APHUG S1 exam units 1-2 + 3.1/3.2
1/181
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sem 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
182 Terms
formal economy
all economic activities operating within the official legal framework that are paying taxes on all generated incomes.
quaternary economic activities
consists of intellectual activities often associated with technological innovation.
secondary economic activities
produces finished goods from the raw materials extracted by the primary economy.
colonialism
the policy or practice of acquiring full or partial political control over another country, occupying it with settlers, and exploiting it economically.
commodity
a raw material or primary agricultural product that can be bought and sold, such as copper or coffee.
commodity dependence
when commodities constitute the predominant share of its exports.
core countries
countries that dominate trade, control the most advanced technologies, and have high levels of productivity within diversified economies.
dependency theory
resources flow from a 'periphery' of poor and underdeveloped states to a 'core' of wealthy states, enriching the latter at the expense of the former.
Gender Inequality Index (GII)
an index for measurement of gender disparity that was introduced in the 2010 Human Development Report; measures the human development costs of gender inequality.
globalization
a reference to the increasing interconnection of all parts of the world as the full range of social, cultural, political, and economic processes becomes international in scale and effect.
gross domestic product (GDP)
the total value of goods produced and services provided in a country during one year.
Human Development Index (HDI)
a summary measure of average achievement in key dimensions of human development: a long and healthy life, being knowledgeable and have a decent standard of living.
imperialism
policy or ideology of extending a country's rule over foreign nations, often by military force or by gaining political and economic control of other areas.
Infant Mortality Rate
the number of deaths per year of infants less than one year old for every 1000 live births.
LDC (Less Developed Countries)
a term applied to countries considered not yet fully developed or in a state of underdevelopment in economic and social terms.
life expectancy
a figure indicating how long, on average, a person may be expected to live.
literacy rate
the percentage of a country's people who can read and write.
mass consumption
the purchase of standardized products or services by large numbers of customers.
MDC (more developed country)
countries with highly developed economies, high levels of industrialization, urbanization, advanced technological infrastructure and high standards of living.
microloan
small loans that are issued by individuals rather than banks or credit unions.
periphery countries
the least developed and least powerful nations; often exploited by the core countries as sources of raw materials, cheap labor, and markets.
primary economic activities
extracts or harvests products from the earth such as raw materials and basic foods.
quinary economic activities
includes the highest levels of decision-making in a society or economy.
semi-periphery countries
nations ranking in between core and periphery countries.
service sector
provides services, rather than producing material commodities.
sustainable development
the organizing principle for meeting human development goals while simultaneously sustaining the ability of natural systems.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
the average number of children a woman would have during her reproductive years if she were to experience the current age-specific fertility rates.
W.W Rostow
American economist who proposed his five stage model of development.
Wallerstein's World System Theory
an approach to world history and social change that suggests there is a world economic system in which some countries benefit while others are exploited.
Brandt Line
line on world map dividing MDCs and LDCs
development
the process of growth, expansion, or realization of potential; bringing regional resources into full productive use.
gross national income (GNI)
previously known as gross national product, is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product, plus factor incomes earned by foreign residents, minus income earned in the domestic economy by nonresidents.
gross national product (GNP)
an estimate of total value of all the final products and services turned out in a given period by the means of production owned by a country's residents.
Industrial Revolution
the transition to new manufacturing processes in Europe and the United States, in the period from about 1760 to sometime between 1820 and 1840.
informal economy
the part of any economy that is neither taxed nor monitored by any form of government.
microlending
a form of financing that provides small amounts of money to typically very poor fledgling entrepreneurs to encourage self-sufficiency and to end poverty.
newly industrialized countries (NICs)
developing economies that have advanced towards industrialization and might become developed, at some point, in the near future.
raw materials
unprocessed natural products used in production.
tertiary economic activities
also known as the service industry; this sector sells the goods produced by the secondary sector.
underdevelopment
a level of economic and social achievement below what could be reached given the natural and human resources of an area.
physiological
the number of people per unit of area of arable land, which is land suitable for agriculture.
possibilism
the theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action form many alternatives.
absolute Location
the exact position of an object or place stated in spatial coordinates or a grid system designed for locational purposes, e.g., latitude and longitude.
built landscape
the part of the physical landscape that represents material culture; the buildings, roads, bridges, and similar structures large and small of the cultural landscape.
census
an official enumeration of the population, with details as to age, sex, occupation, etc. The USA has a census every ten years (2010, 2020, 2030, etc.)
contagious
the rapid, widespread diffusion of a feature or trend though out a population; person to person spread of culture.
diffusion
the process of spread of a feature or trend from one place to another over time.
distance decay
the diminishing in importance and eventual disappearance of a phenomenon with increasing distance from its origin.
dot
a thematic map in which a dot represents some frequency of the mapped variable.
environmental determinism
a nineteenth and early twentieth century approach to the study of geography that argued that the general laws sought by human geographers could be found in the physical sciences; physical environment caused human activities.
equator
an imaginary east-west line that encircles the globe halfway between the North and South Poles.
Gall-Peters projection
a rectangular, equal-area map projection. Like all equal-area projections, it distorts most shapes.
Geographic Information System (GIS)
a computer hardware and software system that handles geographically referenced data; it uses and produces maps and has the ability to perform many types of spatial analysis.
geography
the study of the physical features of the earth and its atmosphere, and of human activity as it affects and is affected by these, including the distribution of populations and resources, land use, and industries. Describing the earth.
geospatial
relating to or denoting data that is associated with a particular location.
globalization
the tendency of businesses, technologies, or philosophies to spread throughout the world, or the process of making this happen.
hierarchical
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places; spread of culture from one important / large area to another important / large area.
isoline
a thematic map with lines that connect points of equal value.
latitude
the numbering system used to indicate the location of parallels drawn on a globe and measuring distance north and south of the Equator.
longitude
the numbering system used to indicate the location of meridians drawn on a globe and measuring distance east and west of the Prime Meridian.
map
a two-dimensional, or flat, representation of Earth's surface or a portion of it.
mental map
(cognitive map) the map like image of the world, country, region, city, or neighborhood a person carries in mind.
Mercator projection
a projection of a map of the world onto a cylinder in such a way that all the parallels of latitude have the same length as the equator, used especially for marine charts and certain climatological maps.
meridian
line of longitude
place
a specific point on Earth distinguished by a particular characteristic.
place name (toponym)
the name given to a portion of Earth's surface.
prime meridian
an imaginary line passing through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England, serving by agreement as the 0º line of longitude.
projection
the system used to transfer locations from Earth's surface to a flat map.
region (formal/uniform, functional / nodal, perceptual / vernacular)
an area distinguished by a unique combination of trends or features.
remote sensing
the acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods.
scale (implied degree of generalization)
the size of an area student, from local to global.
site
the physical character of a place; the absolute location of a place or activity described by local relief, landform, and other physical characteristics.
spatial interaction
the movement and flows involving human activity.
thematic
a map that demonstrates a particular feature or a single variable. Four types: dot, isoline, choropleth, and proportional symbol.
time zone
a geographic region within which the same standard time is used.
azimuthal projection
a map projection that transforms points from a spheroid or sphere onto a tangent or secant plane. Preserves global directions.
cartogram
a map that has been simplified to present a single idea in a diagrammatic way: the base is not normally true to scale.
choropleth
a thematic map in which ranked classes of some variable are depicted with shading patterns or colors for predefined zones.
connectivity
the directness of routes linking pairs of places; an indication of the degree of internal connection in a transport network; all of the tangible and intangible means of connection and communication between places.
formal region
an area in which everyone shares in one or more distinctive characteristics (usually cultural).
friction of distance
a measure of the retarding or restricting effect of distance on spatial interaction; the greater the distance, the greater the "friction" and the less the interaction or exchange, or the greater the cost of achieving the exchange.
functional region (nodal)
an area organized around a node or focal point.
geospatial technology
refers to equipment used in visualization, measurement, and analysis of earth's features, typically involving such systems as GPS (global positioning systems), GIS (geographical information systems), and RS (remote sensing).
Global Positioning System (GPS)
a system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
International Date Line
an arc that fro the most part follows 180º longitude, although it deviates in several place to avoid dividing land areas. When you cross it heading east, the clock moves back 24 hours, and when you cross it going west the calendar moves ahead one day.
perceptual / vernacular
an area that people believe to exist as part of their cultural identity.
proportional symbol
a thematic map in which the size of a symbol varies in proportion to the frequency or intensity of the mapped variable.
regionalism
the expression of a common sense of identity and purpose combined with the creation and implementation of institutions that express a particular identity and shape collective action within a geographical region.
relative location
the position of a place or activity in relation to other places or activities; implies spatial relationships and usually suggests the relative advantages or disadvantages of a location with respect to all competing locations.
Robinson projection
a map projection of a world map that shows the entire world at once. It was specifically created in an attempt to find a good compromise to the problem of readily showing the whole globe as a flat image.
sequent occupance
successive habitation of same area over time; builds layer after layer in the region.
situation
the relative location of a place or activity in relation to the physical and cultural characteristics of the larger regional or spatial system of which it is a part; the location of a place relative to other places.
spatial
of or pertaining to space on or near Earth's surface. Often a synonym for geographical and used as an adjective to describe specific geographic concepts or processes.
time - spaced compression
an influence on the rate of expansion diffusion of an idea, observing that the spread or acceptance of an idea is usually delayed as distance from the source of the innovation increases.
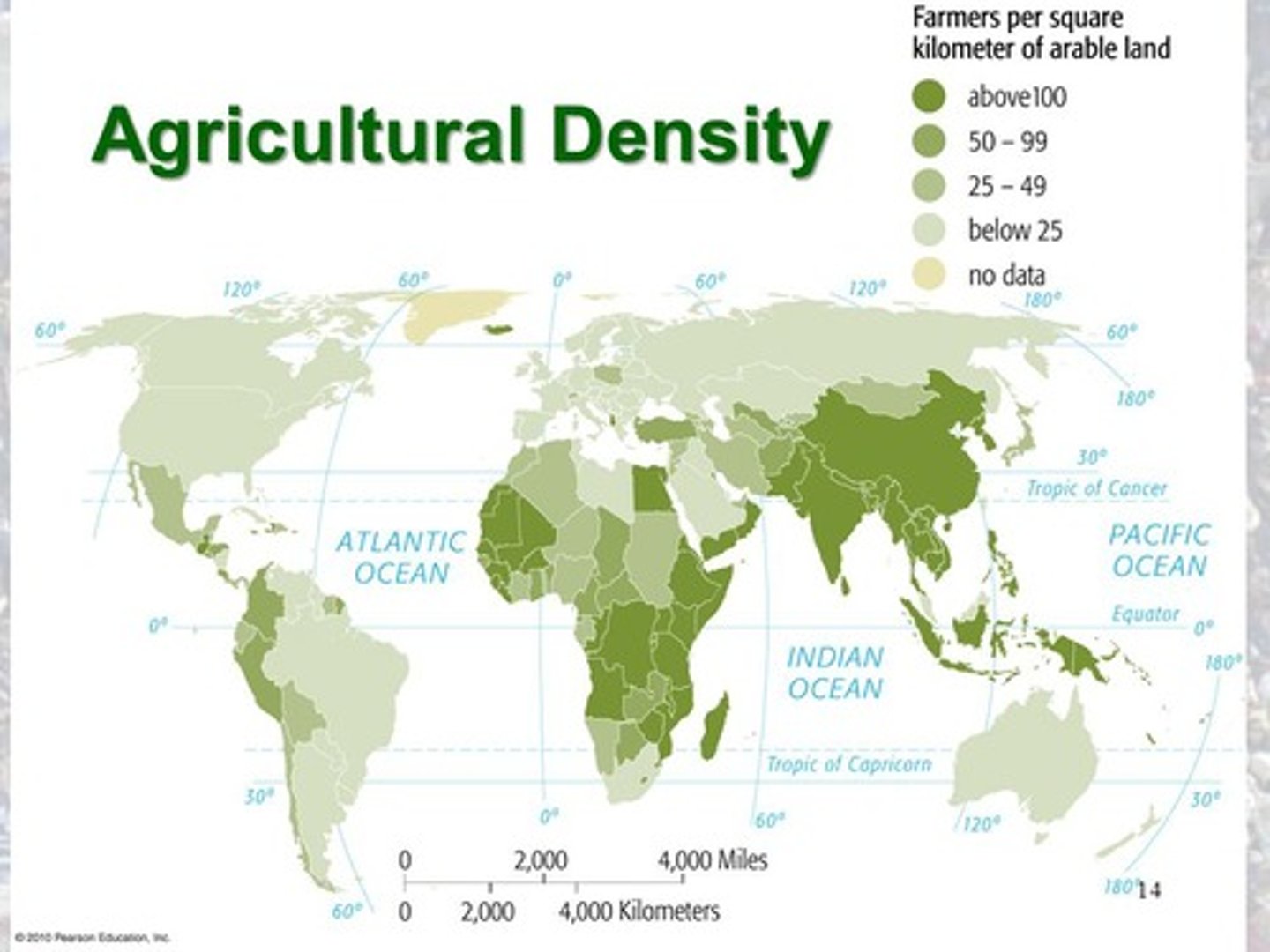
Agricultural Population Density
Number of Farmers divided by the arable land
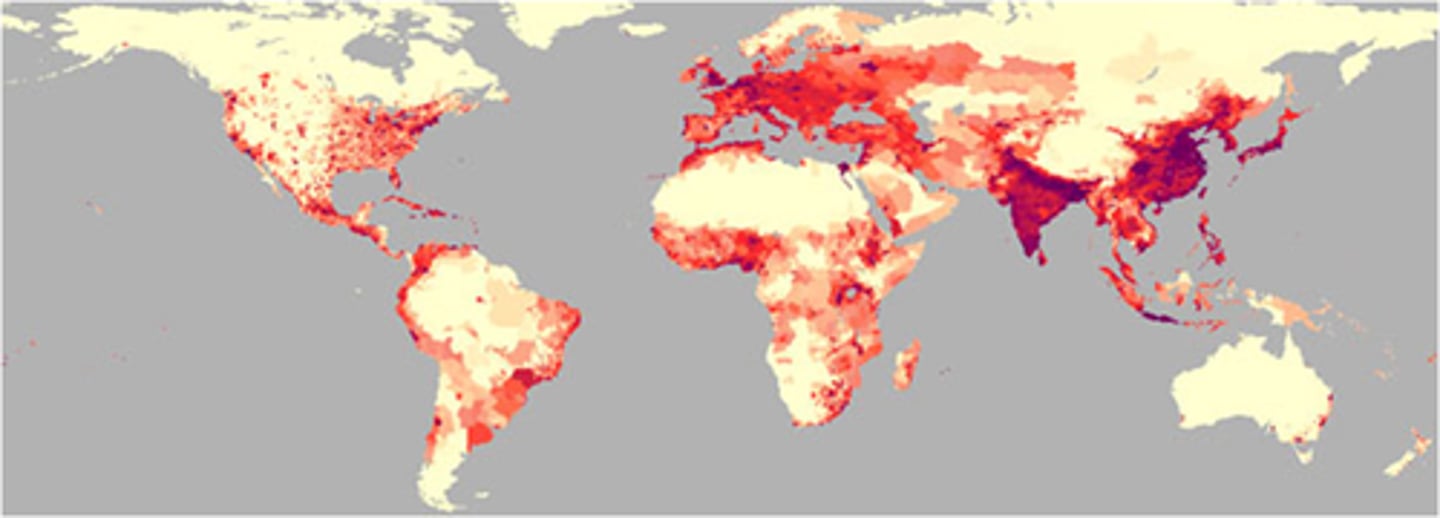
Physiological Population Density
Population of a region / arable (farmable) land

Arithmetic Population Density
Population of a region divided by total land area.
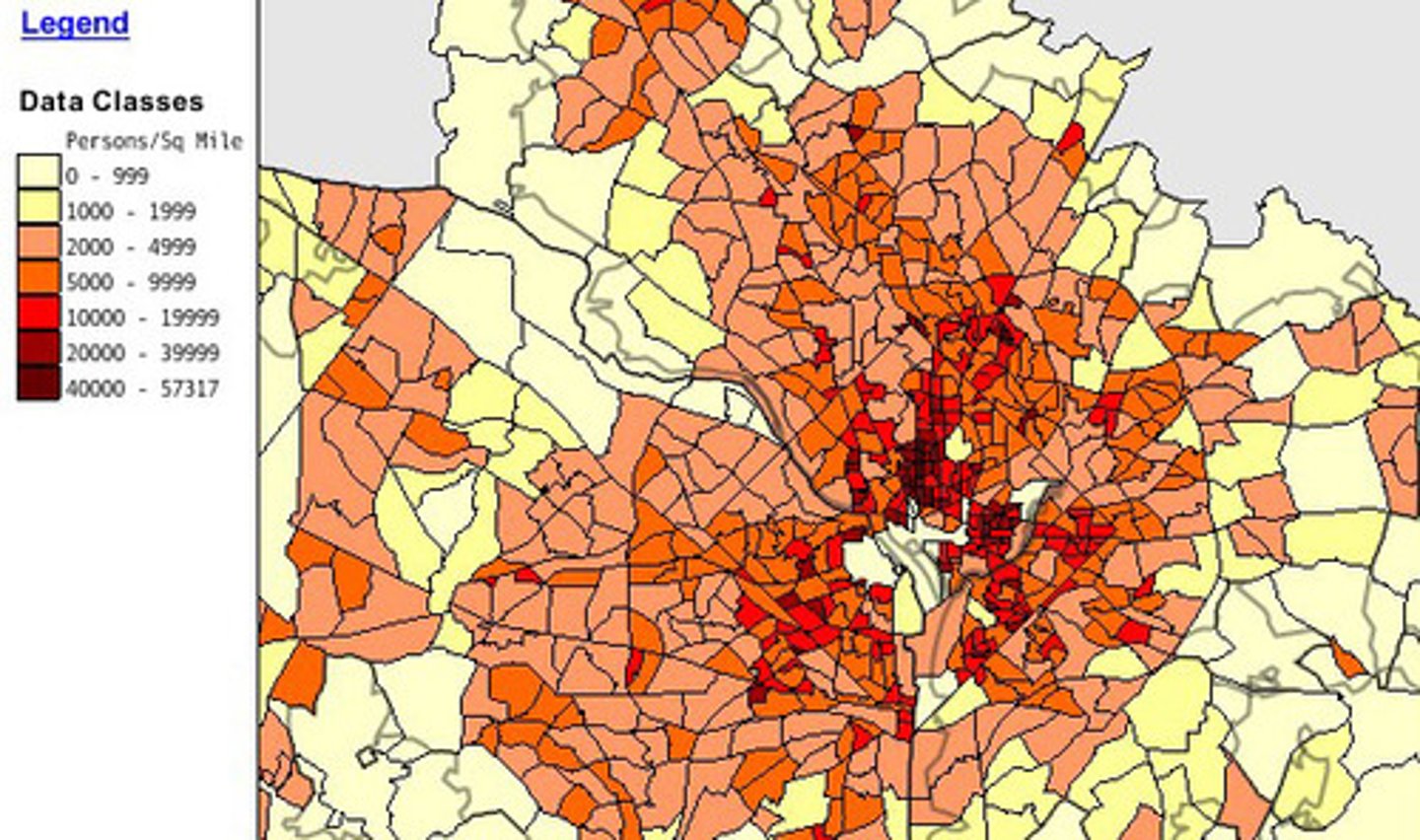
Census
A complete count of of a population
Child Mortality Rate
Total number of child deaths per 1,000 live births

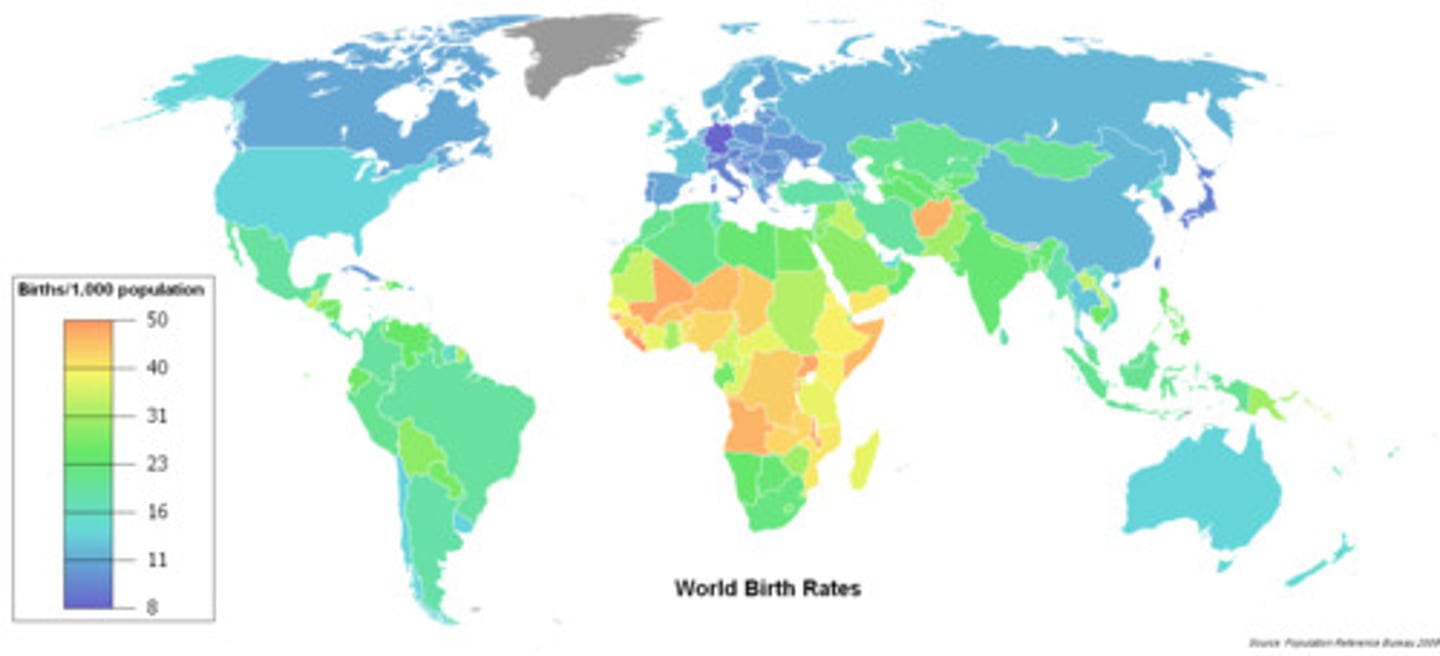
Crude Birth Rate
Total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people in the society