1- benthic invertebrates
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
how many phyla are there for marine invertebrates?
17
major phyla of marine invertebrates
1. porifera
2. cnidaria
3. ctenophora (comb jellies)
4. platyhelminthes (flatworms)
5. nemertea (ribbon worms)
6. nematoda
7. chaetognatha (arrow worms)
8. annelida (segmented worms)
9. sipuncula (peanut worms)
10. mollusca
11. arthropoda
12. bryozoa
13. phoronida (horseshoe worms)
14. brachiopoda (lamp shells)
15. echinodermata
16. hemichordata (acorn worms)
17. chordata
which of these phyla had planktonic species?
cnidaria, ctenophora, mollusca, and arthopoda
phylum porifera
- sponges
- all are sessile
- have numerous tiny pores for filter feeding
- water flow also carries waste and gametes
- mostly marine
- asymmetrical body plan

sponge cells
- collar cells
- pinacocytes
- pore cells
- spicules
collar cells
- flagella create a water current that brings in food particles
- collar on choanocyte traps food particles
pinacocytes
flattened cells that cover exterior of body
pore cells (porocytes)
cells with a pore to allow water to pass into the body
sponge structural support
- spongin: support protein
- spicules: support structures made of silica or calcium carbonate; have a variety of shapes
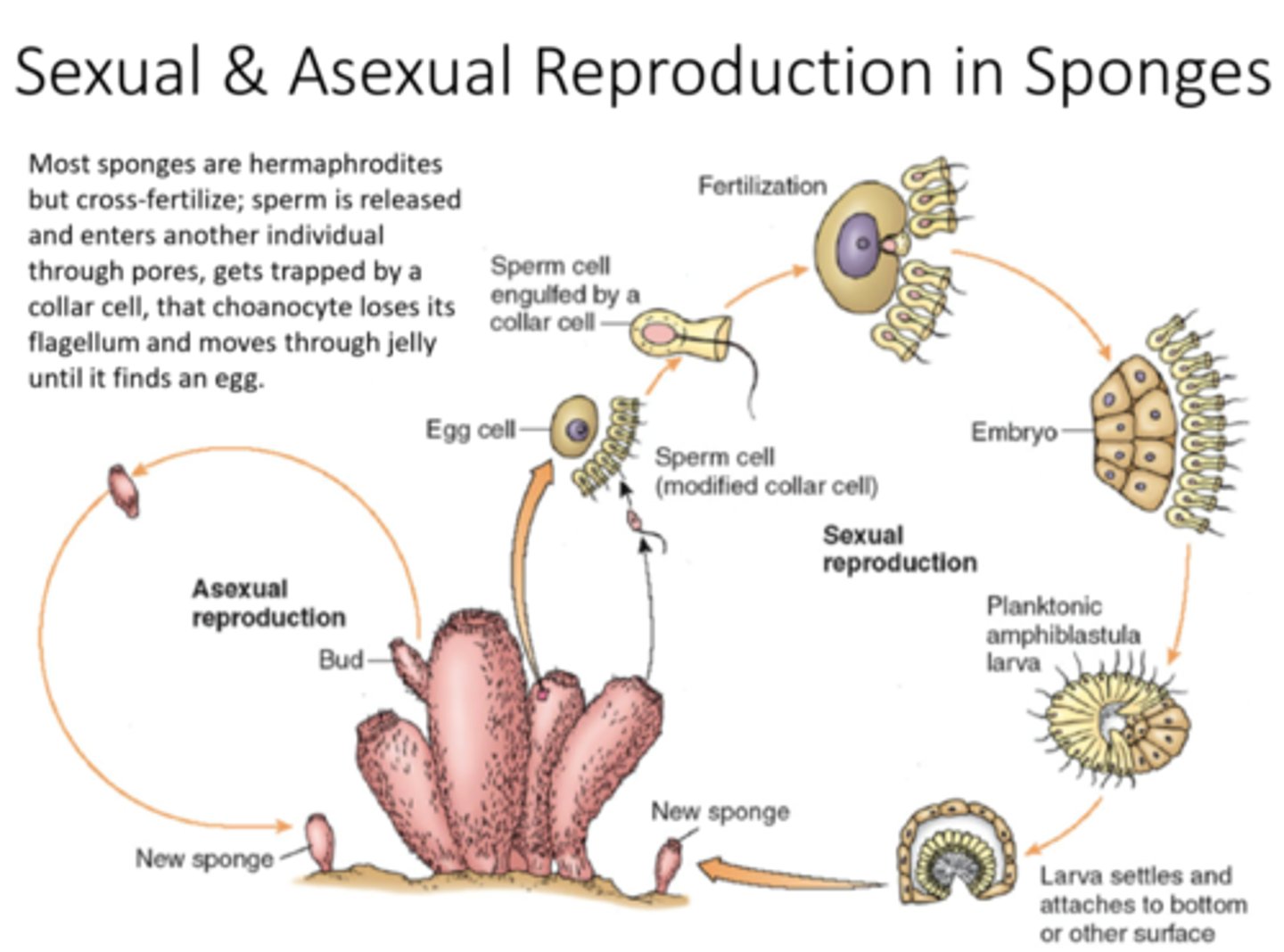
sponge reproduction
- asexual budding: buds break off and grow into a new sponge
- sexual: sperm released into the water to be picked up by a nearby sponge and directed to egg
- most sponges are hermaphrodites
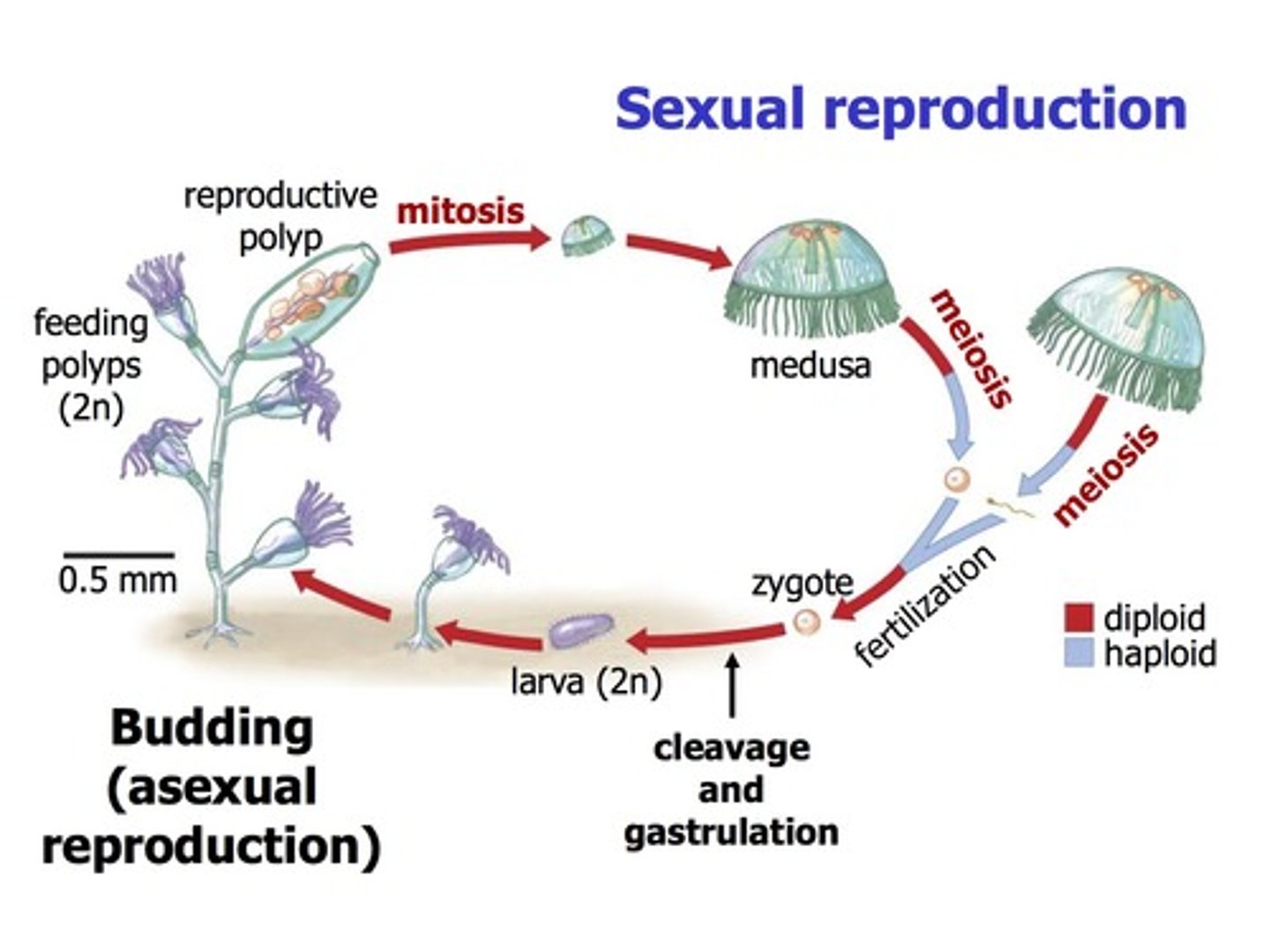
phylum cnidaria
- radial symmetry
- mostly marine
- two forms: medusa and polyp
- two tissue layers: ectoderm and endoderm
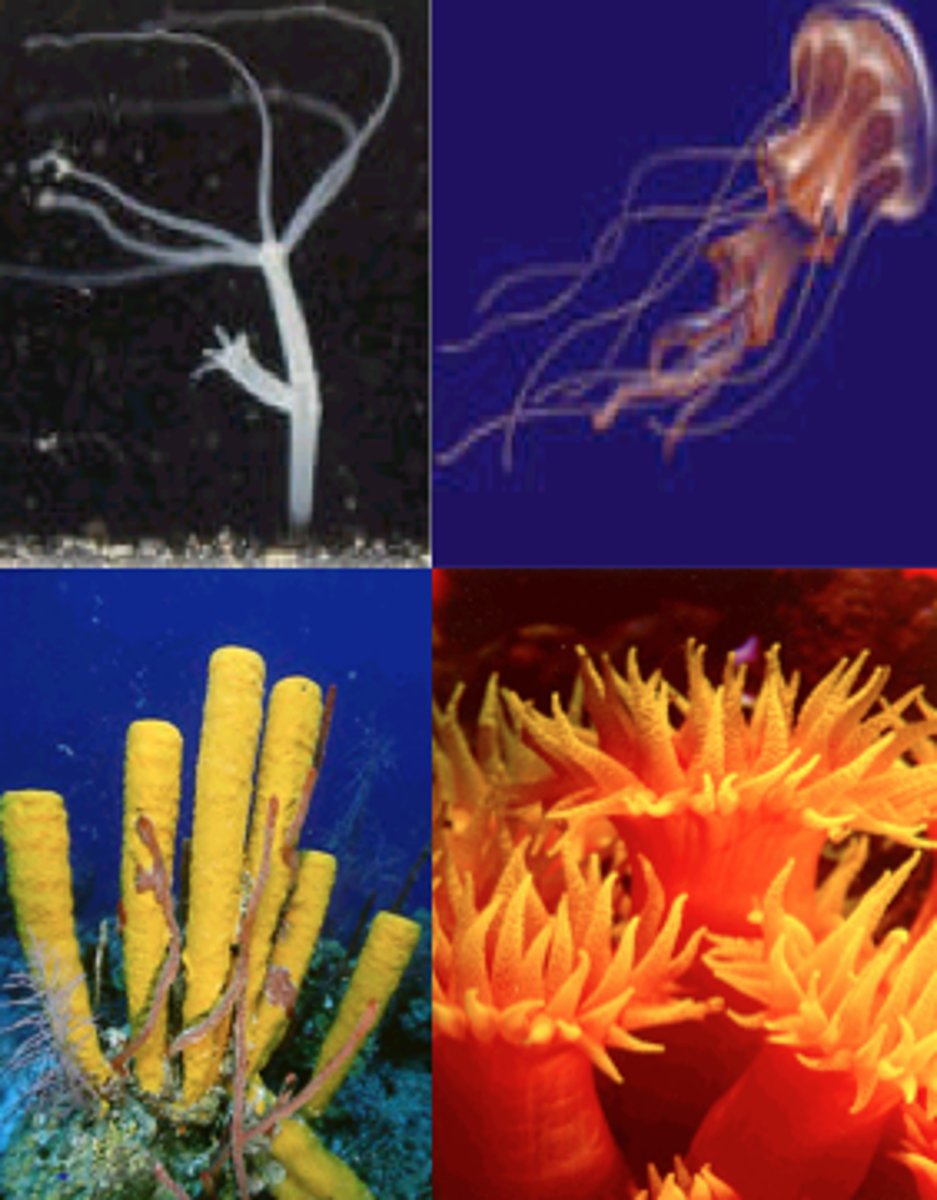

medusa stage
free-swimming form that is transported by water currents, mouth with surrounding tentacles positioned downwards
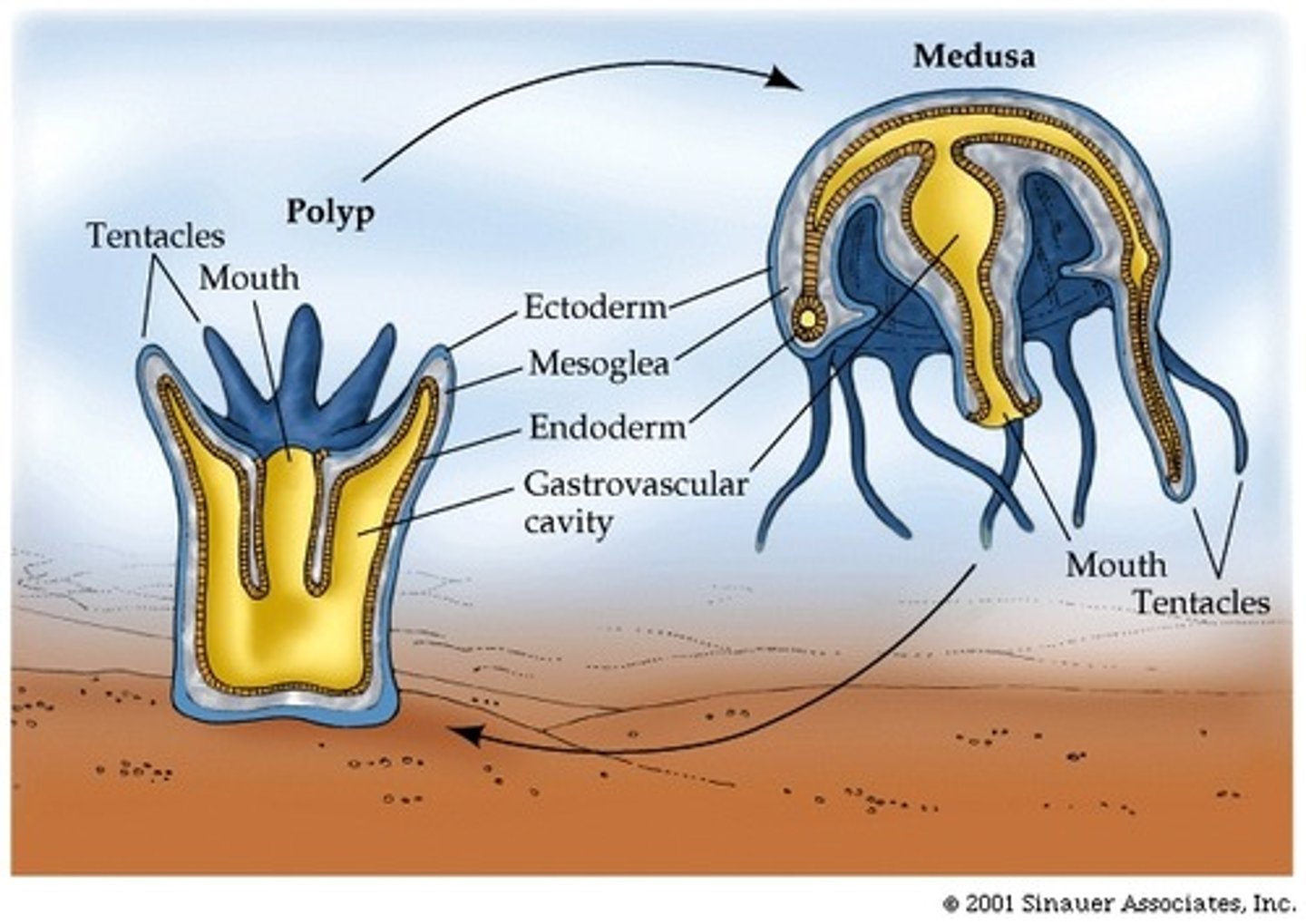
polyp stage
attached form with mouth and tentacles positioned upwards
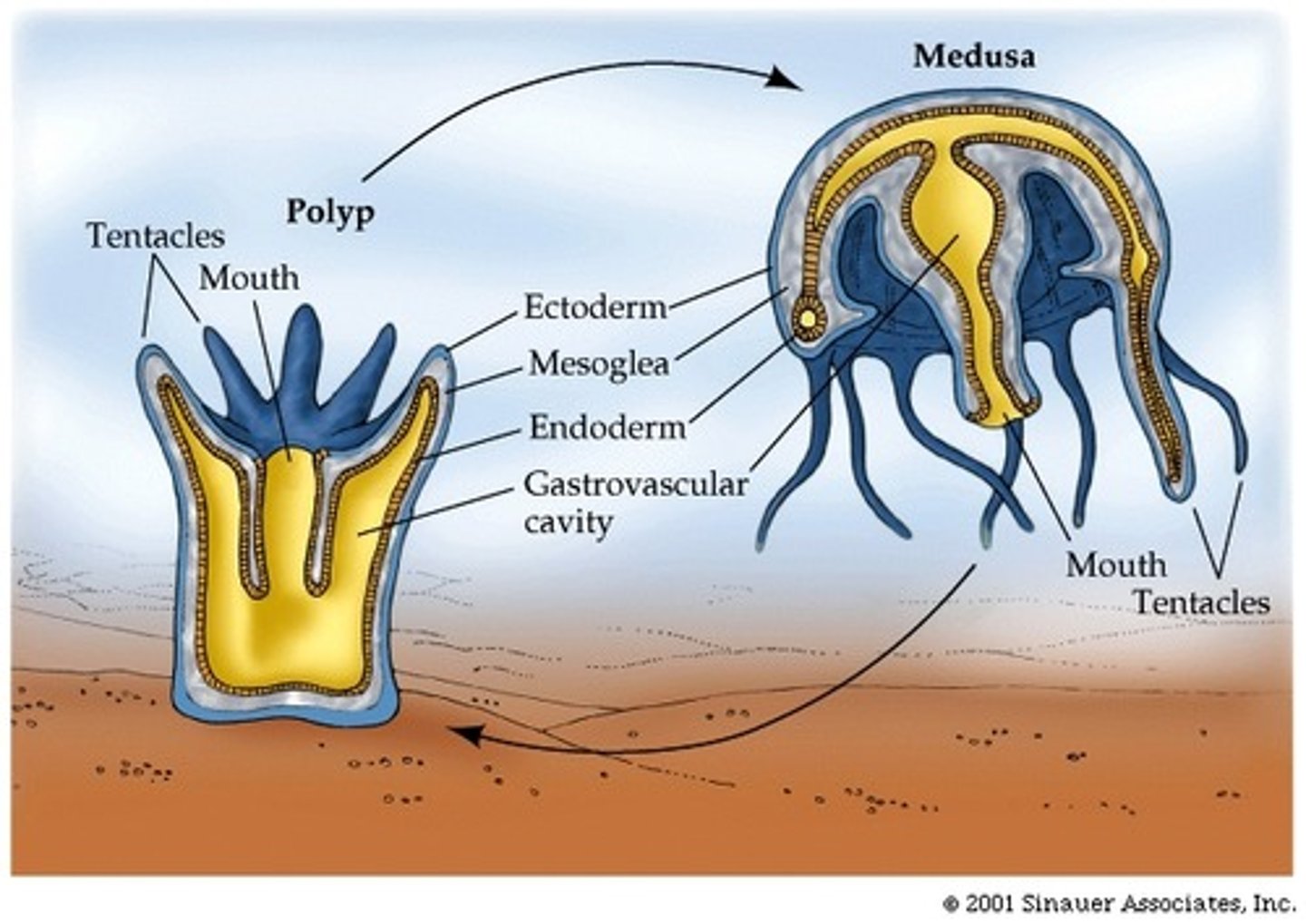
cnidarian characteristics
- nematocysts: stinging cells within specialized cells on tentacles; used for protection and feeding
- digestive system is incomplete
- nerve net throughout body coordinates movements
benthic cnidarians
- corals and anemones; singular or colony of polyps attached to a substrate
- hydroids: most consists of colony of polyps
cnidarian reproduction
- sexual: medusa is the sexual stage, releasing eggs and sperm; fertilized egg results in a zygote
- asexual: polyps reproduce by budding
phylum platyhelminthes
- flatworms
- bilateral symmetry
- three tissue layers
- central nervous system with brain
- incomplete digestive tract (gut without anus)
- many are marine
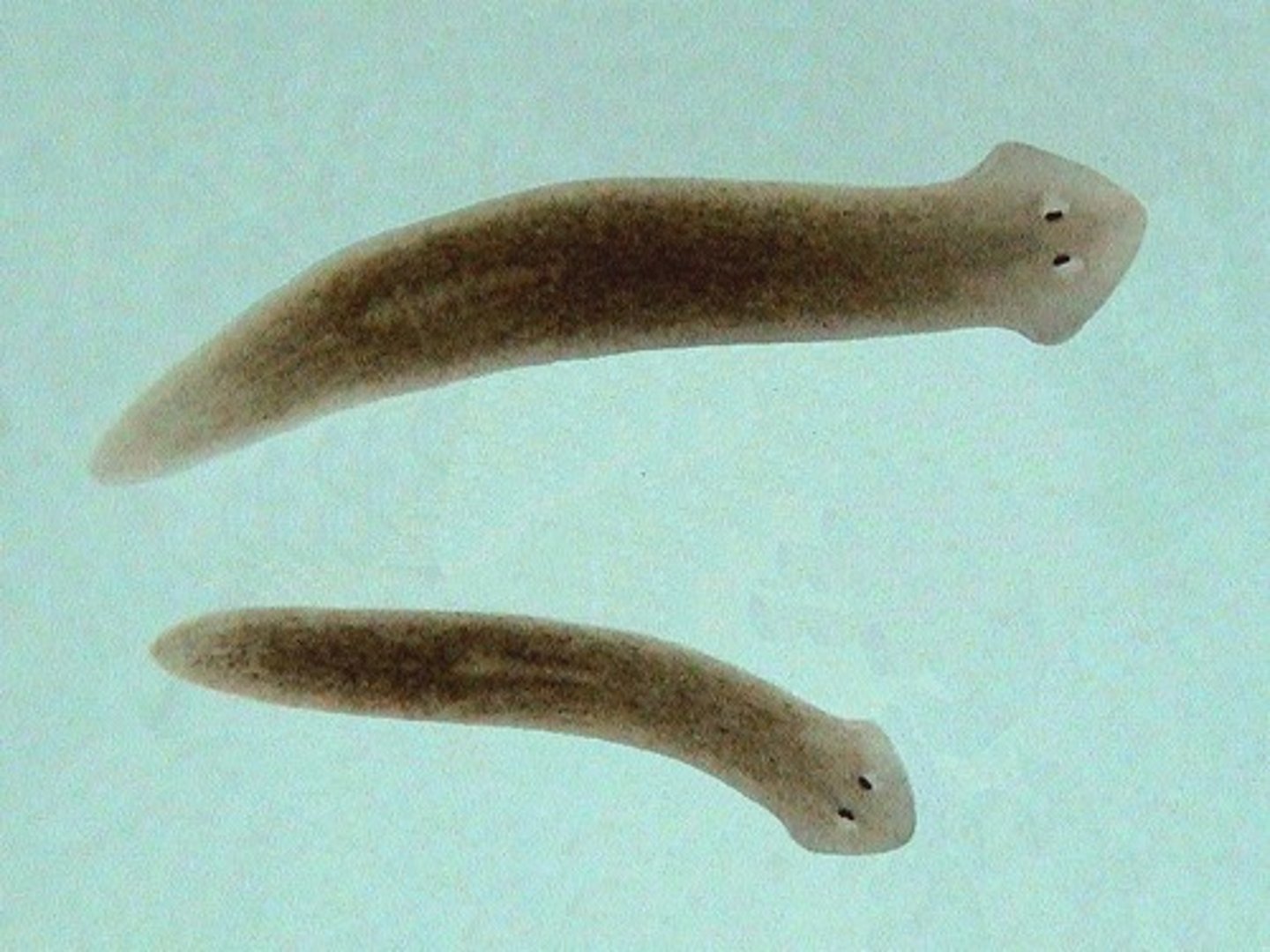

phylum nermertea
- ribbon worm
- predatory
- capture prey with web-like proboscis
- swallow prey whole

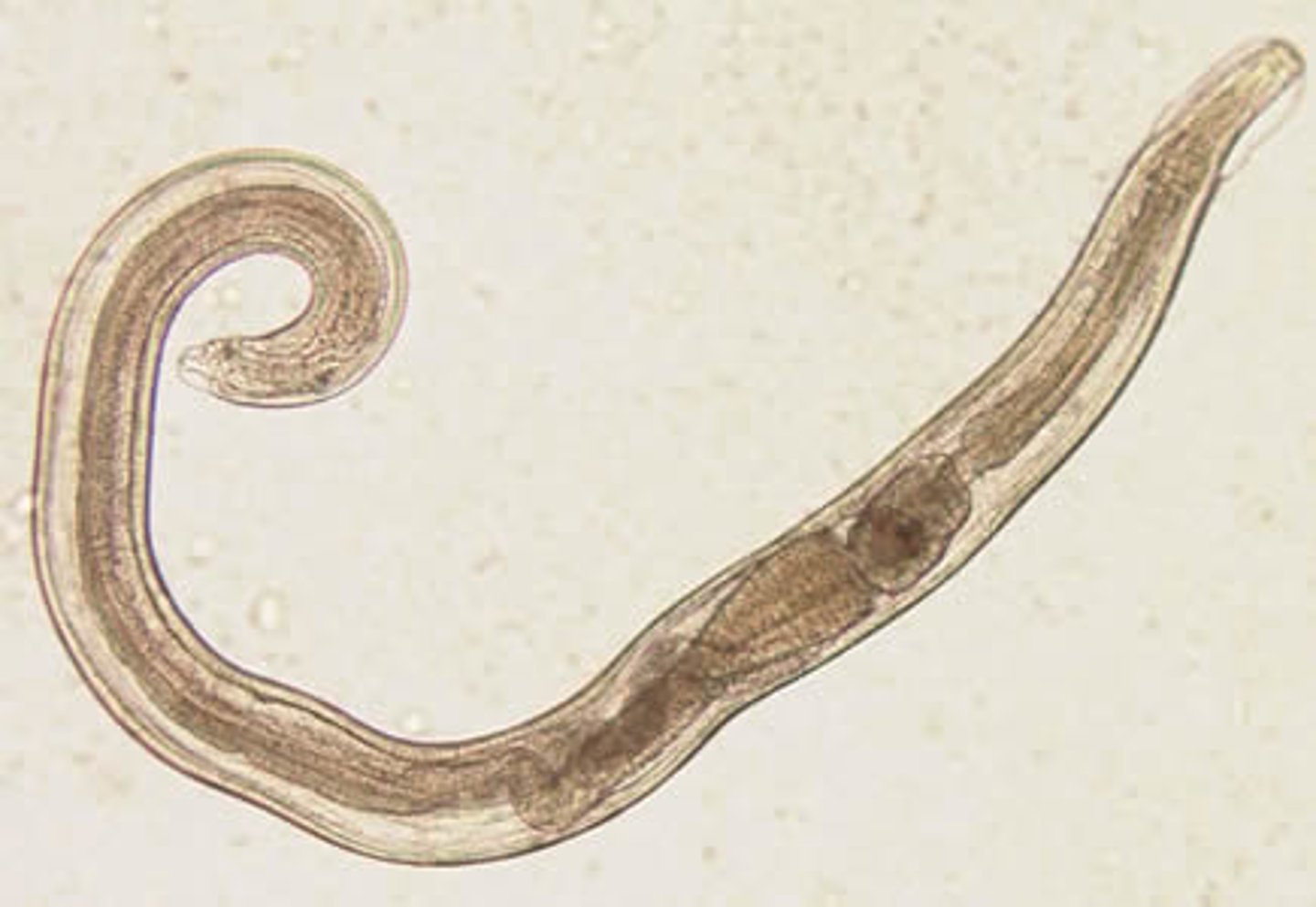
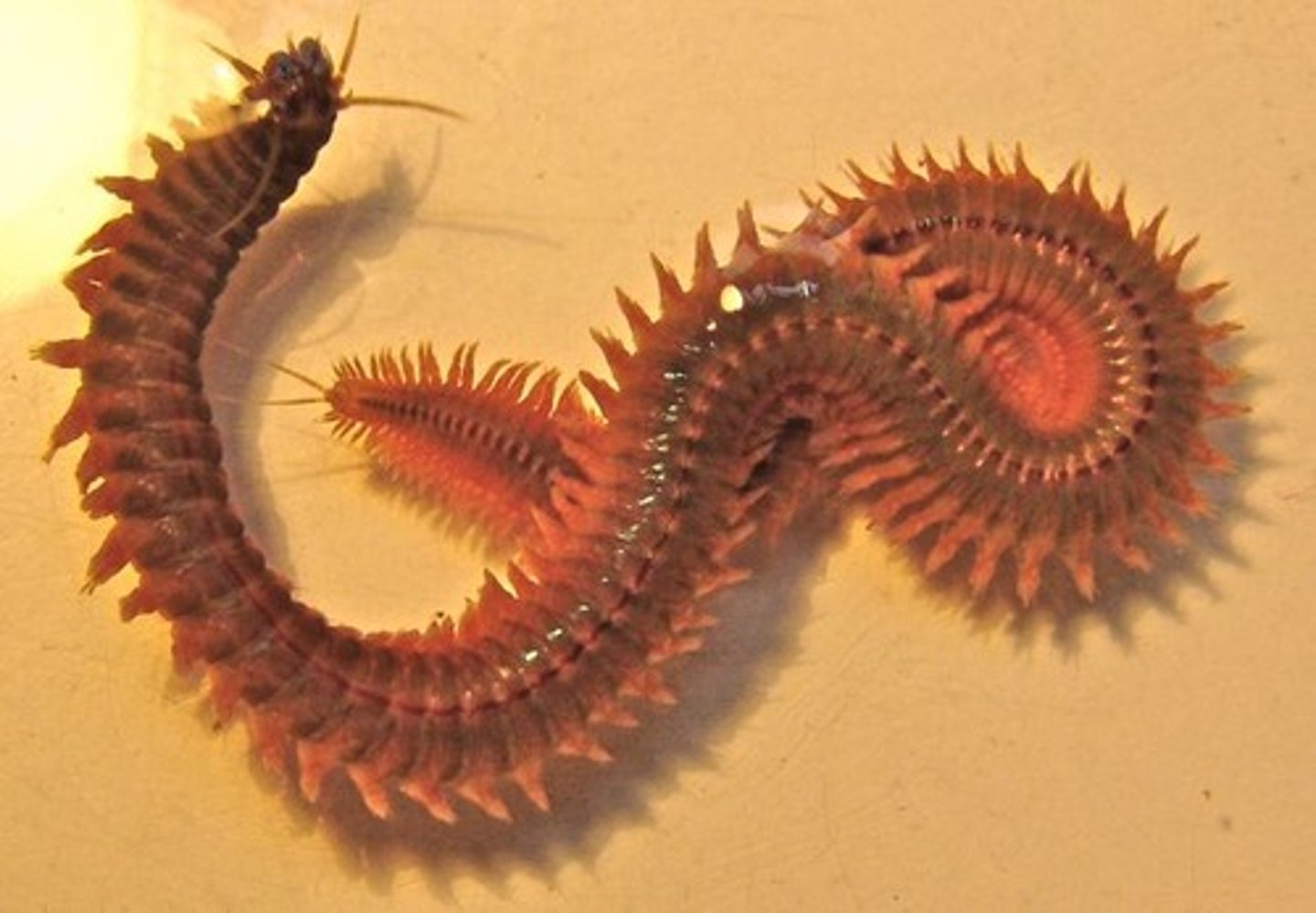
phylum nematoda
- roundworm
- often parasitic
- sometimes predatory or scavenging
- important bioturbators in some sediment environments
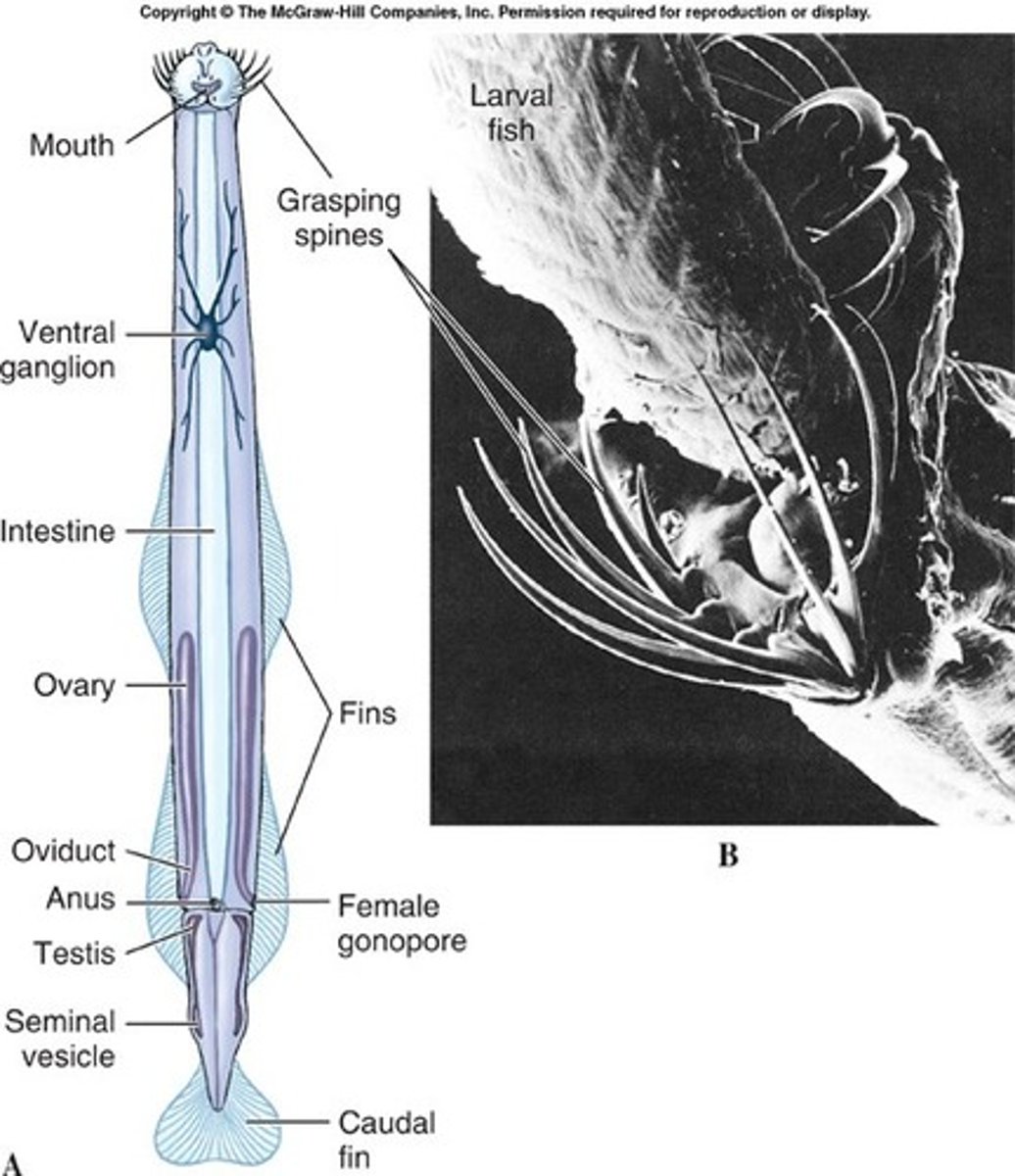
phylum chaetognatha
- arrow worm
- voracious predators
- grasping spines
- long, streamlined bodies for swimming
phylum annelida
- segmented worms
- abundant in marine environments
- internal and external segmentation
- well-developed nervous system with brain
- closed circulatory system
- bilateral symmetry
- body cavity with coelom

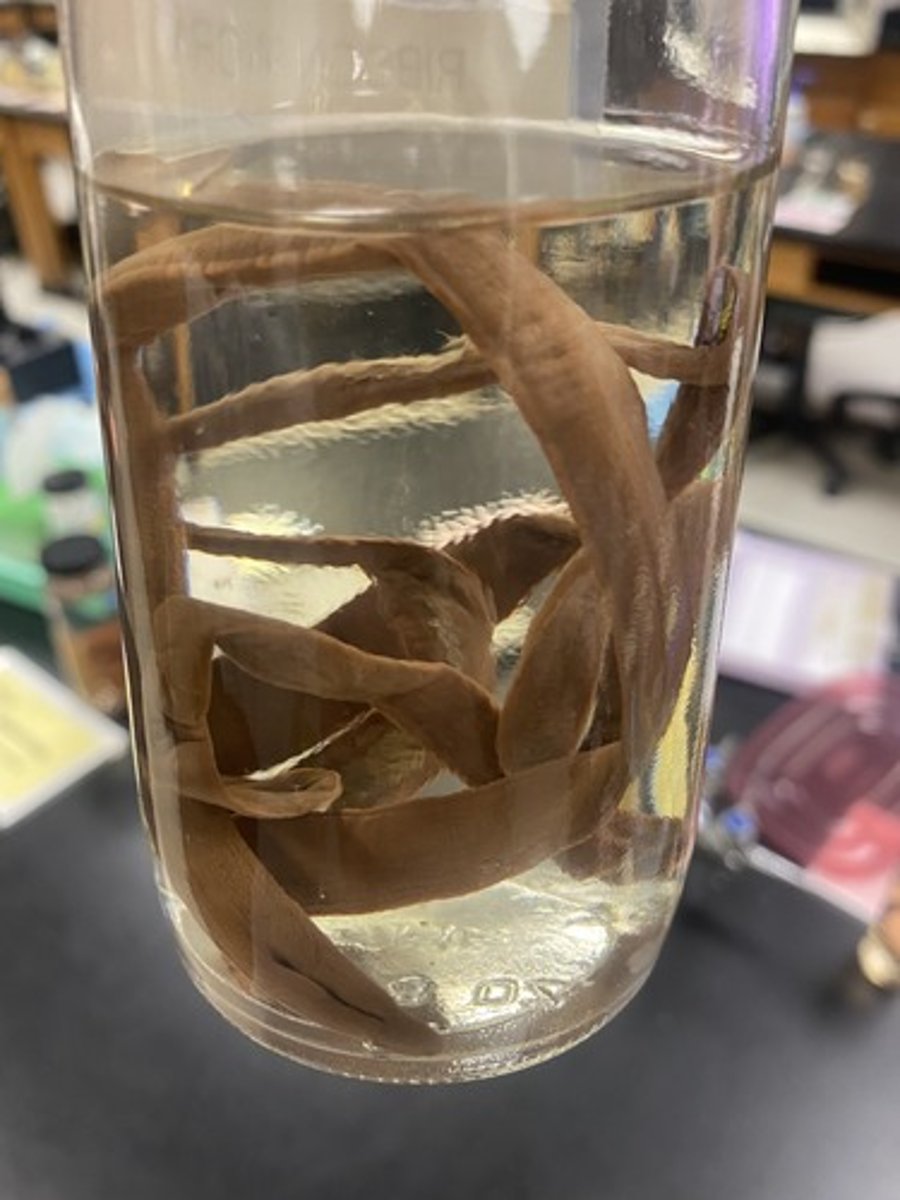
types of segmented worms
- class polychaeta
- class oligochaeta
class polychaeta
- largest and most diverse group of segmented worms
- each segment has a pair of flattened extensions, often with gills for gas exchange and bristles
- free-living carnivores, deposit feeders, or suspension feeders
- planktonic larva
- ex. bear worms: lack digestive system, have chemosynthetic bacteria
- ex. echiurans: soft, externally non-segmented body; deposit feeders

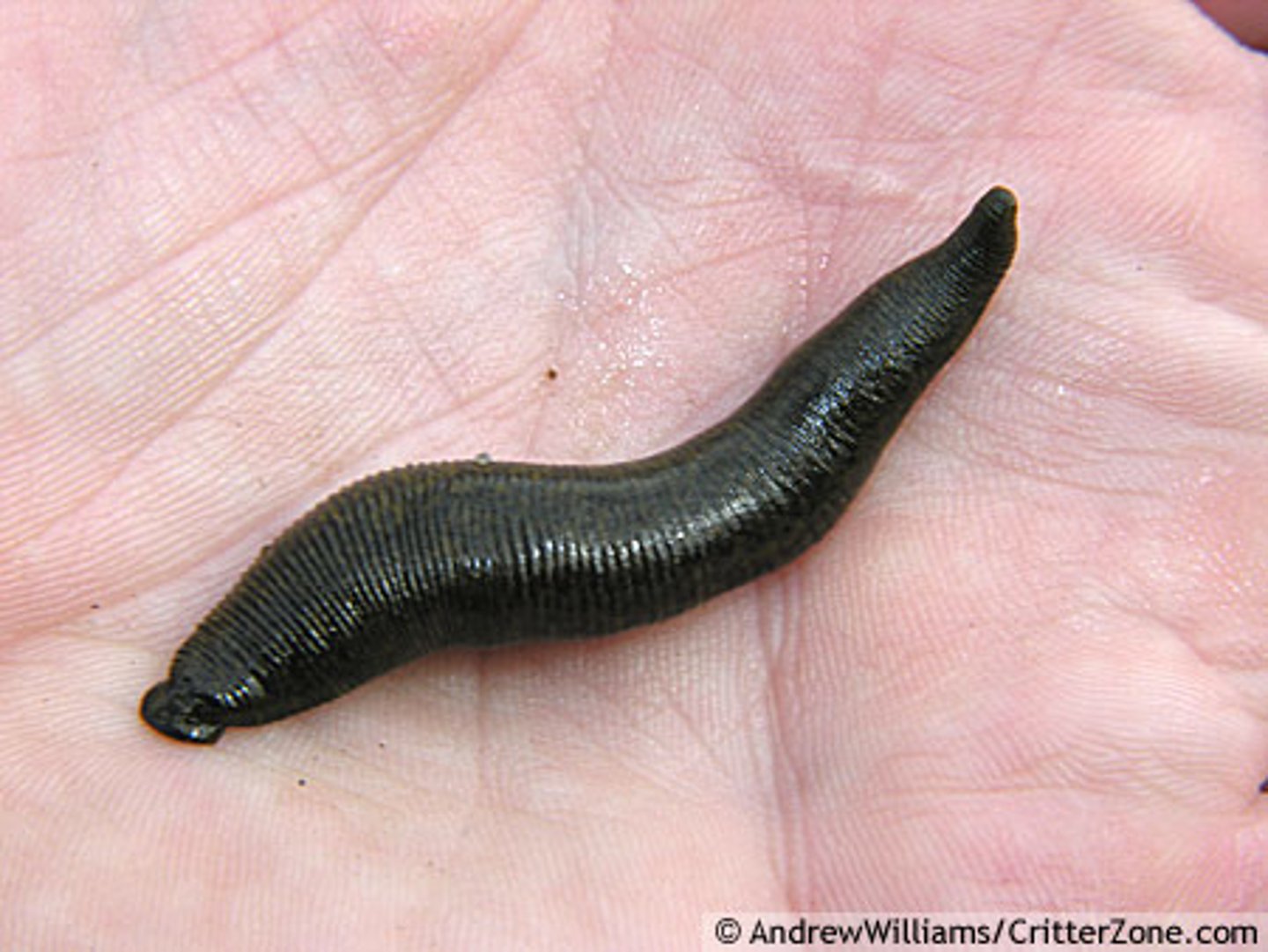
class oligochaeta
- anterior and posterior suckers to hold prey
- parasites of other invertebrates and fish
phylum sipuncula
- soft, unsegmented bodies
- retractable proboscis for feeding
- all marine
- deposit feeders
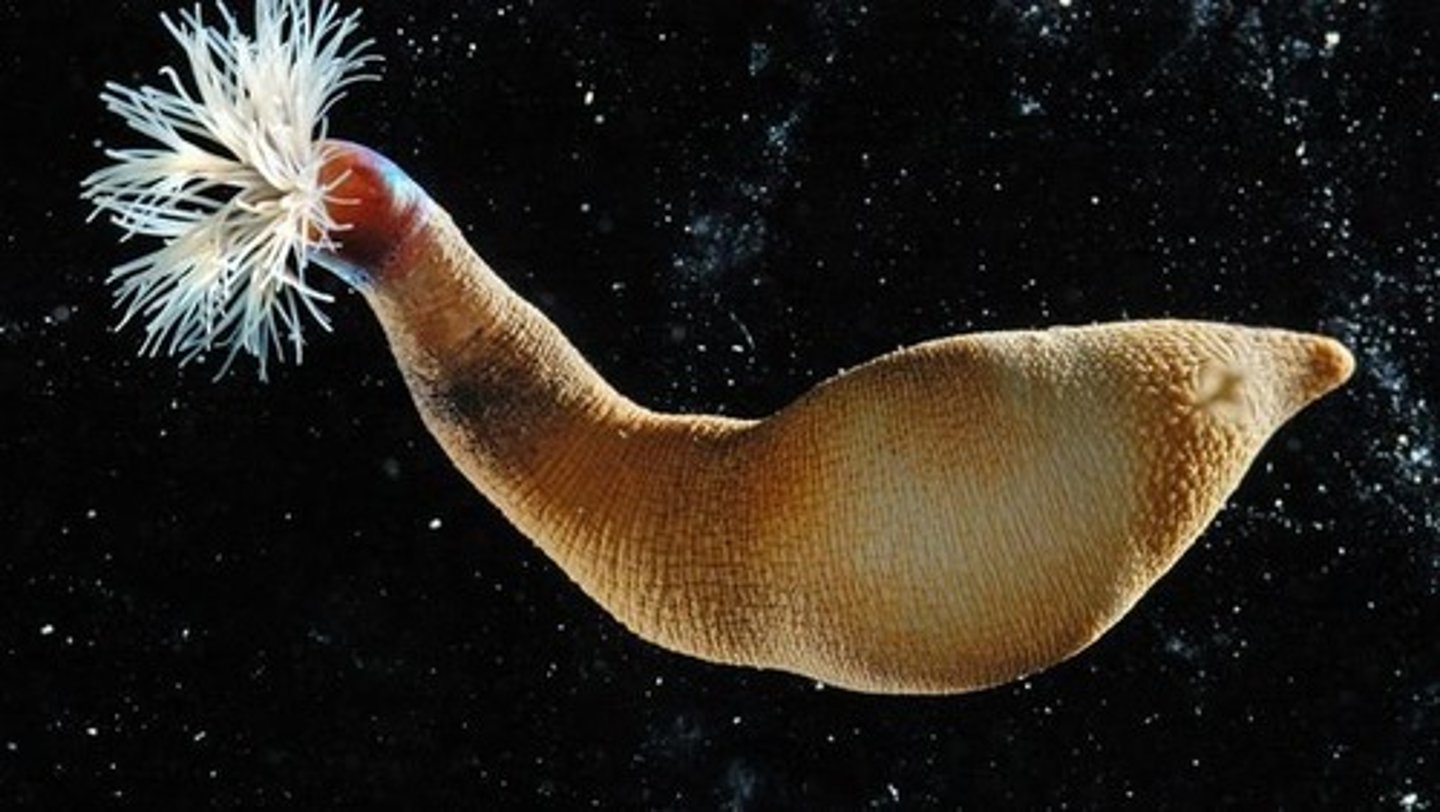

phylum mollusca
- head, muscular foot, and visceral mass of internal organs
- body covered by mantle that often secrets shell of calcium carbonate
- radula for grazing and other types of feeding
- well-developed nervous system with brain
- open circulatory system, complete digestive system
- large, successful group
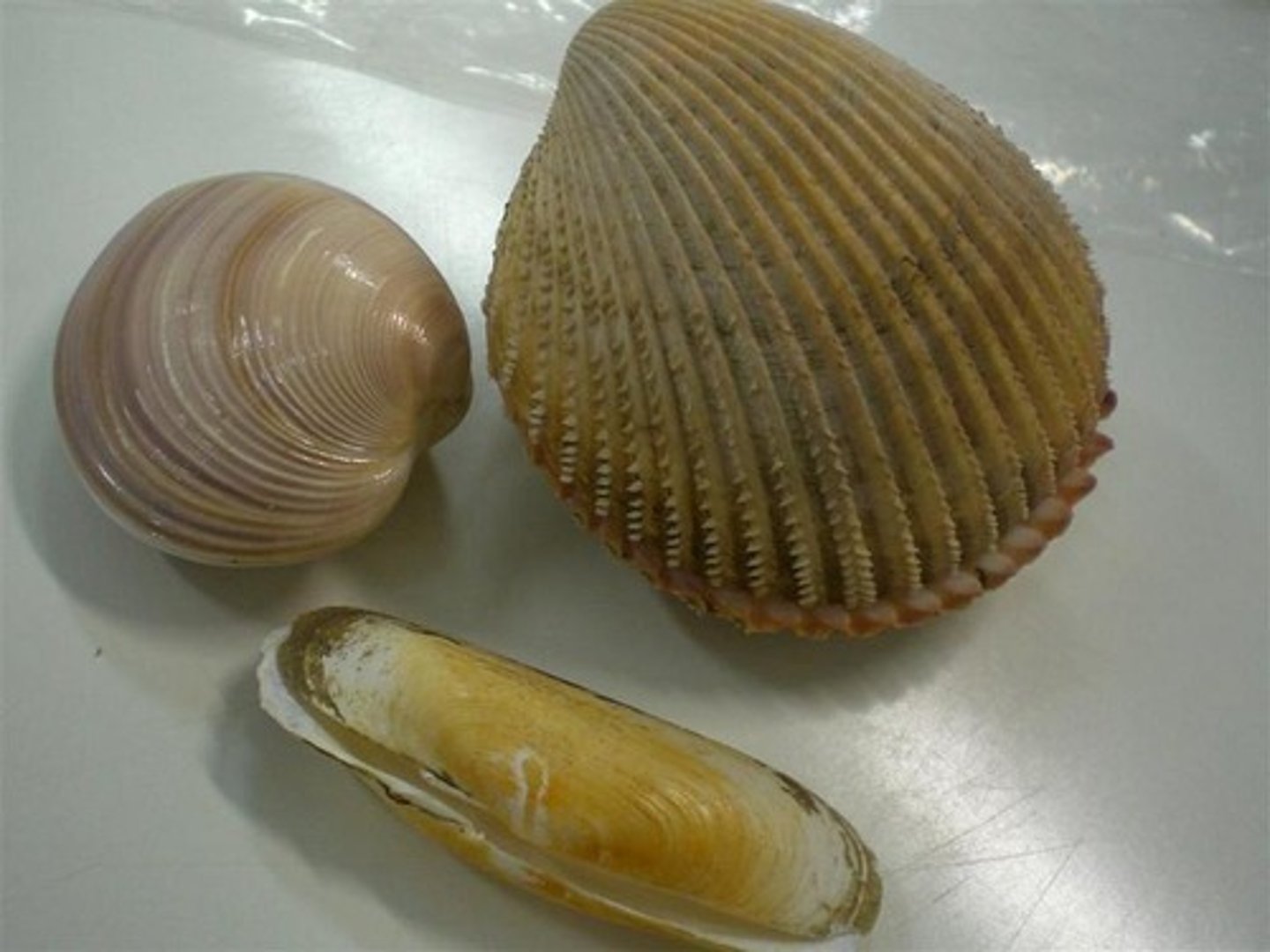

types of molluscs
- class gastropoda
- class bivalvia
- class polyplacophora
class gastropoda
- largest group of molluscs
- coiled shell on most species
- shell absent in sea slugs (nudibranchs)
- radula for grazing on seaweeds
- some are deposit or suspension feeders
- some are carnivores
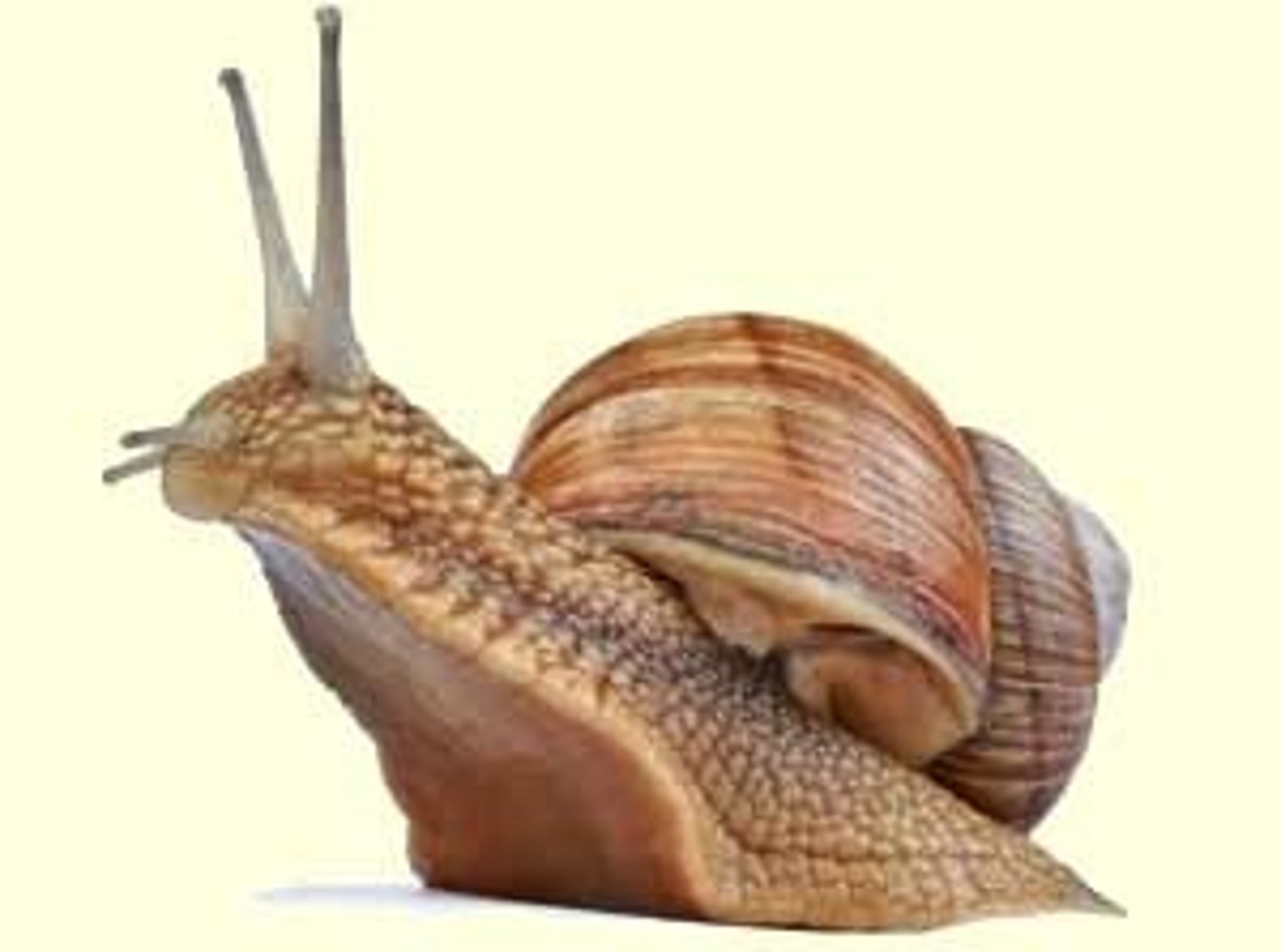

class bivalvia
- specialized filter feeders: clams, oysters, scallops, mussels
- compressed body in mantle cavity between two shells
- gills for respiration and filter feeding
- water enters and exits mantle cavity through siphons
- head and radula absent
- clams burrow, oysters and mussels attach to hard substrates, scallops are free-living
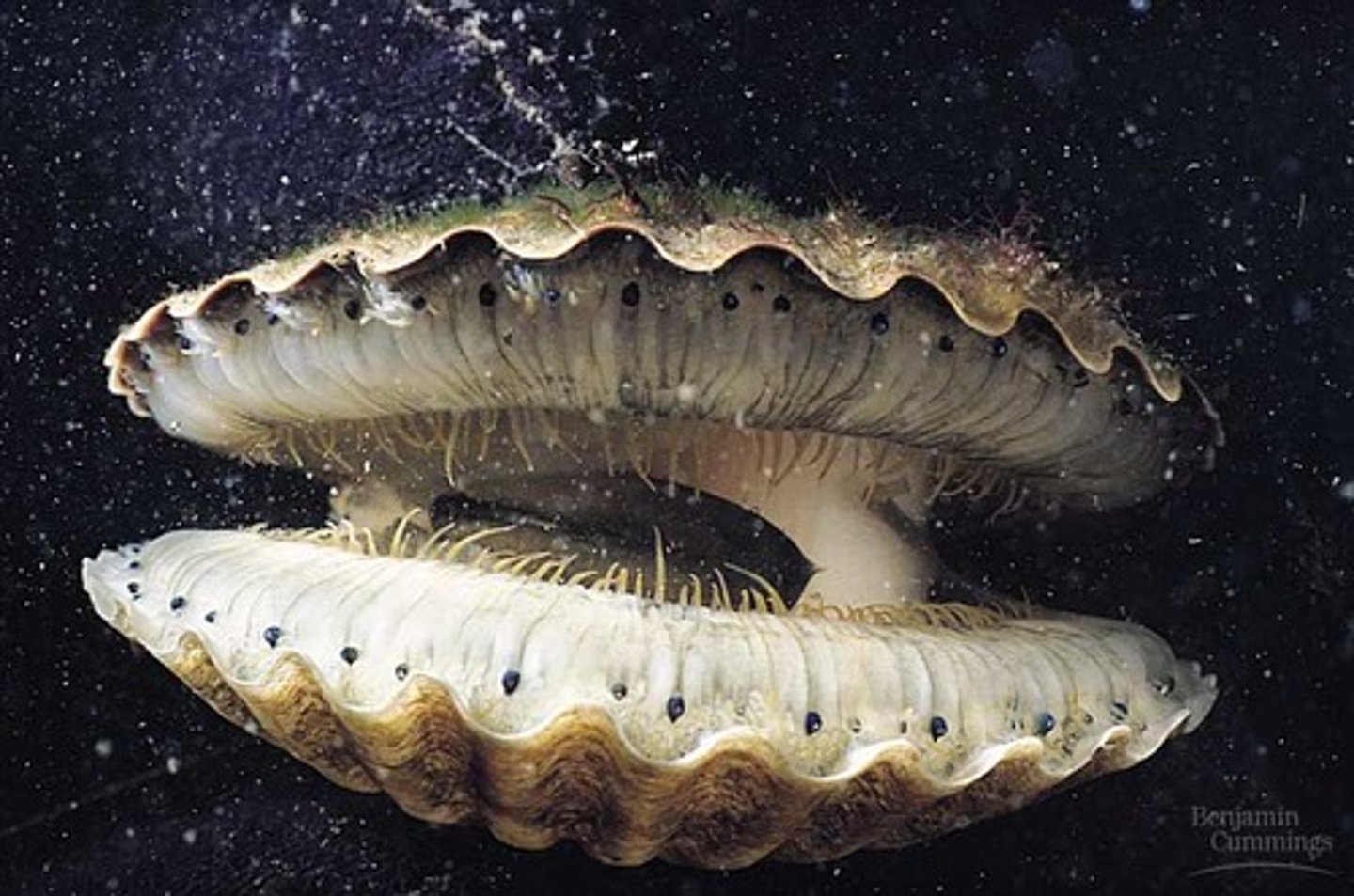

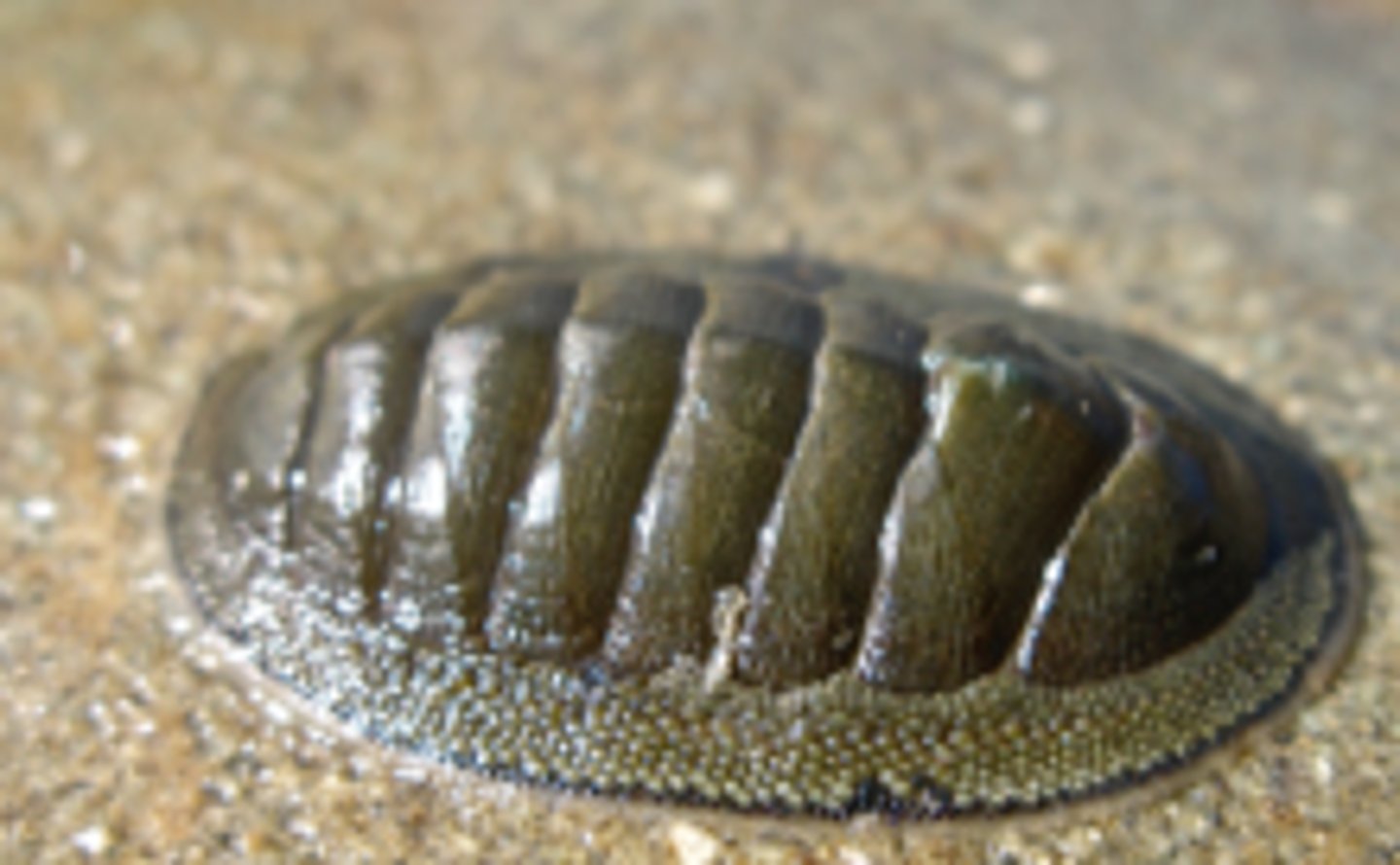
class polyplacophora
- dorsal shell of 8 plates
- ventral muscular foot
- ventral mouth with radula
- many graze on seaweeds and small invertebrates on rocky shores

which class are nekton molluscs?
class cephalopoda: octopus, squid, et.
phylum arthropoda
- animal phylum with largest number of species
- jointed legs and other appendages
- chitin exoskeleton that must be shed to grow (molting)
- body often divided into head, thorax, and abdomen
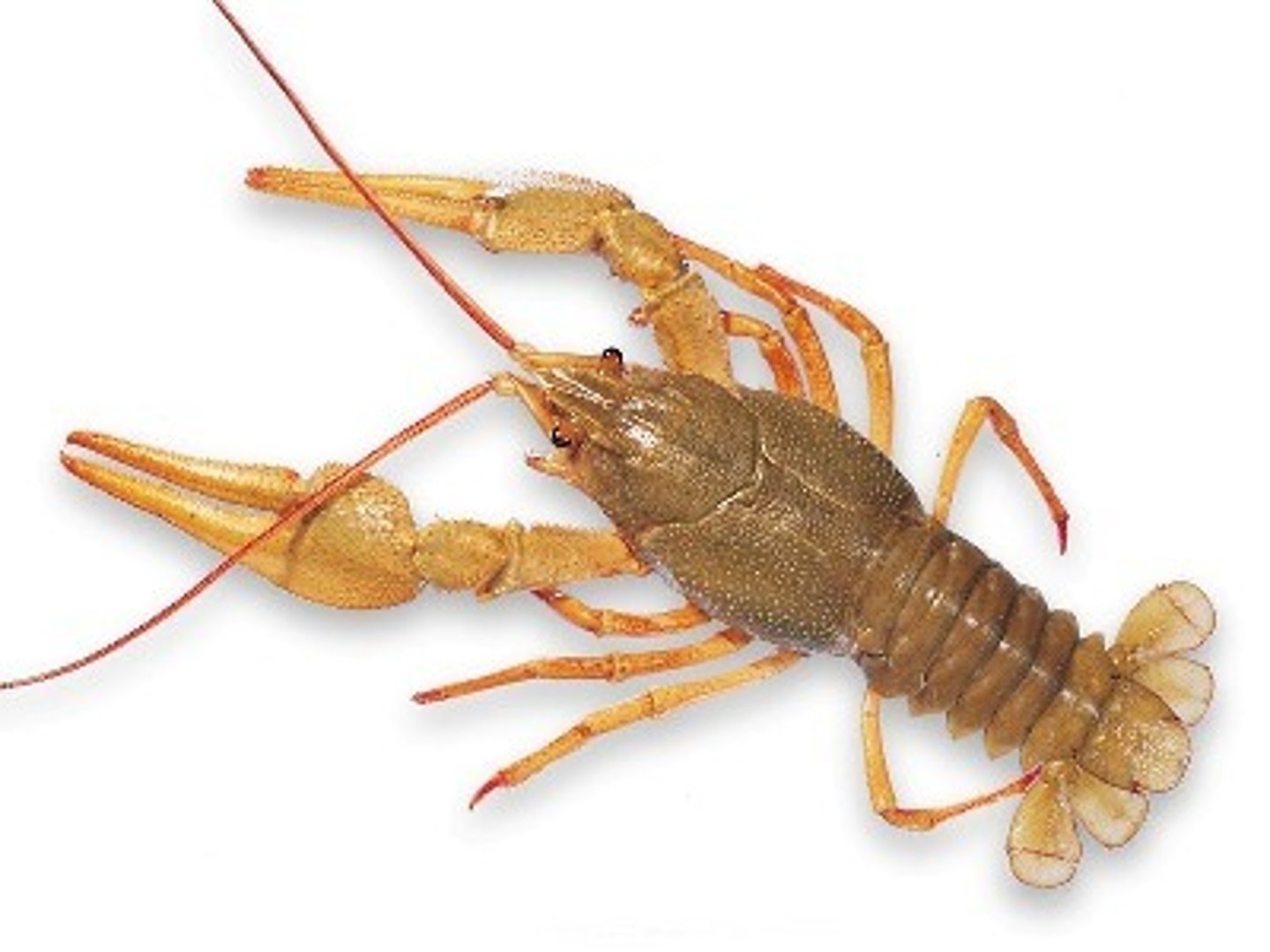

subphylum crustacea
- dominant marine arthropods
- two pairs of antennae
- gills used for gas exchange
- head and thorax fused as a cephalothorax
- some are filter feeders, others scavengers, parasites, carnivores
- appendages specialized for different functions: feeding, swimming, carrying eggs, etc.

barnacle reproduction
- internal reproduction
- use a large penis
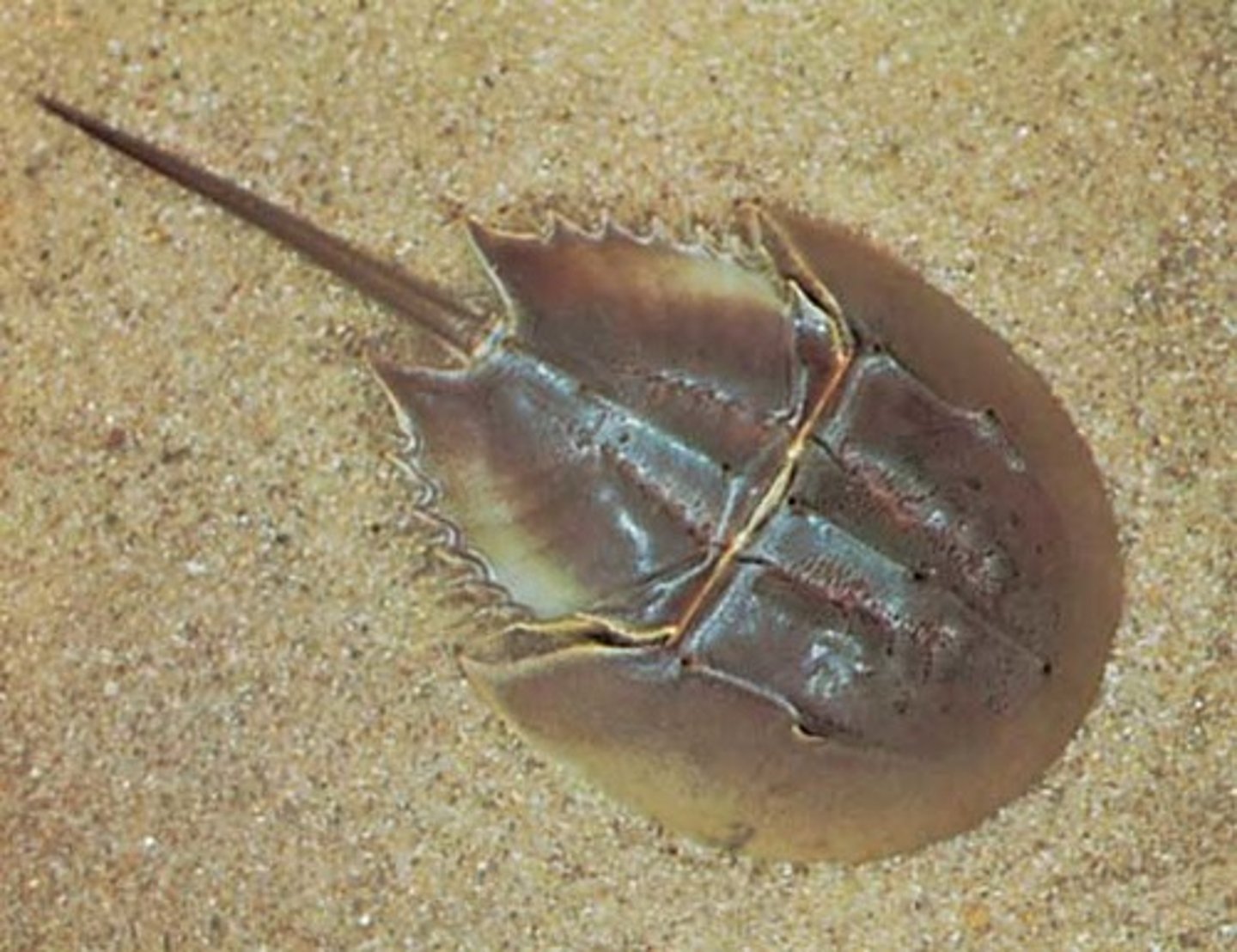
subphylum chelicerate
- horseshoe crabs: used for biomedical research
- 5 pairs of legs
- mating pairs come onto beaches each spring to breed and lay their eggs in wet sand
- among the oldest creatures on earth
- they live and burrow in soft, sediments

class pycnogonida
- sea spiders
- four or more pairs of jointed legs
- proboscis for feeding on soft invertebrates like sea anemones and hydrozoans
- more common in cold water
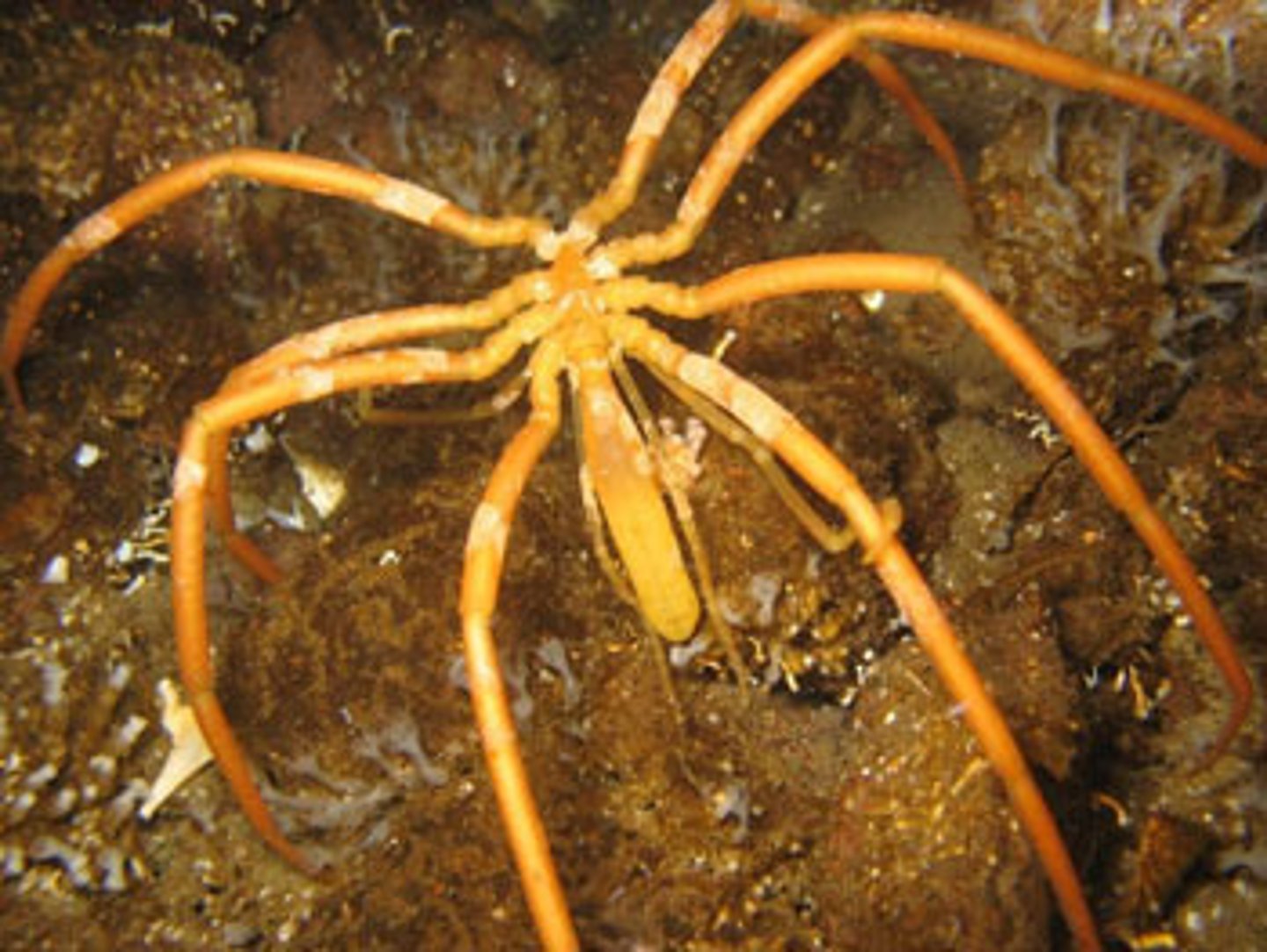

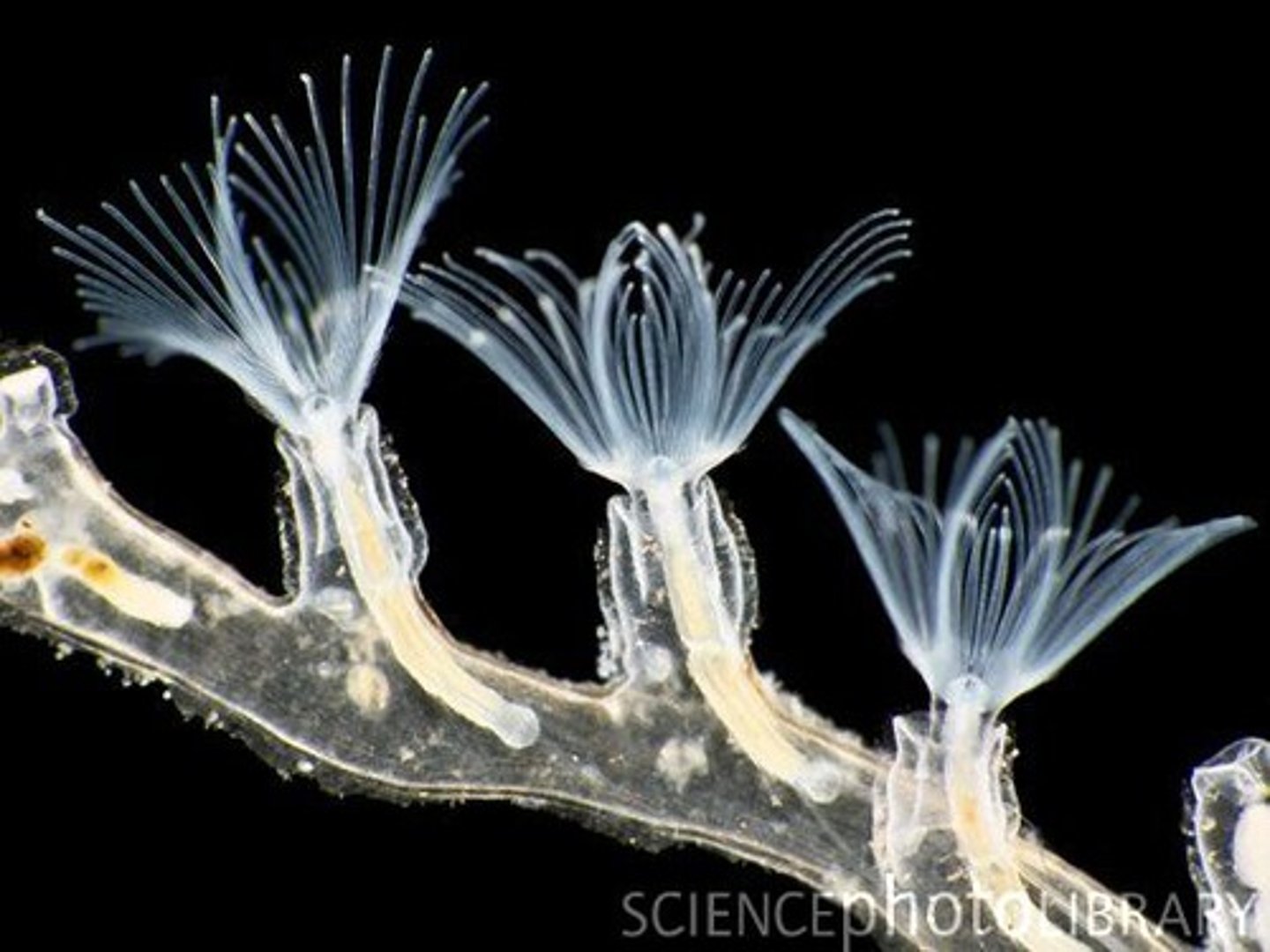
phylum bryozoa
- calls moss animals or ectoproctans
- all form small colonies
- some are encrusting, others form small fan or tree-shaped colonies
- suspension feeders
- use a lophophore: ciliated tentacles surrounding the mouth
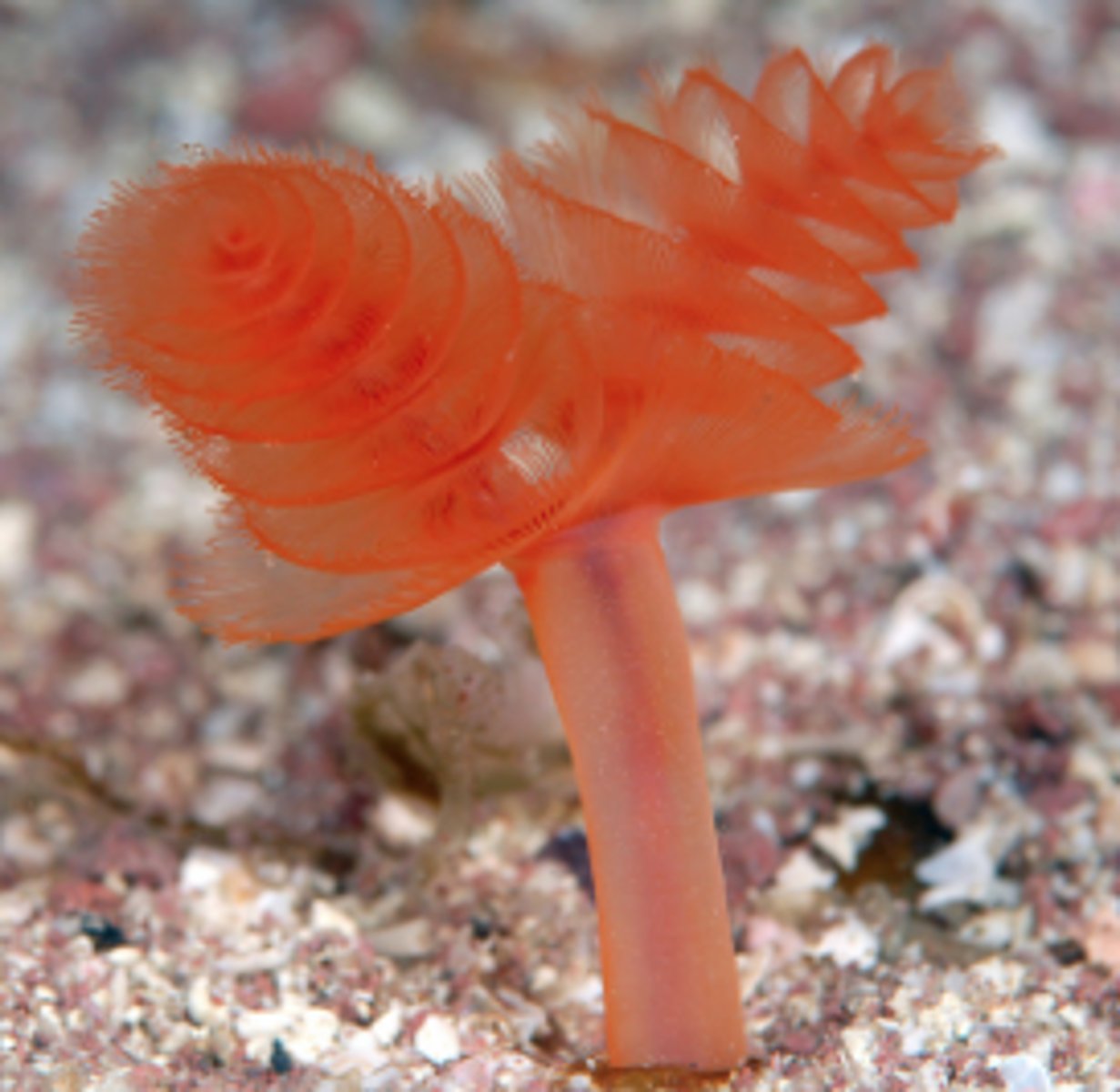
phylum phoronida
- horseshoe worms
- worm-like, living in tube of sand grains
- circular or horseshoe-shaped
- 32 species

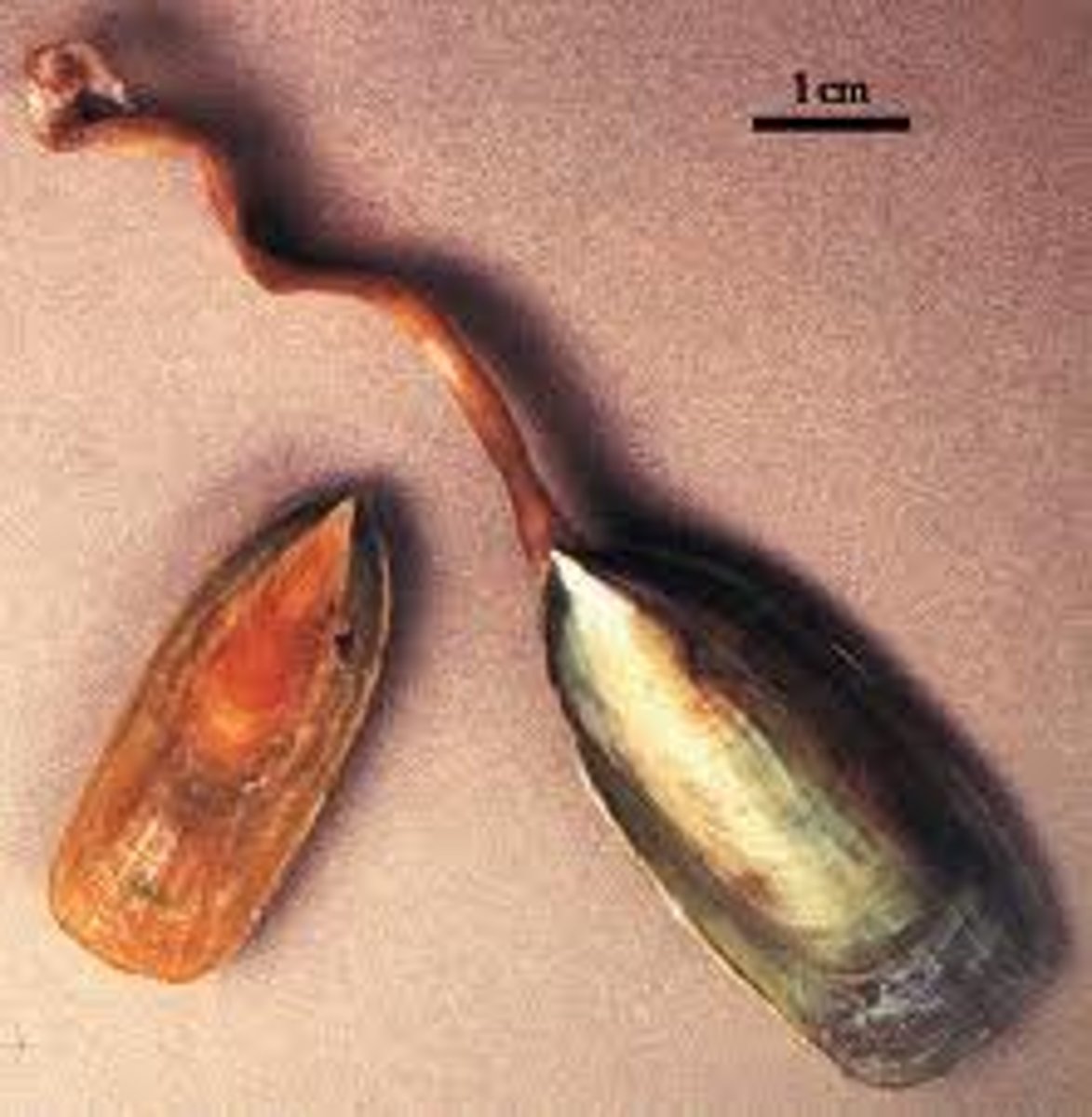
phylum brachipoda
- two shells enclosing body
- coiled lophophore
- many fossil species

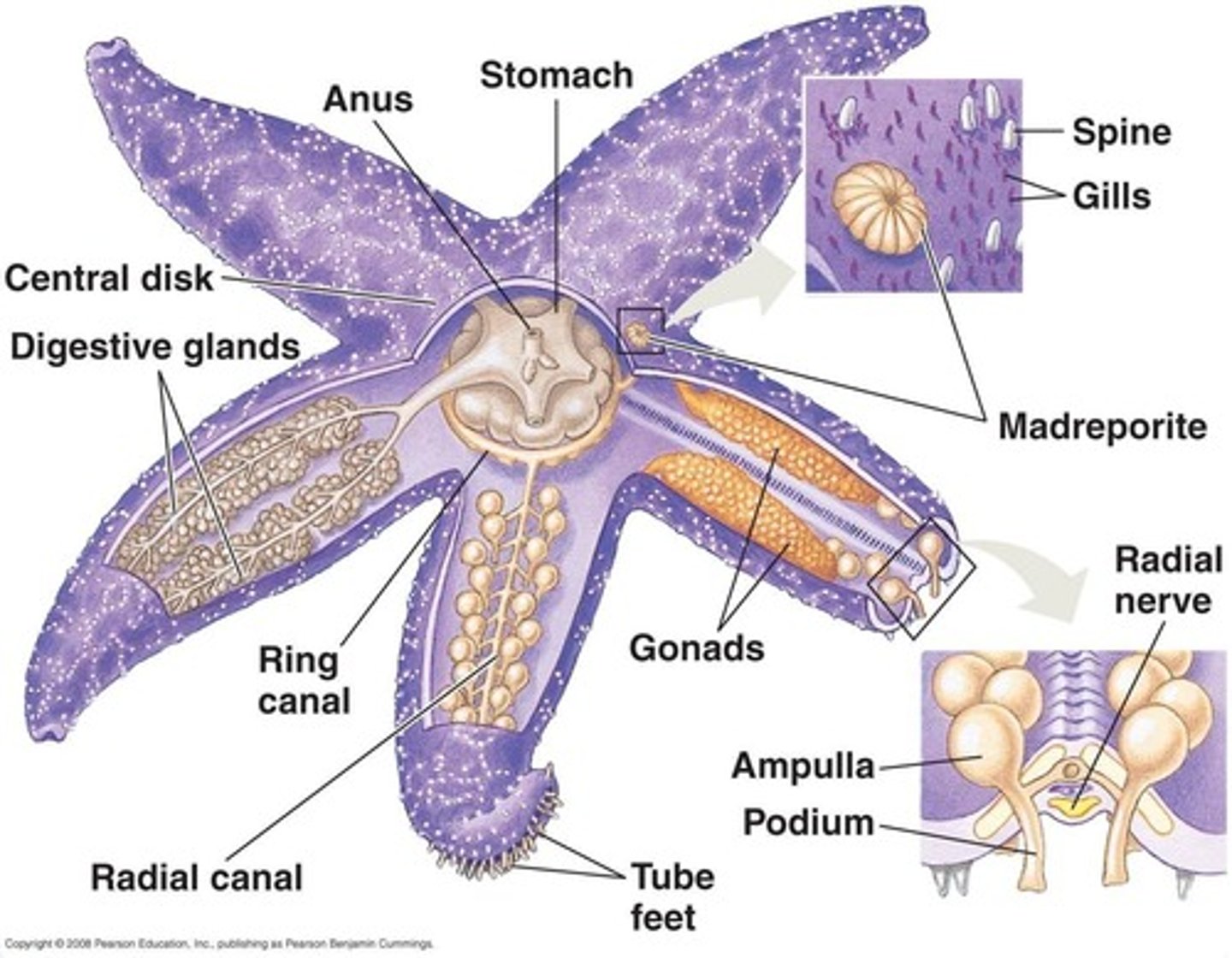
phylum echinodermata
- pentaradial symmetry in adults
- bilateral symmetry in larvae
- water vascular system with tube feet for locomotion and feeding
- nervous system is decentralized: brain is absent
- many can easily regenerate lost body parts
- exclusively marine
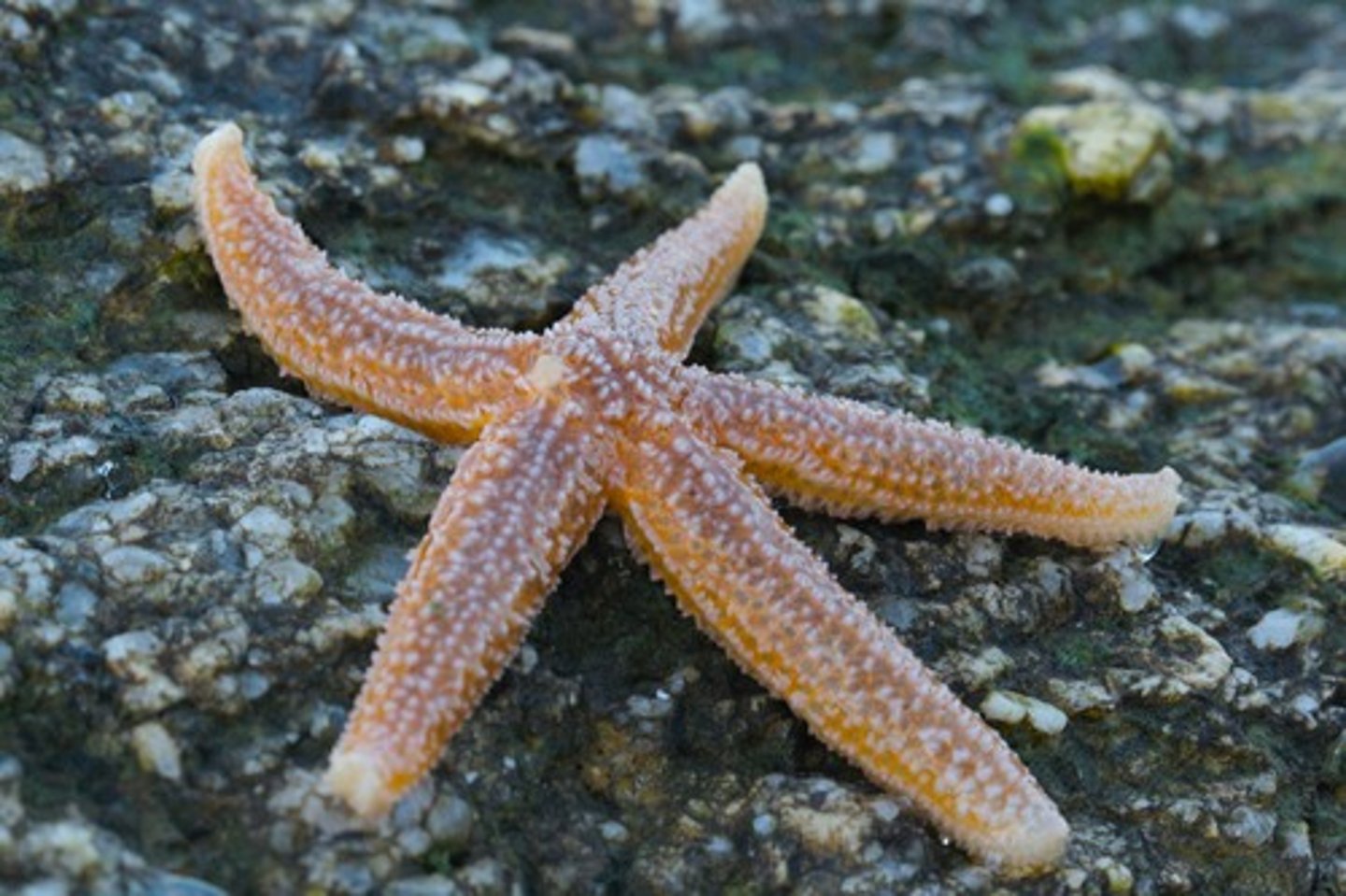

class asteroidea
- sea stars
- move with tube feet
- have a central disc in center of body surrounded by five arms
- internal organs extend through the entire body
- calcium carbonate plates are loosely embedded in spiny skin making them slightly flexible
- pedicellariae: pincer-like organs that keep skin clean
- mostly carnivores
class ophiuroidea
- brittle stars
- central disc surround by thin, flexible arms
- internal organs are restricted to the central disc
- tube feet without suckers used for feeding on detritus and small animals

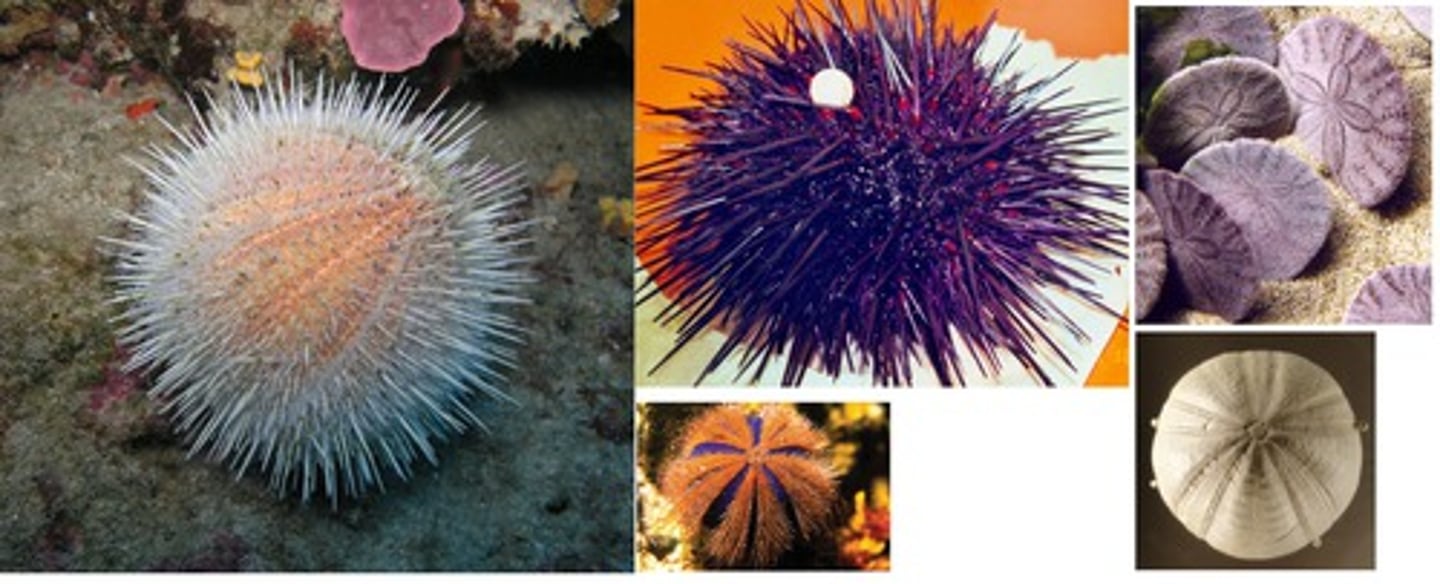
class echinoidea
- sea urchins and sand dollars
- conspicuous, movable spines
- rigid plates fused into a solid test
- move with tube feet
- mouth on the bottom, anus on top of body
- biting mouth for grazing with artistotle's lantern, a feeding structure of jaws and muscles
- feed on seaweeds, detritus, and encrusting organisms they scrape off surfaces

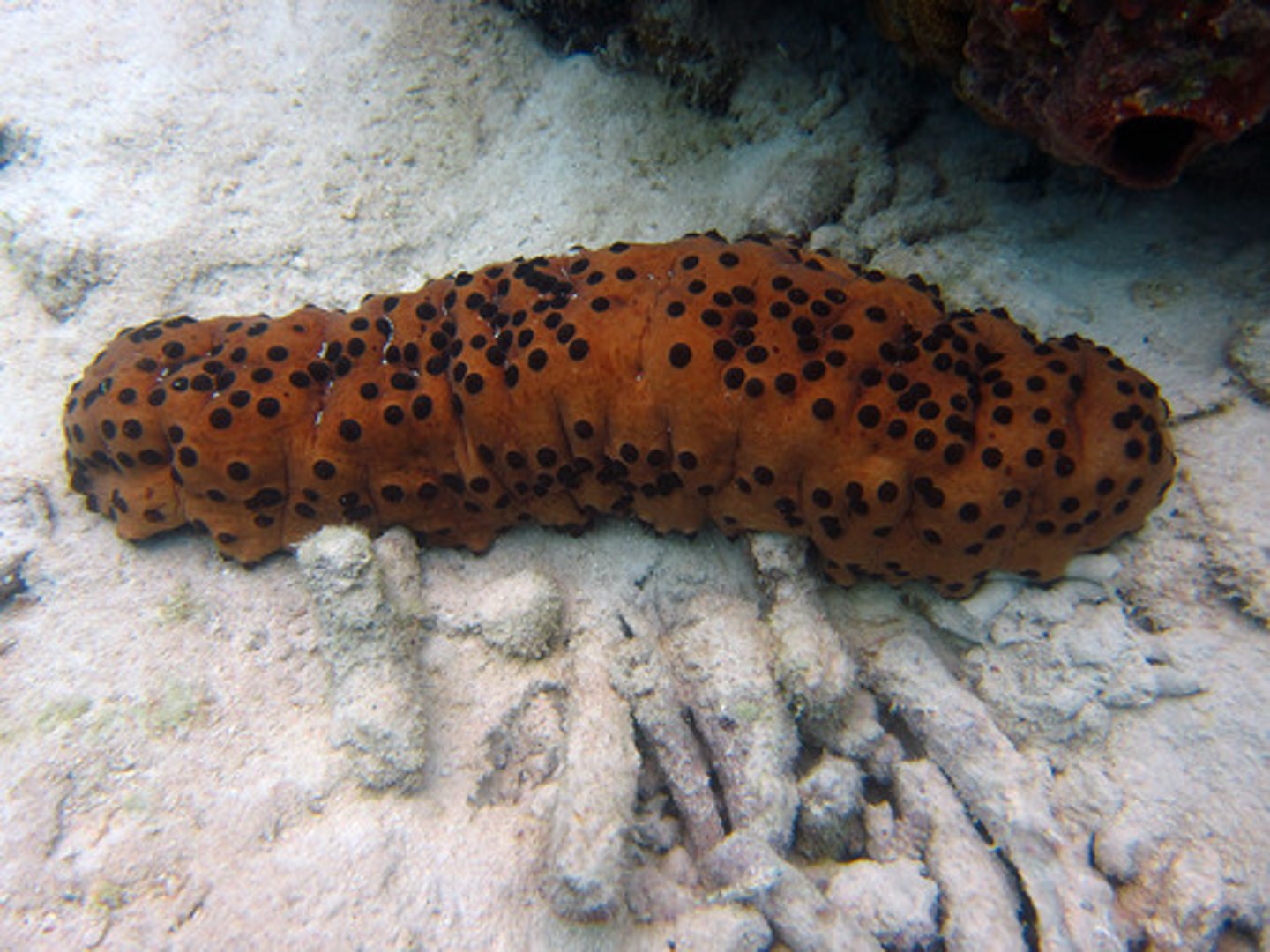
class holothruroidea
- sea cucumbers
- worm-like, with a mouth and anus on opposite ends and five rows of tube feet
- radial symmetry
- skin embedded with calcareous spicules, no spines
- deposit feeders, most species obtaining organic matter from ingested sediment
- evisceration: expulsion of the internal organs when disturbed, organs regenerate back

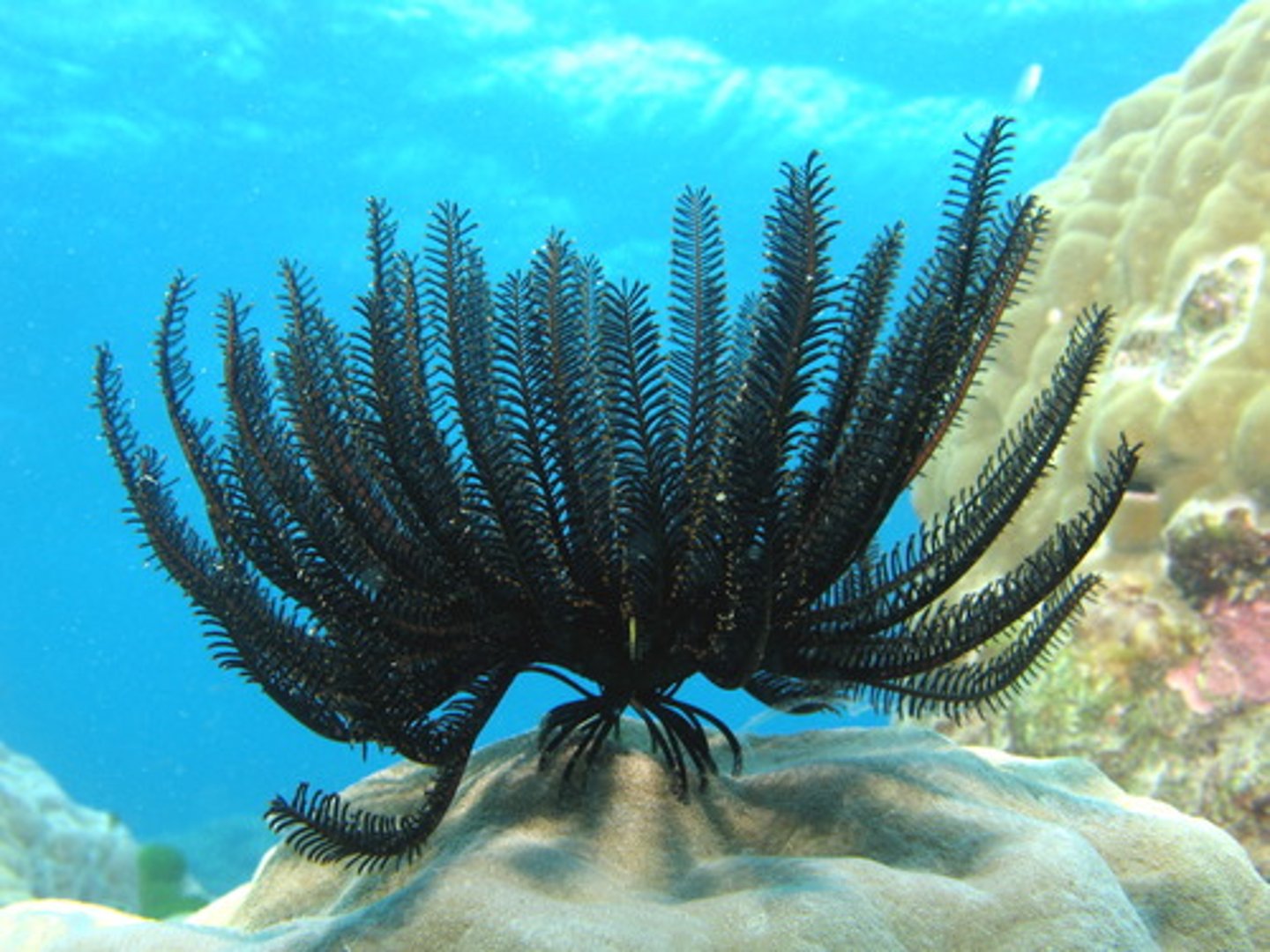
class crinoidea
- five or more arms that branch out for suspension feeding
- mostly in deep water
- sea lilies live attached in deep water
- feather stars crawl on the bottom and live mostly in shallow-water coral reefs

phylum hemichordata
- acorn worms
- pharyngeal gill slits and hollow dorsal nerve chord
- deposit feeders that use proboscis for feeding
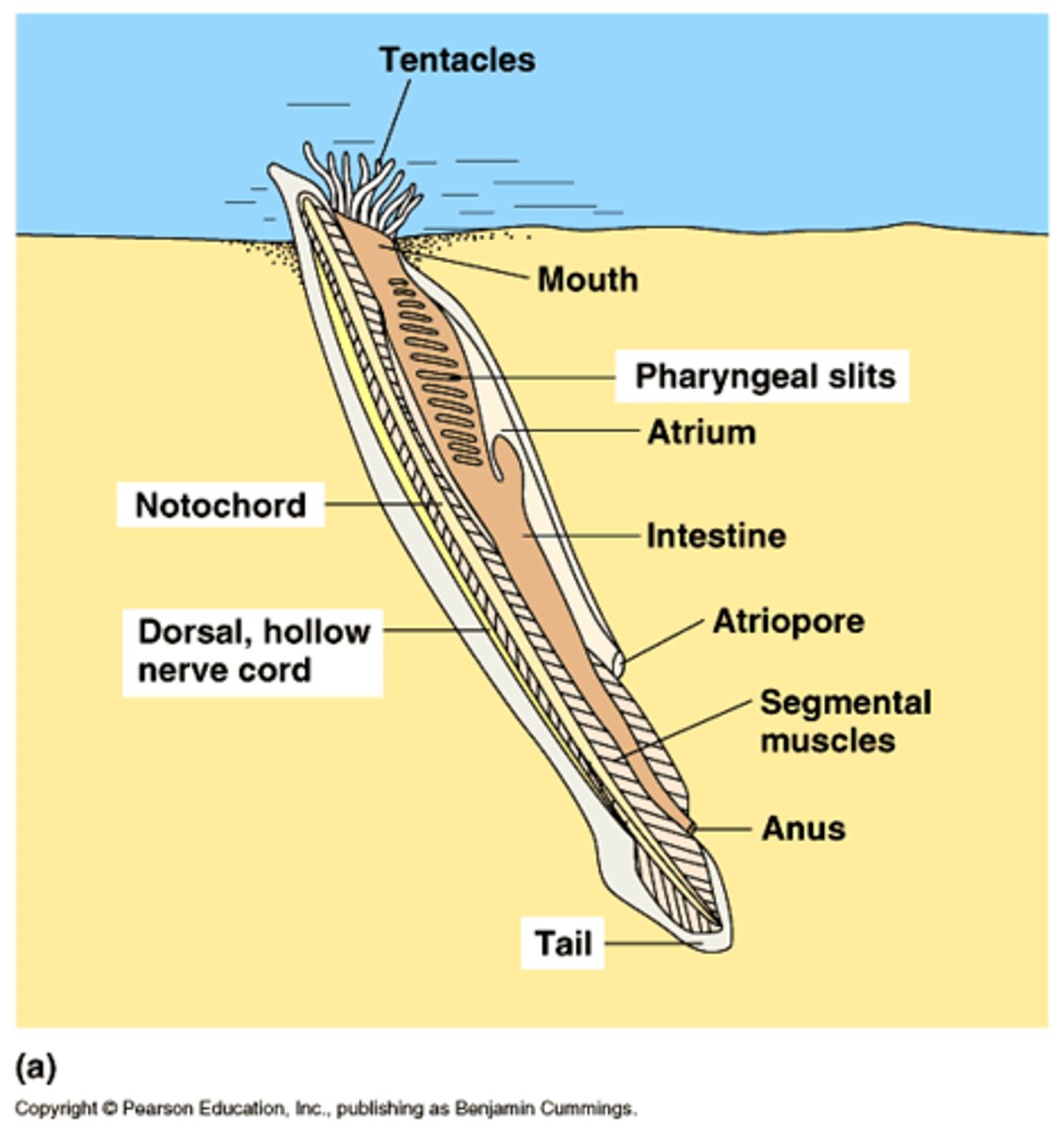
phylum chordata
- one hollow, dorsal nerve chord
- notochord: flexible rod for support of nerve chord
- gill slits along anterior half of pharynx
- post-anal tail
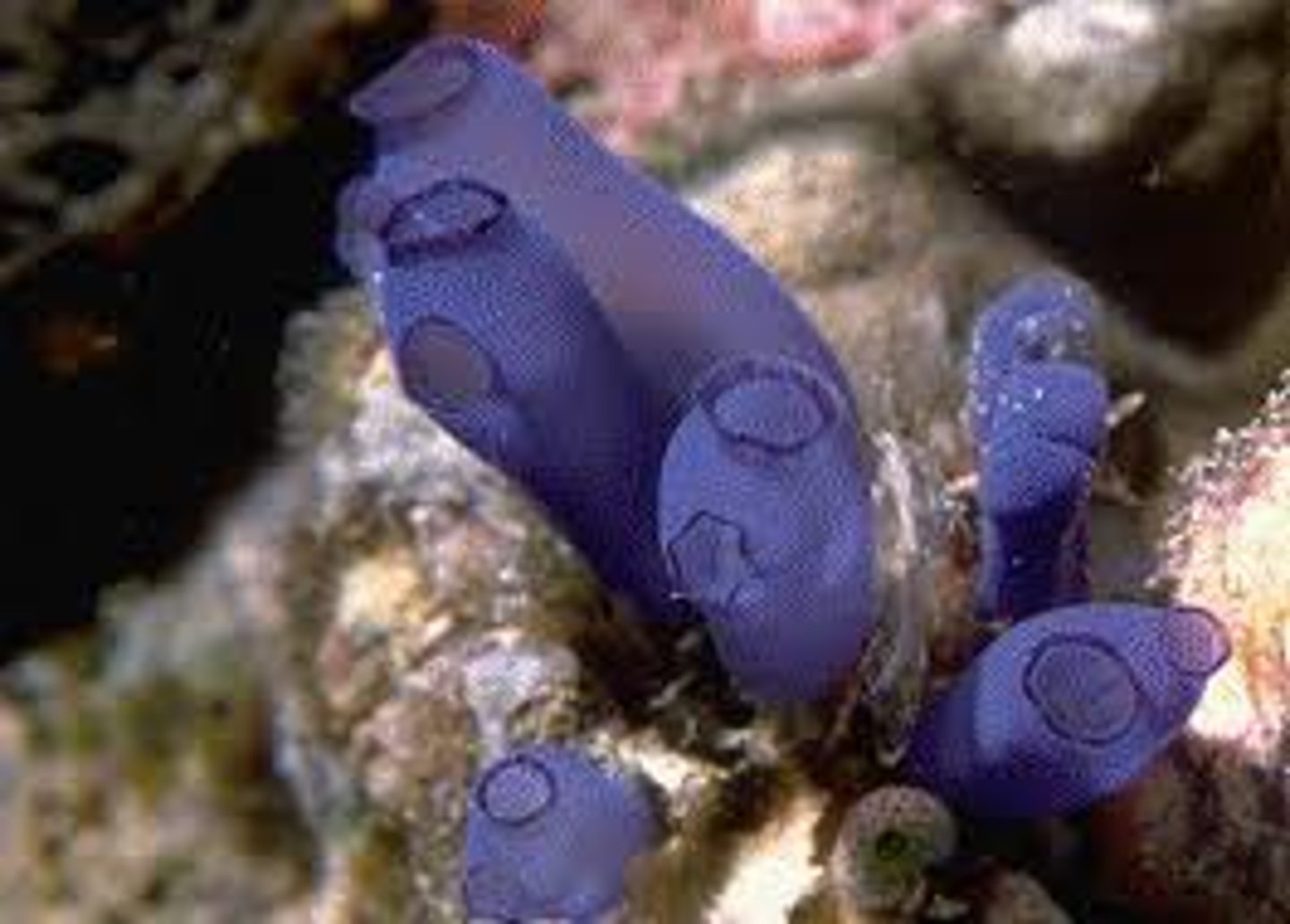
subphylum urochordata
- only larvae have chordate characteristics (not seen in adults)
- includes the sea squirts or ascidians (sessile filter feeders)
- tunic: thick outer cover of sac-like body

subphylum cephalochordata
- lancelets
- posses all chordate features as an adult
- fish-like body except the absence of a backbone
- small, only up to 8 cm long
- filter feeders in shallow, soft sediments
- gills are used to filter food