Atmospheres test Practice
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms

Define the atmosphere:
The atmosphere is a layer of gases that surrounds Earth. It consists mostly of nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. It also has a variable amount of water vapour, usually around 2 - 3%. Methane can also be found.

Define the lithospere:
The lithosphere is the outermost rocky layer of the Earth, consisting of the mantle and crust. It contains the continents and is made up of basalt and granite. Fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas can also be found.

Define the Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere is all the liquid and frozen water on Earth. This including oceans, lakes, rivers. Dissolved CO2 can be found in water.

Define the cryosphere
The cryosphere is the frozen part of the hydrosphere. includes sea ice, glaciers and ice caps.

Define the biosphere
The biosphere is made up of all living things on Earth, including plants, animals and bacteria. There is a great interdependence between different parts of the living world.

Why are the earth’s spheres balanced?
The Earth's spheres stay balanced because they constantly exchange materials like gases, water, minerals, and nutrients.

What would happen if the Earth’s spheres were unbalanced?
If Earth's spheres were unbalanced, materials like gases, water, minerals & nutrients would fall out of sync. That could trigger pollution, ecosystem collapse, or sudden climate shifts.
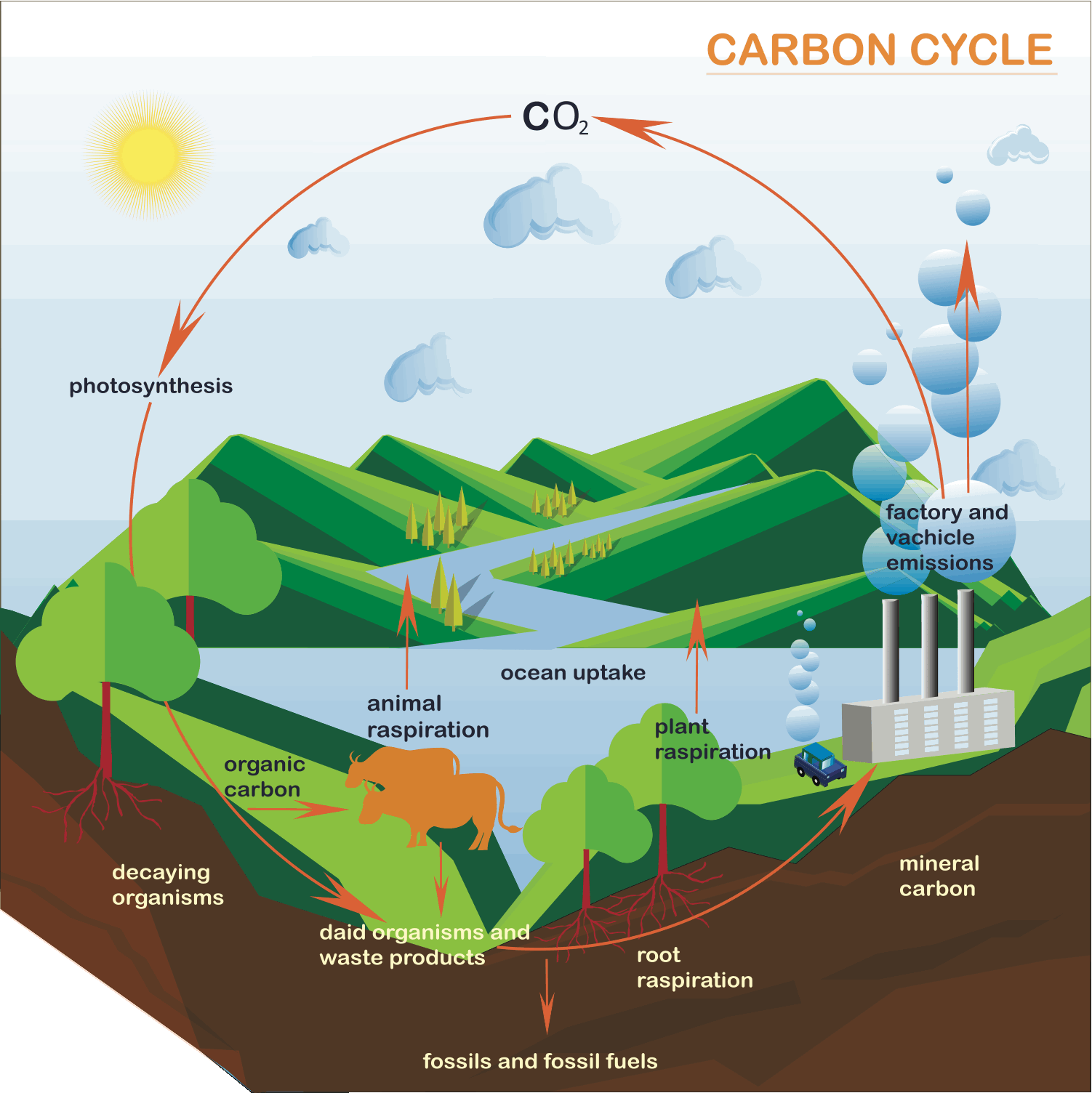

Explain why the carbon cycle is a global system
The carbon cycle is a global system because it moves carbon from the different global stores over long and short timeframes

Describe the two types of carbon.
Organic carbon: found in plants, animals and soil
Inorganic carbon: e.g. CO2 found in water and atmosphere, or carbon in minerals and rocks.
Provide an example of carbon stored in each of Earth's spheres.
Lithosphere – Carbon stored in fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas.
Atmosphere – Carbon stored as carbon dioxide gas.
Hydrosphere – Carbon dissolved in oceans as carbon dioxide or carbonate.
Biosphere – Carbon stored in trees and plants as biomass.
List and briefly describe the 5 processes that cycle carbon.
Combustion
Combustion is the process where a fuel or biomass reacts with oxygen, releasing energy whilst producing carbon dioxide and water.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process where plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and glucose
Respiration
Respiration is the process where living organisms convert glucose and oxygen to release energy, producing carbon dioxide and water.
Decomposition
Decomposition is the process where dead organic matter is broken down into simpler substances, releasing carbon back into the atmosphere.
Carbon Ocean exchange
Carbon ocean exchange is the process where carbon dioxide moves between the atmosphere and the ocean’s surface. Warm water releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere whilst cool water absorbs it.
Which processes add carbon into the atmosphere?
Respiration
Decomposition
Combustion
Warm ocean carbon exchange
Which processes remove carbon from the atmosphere?
Photosynthesis
Cool ocean carbon exchange
*practice carbon cycle model
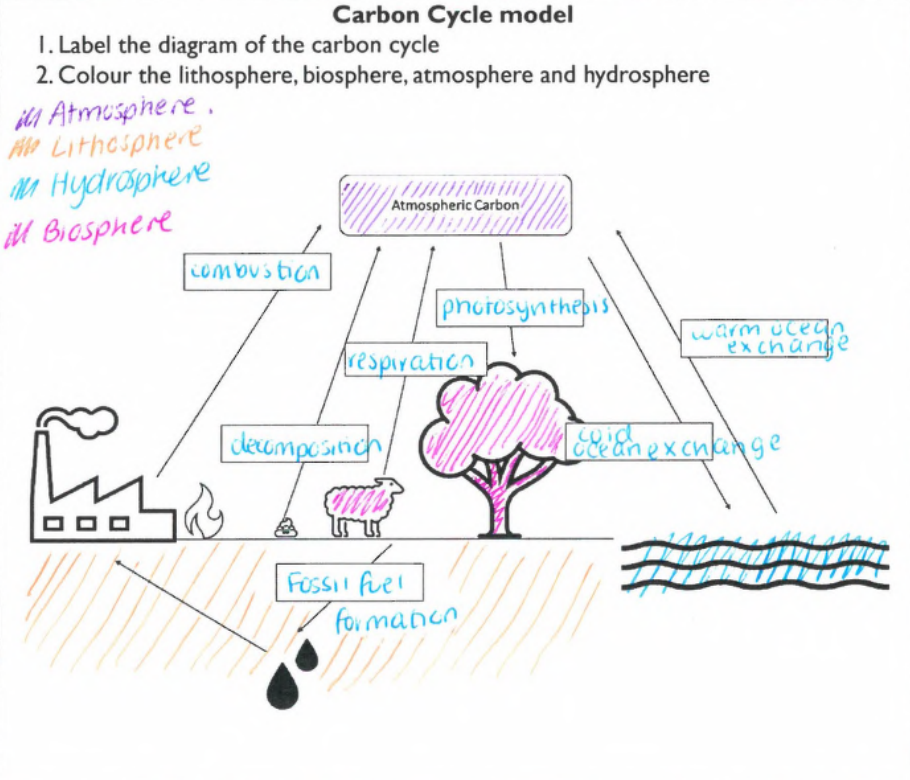
Explain what will happen to each sphere when the carbon cycle becomes unbalanced.
Atmosphere - increased carbon dioxide which traps more heat in the atmosphere.
Biosphere - The temperature will increase, harming ecosystems and food chains eventually leading to extinction events
Hydrosphere - Increased temperature, rising sea levels and ocean acidification
Lithosphere - less carbon stored in sinks.
Define the term carbon sink
A long term store of carbon dioxide form the atmosphere. includes forests, ocean, fossil fuels.
Describe the greenhouse effect.
The greenhouse effect is natural process in which gases trap heat in the atmosphere, stopping it radiating back out into space.
Identify three examples of the greenhouse gases.
Examples of greenhouse gasses include carbon dioxide, water vapour and methane
What are some positive effects of the greenhouse effect on Earth?
The moderate temperatures created by the greenhouse effect allows for the existence of life forms. Without it, many organisms would die.
What is the enhanced greenhouse effect?
The enhanced greenhouse effect refers to the intensification of the natural greenhouse effect due to increased levels of greenhouse gases caused by human activities.
How are humans causing an enhanced greenhouse effect?
Humans are causing an enhanced greenhouse effect primarily through the emission of greenhouse gases, largely from burning fossil fuels, industrial processes, deforestation, leading to increased amounts of CO2 in the atmosphere.
What are the consequences of an enhanced greenhouse effect on Earth.
The consequences of an enhanced greenhouse effect include, rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise and ocean acidification,
*understand diagram of water cycle
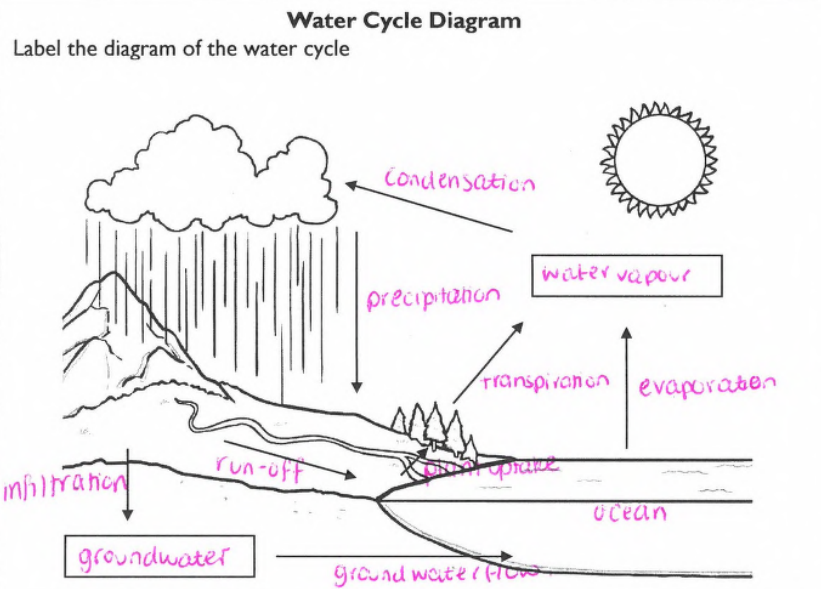
What are the water cycle processes:
Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, runoff, transpiration and infiltration.
Summarise Evaporation
The process of liquid water become water vapour. From the hydrosphere to the atmosphere.
Define condensation.
The process of water vapour becoming liquid water. From the atmosphere to the hydrosphere
Define precipitation
When liquid water falls as rain, hail or snow. From the hydrosphere to the hydrosphere.
Define Run off
liquid water runs off land back to the ocean. From the hydrosphere to the hydrosphere.
Define transpiration.
Water evaporates from the leaves of plants. From the biosphere to the atmosphere.
Define Infiltration
Water soaks into the ground. From the hydrosphere to the lithosphere.
Define plant uptake
Plants take in water via their roots. From the hydrosphere to the biosphere.
Describe how the water cycle is balanced
The water cycle is balanced as the amount of precipitation is roughly equivalent to the amount of evaporation.
Describe 1 way that humans affect the water cycle and cause it to become unbalanced. What effect is had on each sphere.
*make your own answer
Describe how indigenous knowledge is being reaffirmed and contributing to western science
Indigenous knowledge passed on for 1000s of years has been affirmed by science
DiVA studies show aboriginal people have lived there fore thousands of years
Geological studies confirm events like volcanic eruption of Budj Bim from ancient stories.
Define the relationship between indigenous fire burning practices and the use of carbon credits in Australia.
*make your own answer
Define climate chagne
Climate change is a long-term change in the Earth’s temperature with permanent effects.
Describe one solution for the impacts of climate change.
*make your own answer