Understanding Emotional Intelligence and Its Components
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Emotional Intelligence
The ability to identify, understand and manage your emotions and your relationships with others.
Intelligence Quotient (IQ)
A measure of a person's academic abilities, distinct from emotional intelligence which deals with emotions.
Identifying Emotions
The first step in emotional intelligence, crucial for managing emotions.
Understanding Emotions
The capacity to monitor and label our emotions and determine the reasons behind them.
Managing Emotions
The ability to modify and improve feelings, which involves understanding the type of emotion and how to manage it.
Self-Awareness
The ability to recognize and understand your own emotions.
Emotional Self-Awareness
Reading one's own emotions and recognizing their impact on oneself and others.
Accurate Self-Assessment
Knowing one's strengths and limits.
Self-Confidence
Having a sound sense of one's self-worth and capabilities.
Self-Regulation
The ability to recognize our own emotions and appropriately express, regulate, and manage them.
Self-Control
Managing disruptive emotions and impulses.
Trustworthiness
Maintaining standards of honesty and integrity.
Conscientiousness
Taking responsibility for personal performance.
Adaptability
Flexibility in handling change.
Innovativeness
Being comfortable with and open to novel ideas and new information.
Self-Motivation
The personal drive to improve and achieve, commitment to goals, and readiness to act on opportunities.
Achievement Drive
Striving to improve or meet a standard of excellence.
Commitment
Aligning with the goals of the group or organization.
Initiative
Readiness to act on opportunities.
Optimism
Persistence in pursuing goals despite obstacles and setbacks.
Empathy
The ability to understand how other people are feeling and recognize how you would feel in their situation.
Social Skills
The ability to manage relationships and build networks.
Empathy
Sensing others' feelings and perspective, and taking an active interest in their concerns.
Service orientation
Anticipating, recognizing, and meeting customers' needs.
Developing others
Sensing what others need in order to develop, and strengthening their abilities.
Leveraging diversity
Cultivating opportunities through diverse people.
Political awareness
Reading a group's emotional currents and power relationships.
Social skills
What allow people to interact socially with one another and to successfully navigate social situations.
Influence
Exercising effective tactics for persuasion.
Communication
Sending clear and convincing messages.
Leadership
Inspiring and guiding groups and people.
Change catalyst
Initiating or managing change.
Conflict management
Negotiating and resolving disagreements.
Building bonds
Nurturing instrumental relationships.
Collaboration and cooperation
Working with others toward shared goals.
Team capabilities
Creating group cooperation in pursuing collective goals.
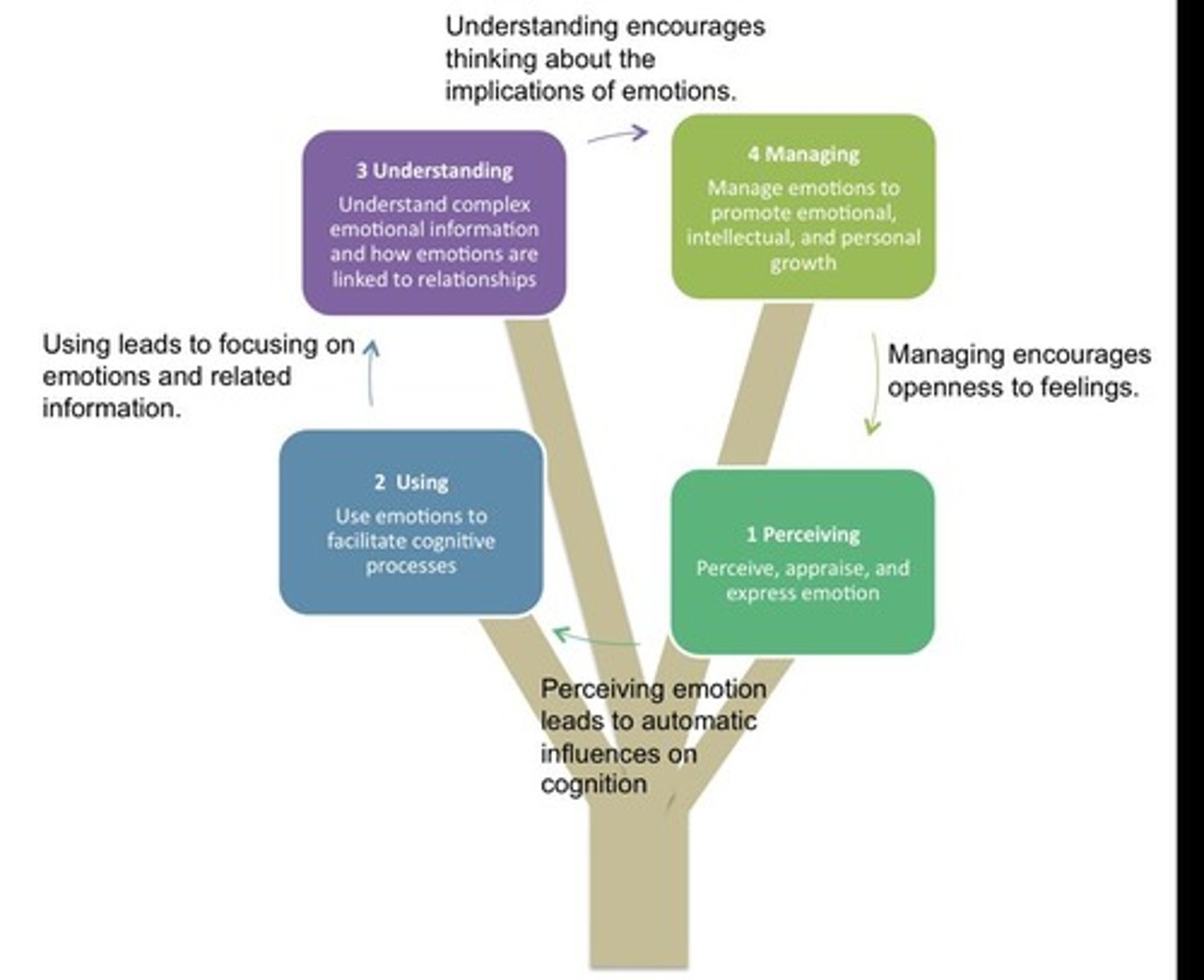
Perceiving emotion
Being aware of and recognizing other people's states, identifying emotions in others, and expressing one's own emotions and needs accurately and appropriately.
Using emotions to facilitate thought
Redirecting and prioritizing your thinking based on the feelings associated with those thoughts.
Understanding emotions
Understanding the relationships among various emotions, perceiving the causes and consequences of emotions, and understanding complex feelings and contradictory states.
Managing emotions
Being open to both pleasant and unpleasant feelings; monitoring and reflecting on your emotions.
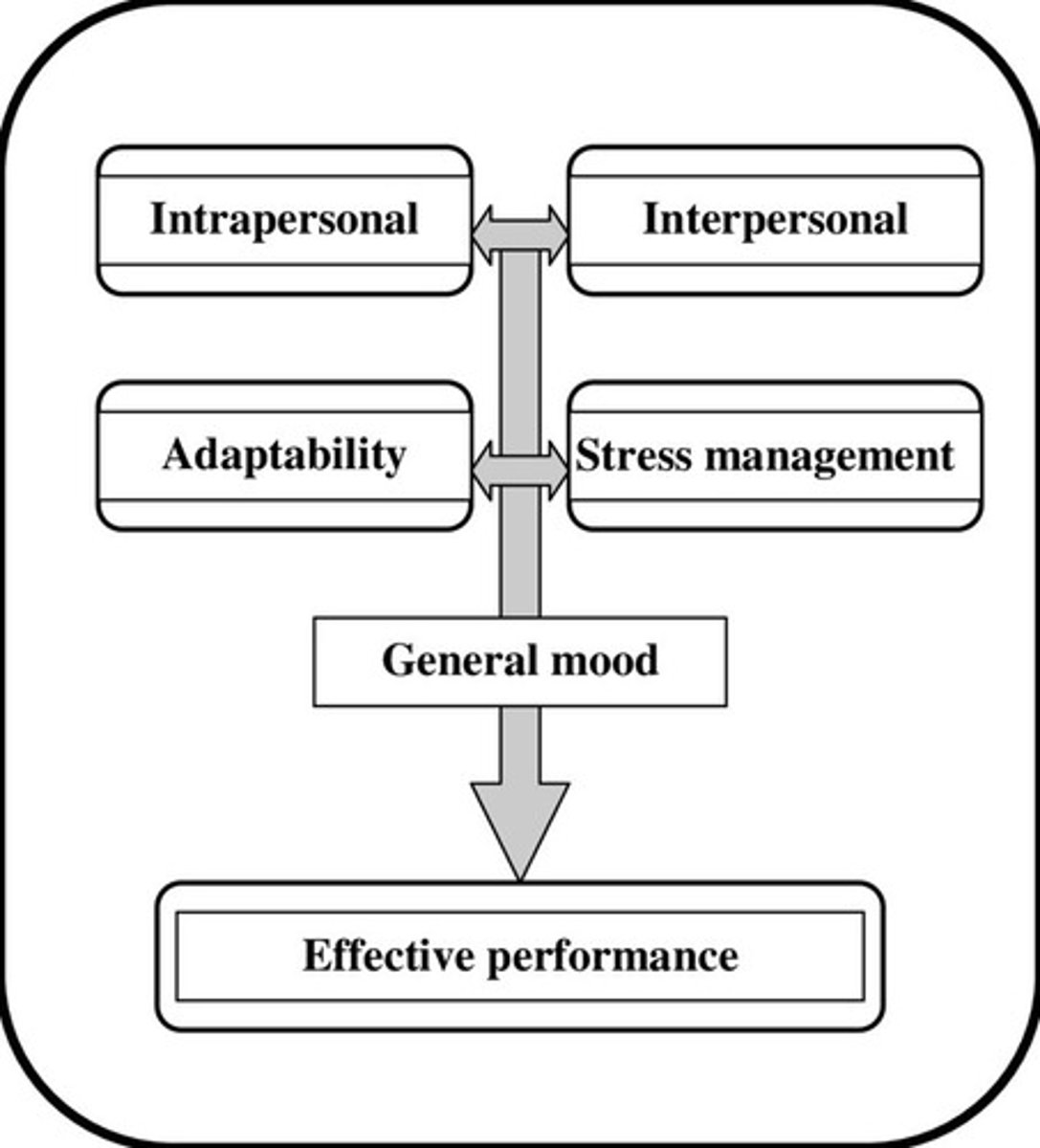
Bar-on Model of Emotional Intelligence
A model developed by a Professor from University of Texas that demonstrates how categories of emotional intelligence directly affect our general mood and lead to effective performance.
Intrapersonal skills
This refers to how well you know and like yourself and how well and effective you can do the things you need to do to stay happy.
Emotional self-awareness
This refers to being aware of one's emotions. This means that you have to know how and why you feel the way you do.
Assertiveness
This refers to the ability to express your beliefs and thoughts openly in a constructive and non-violent manner.
Independence
This refers to making decisions on your own without having to get everyone's opinion.
Self-regard
To accurately perceive, understand and accept oneself. This means that one has to like oneself in spite of their flaws.
Self-actualization
This refers to being satisfied and comfortable with what you have achieved.
Interpersonal skills
Interpersonal skills refers to how well you can relate with others.
Empathy
This refers to making efforts to understand other people's situation or point of view, by putting yourself in their shoes.
Social responsibility
This refers to establishing a personal link with other people and also cooperating with other members in working towards a shared goal.
Interpersonal relationship
To establish mutually satisfying relationships and relate well with others.
Adaptability
Adaptability refers to the ability to adjust your thinking and behavior when faced with new or unexpected situations.
Reality testing
To objectively validate one's feelings and thinking with external reality.
Flexibility
Adapting and adjusting your emotions, viewpoints, and actions as situations change.
Problem solving
This refers to approaching challenges step by step and not giving up in the face of obstacles.
Stress management
There are two skills that help manage stress.
Stress tolerance
This refers to recognizing causes of stress and responding in appropriate ways.
Impulse control
This refers to thinking carefully about potential consequences before you act.
General mood
When a person has a positive attitude, this improves his/her chances of doing well.
Optimism
Refers to looking at the bright side of a problem or difficulty and being confident that things will work out for the best.
Happiness
Being satisfied with yourself, with others and with the situation in general.
Benefits of emotional intelligence
It helps us to accurately perceive, appraise, and express emotions.
Emotional regulation
It helps us to regulate emotions in order to promote emotional and intellectual growth.
Conclusion on emotions
Emotions play a major role in our lives and it's very important that we identify the emotions we are experiencing, what triggered such emotions then we will be able to figure out how to deal with such emotions.