Alcohols
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Why are the boiling points of alcohols high?
They can form hydrogen bonds between alcohol molecules
Why can smaller alcohols dissolve in water?
They form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
What are primary alcohols?
Alcohols where 1 carbon atom is joined to the carbon joined to the oxygen
What are secondary alcohols?
Alcohols where 2 carbon atoms are joined to the carbon joined to the oxygen
What are tertiary alcohols?
Alcohols where 3 carbon atoms are joined to the carbon joined to the oxygen
What role does Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) play in the oxidation of alcohols?
Oxidising agent
When primary alcohols are partially oxidised what do they form?
Aldehydes
How do you identify an aldehyde from its displayed formula?
The C=O bond is on the first carbon in the chain
When writing the formula of aldehydes what do you do?
Write CHO and not COH at the end
Outline the reaction for the partial oxidation of alcohols to an aldehyde
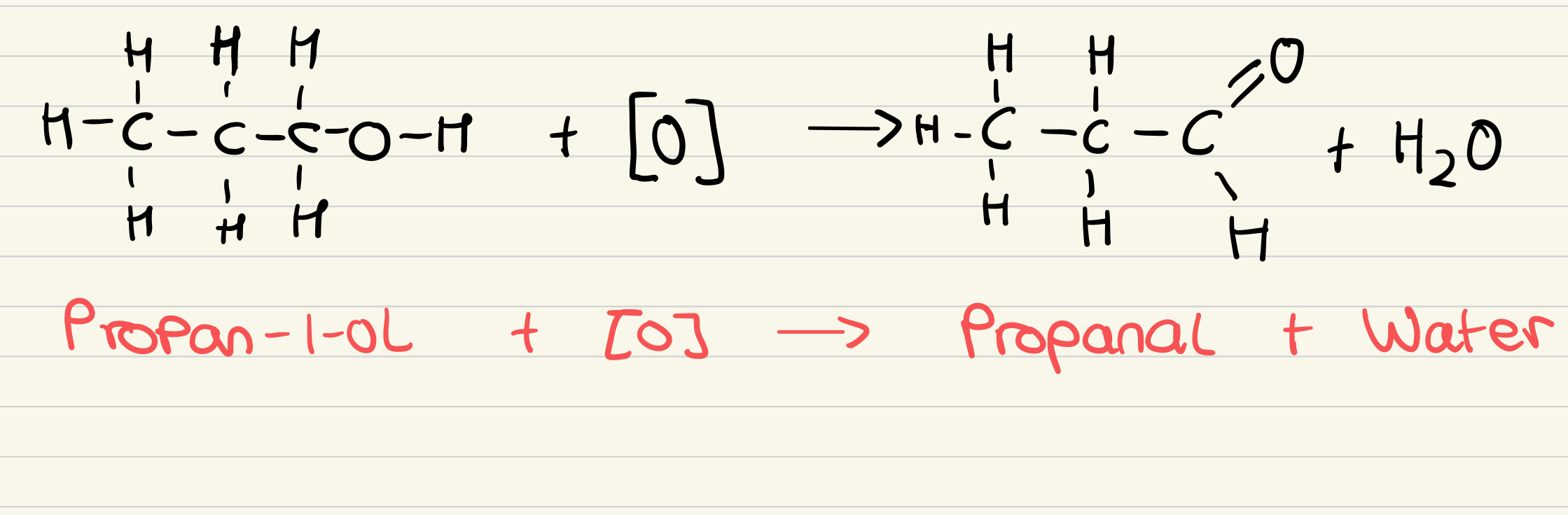
What is the observation when alcohols are oxidised to aldehydes?
Orange to green
Dichromate ion (Cr2O72-) is reduced to Cr3+ ion
What are the reagents for the partial oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes?
Potassium Dichromate (VI) solution and dilute sulfuric acid
What are the conditions for the partial oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes?
Warm gently and distil the aldehyde
Draw a labelled distillation apparatus
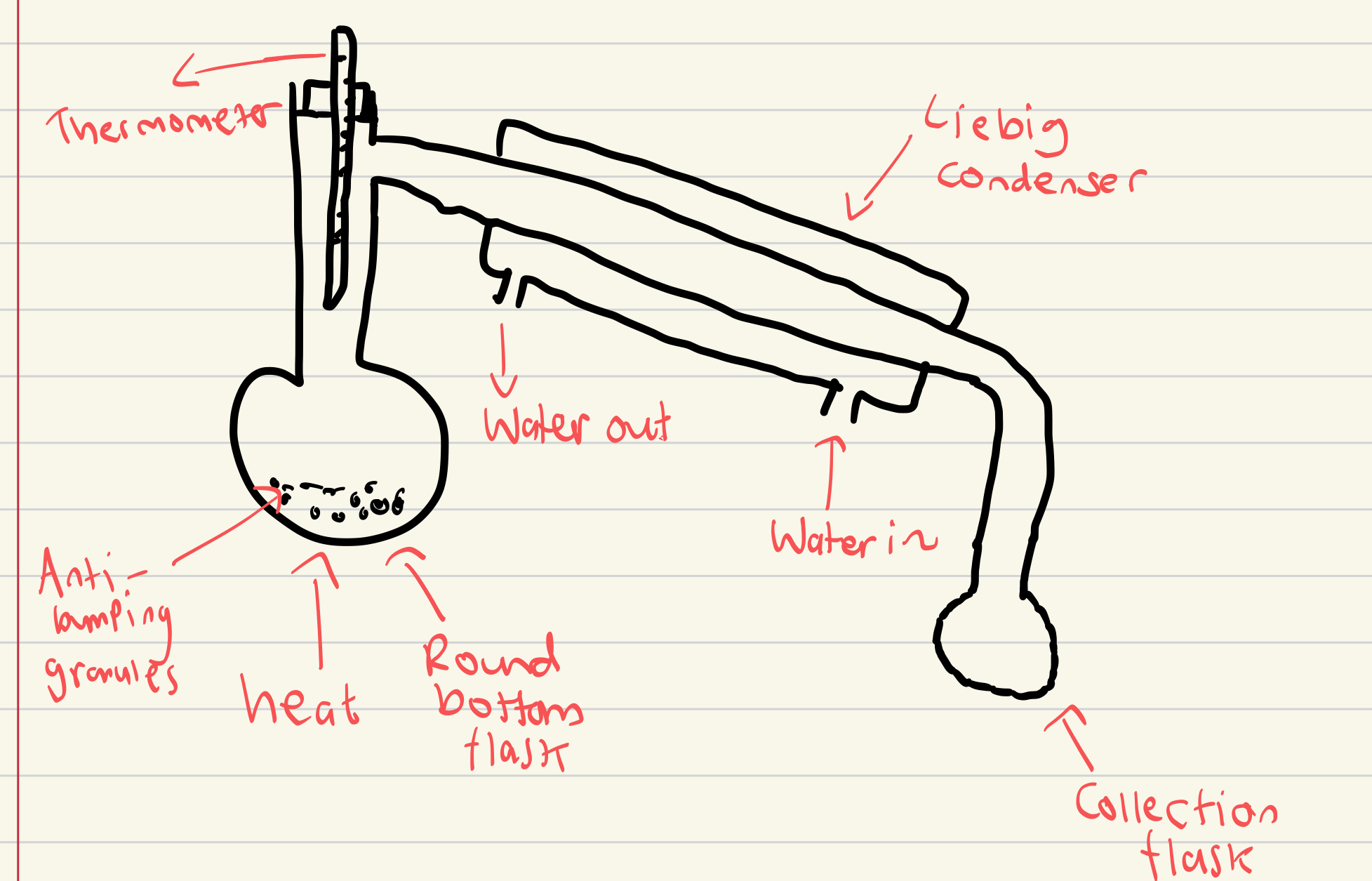
Why does water go in from the bottom of the condenser?
To go against gravity or more efficient cooling and prevents back flow of water.
Why are electric heaters used in distillation and not naked flames?
As organic chemicals are normally flammable
What is formed in the full oxidation of primary alcohols?
Carboxylic acid
How do you identify a carboxylic acid?
It has a COOH group, with a C=O bond and an O-H bond
Outline the reaction for the oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids
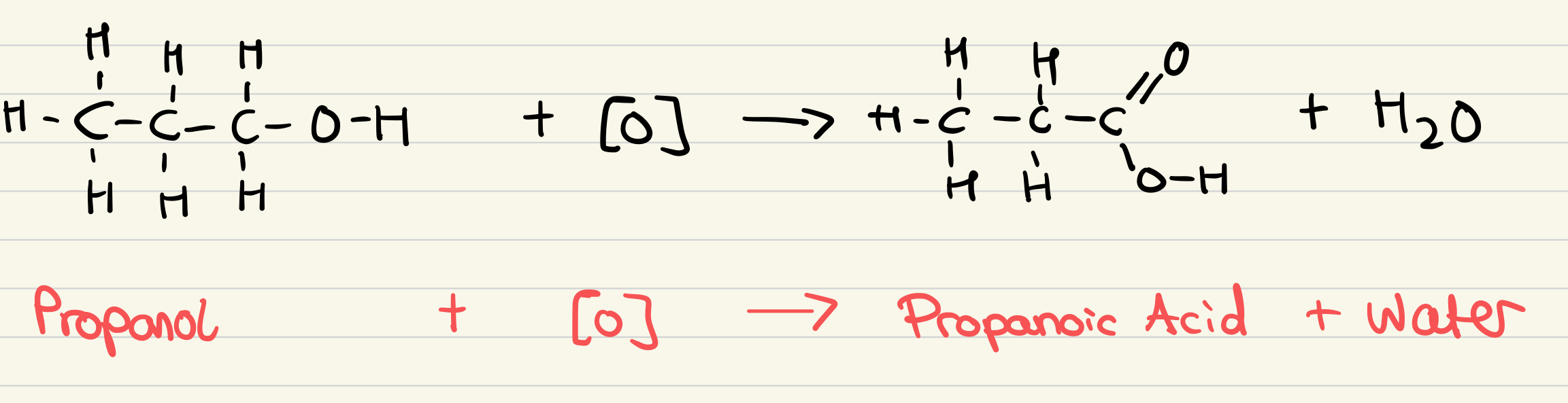
What are the reagents for the full oxidation of alcohols to carboxylic acid?
Potassium dichromate (VI) solution and dilute sulfuric acid
What are the conditions for the full oxidation of alcohols to carboxylic acids?
Excess dichromate, so the alcohol is fully oxidised
Heat under reflux
What is the observation of the full oxidation of alcohols to carboxylic acids?
Orange to green
Dichromate ion (Cr2O72-) is reduced to Cr3+ ion
Draw the labelled apparatus for reflux
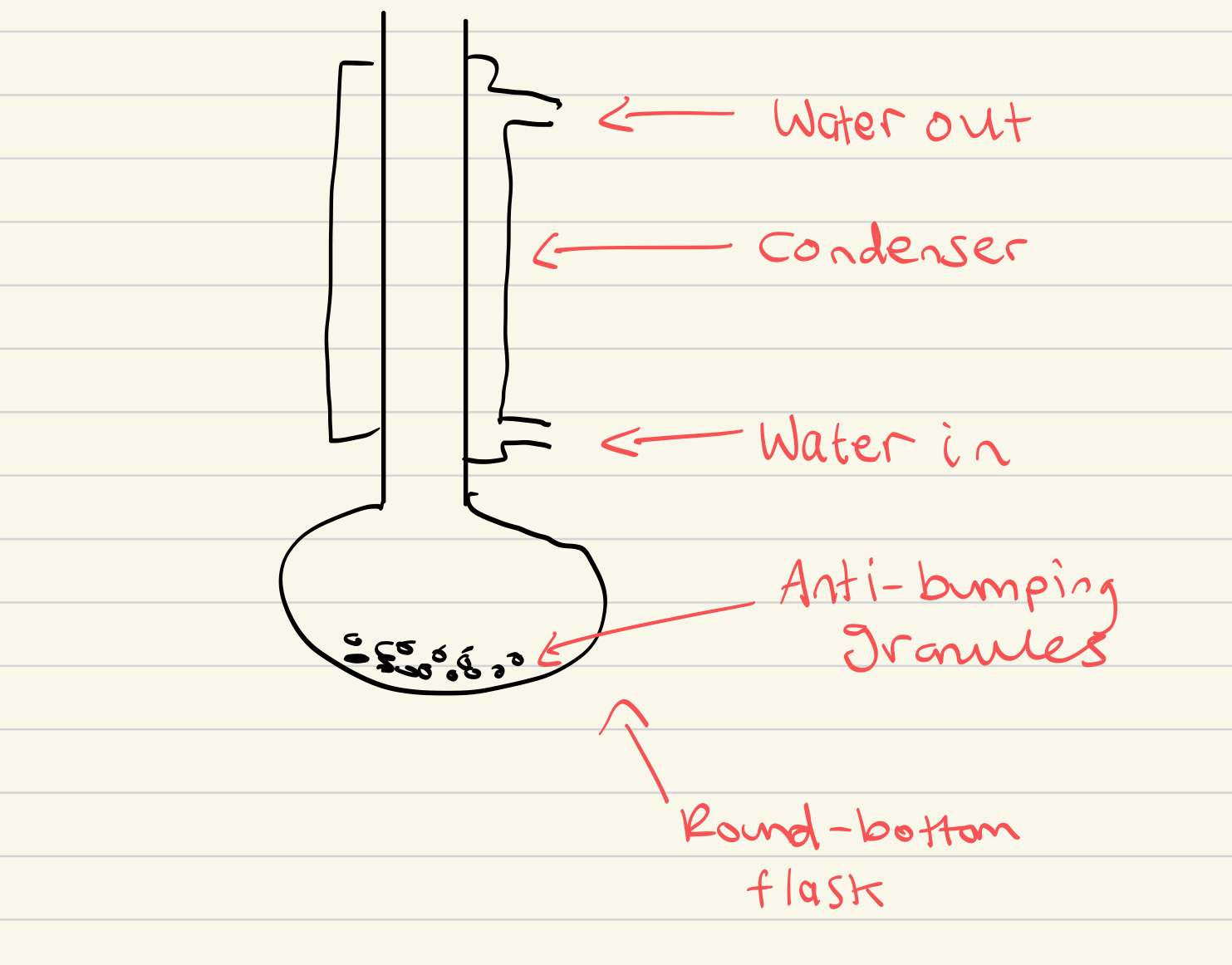
Why should you never seal the end of a condenser during reflux?
Build up of gas pressure could cause an explosion
Why are anti-bumping granules added during reflux and distillation?
To prevent vigorous, uneven boiling by making small bubbles
What are the differences in oxidising alcohols to aldehydes and carboxylic acids?
Aldehydes : Limited dichromate and heat under distillation
Carboxylic Acids: Excess dichromate and heat under reflux
What is formed in the oxidation of secondary alcohols?
Ketones
How do you identify a ketone from its structural formula?
A C=O bond in the middle of the chain
Outline the reaction for the oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones
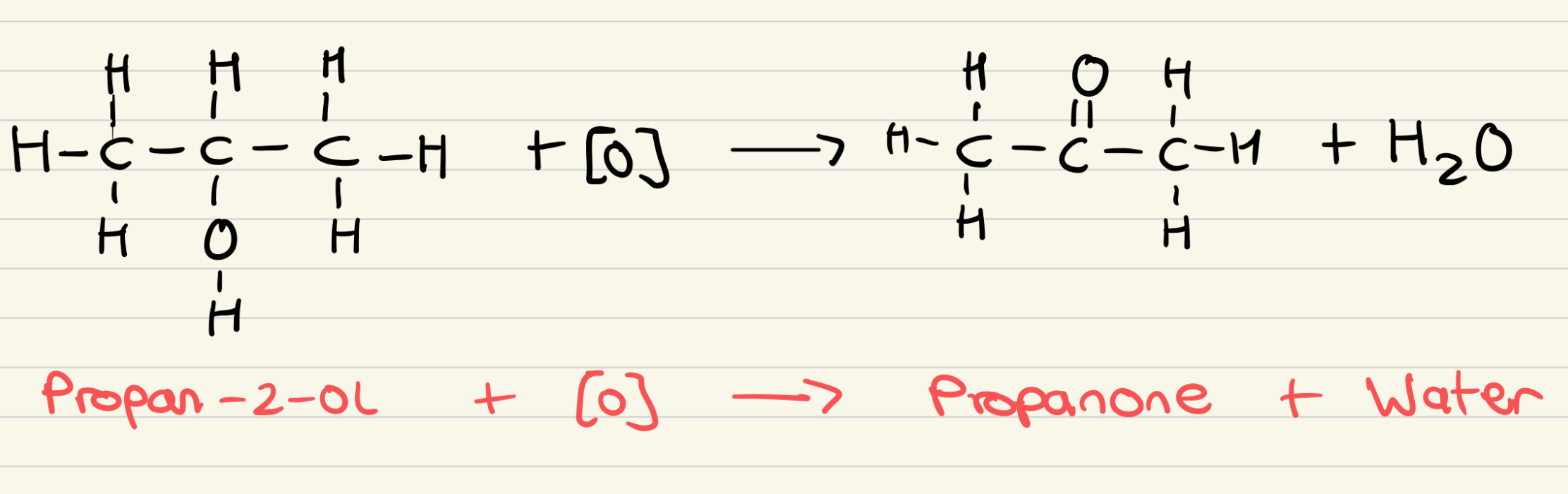
What are the reagents used for the oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones?
Potassium dichromate (VI) solution and dilute sulfuric aid
What are the conditions of the oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones?
Heat under reflux
What is the observation for the oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones?
Orange to green
Dichromate ion (Cr2O72-) is reduced to Cr3+ ion
Why can tertiary alcohols not be oxidised?
There’s no hydrogen bonded to the carbon with the -OH group
How do you use Tollen’s Reagent to distinguish between Aldehydes and Ketones?
Tollens’ reagent oxidises aldehydes to carboxylic acids
Silver mirror forms
Ketones have no visible change
How do you use Fehling’s Solution to distinguish between Aldehydes and Ketones?
Fehling’s solution oxidises aldehydes to carboxylic acids
Blue Cu2+ ions change to a red precipitate of Cu2O
Ketones have no visible change
How do you test for carboxylic acids?
Add sodium carbonate, which fizzes and produces CO2
What are dehydrating reactions?
Removal of a water molecule from a molecule
When alcohols are dehydrated what do they form?
Alkenes
What type of reaction is alcohols to alkenes?
Elimination reaction
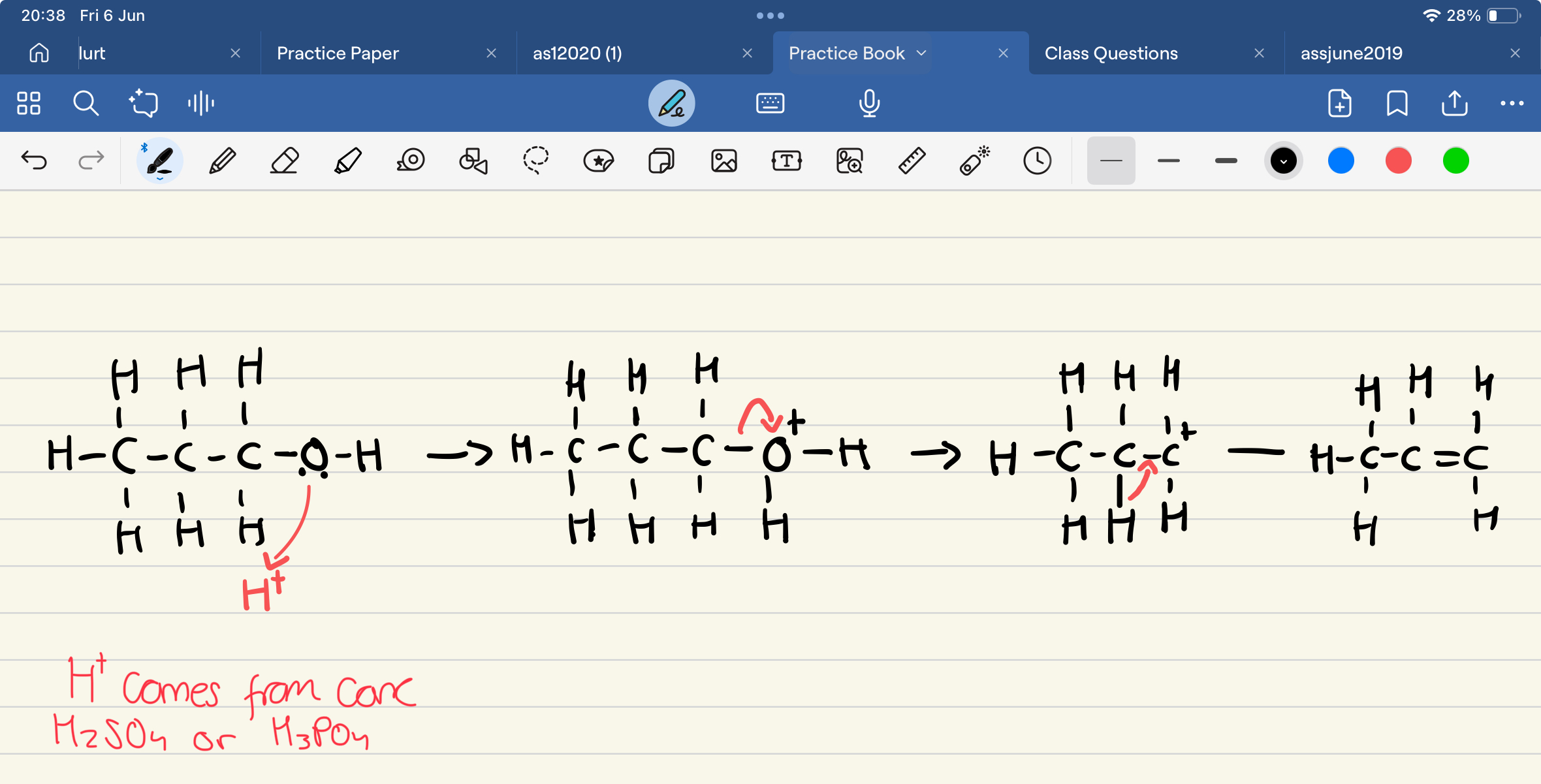
What are the reagents for the dehydration of alcohols to alkenes?
Concentrated sulfuric or phosphoric acid
What is the role of the dehydrating agent?
Catalyst
Outline the mechanism from alcohols to alkenes
Why is producing alkenes from alcohols good for the environment?
Provides a route to creating polymers without using monomers derived from oil
What is the equation for fermentation?
Glucose —> Ethanol + Carbon dioxide
What are the conditions for the fermentation of glucose to form ethanol?
Yeast, No air, temperature 38 degrees
Why is a temperature of 38 degrees used, and not higher or lower
Optimum temperature for fermentation
At lower temps the reaction is too slow
At higher temps the enzymes denature
Why is there an absence of air?
Air can oxidise ethanol to ethanoic acid
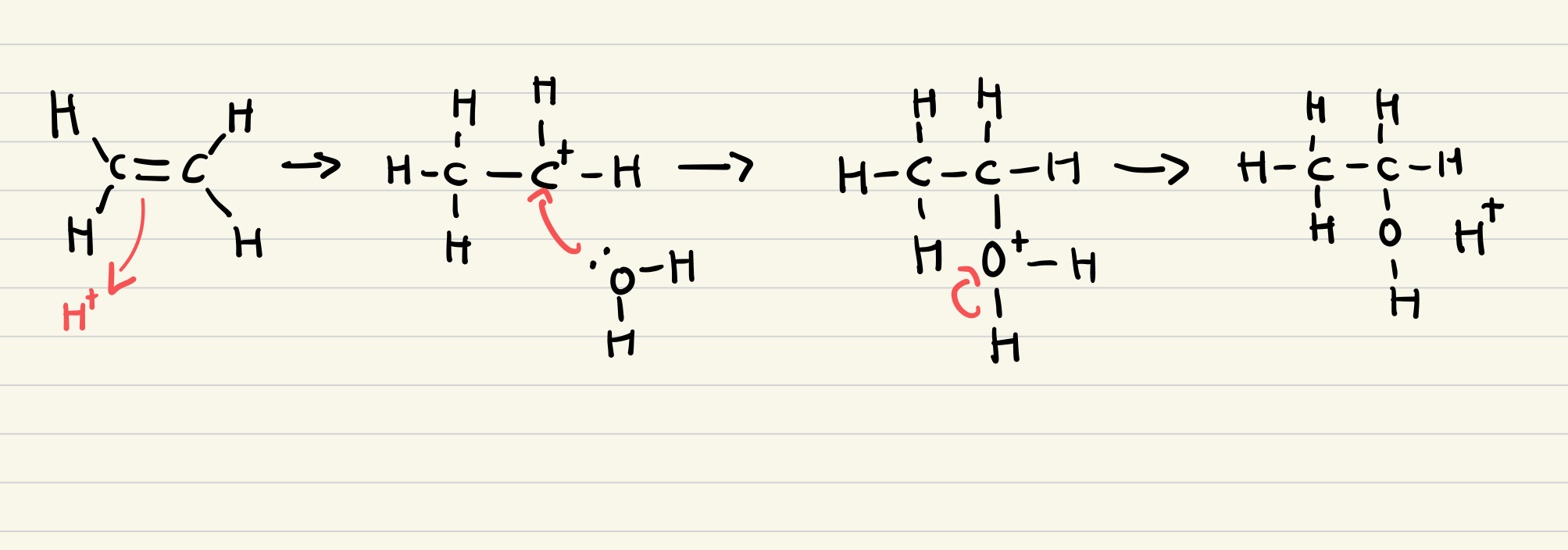
Show the mechanism for the hydration of ethene to ethanol
What is a biofuel?
A fuel produced from plants
Why is ethanol produced from fermentation a biofuel?
As glucose is made in plants during photosynthesis
How is ethanol from fermentation a carbon-neutral process?
As any carbon dioxide given off is taken back in by plants during photosynthesis
What are the equations to show that fermentation of glucose is carbon-neutral?
6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2 (6 CO2 molecules are removed from the atmosphere during photosynthesis)
C6H12O6 —> 2CH3CH2OH + 2CO2 (2 CO2 molecules released during fermentation of glucose)
2CH3CH2OH + 6O2 —> 4CO2 + 6H2O (4 CO2 molecules released during combustion of ethanol)
6 molecules absorbed and 6 emitted