Topic 11: Standard costing and variance analysis
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
standard costing
enables derivations from budget to be calculated and analysed
typically applied in cost centres
standard costs
predetermined costs that should be incurred under efficient operating conditions
CPU
standard v budget
standard = CPU while budget = total
how dow standard costing systems work?
input required to produce a unit of output can be specified
fast food restaurants
banks - loan applications
must be a repetitive activity to set standard
can have a verity of products as long as they are similar operations
Product standard costs
found by combining the standard costs from the operations necessary to make the product
price standard
the amount that should be paid for each unit of input
quantity standard
the amount of input that should be used per unit of output
who acts on the variance of standard costing
•The accountant identifies variances, and the responsible managers investigate the reasons for the variance.
This should result in appropriate remedial action being taken, or perhaps the standard should be changed
what are the two approaches of cost standards
historical records
widely used
doesnt focus on finding best combination of resources
engineering studies
detailed study of each operation with careful specs of material, labour, and equipment
direct material standards
derived from input quality necessary
establish the most suitable materials for the operation
optimal quality should be used, taking into account unavoidable wastage/loss
material quantity standards
recorded on a bill of materials
shows required quantity of materials for reach operation to complete product
Standard material product cost
multiplying standard quantities by appropriate standard prices
standard prices
obtained from purchasing department
must select suppliers who can provide P & Q
direct labour standards
standard labour time
eliminate unnecessary elements and determine most efficient method
smite # of hours to complete
unavoidable delays are included - machine breakdown and routine patience
standard labour cost
contractual wage rates
why standard costing?
decision making purposes
provides prediction of future costs
preferrable to estimates based on adjusted past costs which may incorporate inefficiencies
challenging target
motivates individuals
Research evidence suggests that the existence of a defined quantitative goal motivates higher levels of performance.
setting budgets
evaluating managerial performance
control device
hihglihts non conforming activities that need corrective action
profit measurement and inventory valuation purposes
variance
the difference between standard and actual cost
material price variance
adverse
failure to get best source of supply
change in market conditions
favourable
inferior quality goods,

material usage variance
Did we use more or less materials than the standard?
controllable by manager
carless handling
purchase of inferior quality
pilferage
changes in quality control
changes in methods of productions
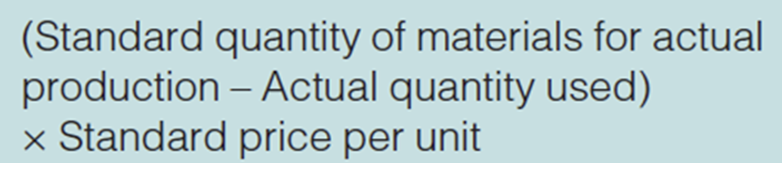
total material variance

wage rate variance
Did we use more or less materials than the standard?
least subject to control by management
changes in wage rate standards

labour efficiency variance
Were our employees more or less efficient than the standard?
controllable by manager
inferior quality materials
failure to maintain machinery
introduction of new equipment/tools/processes

total labour variance

variable overhead expenditure variance
•Did we pay more or less for our variable overheads than the standard?

variable overhead efficiency variance
•The difference between actual and budgeted hours worked, applied to the standard variable overhead rate per hour.

total variable overhead variance
changes due to prices of individual items changing
can be affected by efficiency
not very informative
need comparison of actual expenditure against each line time

fixed overhead
Did we pay more or less for our fixed overheads compared to the budget?
budgeted - actual overheads
sales margin price variance
Did we sell our products for more or less than the standard?

sales margin volume variance
Did we sell our products for more or less than the standard?

total sales margin variance
•It may not be very meaningful to analyse the total sales margin variance into price and volume components, since changes in selling prices are likely to affect sales volume.
•A favourable price variance will tend to be associated with an adverse volume variance, and vice versa.
•A further problem: the sales variances may arise from external factors not controllable by management. E.g. changes in selling prices may be a reaction to changes in selling prices of competitors.
•Alternatively, a reduction in both selling price and sales volume may be the result of an economic recession.
•For control and performance appraisal it may be preferable to compare actual market share with target market share for each product.
•
