNA and may carry additional genes for resistance or pathogenicity.
Complex versions carry other genes
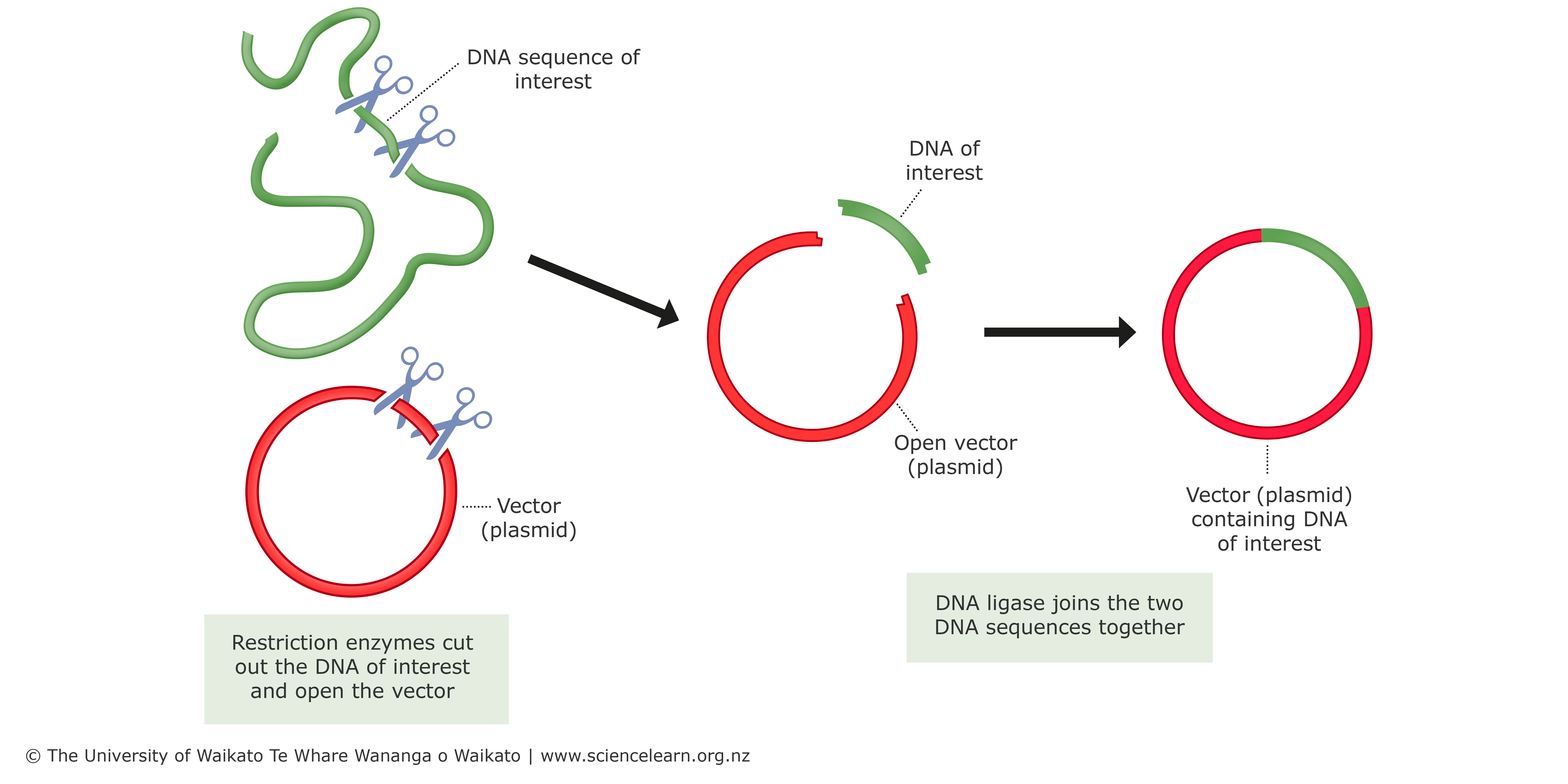
Biotechnology
Use of microorganisms, cells, or cell components to make a product (Food, antibiotics, vitamins, enzymes)
Recombinant
_____ Technology: Insertion or modification of genes to produce desired proteins
Vector
Self-replicating DNA molecule
Transport foreign DNA into cell
Ex. Plasmids and viruses
Clone
Population of genetically identical cells arising from one cell
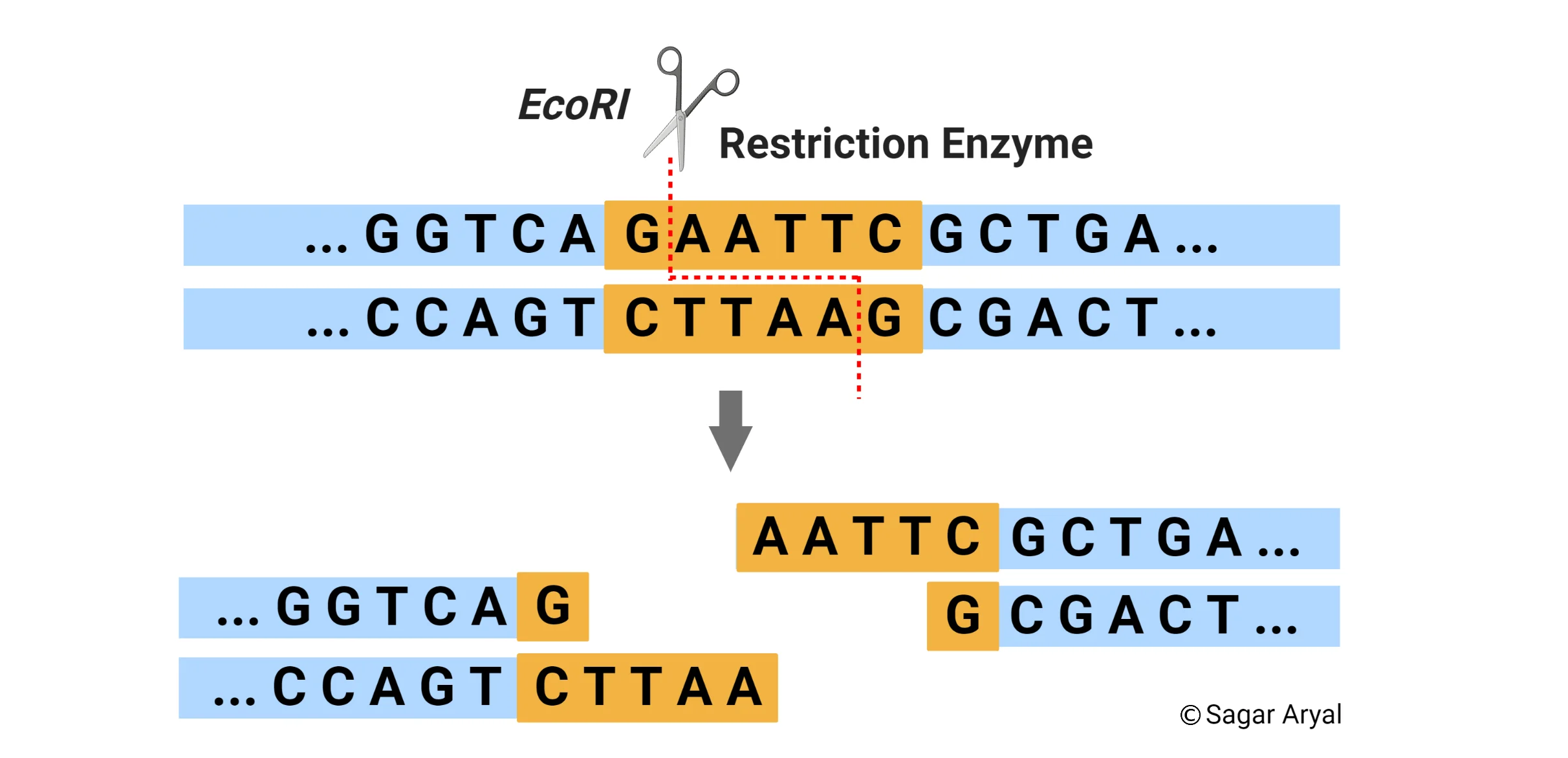
Restriction
_____ Enzyme: Cut specific nucleotide sequences from DNA
Polymerase
_____ Chain Reaction: Process that amplifies DNA for analysis
Used for;
Identifying microbes that can’t be cultured
Detecting pathogens
Diagnostic tests for genetic diseases
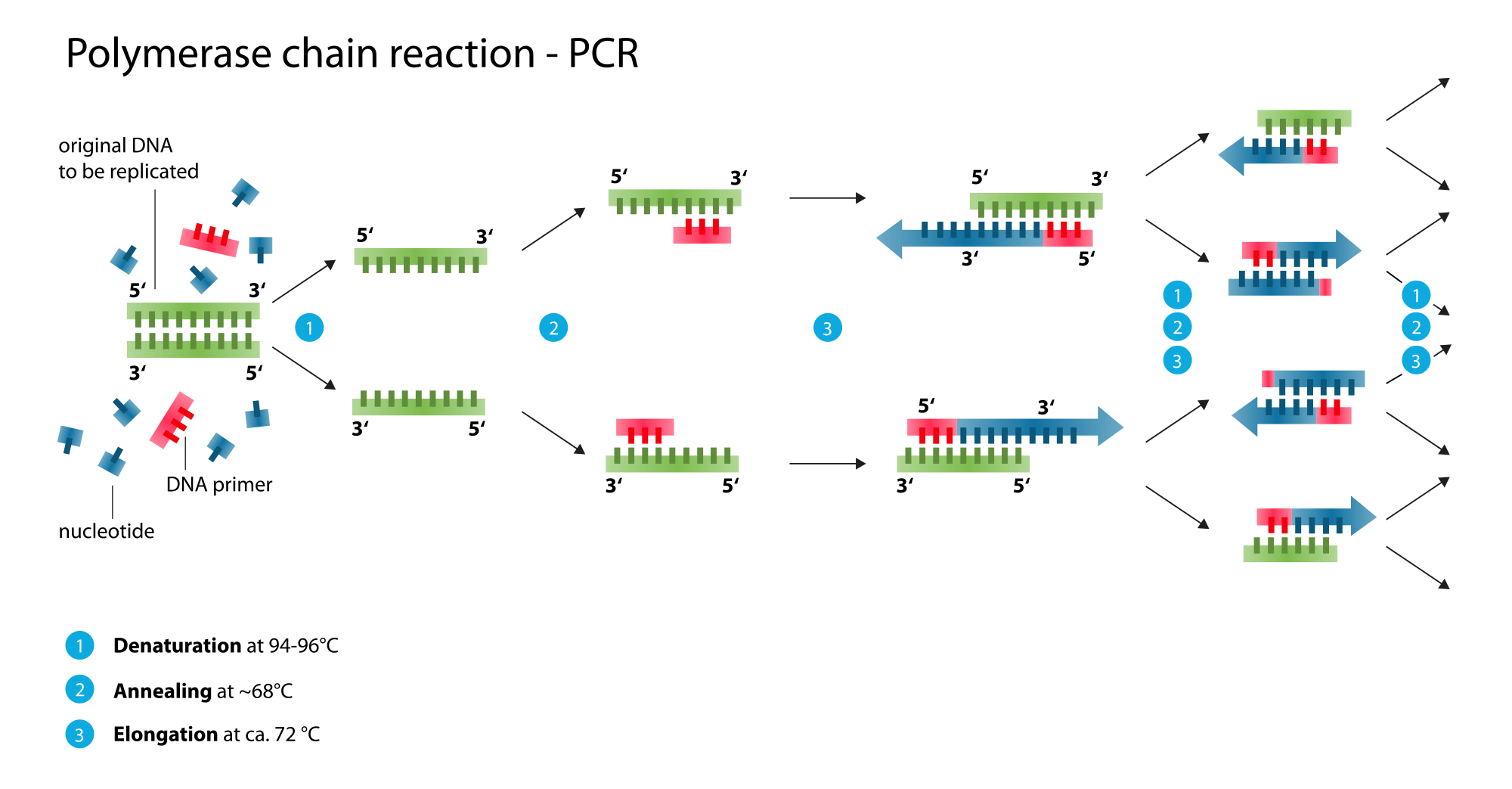
doubles
In each PCR cycle, the amount of DNA _____
DNA Ligase
An enzyme that makes covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate groups in another nucleotide in DNA is…?
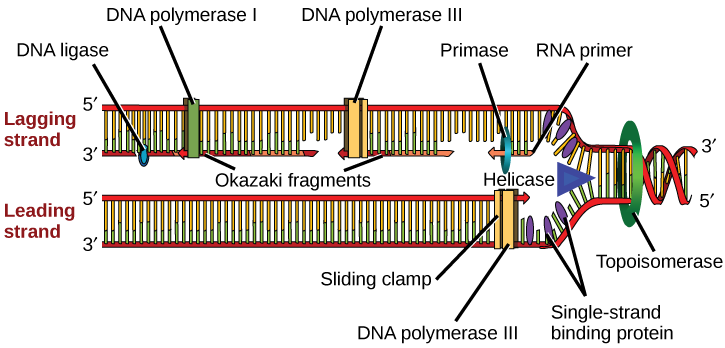
RNA Polymerase
Responsible for building RNA from a DNA template during transcription.
DNA Helicase
Unzips the DNA double helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between base pairs
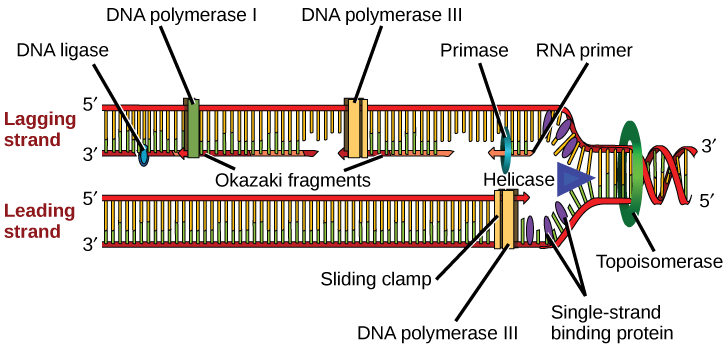
DNA Polymerase
Adds new nucleotides to a growing DNA strand during replication & forms the covalent bonds (phosphodiester bonds) between them
Is essential for proofreading and error correction.

Use codons to determine polypeptide sequences
Protein synthesis in eukaryotes is similar to the process in prokaryotes in that both eukaryotes and prokaryotes…?
Photolyase
Thymine dimers can be repaired by light-repair enzymes known as…?
Conjugation
The process for gene transfer which requires cell-to-cell contact and a particular type of plasmid is called…?
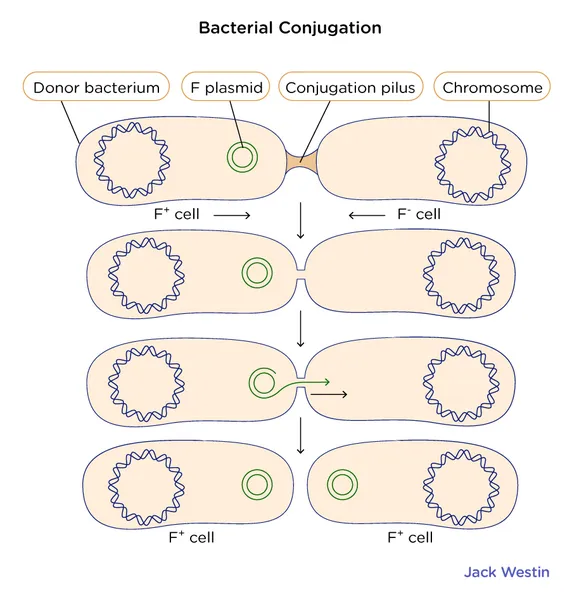
Conjugation
Transduction
Crossing over
Transformation
_____ - a type of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria that:
Requires direct cell-to-cell contact.
Involves a conjugative plasmid (like the F plasmid in E. coli).
DNA is transferred through a pilus from a donor to a recipient cell.
_____ - Gene transfer mediated by a bacteriophage (virus), not direct contact.
_____ _____ - Occurs during meiosis in eukaryotes, not in bacterial gene transfer.
_____ - Involves uptake of free DNA from the environment, no contact required.
Transposons
The small segments of DNA that can move from one region of a DNA molecule to another
Operons
In bacteria, are groups of genes regulated together. Control gene expression.
Transposition
The process where a specific DNA segment, called a transposon, moves from one location in a genome to another, either within the same DNA molecule or between different DNA molecules