Ocular Pathology: Cornea and Glaucoma 2
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What are the two types of glaucoma?
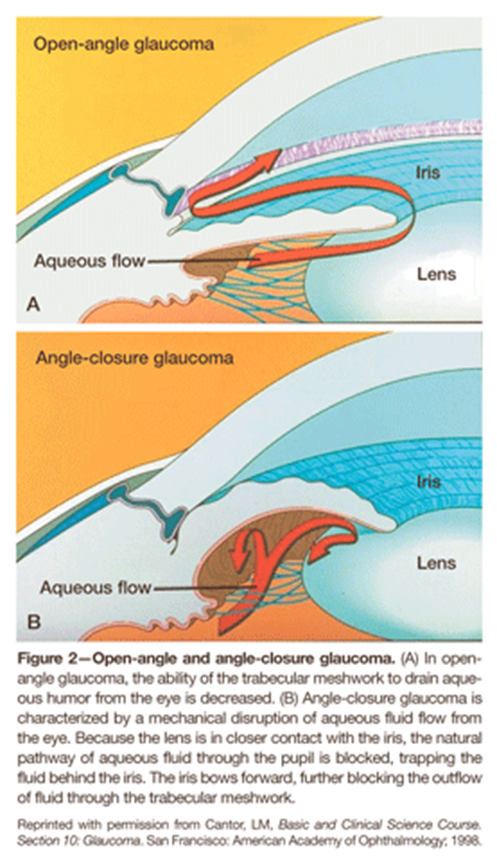
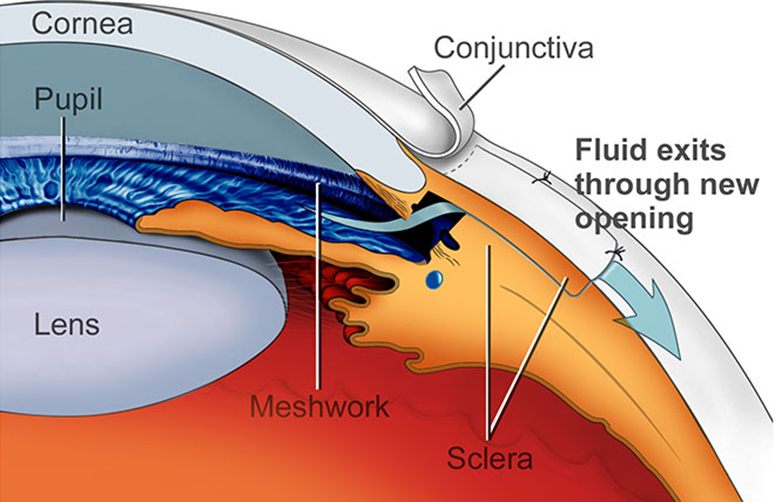
1) Aqueous Humor is produced in the ciliary body epithelium where it will flow around the lens and through the pupil into the anterior chamber
→ here it will be drained through the trabecular meshwork then Canal of Schlemm into the episcleral veins
Because of this patients can have two forms of glaucoma depending on what kind of obstruction is occurring
1) Open Angle - most common form of glaucoma
→ Outflow of aqueous through trabecular meshwork and Schlemm’s canal is impaired
→ fluid still reaches the angle but has a difficult time passing through the meshwork
2) Closed Angle
→ Resistance to outflow is increased due to the iris obstructing the path to the trabecular meshwork
What is a glaucoma?
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve leading to irreversible blindness. There are two types of glaucoma but they all share two things
→ damage to the optic nerve (optic neuropathy) - leading to cupping of the optic nerve
→ associated visual field loss
While patients often have elevated intraocular pressure as a primary risk factor it is not the cause of glaucoma
What are the risk factors associated with developing open angle glaucoma?
1) Hereditary
→ patients with a primary family member with open angle glaucoma you have a ten percent chance of also developing it
→ first degree relative having the disease puts you at a 10x risk of developing the disease
2) Increased Age
→ adults over the age of 40 will have a increased risk
3) Increased Intraocular Pressure
→ the average intraocular pressure is around 10-21 mmHg with a variation of 2-6 mmHg over a 24 hour period
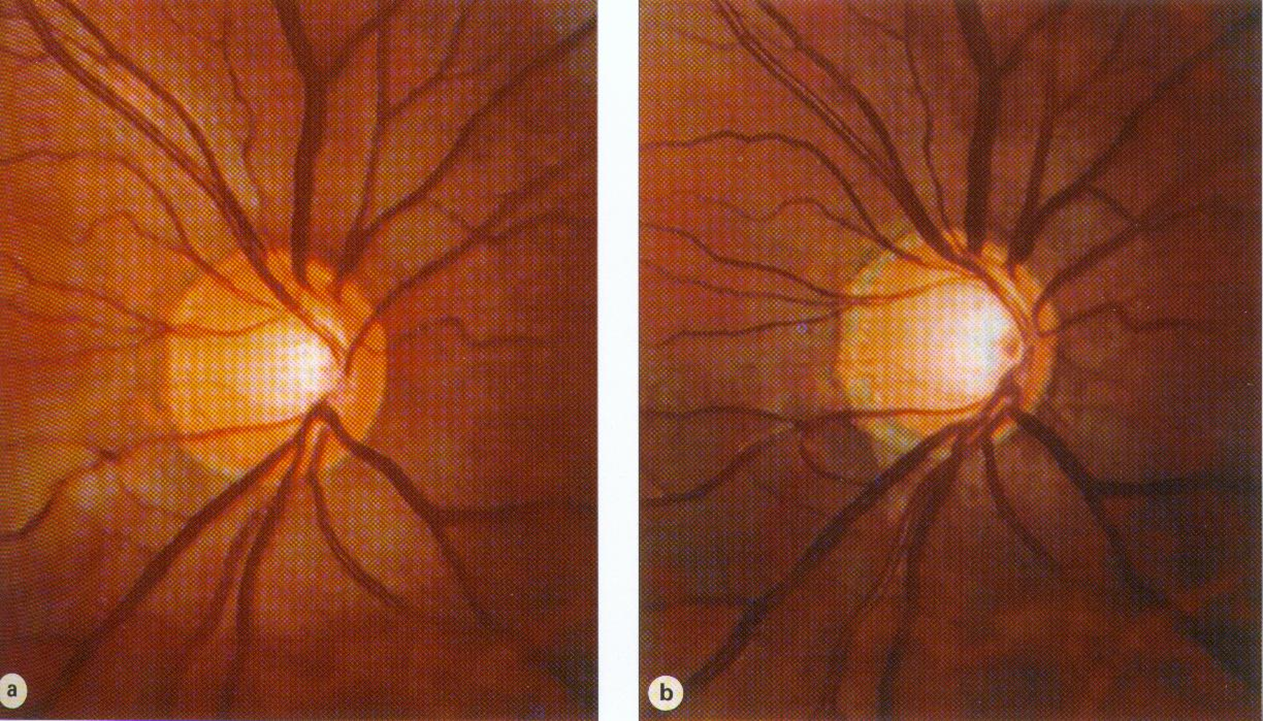
4) Optic Neuropathy
→ patients with pathologic cupping of the optic nerve or a pathologic depression in the optic nerve
5) Pachymetry
6) Race
What happens to the nerve fiber layer in patients with glaucoma
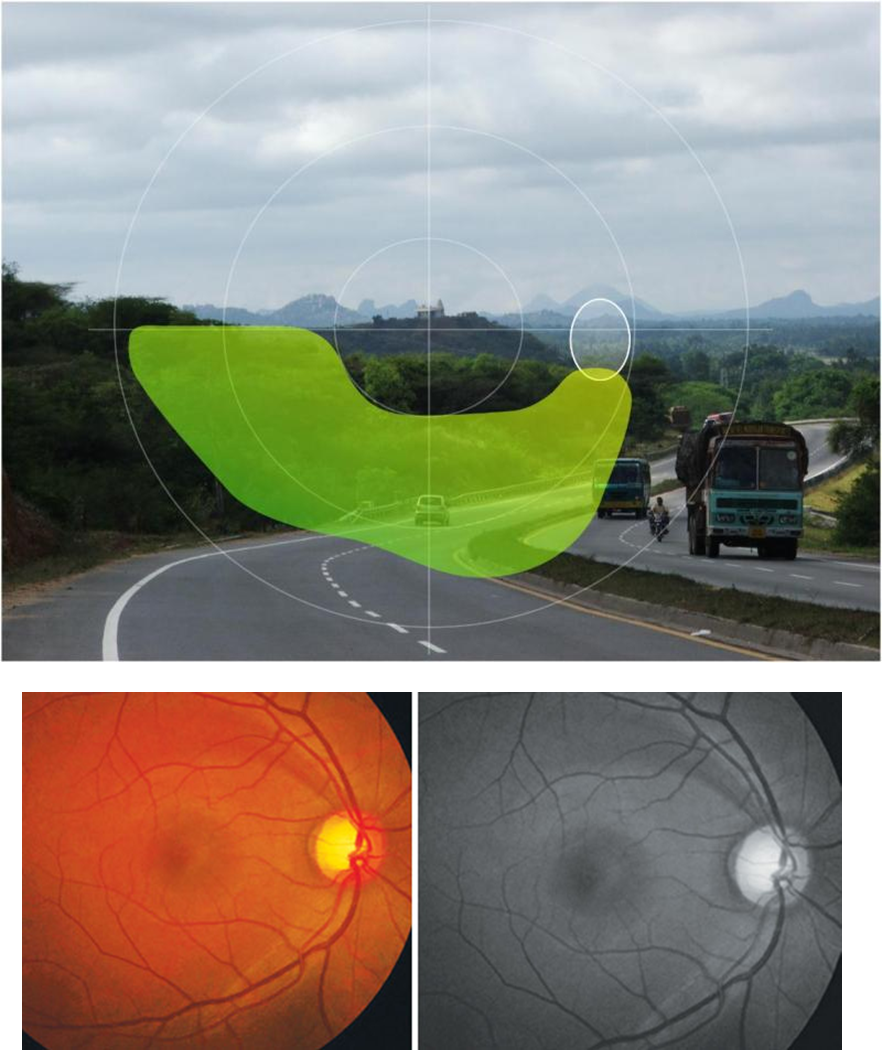
Patients with open angle glaucoma will often experience is loss and thinning of the nerve fiber layer
1) Axons of the eye will become damaged and stressed especially as they enter into the optic disc to become the optic nerve
→ leads to the formation of a blind spot
2) Creates this dark area as the axons enter into the optic disc where the axons have died off in an arcuate pattern
→ creates a visual defect in a similar arcuate pattern
What is Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging
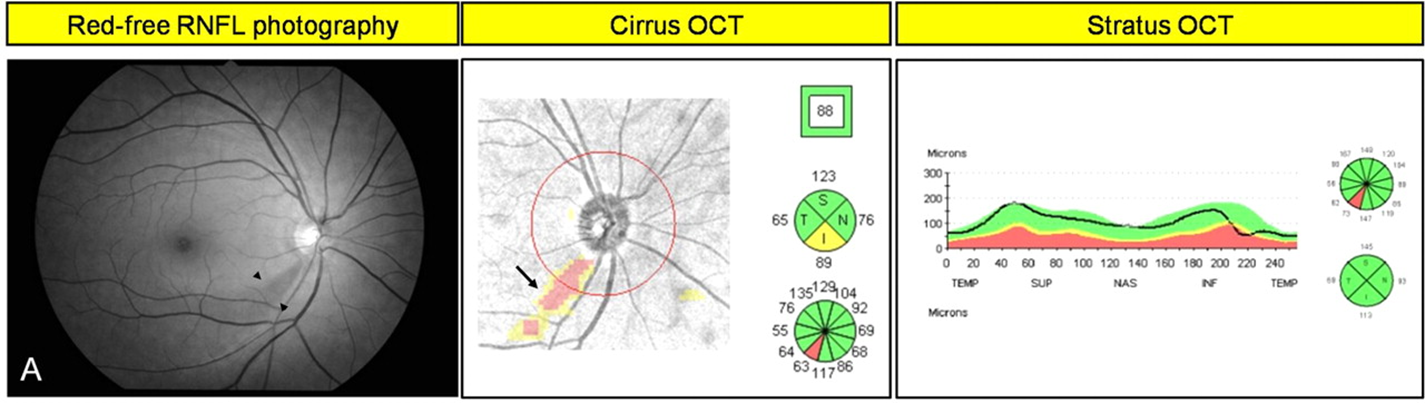
Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging is a non-invasive imaging method in order to get cross-sectional images of the retina and optic nerve
1) Used in diagnosis of open angle glaucoma as an objective measure of retinal thickness allowing us to quickly identify damage to the retinal axons in patients with glaucoma
How is open-angle glaucoma treated? (goals, who should be treated, and options)
The main goal with treating glaucoma is to treat the optic nerve pathology and their visual field defect
1) Patients with intraocular pressure greater than 30 should be treated immediately
→ goal is to decrease intraocular pressure
2) There are three treatment options:
→ Topical Medications
→ Laser Therapy to the Trabecular Meshwork (trabeculoplasty) - using lasers to open up the trabecular meshwork
→ Surgery (Trabeculectomy or Shunt) in order to create new paths for aqueous flow
What is acute angle closure glaucoma and what is its presentation?
Acute angle-closure glaucoma is a medical emergency characterized by sudden blockage of the aqueous humor drainage leading to an rapid increase in intraocular pressure
→ The iris is pushed forward and physically blocks the trabecular meshwork at the drainage angle, preventing aqueous humor from exiting
Patients will have:
→ sudden onset
→ painful red eye and headache
→ blurry vision and halos around lights
→ fixed mid-dilated pupil
→ shallow anterior chamber
→ angle closed on gonioscopy
→ nausea and vomiting
What is the treatment of acute angle closure glaucoma?
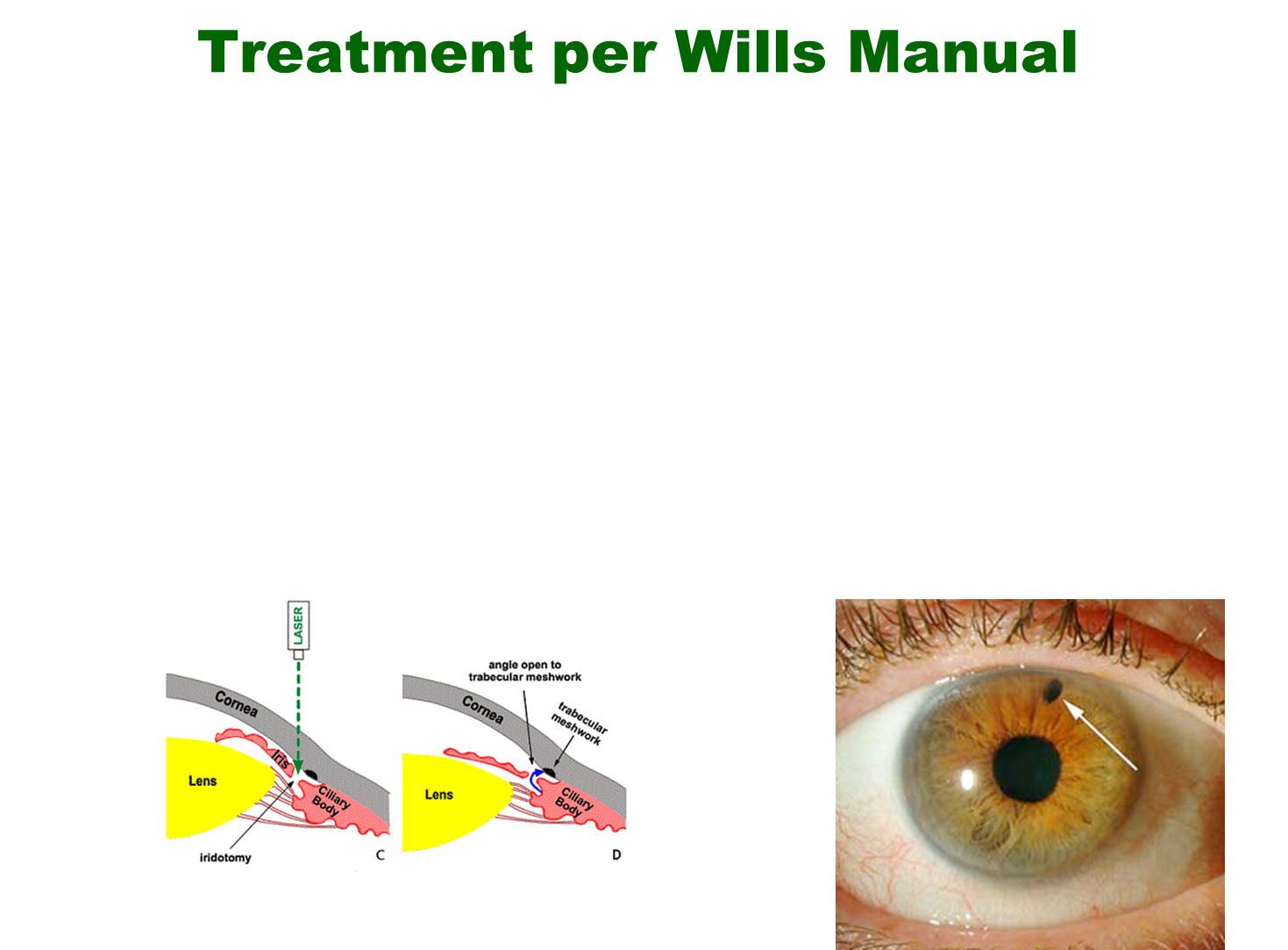
1) Topical beta blocker, alpha agonist and steroid
2) Intraocular pressure still elevated after first step consider acetazolamide
→ if IOP is greater than 50
3) if IOP is still elevated use mannitol
4) May need to do laser surgery creating a hole in order to create a safety valve out of the eye (Peripheral Iridotomy)