Postpartum Complications and Management Strategies
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is the definition of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH)?
Clinically, any blood loss that has the potential to cause hemodynamic instability, with specific thresholds for vaginal (≥500 ml) and Caesarean (≥1000 ml) births.
What are the two types of postpartum hemorrhage based on timing?
Primary (within 24 hours) and secondary (more than 24 hours but less than 12 weeks post-birth).
What are some common causes of postpartum hemorrhage?
Uterine overdistension, anesthesia and analgesia, previous history of uterine atony, rapid labor, prolonged or induced labor, high parity, chorioamnionitis, uterine subinvolution, obesity, and magnesium sulfate administration.
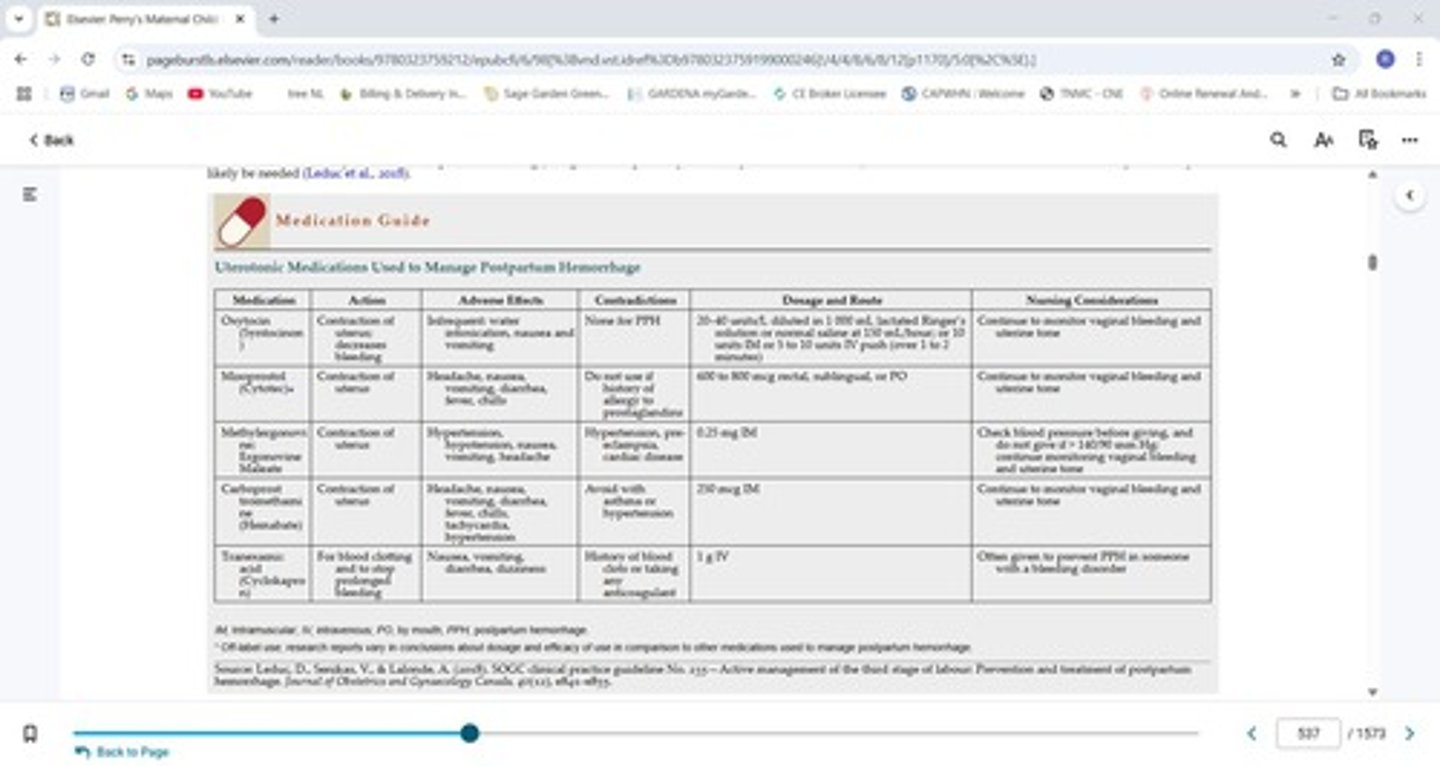
What is the primary treatment for uterine atony in postpartum hemorrhage?
Uterine massage, mechanical therapies (like Bakri Balloon), and uterotonic agents.
What are the types of trauma that can lead to postpartum hemorrhage?
Lacerations, hematomas, uterine inversion, uterine rupture, and manual removal of retained placenta.
What are the signs and symptoms of lacerations in postpartum hemorrhage?
Bleeding after the uterus is firm, often requiring suturing.
What are the common origins of hematomas in postpartum hemorrhage?
Vulvar, vaginal, and retroperitoneal.
What are the signs and symptoms of a hematoma?
Persistent vaginal or rectal pain and pressure, signs of shock.
What are the types of uterine inversion?
Complete, incomplete, prolapsed, and total.
What are the signs and symptoms of uterine inversion?
Sudden onset, hemorrhage, shock, pain, and the uterus not being palpable abdominally.
What is the treatment for uterine inversion?
Fluid resuscitation, repositioning of the uterus, tocolytic agents before repositioning, oxytocin after repositioning, prophylactic antibiotics, and monitoring for recurrence.
What are the complications associated with retained placental fragments?
Severe postpartum hemorrhage, infection, and potential need for hysterectomy.
What are the preexisting coagulopathies that can lead to postpartum hemorrhage?
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), von Willebrand's disease (vWD), and Hemophilia A.
What is the collaborative care approach for postpartum hemorrhage?
Early recognition, accurate assessment of blood loss, medical management, and nursing care including uterine massage and IV oxytocin administration.
What are the clinical manifestations of venous thromboembolic disorders postpartum?
Unilateral pain, calf tenderness, swelling, warmth, redness, and enlarged, hardened veins.
What is the incidence of venous thromboembolic disorders postpartum?
1 in 500.
What are the common infections that can occur postpartum?
Endometritis, wound infections, urinary tract infections, and mastitis.
What are the common causative organisms of postpartum infections?
Numerous streptococcal and anaerobic organisms.
What are the risk factors for postpartum infections?
History of previous infections, diabetes mellitus, alcohol and substance misuse, anemia, malnutrition, obesity, and pre-eclampsia.
What is mastitis and its common causative organism?
A breast infection commonly caused by S. aureus, with symptoms including inflammatory edema and tenderness.
What are the strongest risk factors for perinatal mood disorders (PMD)?
A history of psychiatric illness, prenatal symptoms of anxiety, and onset of depression during pregnancy or postpartum.
What are the potential complications of perinatal mood disorders?
Mother-infant attachment issues, depression in the partner, long-term emotional and behavioral issues in the child, and relationship problems.
What characterizes postpartum psychosis?
Depression, hallucinations, delusions, and thoughts of harming oneself or the infant, requiring psychiatric hospitalization.
What is the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) used for?
Screening for perinatal mood disorders.

What are the phases of grief after a loss?
Shock and numbness, searching and yearning, disorientation, and reorganization and resolution.
What nursing care is important for families experiencing loss?
Communicating and caring techniques, helping families acknowledge feelings, and providing sensitive care.
What is the emotional toll of maternal death on families and healthcare professionals?
Families may develop complicated bereavement, and healthcare professionals may experience significant emotional distress.