Not finished practical virology wk2 one step growth curve practical assessment
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
infectious diseases
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Titre
Concentration of viruses in a sample.
Plaque Assay
Method to quantify virus by counting plaques.
how do you find LD50
complete a quantal assay study in animals. use the Dose causing 50% mortality in organisms. (not working this out in the exam)
Density Gradient Centrifugation
Separation technique based on particle density.
Multiplicity of Infection (MOI)
Ratio of infecting viruses to target cells.
One Step Growth Curve
Experiment showing stages of virus replication.
Eclipse Period
Time with no detectable infectious particles.
Rise Period
Time when mature virions are released.
Burst Size
Number of phages produced per infected bacterium.
Progeny Viruses
Viruses produced from an infected cell.
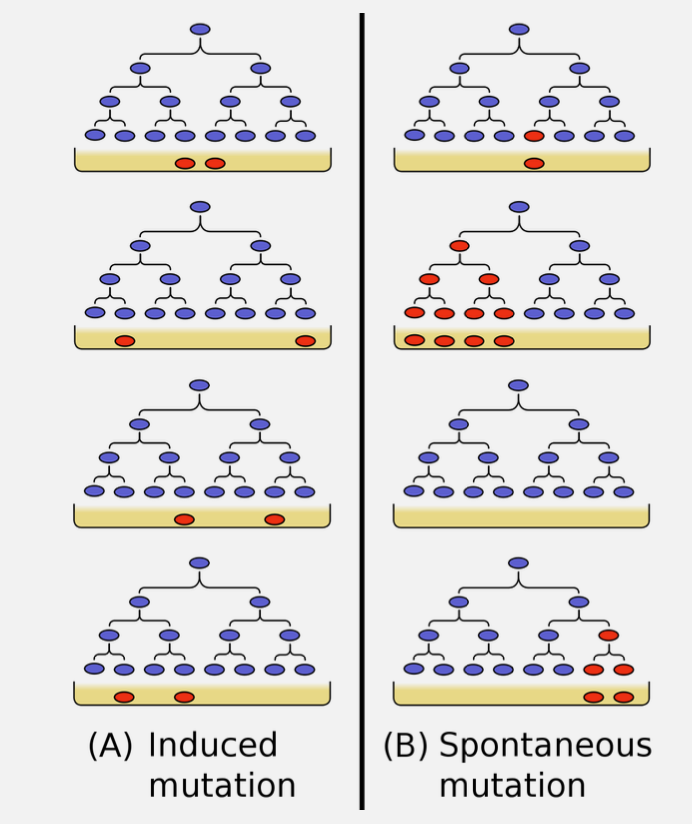
Fluctuation Test
Experiment demonstrating spontaneous mutations in bacteria.
Bacteriophages
Viruses that infect and replicate within bacteria.
Artificial Lysis
Inducing cell death to study virus yield.
what methods can be used for determining virus titre
plaque assays
quantal dose response (LD50)
hemagluttination
how can we find the structure of a virus
electron microscopy and x- ray crystallography
how can we detect the presence and function of a virus
detection=
serological methods ( using proteins and antibodies)
viral nucleic acid, sequencing
function=
using tissue culture in animals
how do you perform a plaque assay
create a serial dilution of a virus plate this onto susceptible cells (bacteria) semi solid media will either be mixed before or added now to restrict diffusion of virus particles - to only infect neighbouring plaques and so they can be seen) restricted cell to cell soread of virus results in localised destruction of cell monolayers which show as plaques- little dots- of killed bacteria/cells
how do you calculate the amount of virus from the plaque assay (PFU/ml)
plaque no/ volume of sample plated (ML) x dilution
How did Hershey and Chase show that DNA is passed to new phages in phage reproduction? 1952
used 2 samples of phage T2.one sample was labelled with radioactive phosphourus and infected e.coli, homogenised and then centrifuged to separate the bacterial cells and phage coats. results were analysed and supernatant contains 25% radioactivity whilst the pellet (phage coats) had 75%- meaning phage are using the DNA and its not remaining on the bacteria insteadwhen repeated with labelled sulphur, the supernatant had 85% radioactivity showing the phage inserted DNA into the bacteria
how did luria and delbruk find out about mutations
observed resistant bacteria in two phage experiments. when mutations were induced, there would be limited variability in the simple. with spontaneuos mutation they were highly variable
what does one step growth curve show
ellis and dubruck 1939,
showing that viral re1.plication is in stages.
initiation of infection
replication and expression of virus genome
assembly and release of mature virions from infected cells
key is to synchronise culture so all cells are infected at t=0
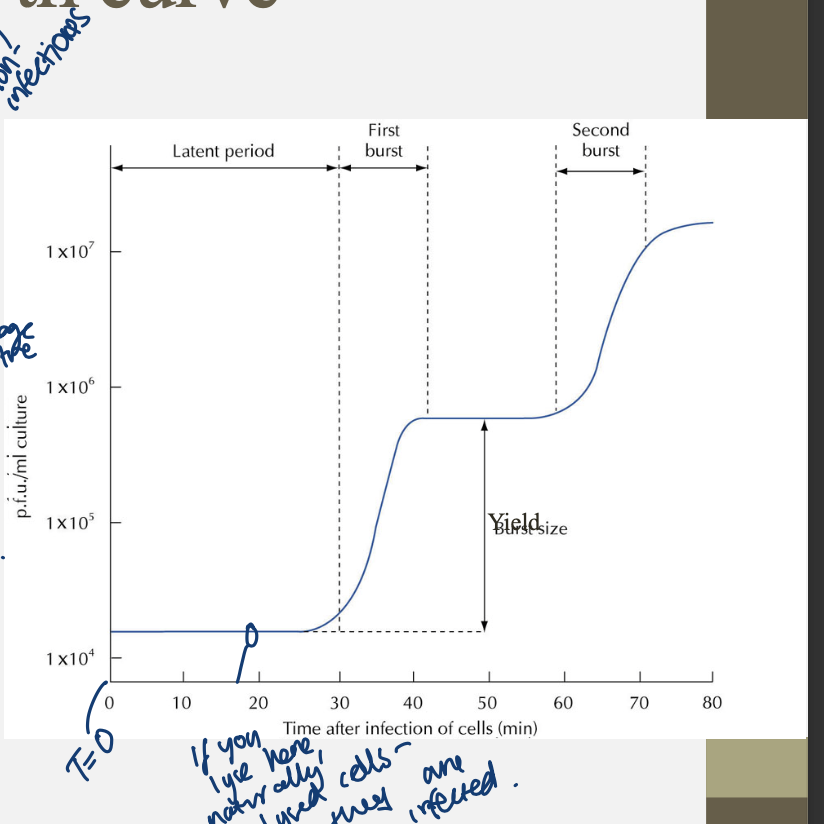
what happens in latent period
eclipse period- no infectious particles. none are released as viral dna is inserted into bacteria. intracellular accumulatio, the viruses are assesmbled but not released
artificial lysis of cells can show eclipse and intracellular accumulatio period