Ch. 10 - Stratification and Social Class: Urban and Suburban Lifestyles
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Introduction
sociology research often shows us that what people think is not necessarily true
no large city/suburb is accurately described with any single stereotype
some urbanites experience ‘the good life’ while others contend with problems
Social Stratification I
NA countries are stratified societies
Marx and Weber offered ideas about social stratification
Weber agreed w/ Marx that social stratification caused conflict, but viewed his 2-class view as too simplistic.
Weber’s dimensions include:
class, status, power, income is an DV rather than IV
social difference → social inequality
Social Stratification II
= the hierarchical ranking within a society of various social class groups according to wealth, power, and prestige.
socioeconomic status= a composite ranking based on various dimensions of social inequality
‘yankee city’
reputational method= subjective input in which people compare others to themselves in terms of status
Upper Class
‘distinction of upper-upper and lower-upper classes is old money’ and ‘new money’
2-3% of the total population, cohesive group
both men and women
exclusive neighborhoods, political clout, not really 9-5
Middle Class
45% to 50%, diverse
most often depicted
Upper-middle-class women may or may not work
larger portion works either in less prestigious white-collar occupations or highly skilled blue-collar jobs
Working Class
1/3 of society, family income below the national average
vulnerable to financial crisis
1/3 of children will go to college
both men and women are likely to restrict their outside activities to religious-related or neighborhood association activities
Lower Class
about 18%, working-poor, inner cities or rural areas
no medical insurance
$ segregated neighborhoods w/ extreme levels of poverty and unemployment
Income Distribution Nationwide
disparity between rich and poor is not just a matter of difference in incomes
Canadian households, unequal distribution is pronounced and worsening
income= the money you obtain through work
wealth= anything you or your previous have accumulated in the form of marketable assets
as with income, wealth disparity exists as well
net worth= all of one’s assets minus all liabilities
tends to stay negative in an individual’s lifetime
born into a family that is struggling economically
more accurate indicator of economic well-being
poverty is subjective in terms of numbers
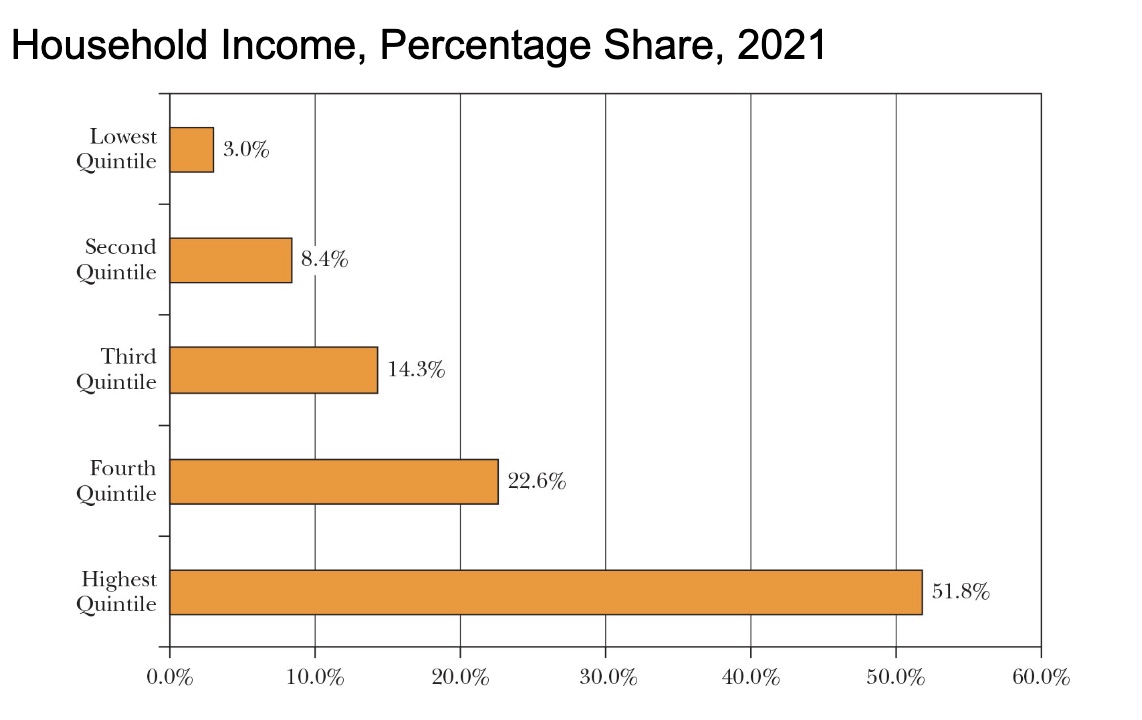
Incomes within and outside cities
differences between urban and suburban dwellers gives us an understanding of the greater financial resources available to many of those living beyond city limit
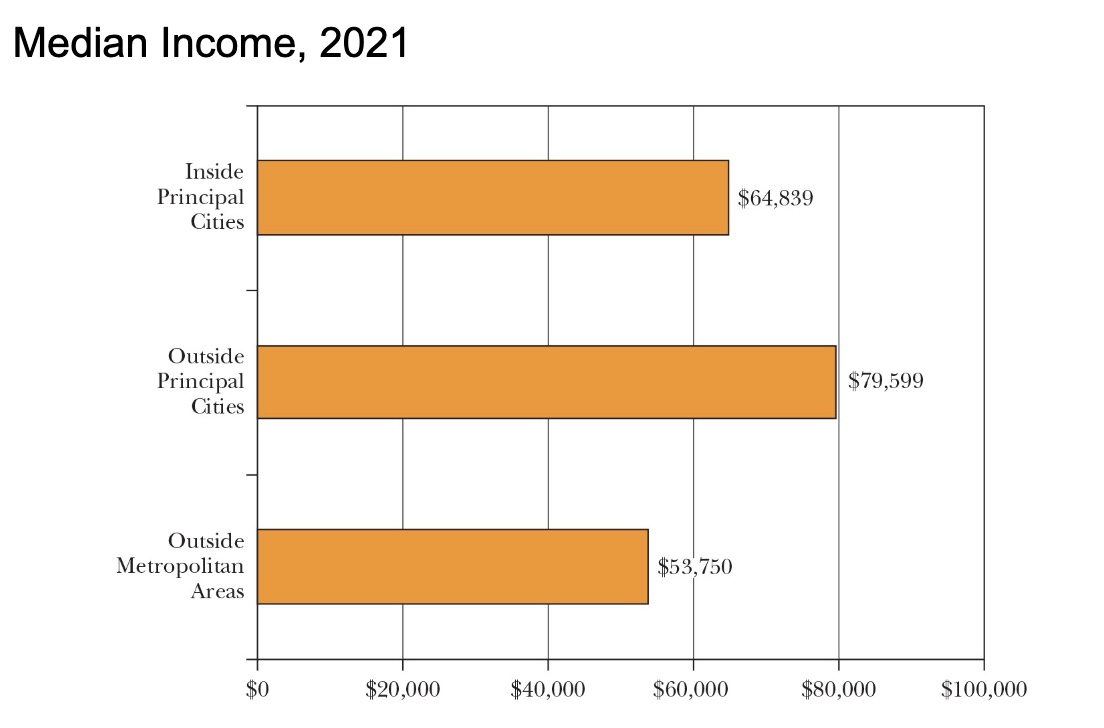
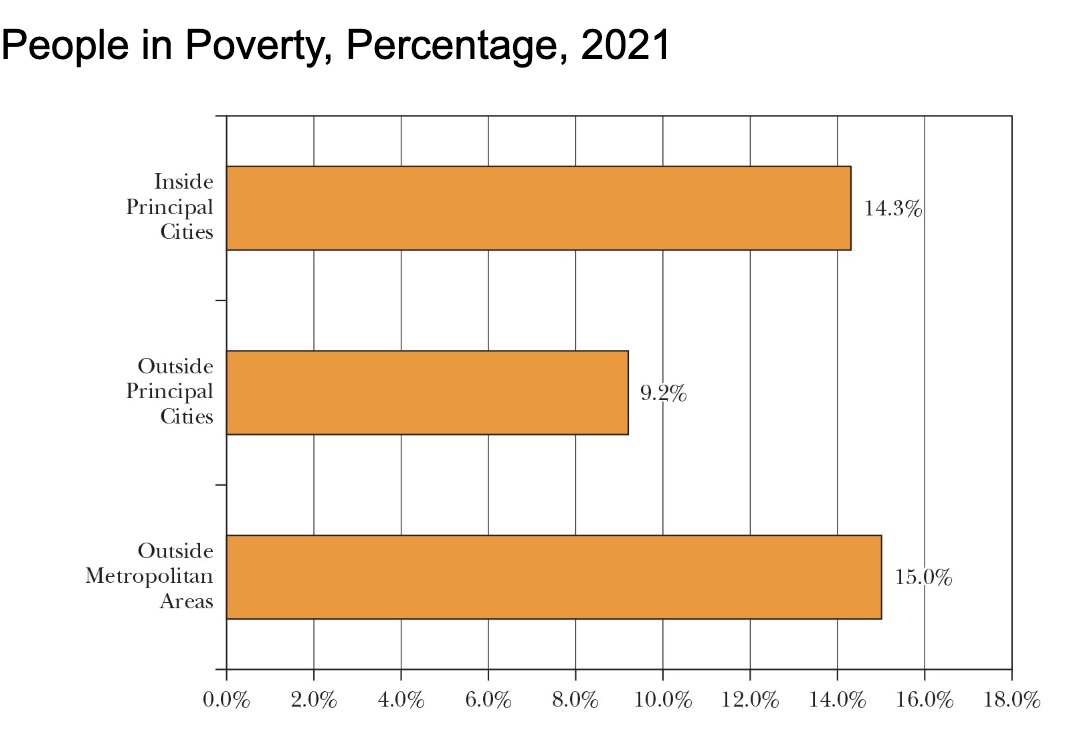
Poverty Nationwide
the poverty threshold for a US family of 4 (2021)= $27949
official poverty rate was 11.6%
In Canada, 8.1% was classified as being below income after taes in 2020
immigrants= huge portion
Urban Social Class Diversity
the essence of urban life is tremendous human variety
upper-class urban neighborhoods vs. upper east side
10065 is the most prestigious zip code in NYC
Middle-Class Urban Neighborhoods
mostly in suburbia
some city blocks evolve as middle-class neighborhoods through gentrification
growth of the service sector generated has brought certain people to the city:
yuppies and dinks
not all middle-class urban neighborhoods are recently evolved entities
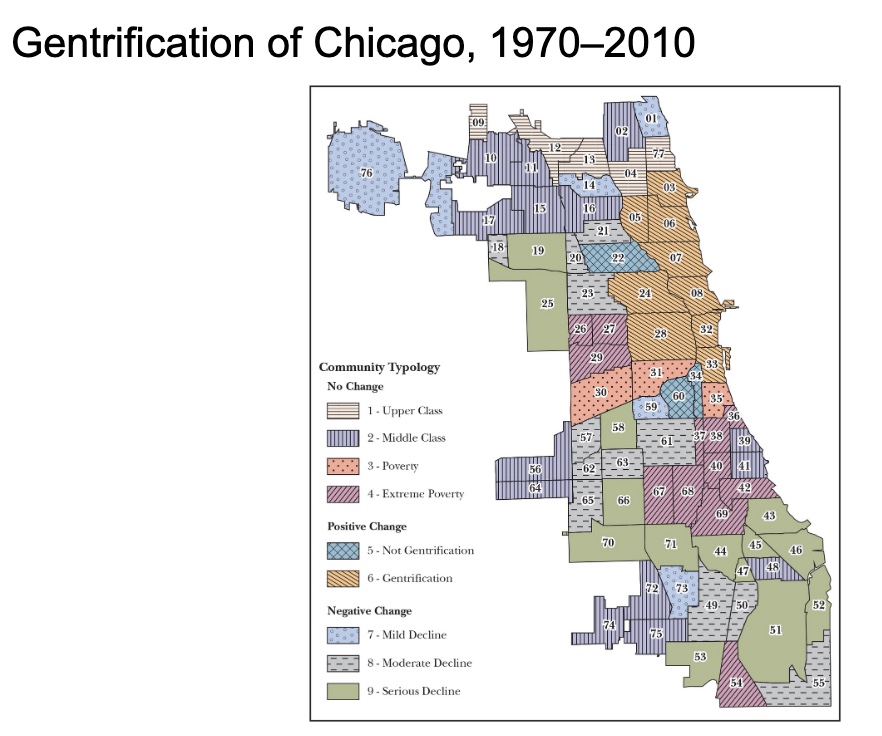
Chicago
some low-income neighborhoods in 1990 are now among the most desirable residential areas
the arrival of yuppies further spurred redevelopment
population demographics give strong evidence of a higher social class taking over the neighborhoods
Milwaukee
sherman park
dates back to 1890s
racially and culturally diverse
3 of its streets= historic districts
long-term residents, religious tolerance and integration
competition with suburban store
Working-Class Urban Neighborhoods
disappearing, distinctive by the ethnic and racial minority
many visual cues give distinctive sense of place and form a part of the community’s social life
gemeinschaft, urban villages
Newark’s Ironbound
multiethnic working-class area in the East War of Newark
once the industrial center of the city
mix of homes, stores, and industrial buildings, with vibrant commerical center
local economy is sound
Mixed-Income Urban Neighborhoods
may have been a result from intervention, such as public housing or planned gentrification
can remain stable in their income diversity
deteriorating as middle class moves out
the keys to QOL as household income levels and desire and ability of residents to remain there
Toronto
Low-Income Urban Neighborhoods
found in oldest districts
near the central business district= inner-city neighborhoods, ghettos, slums
trapped poor left behind in the inner city
Homelessness
2021, 582 500 ppl experience homelessness nightly
no stereotype gives a complete picture of people experiencing homelessness
families with children
Suruban Social Class Diversity
the suburbs no longer fit the white stereotype
minorities, working class, poverty, older adults
vary wide in terms of age, income, racial composition, length of residence
Income Suburbs
upper
before, resembled the well-todo
now, the old aristocratic families
older, white, highly educated
middle
life centers on the family and child-centered activities
fewer people are poor
racially mixed
working
some developed as a home for both factories and workers
some are more urbanized than others
some of the older suburbs are suffering from a loss of jobs
Suburban Cosmopolitan Centers
Princeton
academics, professionals, writers, etc
resemble the university areas, bohemian enclaves, ‘high-culture’
Diverse Suburbs
racially diverse, but some remain racially segregated
attracts black middle-class families
invasion-succession