Bio 12-Final Review
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
Which of the following is NOT one of the core concepts of biology?
Life is subject to chemical and physical laws (systems)
Living systems depend on flow and exchange of information
Scientific theories are the basis of biological understanding
Evolution explains the unity and diversity of life
Scientific theories are the basis of biological understanding
Which of the following core concepts best represents the following statement:
The cell membrane of plant cells has many specialized protein channels that allow large amounts of water to pass into and out of the cell, which are crucial for supporting plant-specific processes such as root water absorption and stomatal opening and closing.
Transformations of energy and matter
Information flow
Structure function
Evolution
Structure function
On the following graph, what is the difference in height at 4 days between plants gown with fertilizer and plants grown without fertilizer?
2.2 cm
1.5 cm
0.7 cm
1.7 cm
0.7
On the following graph, at what point did plants grown with 6 hours of sunlight reach a height of 40 mm?
Between day 8 and day 9
On day 50
Just before day 4
Between day 5 and day 6
Between day 5 and day 6
What is the variable on the x axis of the following graph?
Meal size
Time
Energy source
Metabolic rate
Time
Which of the following CANNOT undergo evolution?
The two new kitties you adopted from the animal rescue
Petri dish covered with a population of yeast cells sitting in the laboratory
The different species of mold covering a piece of fruit on your counter
A population of mice in a research lab
The two new kitties you adopted from the animal rescue
What is the difference between microevolution and macroevolution?
Microevolution describes the evolution of microbes, while macroevolution describes the evolution of larger, multicellular organisms.
Microevolution describes the evolution of organisms over their lifetimes, while macroevolution describes the evolution of organisms across multiple generations.
Microevolution describes the evolution of molecules, while macroevolution describes the evolution of organisms.
Microevolution describes evolution occurring within populations, while macroevolution describes evolution of species or groups of species over long periods of time.
Microevolution describes evolution occurring within populations, while macroevolution describes evolution of species or groups of species over long periods of time.
Which of the following are the best examples of homologous structures?
eyelessness in the Australian mole and eyelessness in the North American mole...because both traits originated independently in response to occupying a dark underground environment
bat wing and bird wing...because wings evolved independently in each group to solve the challenge of acquiring airborne food resources
bones in the bat wing and bones in the human forelimb...because both bats and humans originated from a common mammalian ancestor
owl wing and hornet wing...because they both have wings despite being in completely different evolutionary lineages
bones in the bat wing and bones in the human forelimb...because both bats and humans originated from a common mammalian ancestor
Broccoli, kohlrabi, cauliflower, cabbage, and kale are all agricultural crops that arose via selection for different traits found in their shared wild mustard plant ancestor. This is an example of:
Convergent evolution
Invasive species
Anatomical homology
Artificial selection
artificial selection
Researchers have discovered fossils from small "dwarf" mammoths on different islands around the world. In some cases, the dwarf island mammoths have been taxonomically classified as a different species than the mainland species. In other cases, they have been classified as just a separate population with smaller individuals than the mainland population. These dwarf mammoths have been found on the Channel Islands west of California, on Wrangel Island north of Siberia, on St. Paul Island off the coast of Alaska, and on the island of Sardinia west of mainland Italy. This example provides which of the following kinds of evidence of evolution? Check all that apply.
Artificial selection
Fossil evidence
Biogeographic evidence
Orthologous evidence
Developmental homologies
Fossil Evidence
Biogeographic Evidence
You survey a population and find that one particular gene locus has a dominant allele frequency p =
0.6. Assuming the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and there are two alleles at this locus, which of the following statements is true? (select one)
q2=0.04
q=0.4
2pq = 0.24
p2=60%
q=0.4
You survey a population and find that the allele frequencies are p = 0.75 and q = 0.25. What would
happen to the allele frequency of p if the population followed the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for 200 generations?
It would increase
It would remain the same
It would fluctuate/change randomly
It would decrease,
It would remain the same
Which of the following statements about population genetic factors is true?
Most populations of most species are in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
Multiple population genetic factors may simultaneously alter allele and genotype frequencies within a natural population.
Genetic drift is the primary factor altering allele and genotype frequencies in a population.
Natural selection is not an important factor shaping allele and genotype frequencies within a natural population.
Multiple population genetic factors may simultaneously alter allele and genotype frequencies within a natural population
Invasive quagga mussels are invading many lakes and reservoirs in California. They are typically transported from lake to lake via recreation and fishing boats that have not been fully cleaned after spending time in an infected lake. In some cases, population-level allele and genotype frequencies within a lake that already has a population of quagga mussels are altered when there is a new introduction of individuals to the lake from a boater who has not appropriately cleaned their boat.
Which population genetic mechanism is occurring in this scenario?
genetic drift
natural selection
non-random mating
gene flow
gene flow
Which population genetic mechanism is rare, but responsible for producing entirely new genetic variants within a species?
mutation
non-random mating
gene flow
genetic drift
mutation
In a species of moth living within the Amazon rainforest, there are two primary wing colors, green and brown. These moths are eaten by birds, who use the contrast between the moth wing color and the background colors of the forest to locate the moths. As moths with brown wings become less common due to predation and the moths with the green wings become more common, the brown-winged moths become less likely to be eaten and more likely to survive and reproduce. Over time, the brown-winged moths then become more common and the consequences of predation on green- and brown-winged moths reverse. This is an example of:
diversifying selection
sexual selection
negative frequency-dependent selection
stabilizing selection
negative frequency-dependent selection
A region within the Sonora desert is characterized by two types of rocks: light granitic rocks and dark basalt lava flow rocks. A population of pocket mice, Chaetodipus intermedius, lives in this desert. The fur of pocket mice that live on the granite rocks is lighter, and the fur of pocket mice that live on the basalt lava rocks is darker. Fur color is a trait that can arise by genetic mutation. Over many generations, the frequency of mice with darker vs lighter fur fluctuates a bit, but overall, individuals with both fur colors occur in this population over many generations. Which of the following types of natural selection is likely operating in this population?
diversifying selection
sexual selection
stabilizing selection
directional selection
diversifying selection
Two distinct species of monkeyflowers (plants), Mimulus lewsii and Mimulus cardinalis, co-occur at mid-elevations in the mountains of California. When crossed in a greenhouse, the two species produce fertile hybrids but hybrid plants are somewhat less fit and produce fewer seeds than non-hybrid plants. This is likely an example of what reproductive isolating mechanism?
Hybrid breakdown
Behavioral isolation
Hybrid sterility
Mechanical isolation
Hybrid breakdown
At some time within the last 10,000 years, a population of California poppy, Eschscholia californica, gave rise to a new species, Eschscholzia caespitosa. Both species are still living and the geographic range of E. caespitosa is, and always was, entirely within the geographic range of the widespread E. californica. This appears to be an example of ....
allopatric speciation
postzygotic barrier
extensive gene flow between two populations
sympatric speciation
sympatric speciation
Which of the following is an example of a postzygotic barrier?
The failure of fertilized eggs to develop normally
different mating seasons
different (or incompatible) gametic cells
occupying different habitats
the failure of fertilized eggs to develop normally
Which of the following is the correct order for classifying organisms (from most similar to least similar)?
genus, species, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain
domain, kingdom, class, phylum, order, family, genus, species
species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain
species, genus, family, class, order, kingdom, phylum, domain
species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain
In binomial nomenclature, which part of the scientific name is italicized?
Only the species name
Only the genus name
Neither the genus nor the species name
Both the genus and species names
Both the genus and species names
When grouping organisms, which classification is the most general for a particular type of organism?
Class
Kingdom
Domain
Supergroup
Domain
Based on this phylogeny from research by King et al. 2008, which species is the sister group to animals (Metazoa)?
D. discoideum, a slime mold protist
M. brevicollis, a choanoflagellate protist
Zygomycete, a type of fungus
Arabidopsis sp., a member of Plantae
M.Brevicollis, a choanoflagellate protist
What does the "root" of a phylogenetic tree represent?
The most recent common ancestor of all the organisms in the tree.
The most recently evolved species on the tree.
An individual species unrelated to the other species on the tree.
A branching point from the ancestral population.
The most recent common ancestor of all theorganisms represented in the tree.
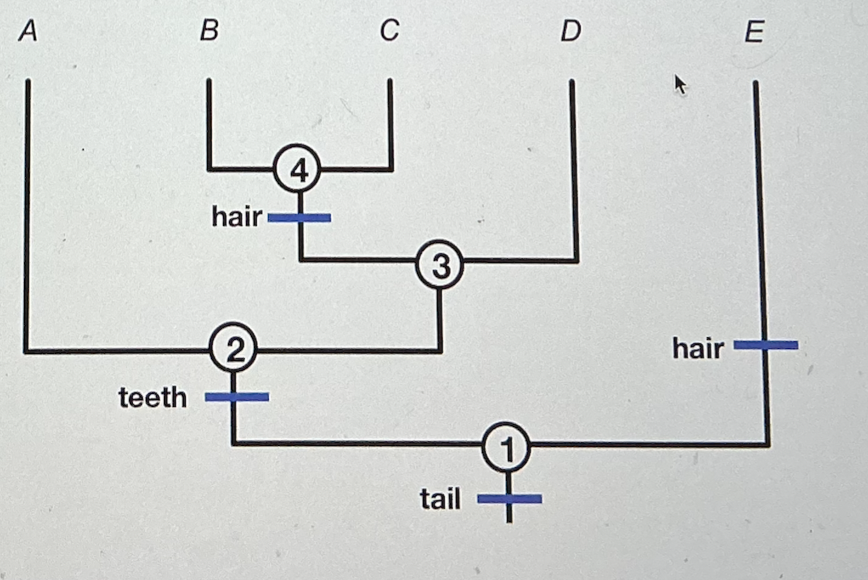
Using the tree below, answer the following question. What is the shared derived trait for A, B, C, and D?
fur
tail
teeth
hair
Teeth
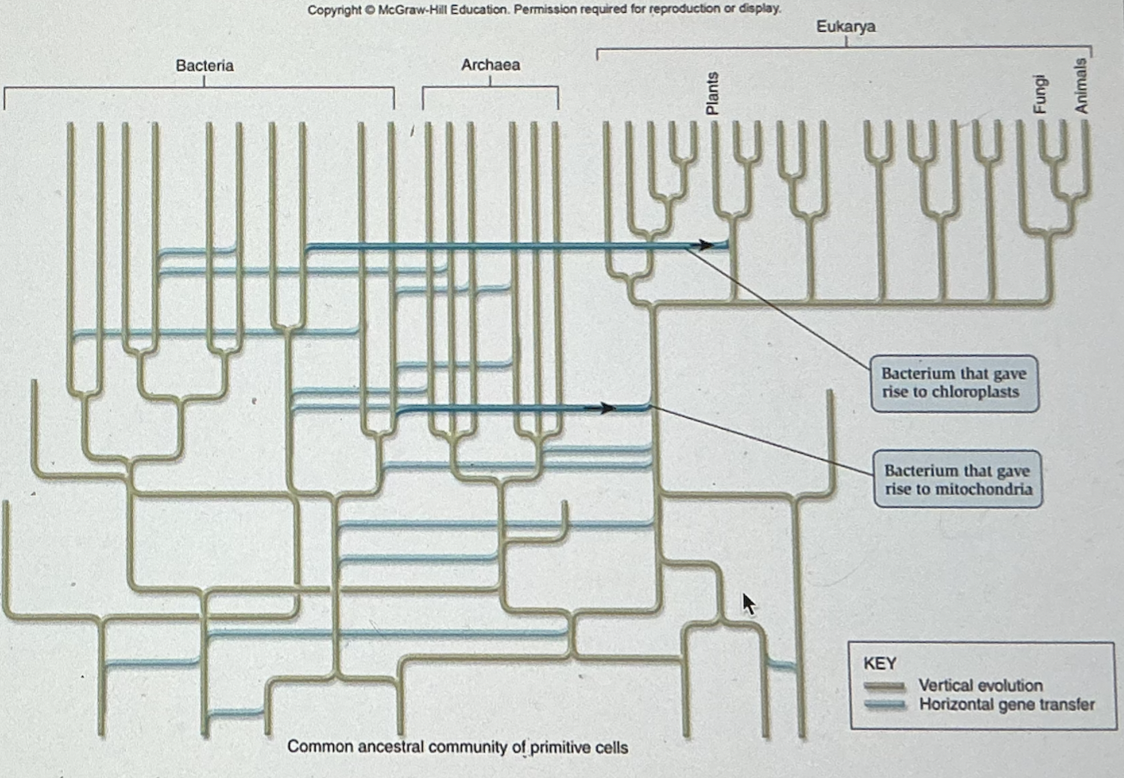
Based on your readings and the figure below, which of the following is not true of horizontal gene transfer?
It is common in the unicellular Domains of Bacteria and Archaea
It was prevalent in the early stages of evolution
It can provide a survival advantage, such as antibiotic resistance
it describes the phenomenon of obtaining genetic material from a parental organism
It describes the phenomenon of obtaining genetic material from a parental organism.
Which of the following is the definition of a chemoheterotroph?
Must obtain organic molecules both for energy and as a carbon source.
Can survive in oxygen-containing environments but do not need oxygen to survive.
Uses light as a source of energy for the synthesis of organic molecules.
Are poisoned by oxygen and obtain energy by fermentation or anaerobic respiration.
Must obtain organic molecules both for energy and as a carbon source
Which of the following are key characteristics of Archaea? Pick all that apply
Can have cell walls made of protein
Has a circular chromosome
Often live in ecologically extreme environments
Has membrane-bound organelles
Divided by mitosis
Can have cells wall made of protein
Has circular chromosome
Often live in ecologically extreme environments
Peptidoglycan is a key structural and molecular characteristic of which type of organism?
fungal cell walls
protist cell walls
bacterial cell walls
archaeal cell walls
Bacterial cell walls
Which of the following is NOT a mode of movement used by protists?
Mycelia
Pseudopodia
Cilia
Flagella
Mycelia
A protist that moves using pseudopodia (aka "false feet") is most likely a member of which group?
Diatoms
Amoebozoa
Flagellates
Ciliates
amoebozoa
Which of the following is a defining feature of a plant-like protist (algae)?
The presence of pseudopodia
Its ability to photosynthesize
The presence of cilia
Its ability to form spores
is its ability to photosynthesize.
What are two ways in which fungi are like plants?
Like plants, fungi have a cell wall and have low mobility.
Like plants, fungi get their energy from the sun and store it as glycogen.
Like plants, fungi are multicellular eukaryotes and have an autotrophic metabolism.
Like plants, fungi are unicellular and absorb their nutrients from the environment.
Like plants, fungi have a cell wall and haw low mobility
Compare the structural components of fungi and animals. How does the presence of chitin relate to both groups?
Fungi have cell walls made of chitin, while some animals have exoskeletons made of chitin, which protect them from predators and desiccation.
Fungi have cell walls made of chitin, while animals have cell walls made of cellulose, another polysaccharide.
Fungi have cell walls made of chitin, while all animals have cell walls made of only phospholipids and proteins.
Fungi and animals all have cell walls made of chitin.
Fungi have cell walls made of chitin, while some animals have exoskeletons made of chitin, which protect them from predators and desiccation.
Which statement best describes the presence of fruiting bodies in fungi?
Fruiting bodies are specialized structures that fungi produce when it is time to reproduce asexually through mitosis.
Fruiting bodies only exist in plants.
Fruiting bodies are the main body of fungi that is specialized in feedin A
Fruiting bodies are specialized sexual structures that are formed after compatible fungal individuals have mated.
Fruiting bodies are specialized sexual structures that are formed after compatible fungal individuals have mated.
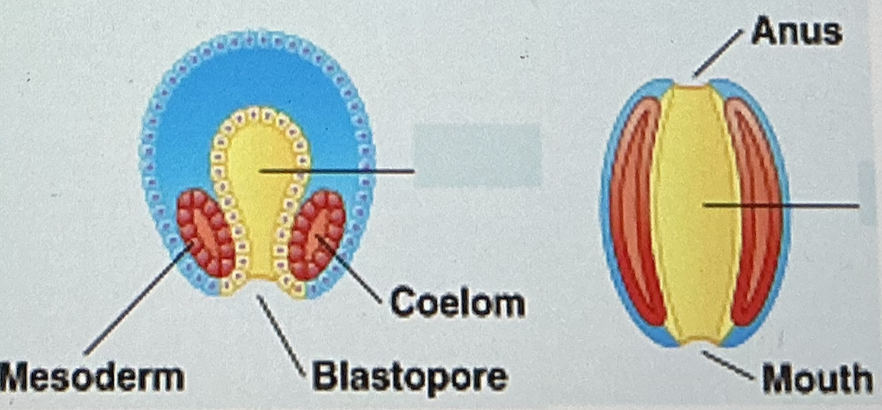
As shown in the developing embryo above, the blastopore can develop into the mouth of an organism.
The fate of the blastopore is an important developmental difference between
diploblasts and triploblasts.
Lophotrochozoa and Ecdysozoa.
Cnidarians and Porifera.
protostomes and deuterostomes.
protostomes and deuterostomes.
Which of the following is not a feature common to most animals?
specialized tissues
heterotrophic nutrient sourcing
asexual reproduction
development into a fixed body plan
asexual reproduction
You have identified a new animal species. You can divide the organism in equal halves through a number of different planes. How would you describe the symmetry of this animal?
diploblastic
bilateral
radial
asymmetrical
radial
Which of the following is NOT an observation that led to Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection?
Poorly adapted individuals never produce offspring
Only a fraction of an individual’s offspring may survive
Species produce more offspring that the environment may support
There is heritable variation
Poorly adapted individuals never produce offspring
According to the phylogenetic tree, which of the following statements is correct?
Lophotrochozoa and Ecdysozoa are both part of Deuterostomia.
Platyhelminthes are more closely related to Arthropoda than to Mollusca.
Bilateria includes both Protostomia and Deuterostomia.
Porifera is more closely related to Cnidaria than to any other group.
Bilateria includes both Protostomia and Deuterostomia.
This clade of animals is characterized by spiny skin and a water vascular system
Echinodermata
Porifera
Chordata
Annelida
Enchinodermata
A researcher discovers an invertebrate with a notochord and pharyngeal slits but no backbone. To which subphylum does it likely belong?
Arthropoda
Mollusca
Cephalochordata
Echinodermata
Cephalochrodata
Which of the following is NOT a distinguishing characteristic of a vertebrate?
a gastrovascular cavity
a vertebral column
an endoskeleton of cartilage or bone
a cranium
A gastrovascular cavity
Which of the following correctly describes homeostasis?
The body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment
The mechanism by which organisms grow and develop
The active transport of water in animal cells
The process of breaking down food into nutrients
The body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment
Which of the following correctly defines the relationship between structure and function in animal tissues?
Function determines the structure of tissues, and all tissues have the same function
Tissue function changes randomly depending on environmental conditions
Structure determines function, and different tissues are specialized for distinct functions
The structure of all tissues is the same, but functions differ based on organ location
Structure determines function, and different tissues are specialized for distinct functions.
Which of the following is NOT an example of homeostasis?
A person shivering when exposed to cold weather
A person's heart rate increasing during exercise to supply more oxygen
Sweating to cool down during exercise
The body increasing glucose production in response to high blood sugar
The body increasing glucose production in response to high blood sugar
What are the main divisions of the nervous system?
the dendritic and the axonal systems
the sensory system and the motor system
the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system
The peripheral nervous system and central nervous system
What is the difference between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems?
Somatic operates during sleep; autonomic operates during activity
Somatic controls voluntary movement; autonomic regulates internal organs
Somatic connects to smooth muscle; autonomic connects to skeletal muscle
Somatic is involuntary; autonomic is voluntary
Somatic controls voluntary movement; autonomic regulates internal organs
Jamie is camping in the woods and a bear has come into his camp looking for food. Upon seeing the bear, Jamie's sympathetic nervous system is activated. Which of the following would not be a response of Jamie's sympathetic nervous system?
A decrease in Jamie's heart rate
The dilation of Jamie's pupils
Inhibited digestion in Jamie's body
The release of adrenaline into Jamie's blood stream
A decrease in Jamie's heart rate
Which of the following components of blood is incorrectly matched with its functions?
Platelets - Blood clotting
Plasma - Osmotic balance, pH buffering
Leukocytes - Defense and immunity
Erythrocytes (red blood cells) - Defense and immunity
Erythrocytes (red blood cells) - Defense and immunity
What is the main difference between an open and closed circulatory system?
Open systems transport oxygen more efficiently
Closed systems don't use a heart
Closed systems separate blood from interstitial fluid
Open systems do not use vessels
Closed systems separate blood from interstitial fluid
Why are open circulatory systems advantageous to some animals?
They help very large insects develop.
They do not need a heart.
They help the animal move faster.
They use less metabolic energy.
They use less metabolic energy
How would you calculate the partial pressure of oxygen at sea level?
100% × 760 mmHg = 760 mmHg
21% × 760 mmHg = 160 mmHg
4% × 760 mmHg = 30 mmHg
70% × 760 mmHg = 532 mmHg
21%× 760 mmHg = 160 mmHg
Gas exchange for animals with gills living in water is more difficult than for animals with lungs living on land because:
gills have less surface area than lungs
gills allow only unidirectional transport
water is less dense than air
water contains lower concentrations of oxygen than air
Water contains lower concentrations of oxygen than air
Why is oxygen considered essential for maintaining homeostasis at the cellular level?
It keeps the immune system active
It is needed for ATP production during cellular respiration
It neutralizes toxins in the digestive system
It provides structure to the cell membrane
It keeps the immune system active
What type of immunity is present in both invertebrates and vertebrates?
Innate immunity
Adaptive immunity
Cell-mediated immunity
Humoral immunity
Innate immunity
What is the main difference between the primary and secondary immune responses?
The primary response produces more antibodies.
The secondary response occurs only in innate immunity.
The secondary response is faster and stronger due to memory cells.
Only the primary response involves B cells.
The secondary response is faster and stronger due to memory cells.
Which of the following is not a form of adaptive immunity?
antibodies
cytotoxic T cells
skin and mucous membranes
secondary response
skin and mucous membranes
Which of the following statements about the human immune system is false?
Protective mechanical barriers, such as skin, are a part of innate immunity and help protect the body against pathogens
Innate immunity is a slow response that has a small effect on human health, and is not frequently used to fight off pathogens that individuals encounter
Helper T cells activate B cells which then produce plasma cells that release antibodies
Vaccines are used to "prime" the body against a pathogen so that the individual will produce a stronger, faster immune response to that pathogen in the future
Innate immunity is a slow response that has a small effect on human health, and is not frequently used to fight off pathogens that individuals encounter
A child receives a flu vaccine for the first time. What is the expected time frame for the adaptive immune system to produce a significant antibody response?
7-14 days
Over 28 days
3-6 days
1-2 days
7-14 days
Plants with vascular tissue can be found in which of the following groups? Check all that apply.
ferns
angiosperm
gymnosperm
moss
ferns
angiosperm
gymnosperm
One of the main criteria used to distinguish one of the major categories of land plants from the others is
presence of xylem and phloem
presence of chlorophyll
color
sporopollenin
presence of xylem and phloem
Land plants and their closest green algal relatives are collectively known as:
lycophytes
streptophytes
bryophytes
chlorophytes
streptophytes
A botanist discovers a new species of plant. After observing its anatomy and life cycle, the following characteristics are noted: true roots, separate gametophyte and sporophyte generations, vascular tissue, and no seeds. This plant is probably most closely related to
the bryophytes
the angiosperms
the gymnosperms
the ferns
the ferns
Which of the following is the correct sequence during the alternation of generations life cycle in a vascular plant?
haploid gametophyte → gametes → spores → meiosis → fertilization → diploid sporophyte
spores→ zygote → meiosis → gametophyte → gametes
sporophyte → meiosis → gametes → gametophyte → spores
sporophyte → meiosis → spores → gametophyte → gametes → fertilization → diploid zygote
sporophyte → meiosis → spores → gametophyte → gametes → fertilization → diploid zygote
The type of plant tissue that is covered by the cuticle and includes trichomes and stomata is called
storage
vascular
ground
dermal
dermal
The plant organ responsible for lifting and separating leaves and reproductive structures is known as the
Correct!
stem
leaf
fruit
root
stem
Tracheids, vessel elements, sieve-tube cells, and companion cells make up the xylem and phloem and therefore are components of __-
meristematic tissue
vascular tissue
dermal tissue
ground tissue
vascular tissue
In a flowering plant's reproductive organs, initial formation of pollen grains occurs in a structure known as the
anther
sepal
pistil
megasporangium
anther
Before fertilization can take place in flowering plants,
the pollen will fuse directly with the ovule.
The pollen will land on the stigma and a pollen tube will grow down the style.
The pollen will enter the ovary as a tube cell and a generative cell.
The pollen will land on the style and a pollen tube will grow down the stigma.
the pollen will land on the stigma and a pollen tube will grow down the style.
In flowering plants, the ovule contains the megasporangium which, via meiosis,
produces 1 surviving megapore that undergoes mitosis to become 7 cells with 8 nuclei.
produces 1 surviving megapore that undergoes mitosis to become sperm.
produces 4 surviving megapores that undergo mitosis become the sporopollenin.
produces 4 surviving megapores that undergo mitosis to become the 64 eggs in an ovule.
produces 1 surviving megaspore that undergoes mitosis to become 7 cells with 8 nuclei.
A form of nitrogen that can be used by plants is _____ and plants can obtain it through _______.
N2; air
nitrogenase; rocks
nitrogen gas; gas pockets in the soil
nitrate; bacteria on their roots
nitrate; bacteria on their roots
A plant that lives on a different host plant, is unable to produce sugars through photosynthesis, and receives all of its nutrients from the host plant is known as a(n)
seedless vascular plant
parasitic plant
rhizobious plant
carnivorous plant
parasitic plant
Which factors) affect soil quality?
all of these responses affect soil quality
presence of living organisms (microorganisms)
number of air pockets or holes
amount of sand versus clay present
all of these responses affect soil quality
As an acorn grows into a large oak tree, from which of the following does it obtain the majority of its biomass (biomass=the non-water parts of the plant):
water
soil
air
light
air
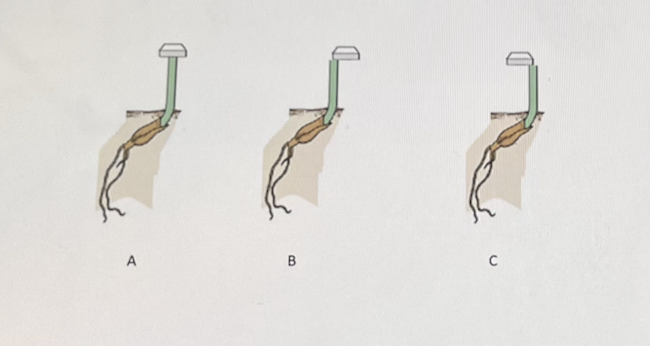
Look at the following picture. The block placed on top of each seedling is an agar block containing the plant hormone auxin. Over time, what is the seedling pictured above letter "C" most likely to do?
Grow towards the right side of the picture due to auxin causing cell elongation on the right side of that plant.
Grow towards the left side of the picture due to auxin causing cell elongation on the left side of
Grow towards the right side of the picture due to auxin causing cell elongation on the left side of that plant.
Grow towards the left side of the picture due to auxin causing cell elongation on the right side of that plant.
Grow towards the right side of the picture due to auxin causing cell elongation on the left side of that plant.
The plant hormone that is associated with fruit ripening and flower wilting is called
abscisic acid
gibberellin
auxin
ethylene
ethylene
A plant is knocked over on the ground so that its root and shoot are now parallel with the floor. After a few weeks, you notice that the shoot of the plant has started to turn upwards, away from the floor.
This change in growth is due to ___and is known as ___.
auxin; positive gravitropism
ethylene; negative gravitropism
auxin; negative gravitropism
ethylene; positive gravitropism
auxin; negative gravitropism
When light shines on a plant from a specific direction, the plant hormone auxin moves toward the
______side of the stem, causing the cells on that side to ______.
shady; elongate
sunny; elongate
shady; shorten
sunny; shorten
shady; elongate
A researcher is studying how different levels of total annual precipitation influence decomposition rates and biomass accumulation within plant communities. This is an example of which level of ecological study?
ecosystem
community
population
organismal
ecosystem
Which of the following is an abiotic factor that impacts the distribution and abundance of organisms?
wind speed
temperature
total annual precipitation
ocean currents
tree canopy cover
wind speed
temperature
total annual precipitation
ocean currents
A group of ecologists is using camera trapping techniques to understand what factors have contributed to changes in the abundance of hoary marmots in the Rocky Mountains over the last three decades. This is an example of which level of ecological study?
community ecology
population ecology
organismal ecology
ecosystem ecology
population ecology
The solar equator is located 23.5° (degrees) North or South of the geographic equator (at 0°) because:
atmospheric subsidence zones create high precipitation, increasing plant diversity at the solar equators.
the sun's rays have a longer distance to travel at the poles than at the equator.
the earth is tilted on its axis.
all of the other answers contribute to the location of the solar equator.
the earth is tilted on its axis
Which of the following statements describes aspects of Earth's climate? Check all that apply.
It was sort of windy and cold out last week. I was shivering when I was walking my dogs because I forgot to wear a sweatshirt.
I can't wait for summer to return - it's usually so hot in the Central Valley that you don't need to wear a sweatshirt for months!
I'm headed back home to Northern California for winter break. I'll need to pack my rain jacket since it typically rains a lot in my hometown in winter.
We went from a high of 59°F to a high of 85°F over the last week. It was quite a change.
I can't wait for summer to return - it's usually so hot in the Central Valley that you don't need to wear a sweatshirt for months!
I'm headed back home to northern California for winter break. I'll need to pack my rain jacket since it typically rains a lot in my hometown in winter.
Which of the statements describes weather? Check all that apply.
It's been super nice outside recently - I can break out my flip flops again!
We got an unusual amount of rain over the last week
It was pretty cold this morning when I biked to campus
Typically, Merced has average highs of 75 degrees and lows of 45 degrees in April
It's been super nice outside recently - I can break out my flip flops again!
We got an unusual amount of rain over the last week
It was pretty cold this morning when I biked to campus
Using the figure above, what abiotic factors) is/are the most important for separating temperate deciduous forest from tundra?
temperature and vegetation are equally important
temperature
precipitation
temperature and precipitation are equally important
temperature
Fill in the blanks. Cold desert is characterized by whereas tropical deciduous forests are characterized by
temperature and__precipitation,temperature and precipitation.
low, low, high, moderate
low, moderate, moderate, high
high, high, low, low
moderate, low, high, moderate
Moderate, low, high, moderate
Fill in the blank. ______is the most important abiotic factor differentiating lentic vs lotic freshwater aquatic biomes.
light
standing vs. running water
salinity
depth
temperature
standing vs. running water
Fill in the blanks. _____and____are the most important abiotic factors impacting marine aquatic biomes.
light availability, ocean currents
ocean currents, density
freeze/thaw cycles, density
temperature, pH
light availability, ocean currents
The survivorship curve to the right is associated with the life table data on the left. What type of survivorship curve does this species have?
Type II
Type III
Type IV
Type I
Type I
Which of the following factors is NOT an element used in demography? Check all that apply.
population area (e.g., m^2, km^2)
number of individuals
mortality/death rate
abiotic variables associated with a population
survivorship rate
population area (e.g., m^2, km^2)
abiotic variables associated with a population
Using the life table above, how many individuals in this population die between their seventh and eighth birthday?
21
9
31
11
10
11
NOAA biologists are interested in knowing the approximate population density of harbor seals in the Farallon Marine Sanctuary off the coast of San Francisco. You figure out how to live trap the harbor seals and in your first catch you find and mark 5 seals. You wait a month and then sample the population again. This time you catch 10 seals, 2 of which are marked. What is the Farallon harbor seal population?
No calculator needed to answer this question.
25 seals in the sanctuary
15 seals in the sanctuary
17 seals in the sanctuary
5 seals in the sanctuary
25 seals in the sanctuary
Which of the following constitute density-dependent factors that may alter population growth? Check all that apply.
competition between individuals
disease, like the viral pandemic COVID-19
weather events like a freeze or heat wave
natural disasters like wildfires or hurricanes
competition between individuals
disease, like the viral pandemic COVID-19
Which of the following are examples of a density-independent factor influencing population growth?
Check all that apply.
A viral pandemic
A flood
A meteor impact
A volcanic eruption
A flood
A meteor impact
A volcanic eruption
Populations exhibit logistic growth when ____
resources do not matter for population growth
resources are unlimited
resources are limited
resources are limited
Many nest cams monitor bald eagles. Bald eagles tend to mate for life, build very large nests in which they lay 1-3 eggs, and provide a lot of parental care until the babies are capable of flying and dispering away from their natal site. Given all these traits, bald eagles likely have a(n) _ _ life history strategy.
semelparous
K-selected
r-selected
exponential
K-selected
Which of the following are examples of species interactions where one species benefits from the interaction and the other species is harmed? Check all that apply.
Herbivory
Competition
Mutualism
Predation
Mimicry
Parasitism
Herbivory
Predation
Parasitism