SACE Stage 2 Chemistry - Topic 2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
How can the rate of a reaction be measured?
By measuring the amount of reactant consumed against time; or the amount of product formed against time
What does a steep graph gradient represent?
A reaction in which the conversion of reactants into products is occurring rapidly
What does a shallow gradient represent?
A reaction in which the conversion of reactants into products is occurring quite slowly
What does a zero gradient represent?
A reaction that has either stopped or reached equilibrium
How is the average rate of a reaction calculated?
x-step / y-step or rise / run
What must occur for a reaction to take place?
Collisions must occur; reacting particles must collide with energy equal to or greater than the activation energy; collisions must occur at the correct site
How may the rate of a reaction be changed?
Altering the frequency of collisions; changing the energy of the collisions; manipulating the orientation of the collisions
How does an increase in concentration affect the rate of a reaction?
An increase in reactant or product concentration will increase the number of particles in a specific volume. An increase in the frequency of collisions will occur and thus, the rate of the reaction will be increased
How does an increase in temperature affect the rate of a reaction?
An increase in the temperature of a reaction system will increase the average kinetic energy of particles. Subsequently, a greater percentage of particles with energy equal to or greater than the activation energy will be present. This will increase the percentage of successful collisions to increase the rate of the reaction
How does an increase in pressure affect the rate of a reaction, of a gaseous system?
An increase in the pressure of a reaction vessel will have a similar effect to increasing the concentration of a reactant or product. An increased number of particles will exist in a specific volume, which will increase the frequency of collisions between reacting particles to increase the rate of the reaction
What impact does particle size have on the rate of a reaction?
An increase in subdivision of particles will increase the total surface area available for the reaction to occur. Thus, an increased frequency of collisions will occur and increase the rate of the reaction
What impact does the intensity of light have on the rate of a reaction?
Increased light intensity will have a similar impact on the rate of a reaction as an increase in temperature. The average kinetic energy of particles will increase, which increases the percentage of particles with energy equal to or greater than the activation energy. Thus, an increased percentage of successful collisions will occur and the rate of the reaction will increase
What influence does a catalyst have on the rate of a reaction?
A catalyst may either offer an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy, saving energy costs; or by offering a surface or site for the reaction with controls the orientation of one molecule
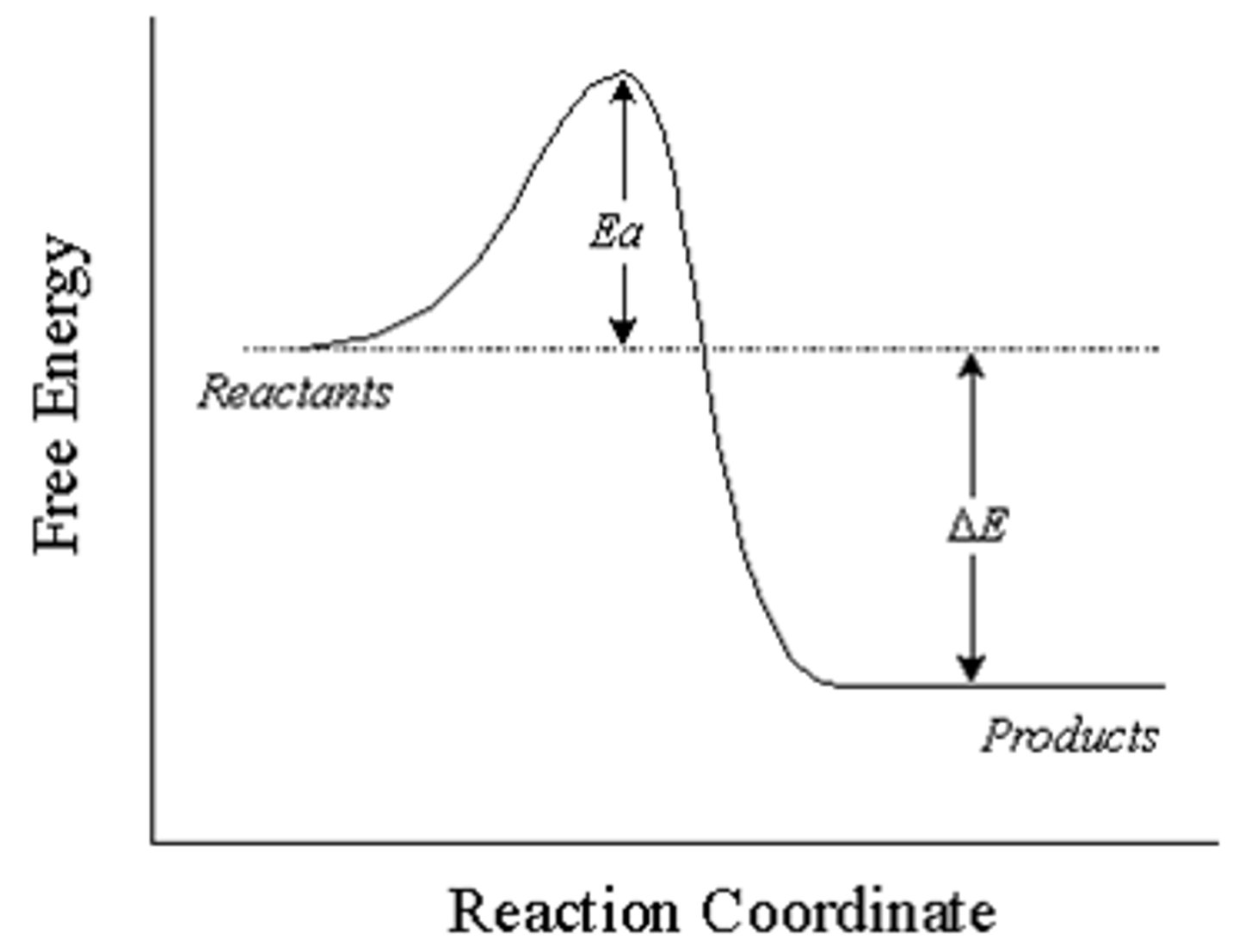
Is this reaction pathway exothermic or endothermic?
Exothermic, as the products contain less energy than the reactants - indicating a release of energy
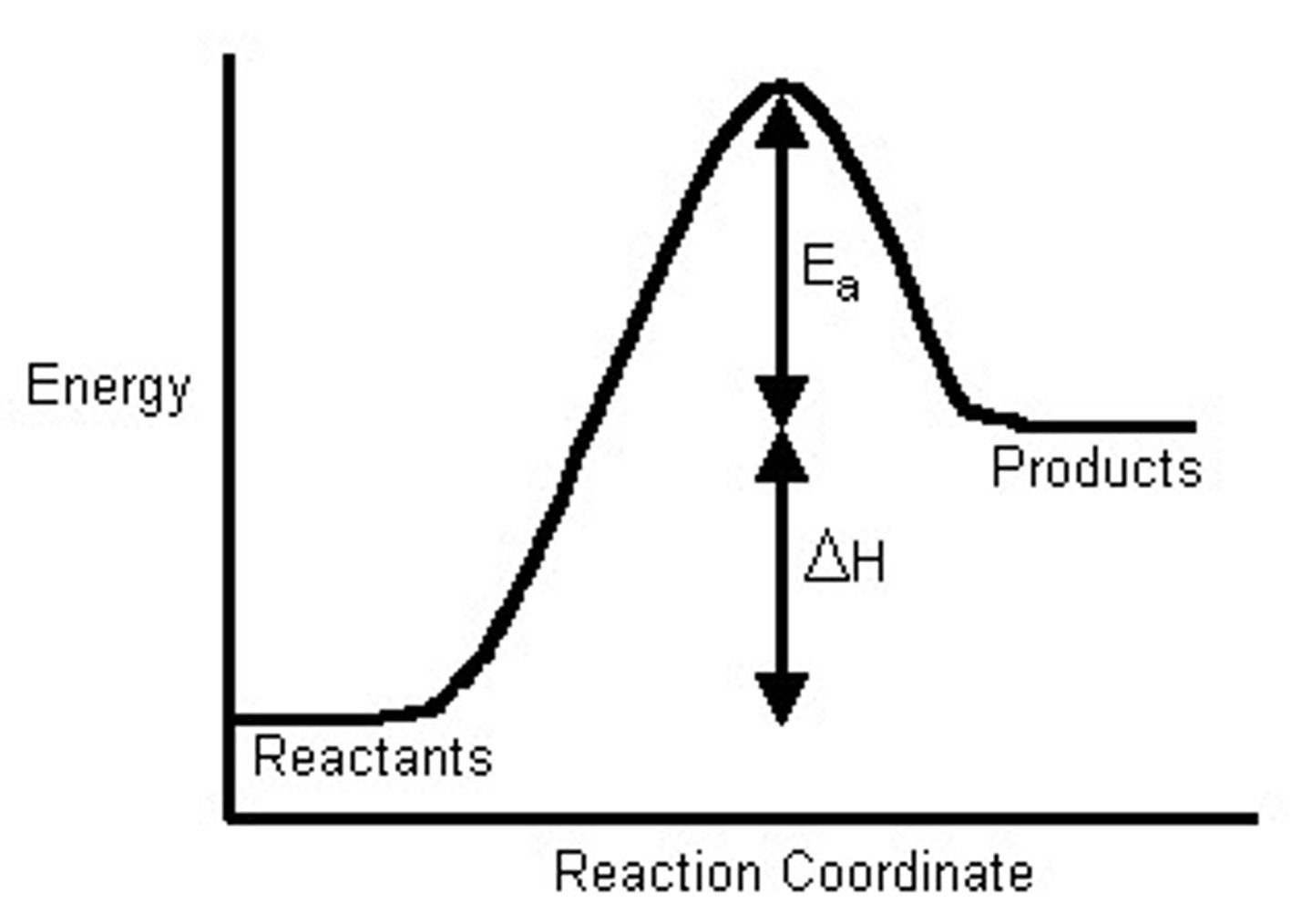
Is this reaction pathway endothermic or exothermic?
Endothermic, as the products contain more energy than the reactants - indicating an absorption of energy
What does equilibrium refer to?
How far a reaction proceeds, rather than how fast the reaction proceeds
What factors must be present for a system to reach dynamic equilibrium?
Closed system preventing escaping or entering of substances to the reaction; and a fixed temperature
Why is equilibrium defined as dynamic?
The forward and backward reactions are still occurring but concentrations of reactants and products remain constant, at equilibrium
When does equilibrium lie to the right?
When the concentration of products is greater than the concentration of reactants at equilibrium
When the concentration of reactants is greater than the product concentration, at which position does equilibrium lie?
To the left
What should answers using Le Chatelier's principle include?
1. Reference to Le Chatelier's principle
2. The change that has been made
3. A general statement as to what any system would do
4. A specific statement as to which way the position of equilibrium will shift
How does pressure affect a gaseous equilibrated system?
Le Chatelier's principle explains that an increase in pressure will cause the system to shift equilibrium to favour the reaction that produces the least amount of moles, so as to alleviate the increase in pressure. Contrarily, a decrease in pressure will cause the system to shift equilibrium to favour the reaction that produces the most amount of moles, so as to reinstate the lost pressure
If a product is removed from an equilibrated system, how will the system respond?
Le Chatelier's principle explains that a decrease in the concentration of a product will cause the system to shift equilibrium to favour the reaction that increases the product concentration, to replace the lost product. The position of equilibrium will shift to the right, favouring the forward reaction, to increase product concentration
If additional product is added to an equilibrated system, how will the system respond?
Le Chatelier's principle explains that an increase in the concentration of a product will cause the system to shift equilibrium to favour the reaction that consumes this additional product, to reduce its concentration. The position of equilibrium will shift to the left, favouring the backward reaction, to decrease product concentration by increasing its conversion into the reactants
If temperature is increased in an equilibrated system, how will the system respond?
Le Chatelier's principle explains that an increase in temperature will increase the rate of both the forward and backward reactions. However, the system will counteract the increase in temperature by shifting equilibrium to favour the endothermic reaction - to reduce temperature of the system. Thus, the rate of the endothermic reaction will increase
True or False: A change in temperature will cause a change in the Kc value?
True
What is a raw material?
An unprocessed material that is used to produce more useful materials or energy in an industrial
process
Define waste products:
Any unusable product of a reaction that occurs during a chemical process. Waste products are
unwanted and undesirable as they are often difficult and expensive to dispose of responsibly
What is a by-product?
Any usable product of a reaction that occurs during a chemical process. By-products may have a
secondary use on site at the industrial plant or could be sold to generate profit.
Write an equation detailing the combustion of sulphur in the first stage of the Contact process:
S + O2 = SO2
Provide an equation for the reaction of sulphur dioxide and oxygen:
2SO2 + O2 = 2SO3
Write an equation showing the formation of sulphuric acid from sulphur trioxide and water:
SO3 + H2O = H2SO4
Write an equation showing the formation of hydrogen from methane and water, during the first stage of the Haber process:
CH4 + H2O = 3H2 + CO
Show the equation for the second stage of the Haber process, secondary steam reformation:
2H2 + O2 = 2H2O
Provide an equation for the reaction of carbon monoxide and water, occurring during the third stage of the Haber process:
CO + H2O = CO2 + H2
Write an equation showing the formation of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen, in the converter stage of the Haber process:
N2 + 3H2 = 2NH3
How is percentage yield calculated?
actual yield / theoretical yield x 100
What are the environmental concerns with generating and maintaining high pressures in industrial processes?
Generating and maintaining high pressures is energy-intensive and potentially dangerous, if an explosion were to occur
Why are high temperatures in industrial processes beneficial?
High temperatures increases the rate of reactions, which increases the amount of a product formed per given time
What is one way manufacturers can maintain high temperatures, at a reduced cost?
Using heat exchangers to transfer heat produced from one reaction, for use to heat another reaction will maintain high temperatures at a reduced cost
True or False: Catalysts are consumed during reactions?
False