Equine Health Management: Vaccinations, Parasite Control, and Behavior
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Vaccination
Important prevent medicine that stimulates the immune system against infection before exposure of disease.
Foal born to a vaccinated mare
Protected against the most infectious diseases for up to 6 months, so long as the foal consumed the antibody-rich mother's milk.

Maternal immunity
Vaccination should be delayed until maternal immunity has weaned.
Tetanus
Bacterial infection that attacks CNS à lockjaw (tighten muscles)
Encephalomyelitis
Viral infections carried by mosquitoes à inflammation of the CNS
Equine Viral rhinopneumonitis
Infectious herpesvirus à respiratory disease
Influenza
Viral respiratory infection
Potomac Horse Fever
Bacterial disease that is multi-systemic
Rabies
Viral infections
Rotavirus
Viral diarrhea
Strangles
Bacterial infection of the throat
West Nile Virus
Viral infections carried by mosquitos
Strongyles
Anemia, dry coat, diarrhea, general loss of condition
Roundworms
Loss of condition, bowel problems, injury to the lungs
Pinworms
Horse rubs its tail, irritation around the anus, discharge & worms around the anus
Bots
Loss of condition, abdominal pain from large numbers of bots in the gut; diarrhea or constipation
Dental care
Equine teeth grow and wear down throughout life
Floating
Process of filing down sharp edges & uneven surfaces on their teeth to improve chewing & efficiency

Farriers
Specialist in equine hoof care

Vision
Primary detector of danger in horses; poor color vision; can differentiate blue, red, gray.
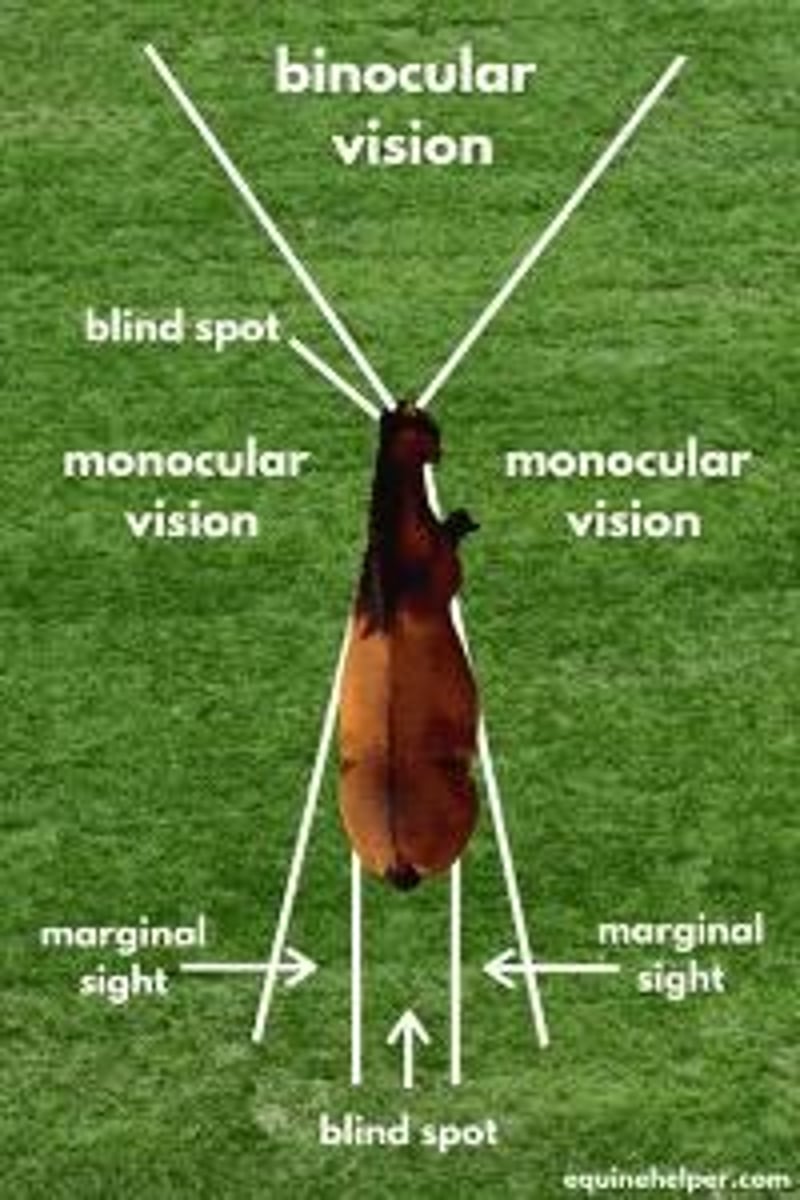
Hearing
Detect sounds, determine location of the sounds, sensory information.
Tactile sensation
Horses are extremely sensitive.
Horse tail signals
High - alert or excited; Low - sign of exhaustion, fear, pain or submission.
Horse leg signals
Pawing - frustrated; One front leg lifted - mild threat.
Facial expression signals
Snapping - foals showing submission to an older horse.
Horse ears signals
Neutral - ears are held loosely, openings facing forward or outward.
Weaving
Horse stands by the stall door & rhythmically shifts its weight back & forth on its front legs while swinging its head.
Cribbing
Horse bites onto a fixed surface, arches his neck & sucks in air, making a grunting noise à release endorphins.
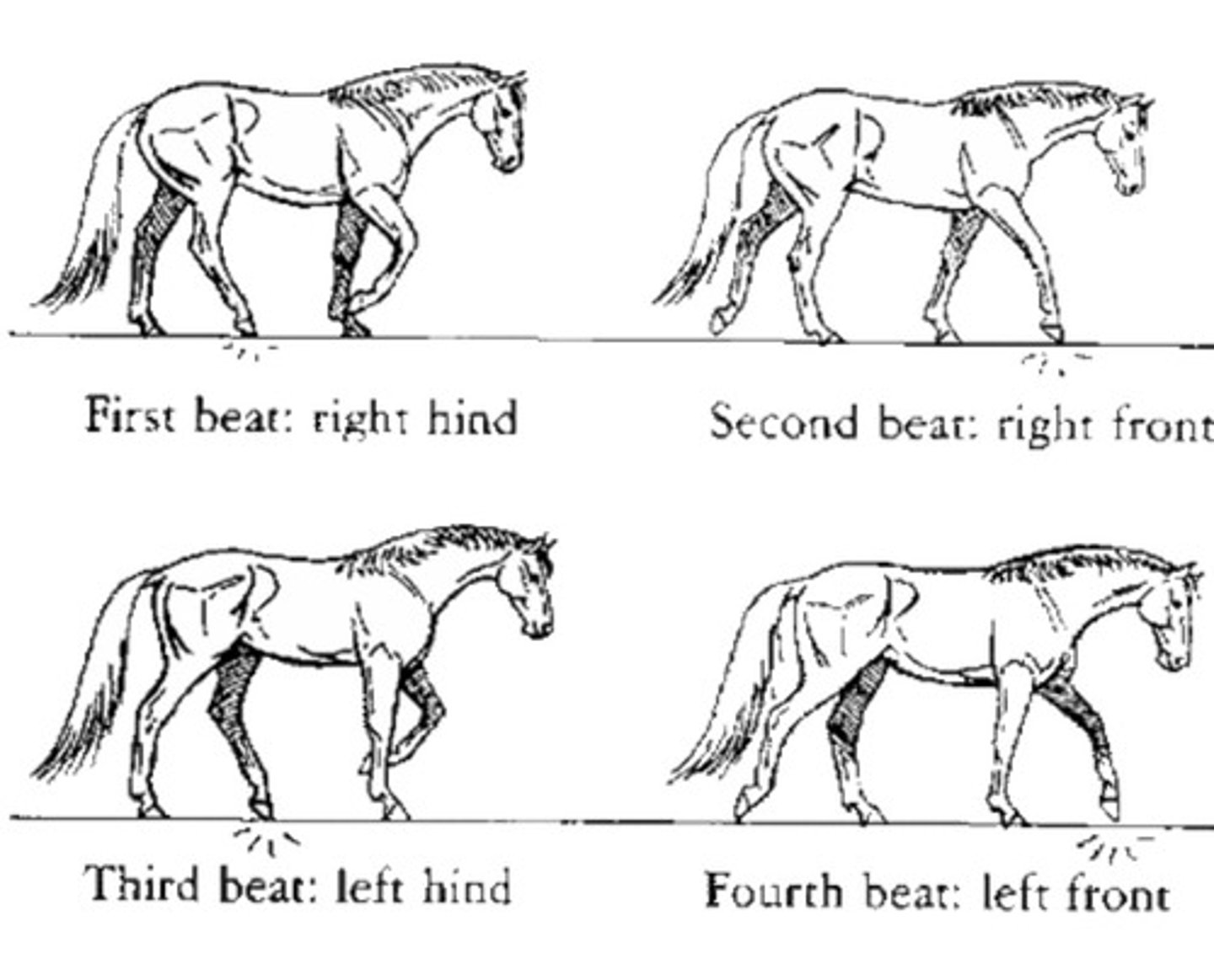
Walk
4-beat gait, slow, natural flat-footed; Average: 7km per hour.
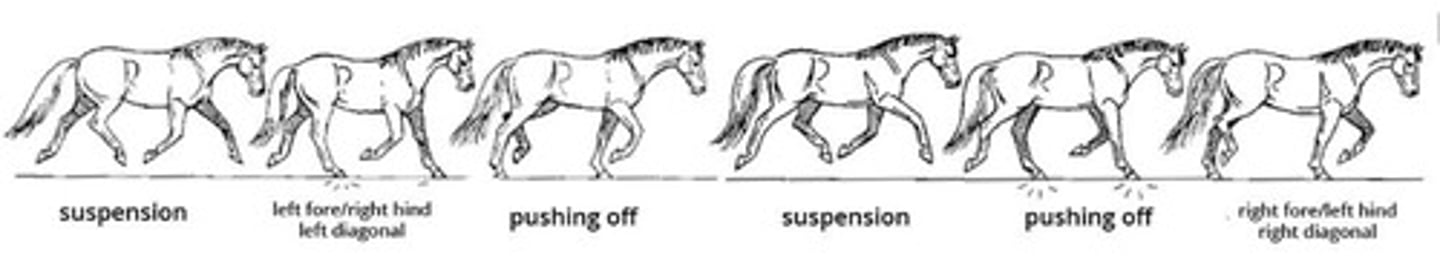
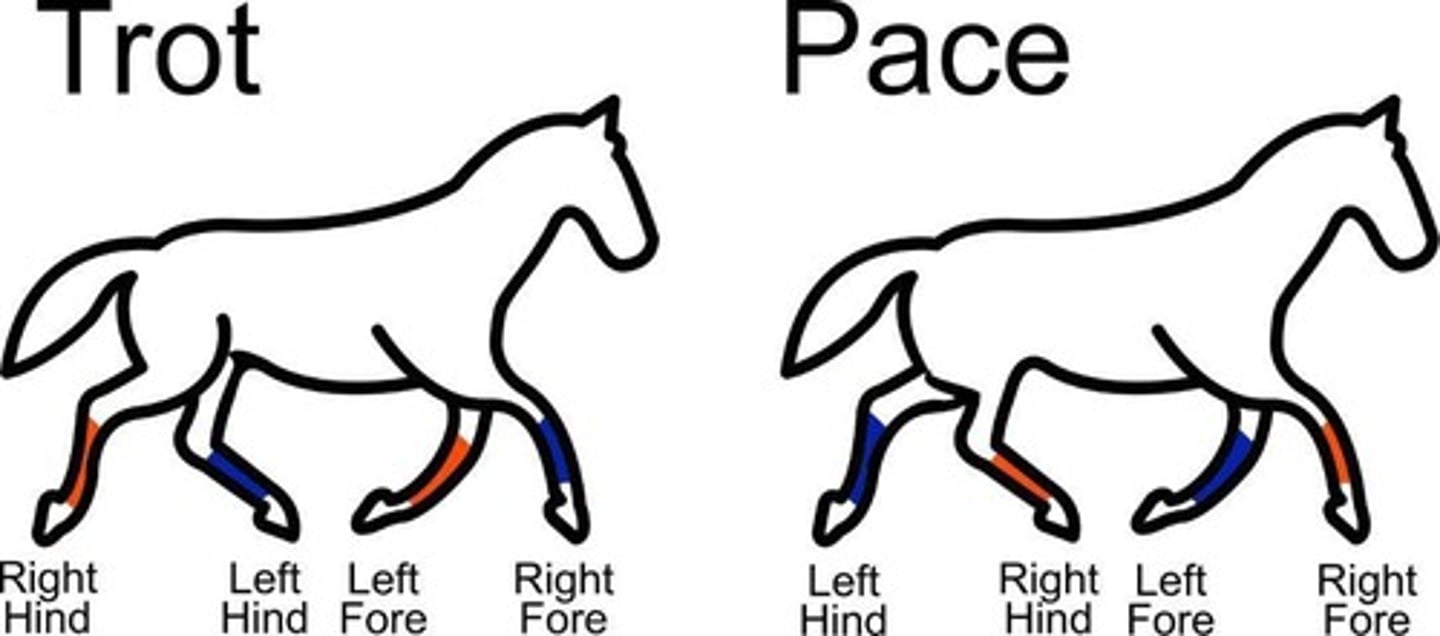
Trot
2-beat gait, moving its legs in unison in diagonal pairs; Averages: 13km per hour.
Canter (Lope)
Controlled 3-beat gait; Average: 16-27km per hour.
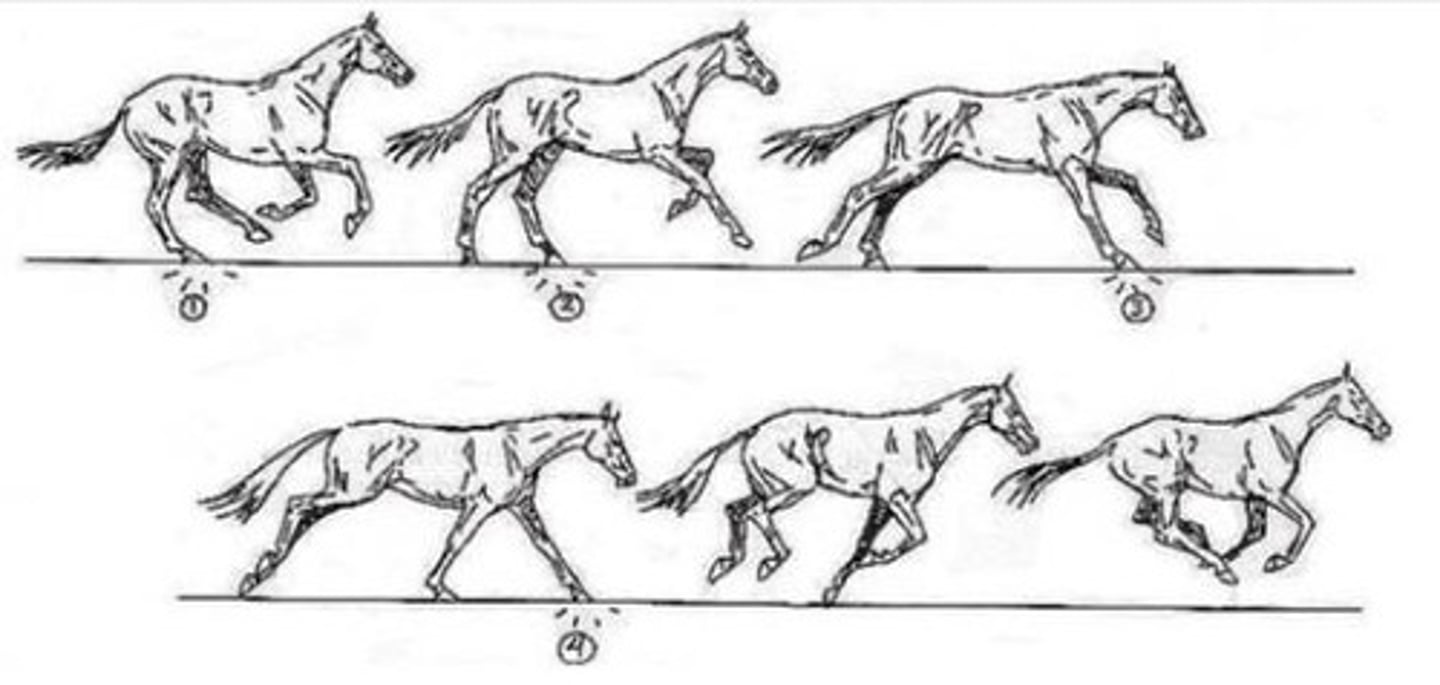
Gallop
Faster, more ground-covering, 3-beat canter; Average: 40-48km per hour.

Pace
Lateral two-beat gait.
Foxtrot
4-beat diagonal gait; Front foot of the diagonal pair lands before the hind.
Paso-fino
Range of smooth intermediate lateral ambling gaits.
Rack or Racking
Lateral gait associated with 5-gaited American Saddlebred.
Running walk
4-beat lateral gait with footfalls in the same sequence as the regular walk.