Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, & Temporal Bones
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
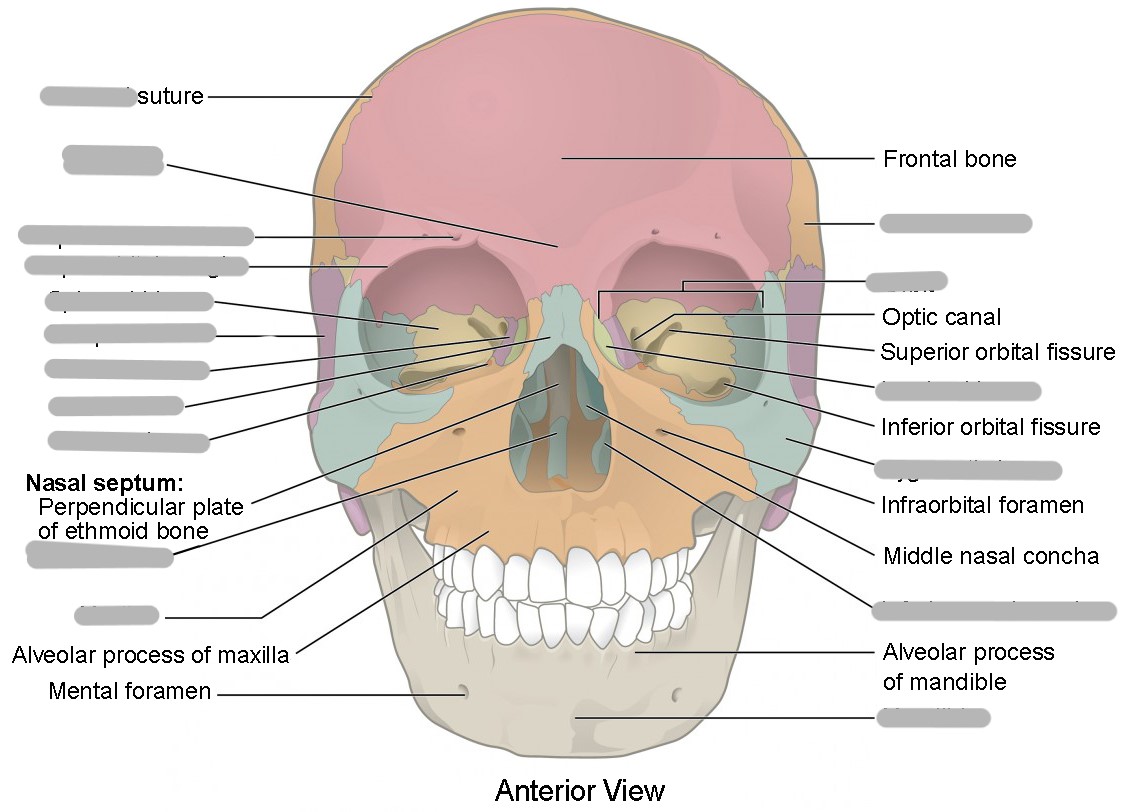
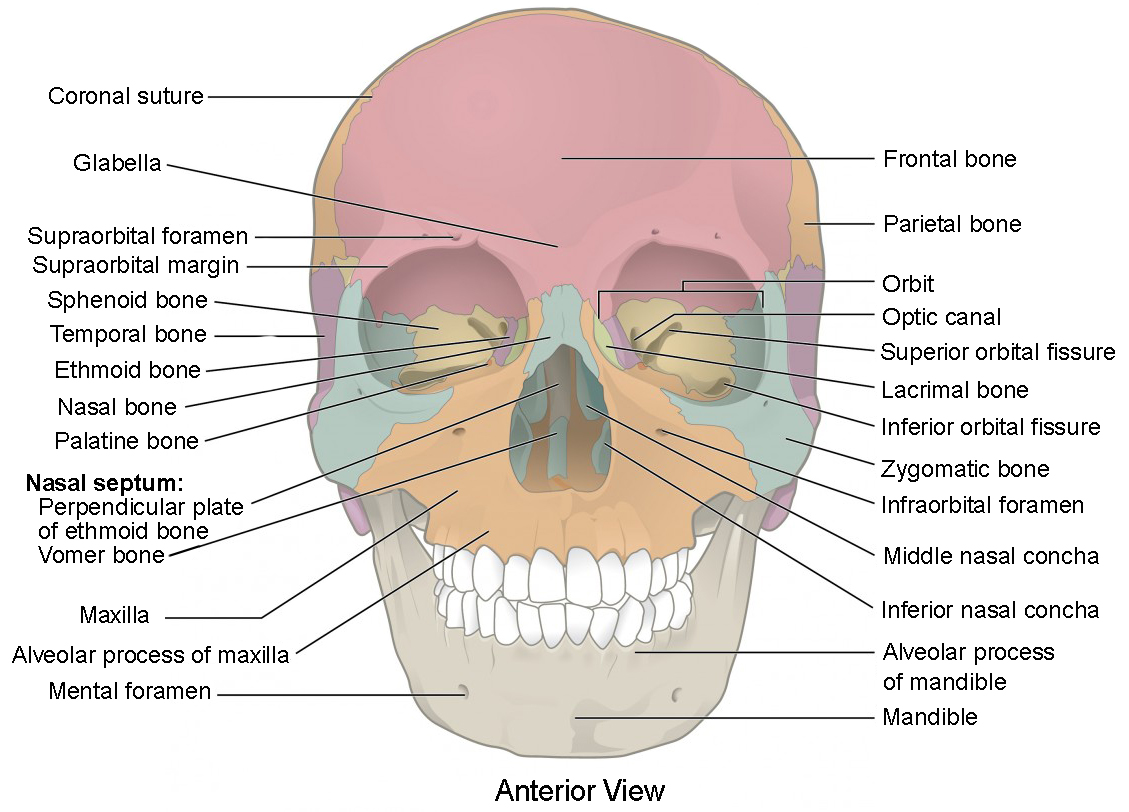
The frontal bone forms the ___
forehead and part of the vertex (calvaria) of the skull
Metopic suture
where the 2 frontal bones meet (they fuse into 1 bone early in life)
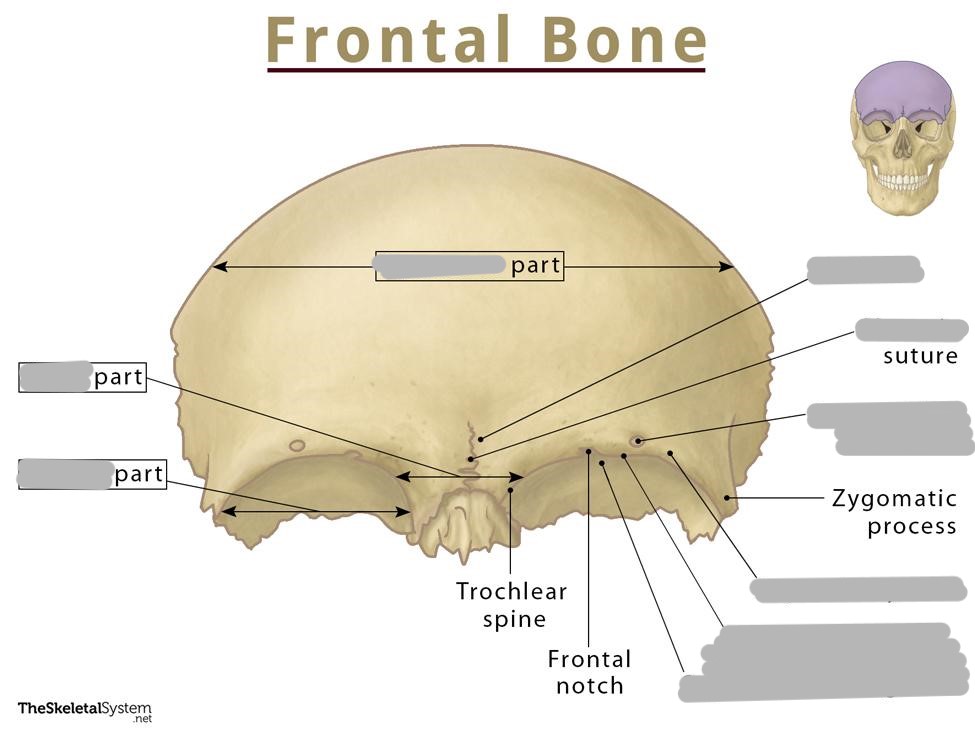
What are the 3 parts of the frontal bone?
squamous part (forehead)
orbital part
nasal part
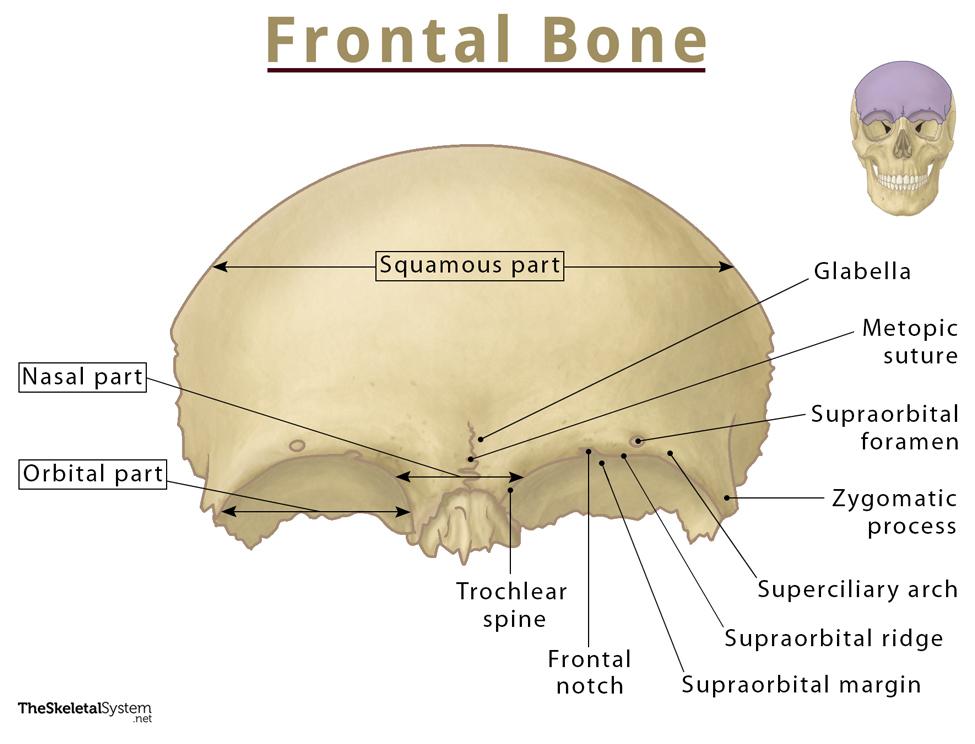
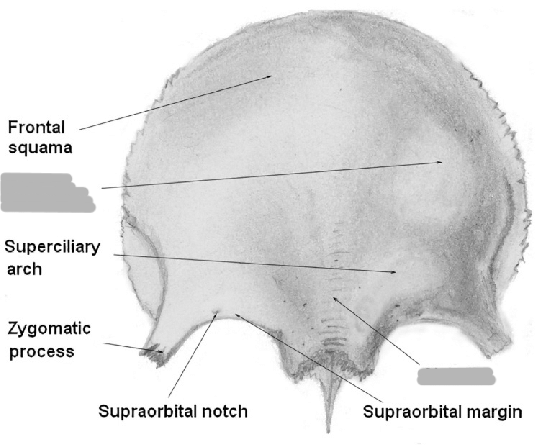
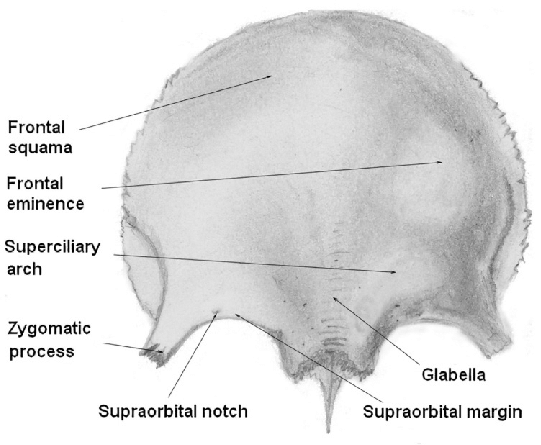
Frontal eminence
2 round prominences on the squamous part of the frontal bone (one on each side of the midline)
Supraorbital margins
ridges of bone that form the superior borders of the circular opening into each orbit
Supraciliary arches
above the supraorbital margin (the part covered by the eyebrows)
Supraorbital notch/foramen
groove or hole located toward the medial end of each supraorbital margin (transmits nerves to the face)
Nasion
landmark between the supraorbital margins
(top of the nose)
Glabella
landmark between the supraciliary arches
(bump between forehead and nose)
Frontal sinus
air filled asymmetric cavity in the frontal bone
What are the features of the squamous part of the frontal bone?
frontal eminence, supraorbital margin, supraciliary arches, supraorbital notches/foramen
Orbital plates
2 flat plates of bone that form the roof of each orbit
a part of the frontal bone
Ethmoidal notch
gap between the medial borders of the 2 orbital plates
What are the features of the orbital part of the frontal bone?
orbital plates and ethmoidal notch
Where is the nasal part of the frontal bone?
extends down the midline between supraorbital margins
Frontal nasal spine
a pointed process that extends down from the nasal part of the frontal bone
Parietal eminence
rounded prominences of the lateral surface of the parietal bones
What gives our skull its greatest transverse diameter?
parietal eminences
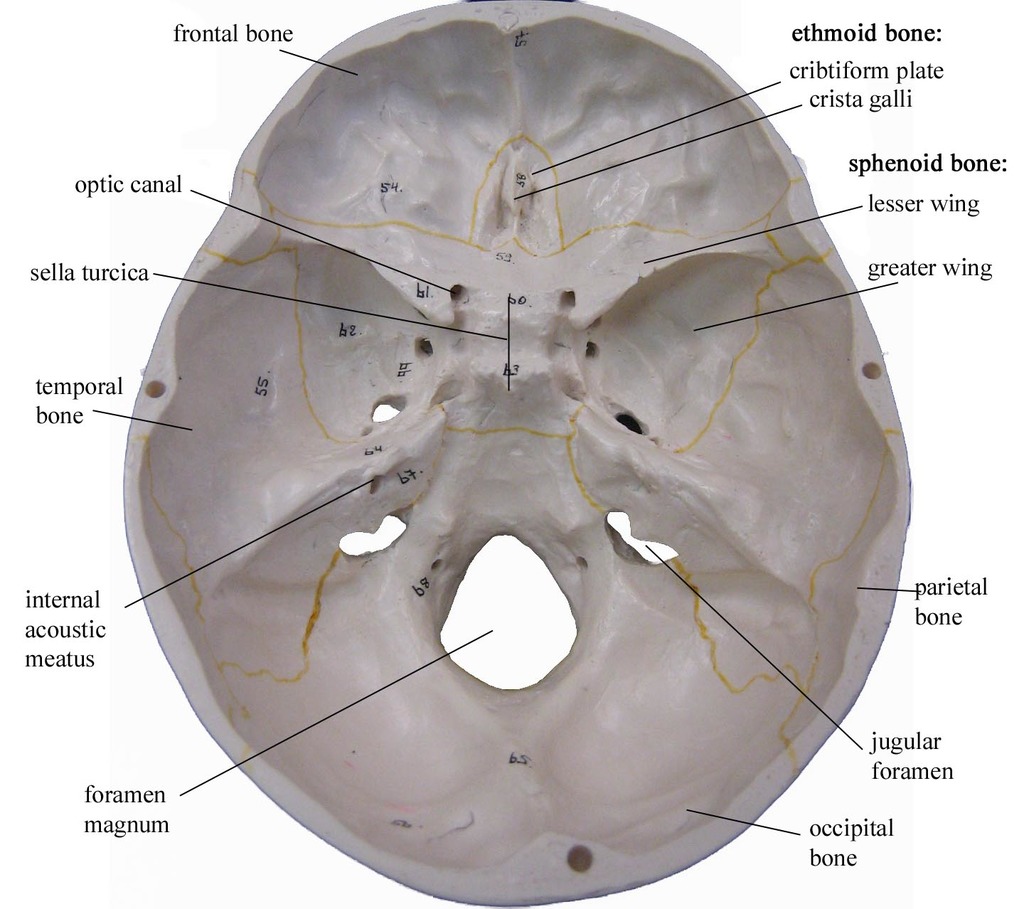
The ___ bone forms the base of the cranium
occipital
Foramen magnum
large opening in the inferior part of the occipital bone (where the medulla oblongata joins the spinal cord)
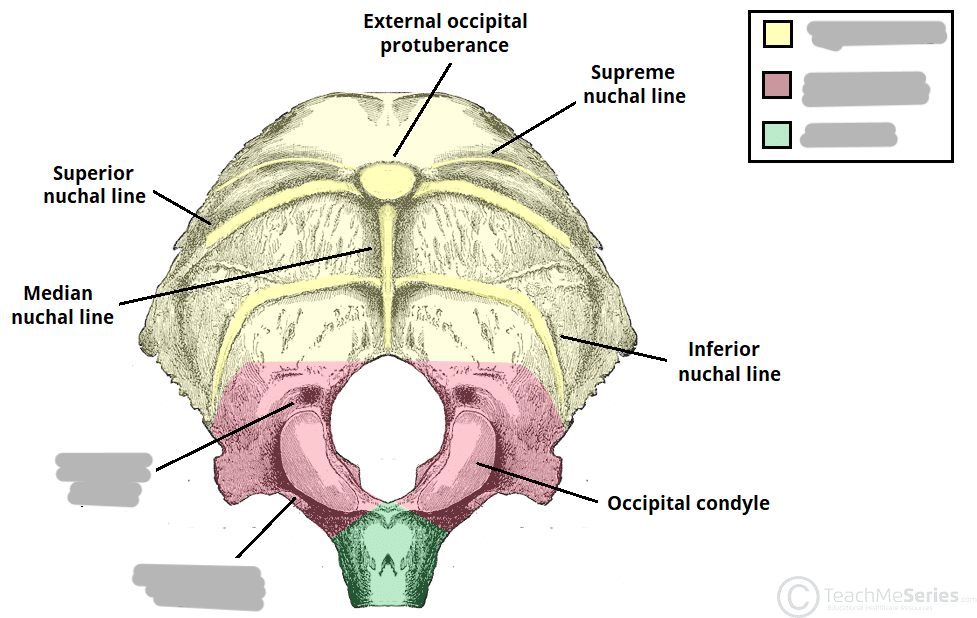
Squamous part of the occipital bone
external occipital protuberance OR inion
Lateral parts of the occipital bone
2 oval shaped regions located on the inferior surfaces of each side of the foramen magnum
Occipital condyles
oval shaped prominences located on the inferior surface (articulates with C1)
Condylar canals/fossa
fossae posterior to the occipital condyles
Hypoglossal canals
fossae anterior to the occipital condyles (passageway for the 12th cranial nerve)
Basilar part (of occipital bone)
part sloping up from occipital bone, anterior portion of foramen magnum (where basilar artery sits)
Clivus
sloping portion between sphenoid bone and basilar part of the occipital bone
The ___ bone contains the organs of hearing
temporal
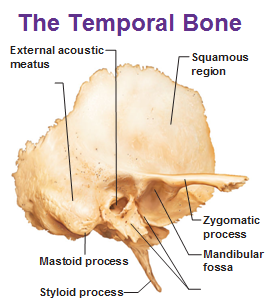
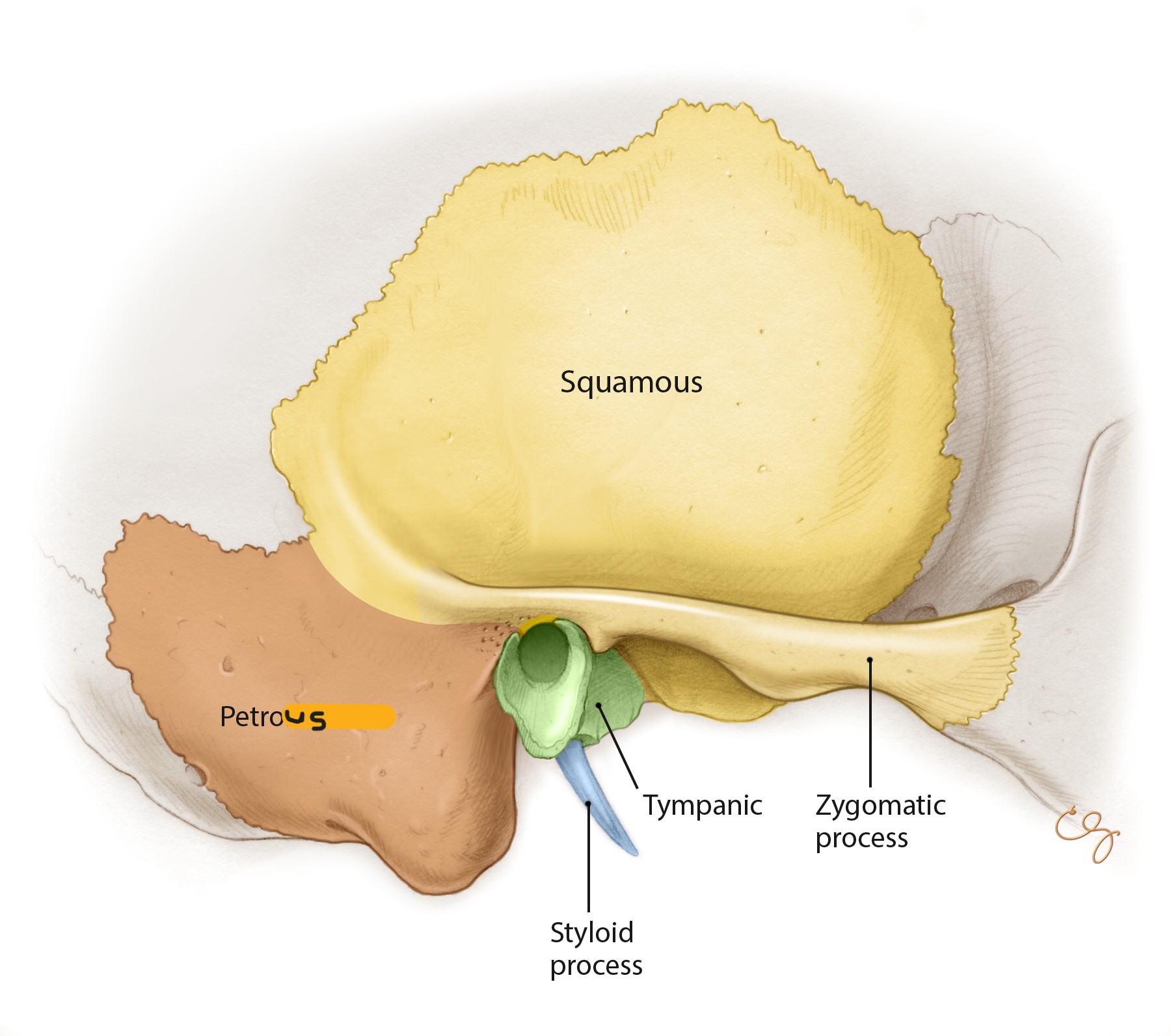
What are the 3 parts of the temporal bone?
squamous part
petrous part
tympanic part
Mastoid process
contains the mastoid air cells and acts as a buffer in the inner ear in case the Eustachian tube malfunctions (large process)
Styloid process
thin process anterior and medial to the mastoid process
Squamous part of the temporal bone
flat part above the ear
Zygomatic process of the temporal bone
slender process that extends forward and meets the zygoma bone to form the zygomatic arch
Petrous part of the temporal bone
“petrous pyramid”
shaped like a pyramid/wedge and houses the parts of the ear that hear
What foramen are contained in the petrous part of the temporal bone?
jugular
carotid
internal auditory meatus
foramen lacerum
Explain the location and function of the jugular foramen
opening in the suture between the occipital and petrous portion
transmits internal jugular vein and cranial nerves 9, 10, and 11
What is the function of the carotid foramen?
transmits internal carotid artery
Explain the location and function of the foramen lacerum
at the articulation of temporal, sphenoid, and occipital bones
pharyngeal artery passes through
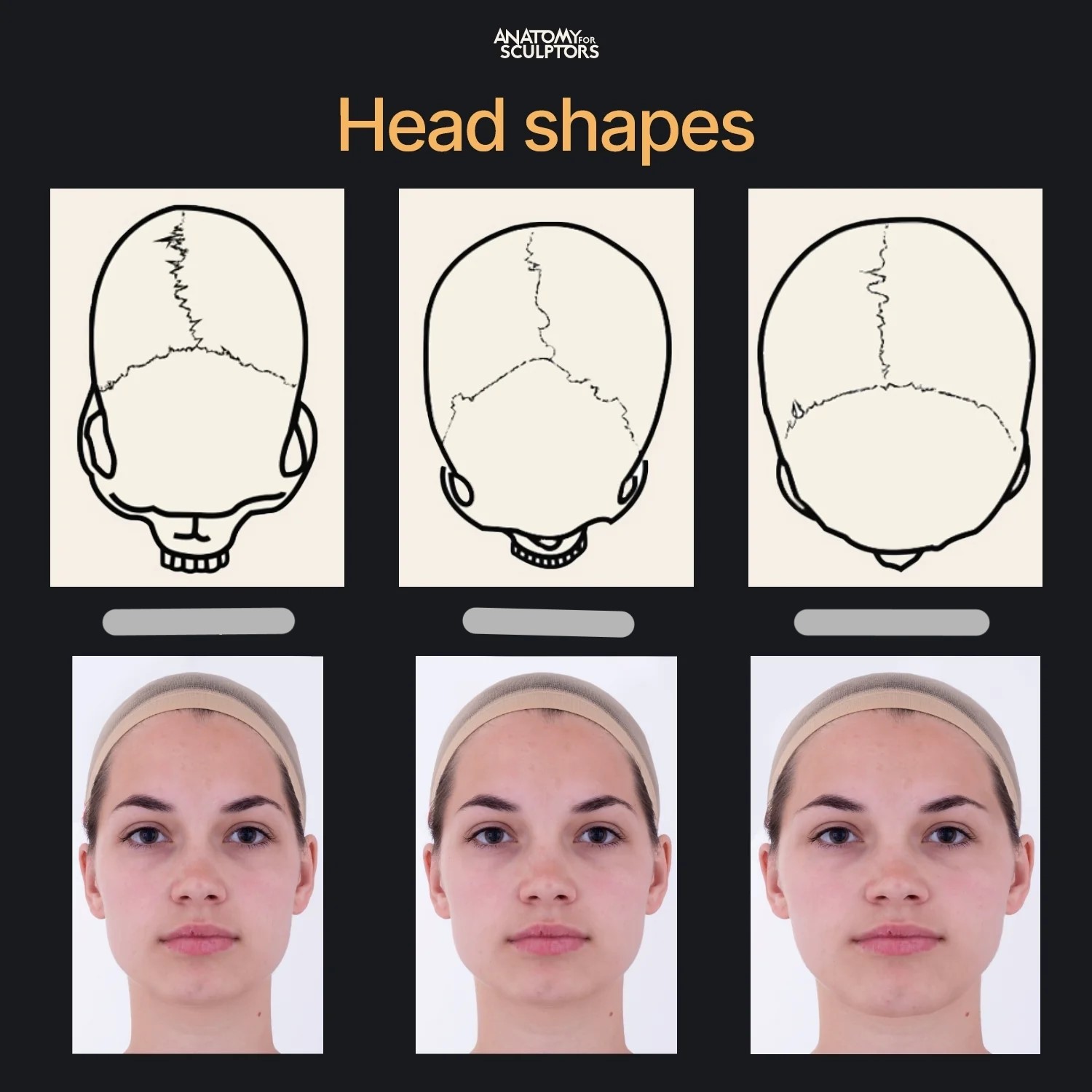
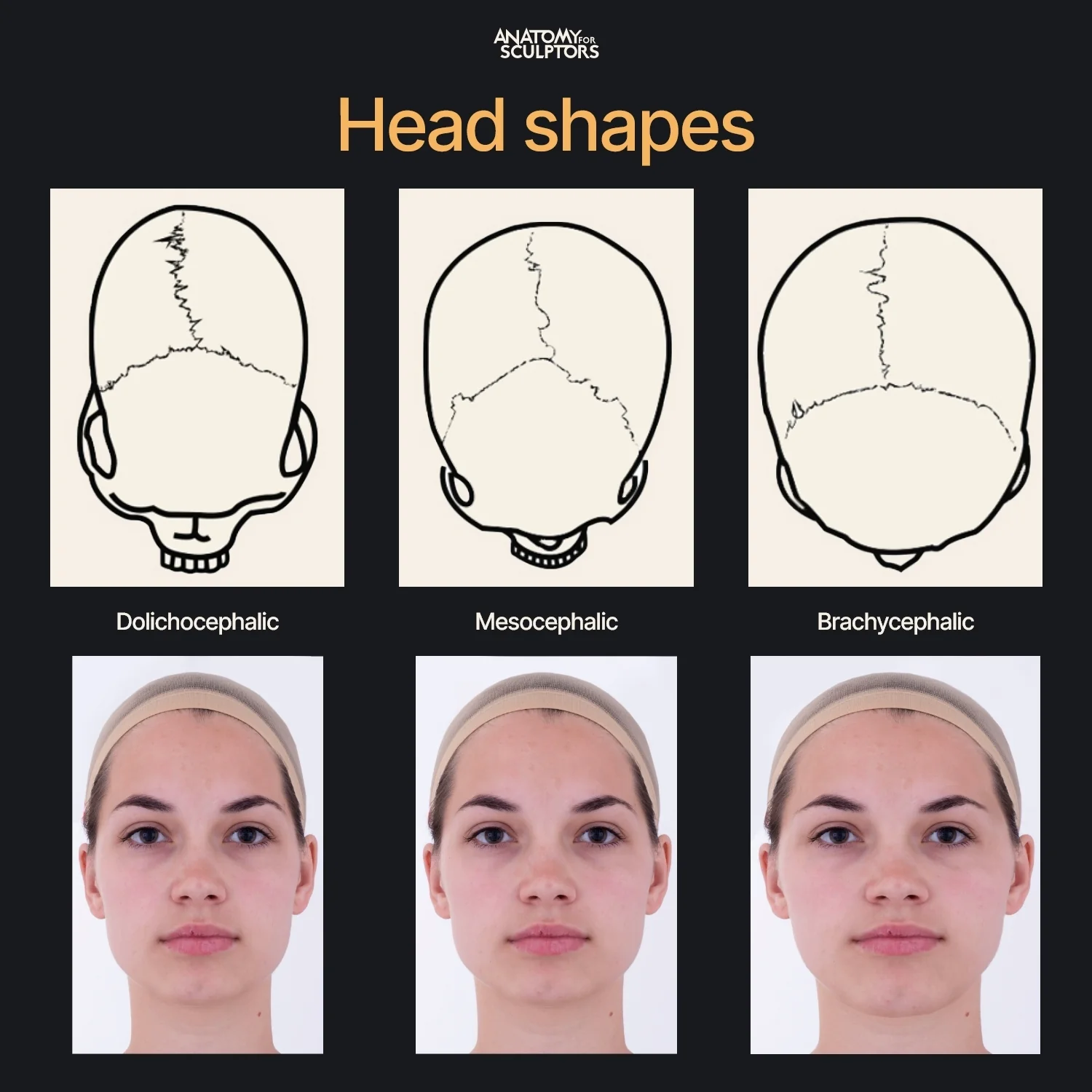
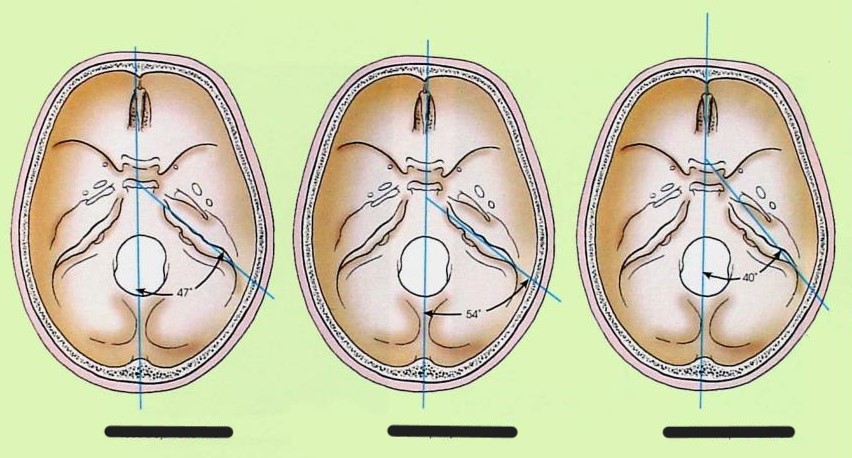
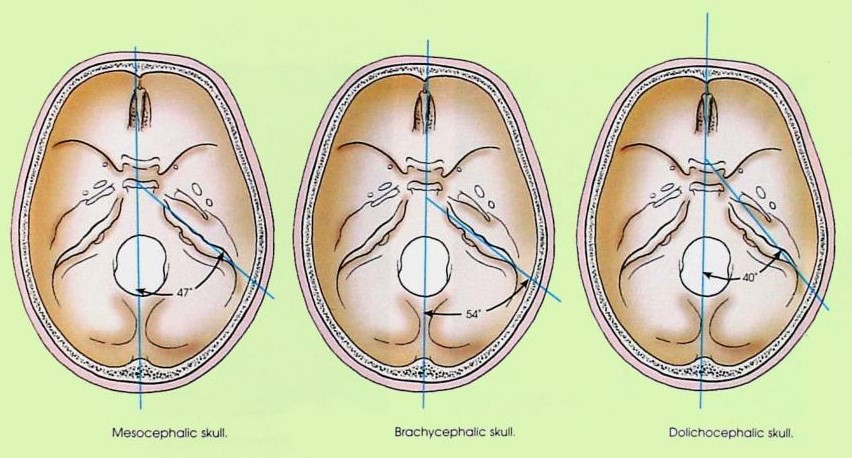
Explain the 3 skull shapes
mesocephalic
45-47o from MSP
normal
brachiocephalic
54o from MSP
short head - coronal craniostenosis
dolichocephalic
40o from MSP
long head - sagittal craniostenosis
Explain the tympanic part of the temporal bone
forms the anterior and inferior walls of the EAM (also helps to form the mandibular fossa)
Explain the mandibular fossa (including joint classification)
depression on temporal bone in front of EAM
condyle of the mandible fits into this to form the TMJ
condylar/ellipsoidal
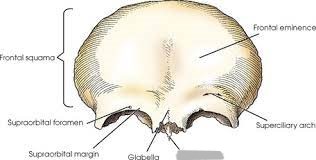
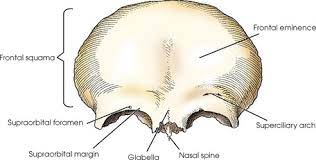
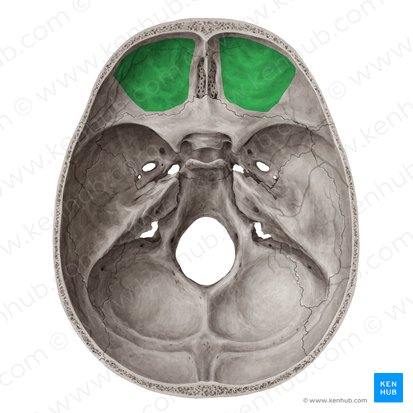
What is shown in green?
orbital plates
What is shown in red?
parietal eminence
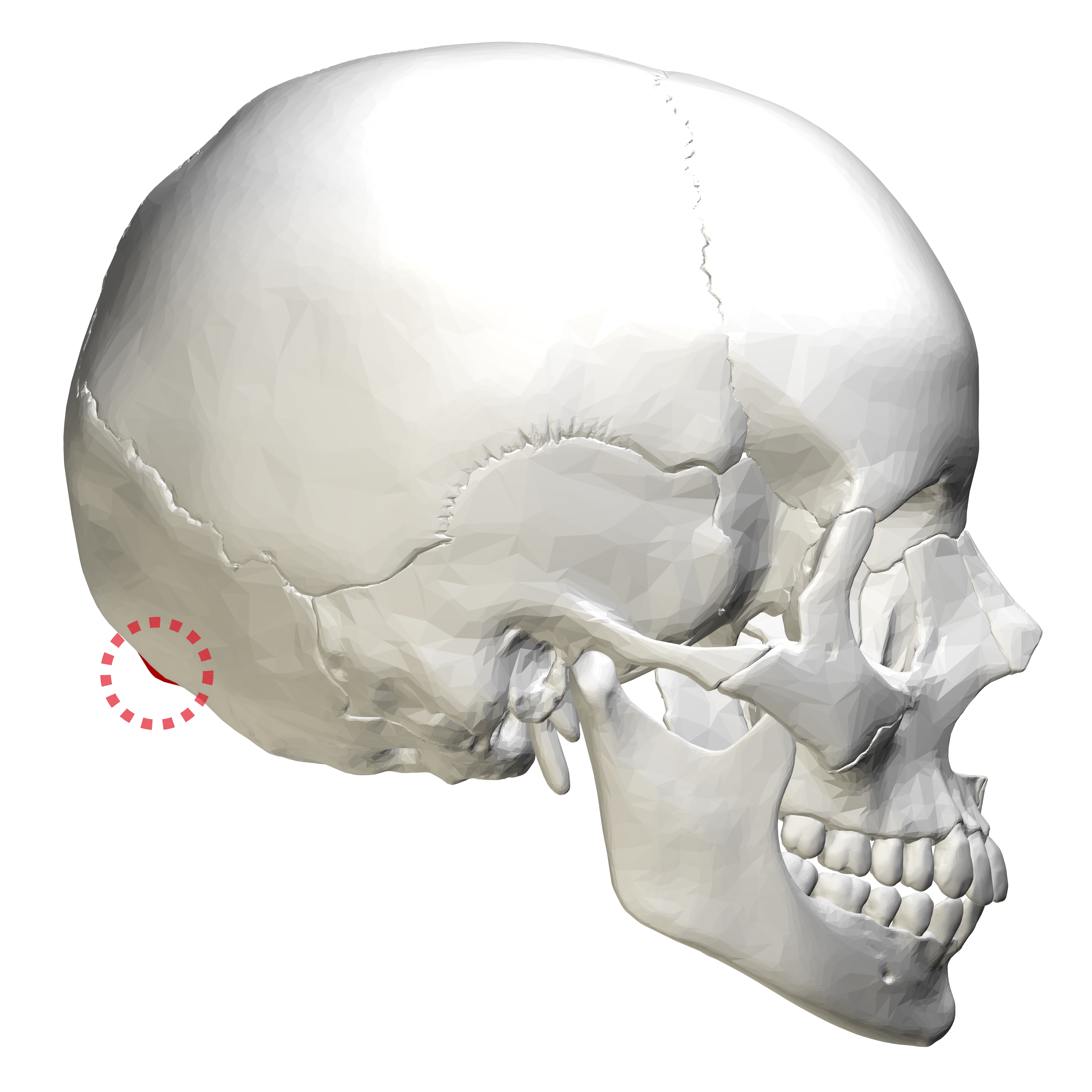
What is shown in red?
inion (external occipital protuberance)
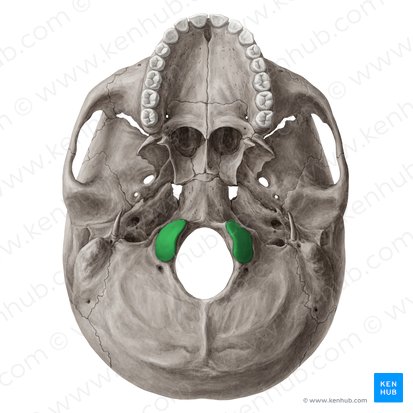
What is shown in green?
occipital condyles
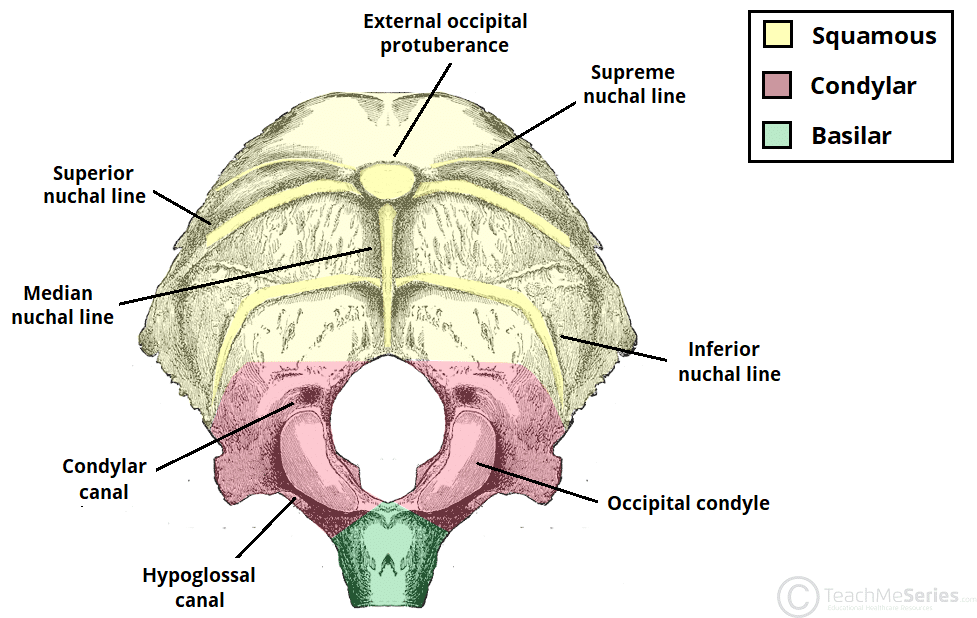
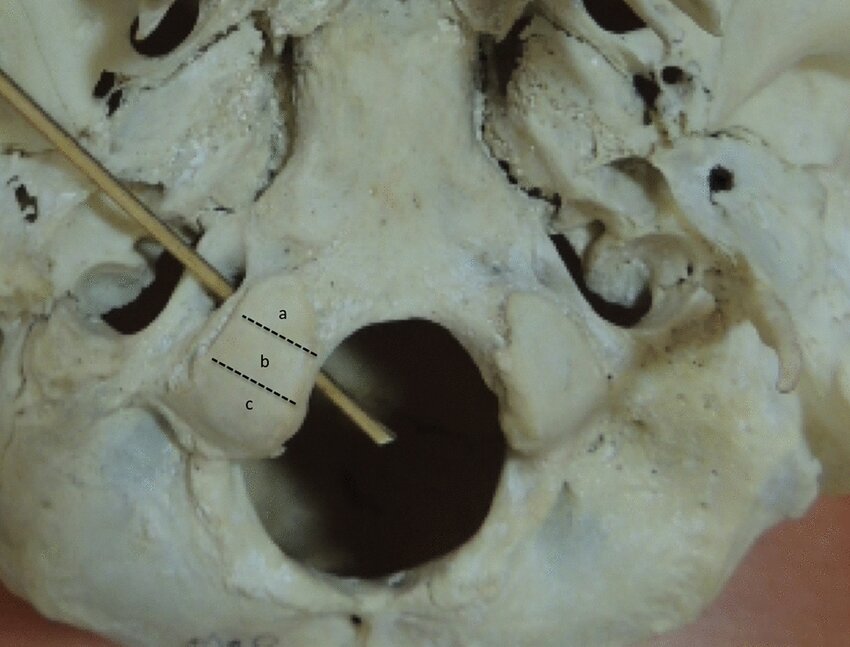
What canal/foramen is the rod going through?
hypoglossal canal
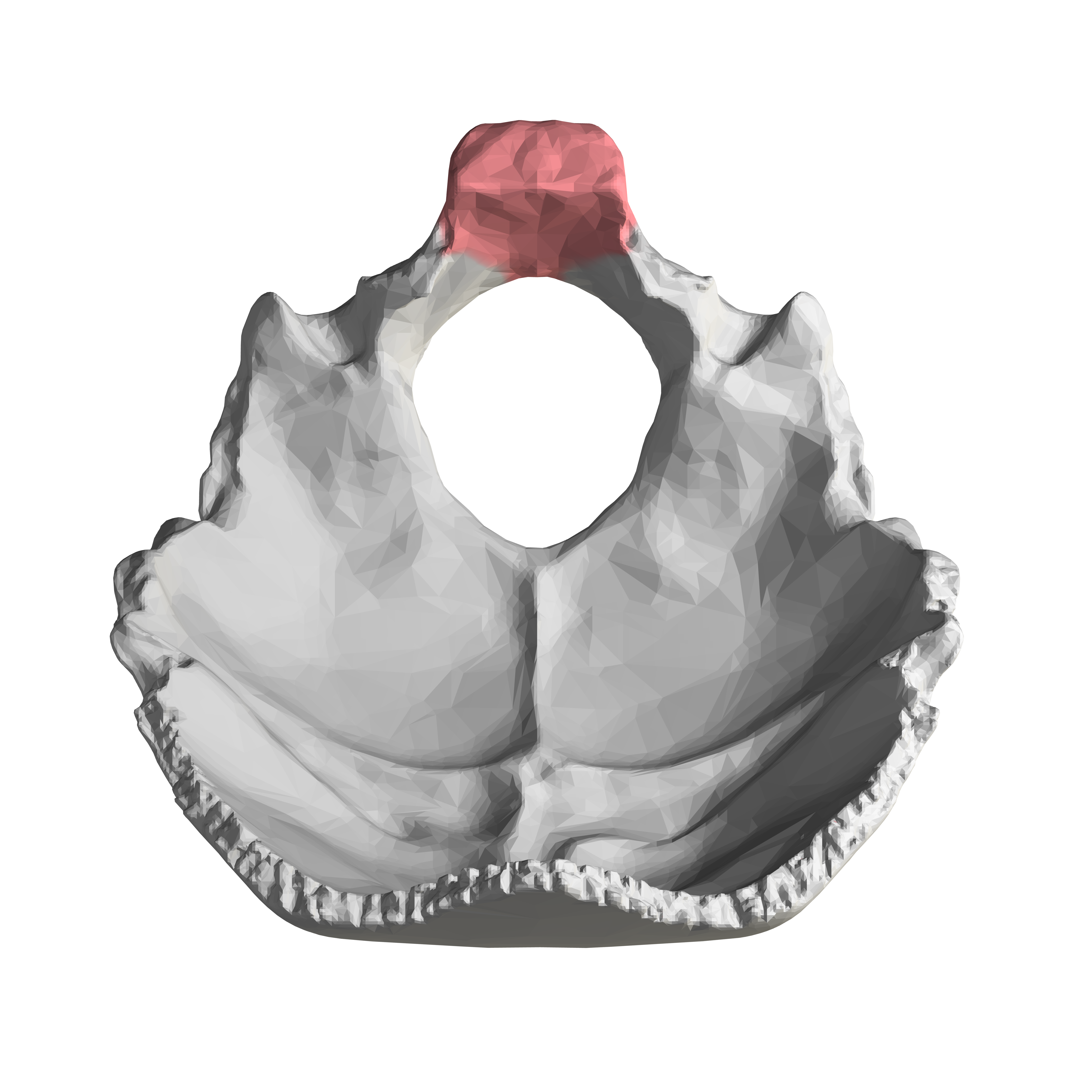
What is shown in red?
the basilar part of the occipital bone (potentially part of the clivus as well)
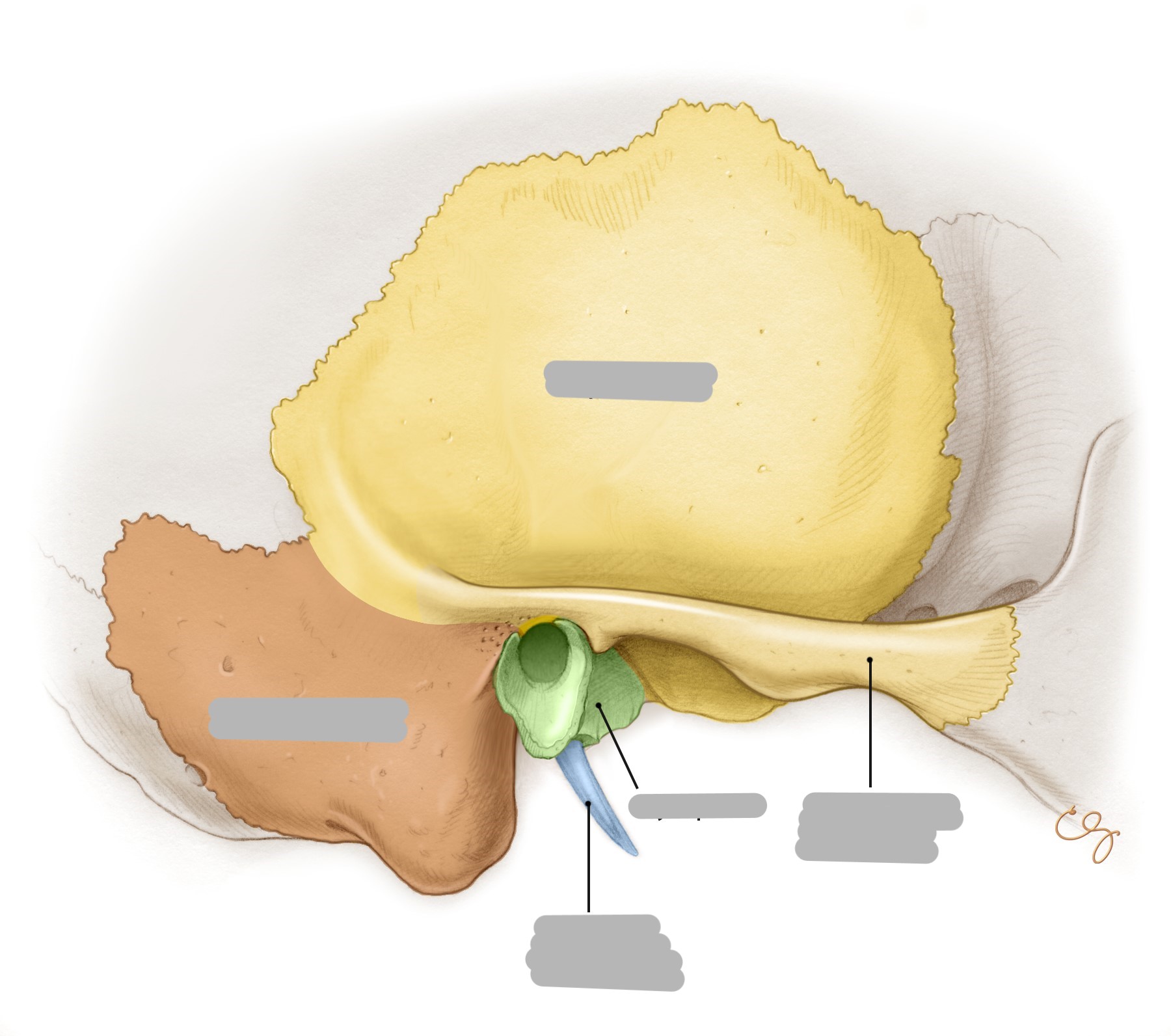
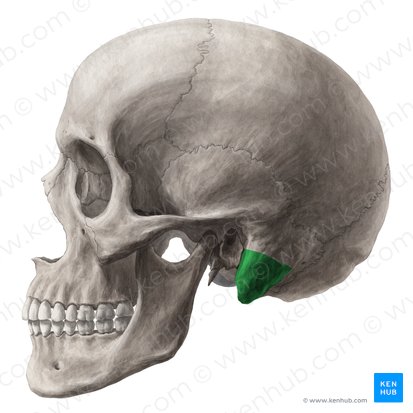
What is shown in green?
mastoid process
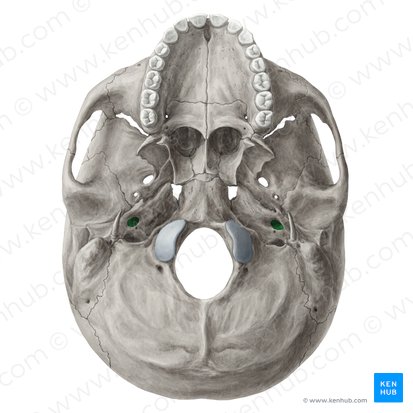
What is shown in green?
carotid canal
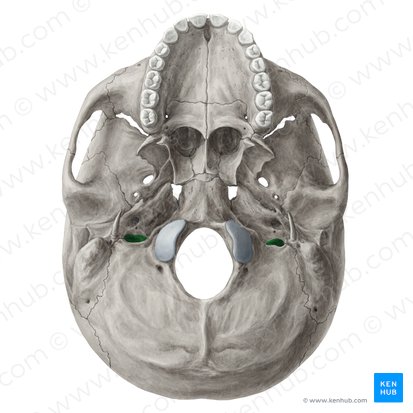
What is shown in green?
jugular foramen
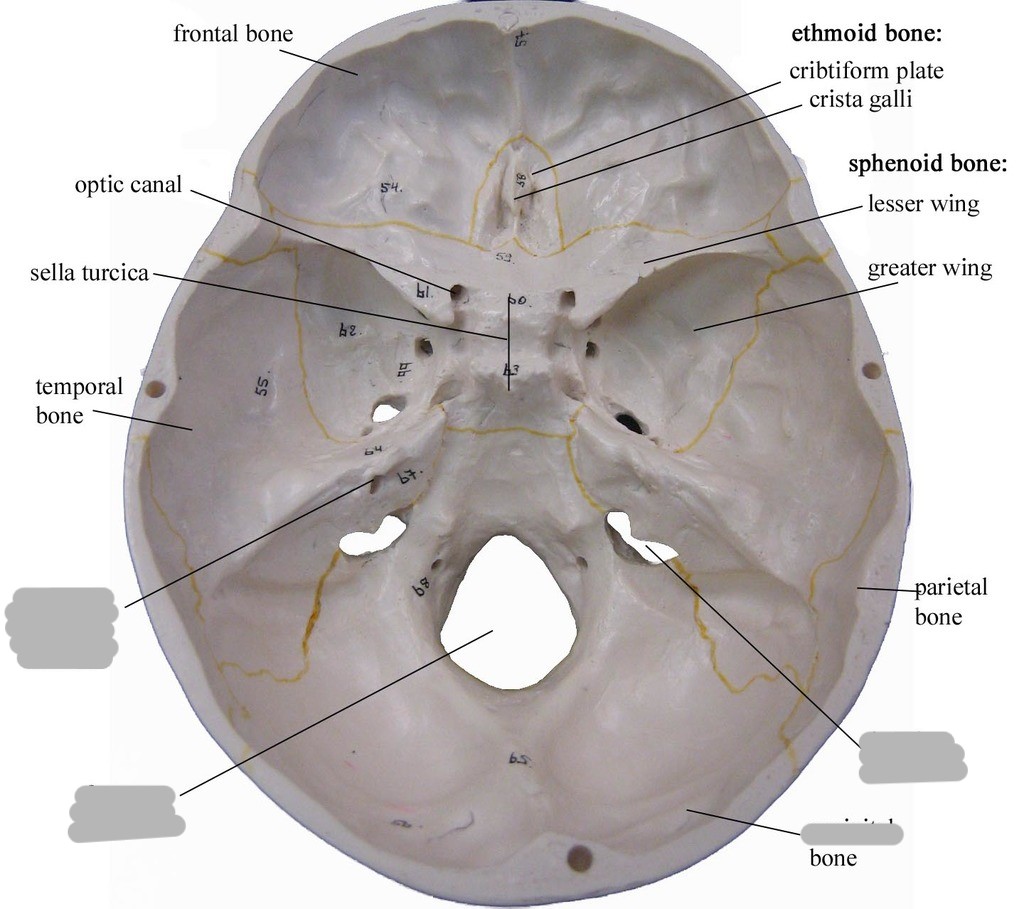
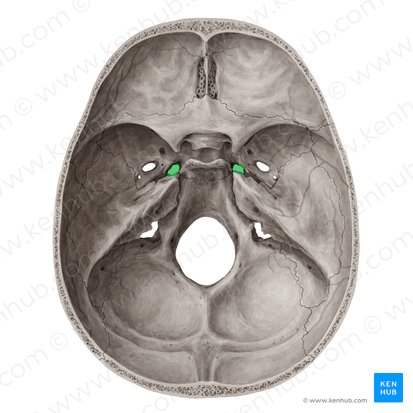
What is shown in green?
foramen lacerum