DCN - Lessons 1-3
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
ARPANET Meaning
Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
UCLA - SRI
ARPANET Purpose
ARPANET
was the first public packet-switched computer network. It was first used in 1969 and finally decommissioned in 1989. Its main use was for academic and research purposes.
Internet
is a global network of linked/interconnected computer networks that allows users to share information and communicate
Interconnected Networks, Network of networks, global network
Other terms of Internet
Intranet
is a private network within organization. The network is only accessible to its employees or members. Creates connections inside an organization.
Extranet
is an intranet that provides secured access to the authorized users outside the organization. Creates connections beyond an organization.
Local Area Network (LAN)
connects computers and devices within a limited area like home, office, or school
Personal Area Network (PAN)
is a network that connects a person's personal devices. It is mostly centered around a person
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
is a network that covers a larger geographic area than a LAN. This spans a city or a region.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
is a network that connects devices or smaller networks over large geographic distances. This may even span countries.
End Devices, Intermediary Network Devices, Cables and Connectors
Network Components
End Devices
are the devices that users interact with directly, such as computers, smartphones, and printers.
Network Interface Card (NIC)
is a piece of hardware that allows a computer to connect to a network.
Media Access Control address
The NIC contains the ____ of the device.
Intermediary Network Devices
These devices facilitate the flow of data between end devices.
Hub
is an old-fashioned device that connects multiple devices in a network.
Packet Sniffing
Hub Security Concern: is the practice of gathering, collecting, and logging some or all packets that pass through a computer network (ex.: Wireshark)
Man-in-the Middle
Hub Security Concern: Performing a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack on a hub-based network involves intercepting and manipulating data packets as they pass through the network (ex.: Ettercap)
Switch
connects multiple devices and sends data directly to the intended recipient based on its unique address (called the MAC address)
Modem
connects a home network to the internet.
Router
It allows multiple devices to access the internet and sends data between networks based on their IP addresses
Wireless Access Point
extends the wireless network so that devices can connect even from a distance
Patch Panel
is used by companies to organize and connect ethernet cables
Cables and Connectors
are physical components that are used to connect devices in a network.
Coaxial
This is a type of cable that is commonly used for cable television and cable internet connections. Has foil shield, braided shield, outer jacket.
Twisted Pair
This is a type of cable that is commonly used for Ethernet connections.
Ethernet Extender
is used to extend ethernet cable beyond the maximum length allowed
Fiber optic cables
use pulses of light to transmit data
Simplex
one device can only send information to another device. It cannot receive the information back
Half Duplex
a device can both send and receive information, but not at the same time.
Full Duplex
devices can send and receive information at the same time.
Physical Topology
refers to the actual arrangement of devices
Logical Topology
refers to the logical connections and data flow patterns.
Bus
all devices connect to a single main cable, or backbone
Star
a central device (like a hub or switch) connects to all other devices.
Ring
each device connects to two others, forming a closed loop.
Mesh
every device connects to all others with multiple cables
Hybrid
combines different topologies, such as star, bus, ring, and mesh, to create a custom network solution
Interface Message Processor (IMP)
early predecessors of modern routers
was the packet switching node used to interconnect participant networks to the ARPANET from the late 1960s to 1989.
Network Control Protocol (NCP)
is a protocol that enables low-cost networking in home environments through peer-to-peer communication and a multi-master system.
the language used in communication on the early years of ARPANET
was initially used to manage and control the transmission of data between computers on the ARPANET
Lack of flexibility
point to point communications (NCP Limitations)
Scalability Issues
unable to accomodate the growing number of post networks on ARPANET (NCP Limitations)
Inefficient Error Handling
NCP’s error recovery mechanisms were limited (NCP Limitations)
Limited Addressing
NCP has restrictions in addressing, hindered the ability to route packets effectively across different networks (NCP Limitations)
Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn
Who developed the design and development of TCP/IP?
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
TCP/IP Meaning
TCP/IP
provides a common set of protocols that could be used by all computers on the internet
protocol used by computer networks, consists of the rules that computers must follow
solved the limitations of NCP, became the foundation of the internet til today
Open Systems Interconnections (OSI)
Blueprint of how networks should work by dividing/breaks down communication process into different layers
framework of how communication should take place for each layer (7)
Application Presentation Session Transport
Upper layer of OSI (handles software applications and how they can communicate)
Network Data Link Physical
Lower layers of OSI (manages the data transmission across the network)
Physical Layer
transmitting data over the physical medium (cables, NIC, hubs) (physical media, topology, data encoding)
Data Link Layer
providing reliable data transmission between devices on the LAN (includes error detection) (switches and bridges) (physical addressing, ethernet, and Error Detection and Correction)
Network Layer
Determines the best path for data to
travel to the right network destination (ex.: routers)
Logical Addressing
Packet Fragmentation and
Reassembly
Routing
Packet Forwarding
Transport Layer
Provides reliable end-to-end
data transmission between
applications on different
devices.
End-to-End Communication
Protocols: Transmission
Control Protocol and User
Datagram Protocol
Flow Control
Session Layer
Establishes, maintains, and ends communication between applications on different devices.
exchanges data in a structured way and provides synchronization and recovery mechanism
Presentation Layer
Handles data representation, encryption
and decryption, and compression.
converts data from one format to another
Application Layer
Provides services to applications and defines protocols for communication between them.
• Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
• File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
• Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
Encapsulation
when you send data from one device to another over a network, the data goes through this process
is the process of adding headers and trailers (or both) to data as it moves through the layers of a network protocol stack, like the OSI model, to ensure proper routing and transmission.
is the process of wrapping data with protocol information at each layer of the OSI model, allowing for proper data transmission between network devices.
Decapsulation
unwrapping the data
is the process of removing headers and trailers from data as it moves up through the layers of a network protocol stack, allowing the original data to be accessed and understood by the receiving device.
Packet Fragmentation
is the process of breaking down packets into smaller pieces to fit into a network's maximum transmission unit (MTU), allowing for efficient data transmission over the network.
speed(UDP) and accuracy/reliability(TCP)
difference of TCP - Transmission Control Protocol and UDP - User Datagram Protocol (apps like gaming)
Digital to digital conversion
is the process of taking digital data and converting it into a digital signal that can be transmitted over a communication channel
Unipolar encoding
uses only high voltage to represent 1 and no or zero voltage to represent 0.
Polar Encoding
here, two voltage levels are used: One positive, and another is negative.
NRZ: NRZ-L & NRZ-I
_____ represents signal in either positive or negative. Two common methods are used: ____ & ____
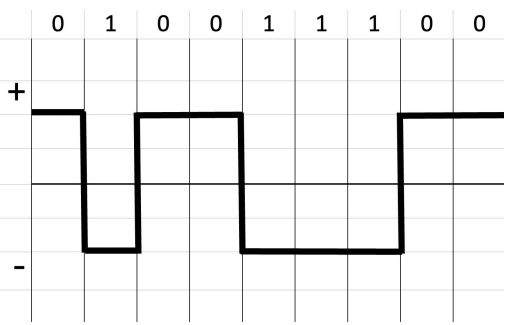
NRZ-L
bit 1 is represented by a negative or low voltage while bit 0 is represented by
positive or high voltage.
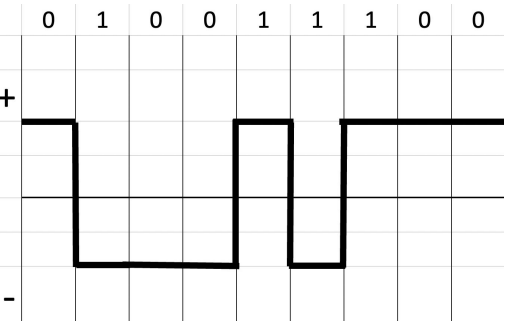
NRZ-I
for every bit 1, there will be an inversion or change in voltage level either positive or negative. While for bit 0, no change in voltage level occurs.
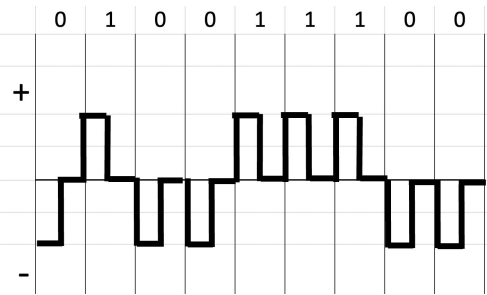
Return Zero Encoding
have three values: positive, negative, and zero. Bit 1 is represented by positive ; bit 0 is represented by negative; and zero level has no representation. For every half duration the signal returns to zero level
Biphase encoding
changes the signal at the middle of the bit interval but does not return to zero.
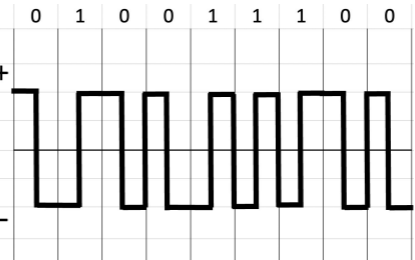
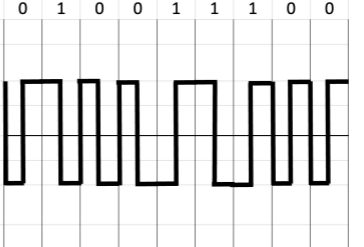
Biphase: Manchester
for every half duration, there is transition voltage level from positive to
negative or negative to positive.
Bit 1 is represented by negative to positive transition
Bit 0 is represented by positive to negative transition
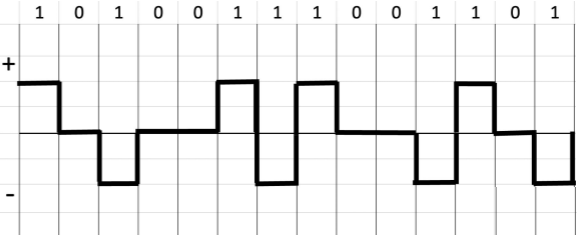
Biphase: Differential Manchester
for every half duration, there is transition voltage level from
positive to negative or negative to positive.
Bit 1 is represented by a transition in the half-duration only.
Bit 0 is represented by a transition in the first duration and transition in the half-duration
Bipolar encoding
represents three voltage levels: positive, negative and zero.
Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI)
0 is represented by zero voltage level. While 1 bit is represented by alternating positive and negative voltages.
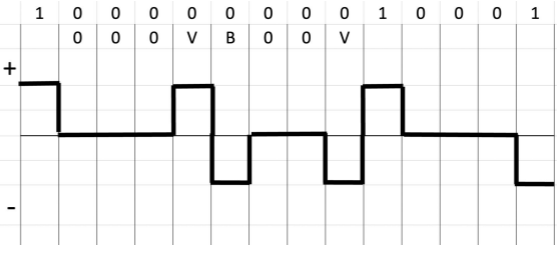
Bipolar 8-Zero Substitution (B8ZS)
It provides a synchronization when there is 8 bits of zero or more. When 8 bits of zero occurs, it implements some changes in 0s string pattern based on the polarity of the previous 1 bit.
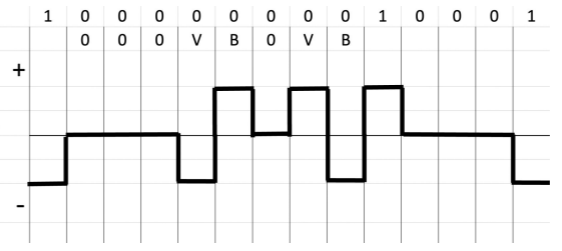
High-Density Bipolar 3 (HDB3)
It provides synchronization when there is 4 bits of zero. When 4 bits of zero occurs, it will look for the number of 1s bits that occurred since the last substitution. If the number of 1s bit is odd, then it will execute 000V. if the number of 1s bit is even, then it will execute B00V.
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)
is a method used to convert analog to digital signals.
Sampling
is used to find the number of samples that represents continuous wave form completely.
Hertz
is used to measure the sample rate per second
Quantizing
involves assigning a numerical value to each sample.
bit depth
Quantizing use _: the number of bits in each sample.
Encoding
involves converting the values into a digital signal that can be transmitted over a communication channel
Transmission Media
is the physical medium used to transmit data from one point to another.
Total Internal Reflection
Fiber Optics has two parts: The core and the cladding. These two parts work together to create a phenomenon called
Single-mode Fiber
Used for long-distance transmissions
guided media
In ___, data is transmitted through the air or space.
Radio waves
are electromagnetic waves that transmit signals at all directions.
Terrestrial Microwave Transmission
is unidirectional. Data is transmitted
from one station to another.
Infrared Transmission
is a wireless technology used for short range communications. It cannot penetrate the walls.
Multiplexing
is a technique used to combine and send the multiple signals over a single medium.
Time Division Multiplexing
is a method that divides time into equal slots and assigns them to each device or user to transmit their data.
Synchronous Time Division Multiplexing
gives fixed time slots to each device.
Asynchronous Time Division Multiplexing
adjusts the slots according to the priority and need of each device.
Frequency Division Multiplexing
the available frequency band is divided into multiple sub-channels, each of which is assigned to a different signal or communication stream.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing
is a fiber-optic transmission technique that enables the use of multiple light wavelengths (or colors) to send data over the same medium.