Intro to biochem MRTs
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
gg
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
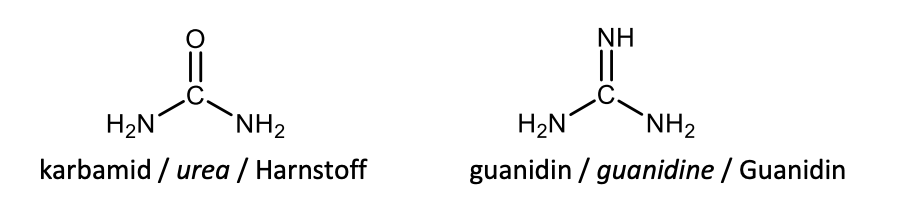
Draw with structures urea and guanidine.
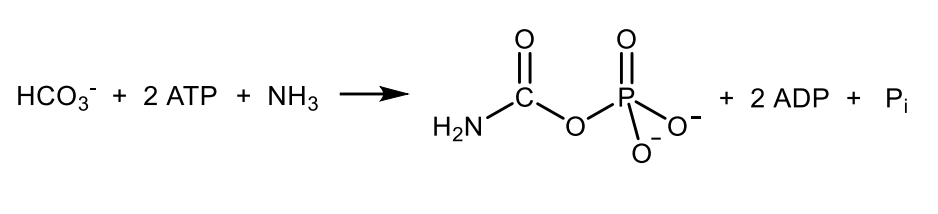
Write with structure the reaction catalysed by carbamoylphosphate synthetase I.
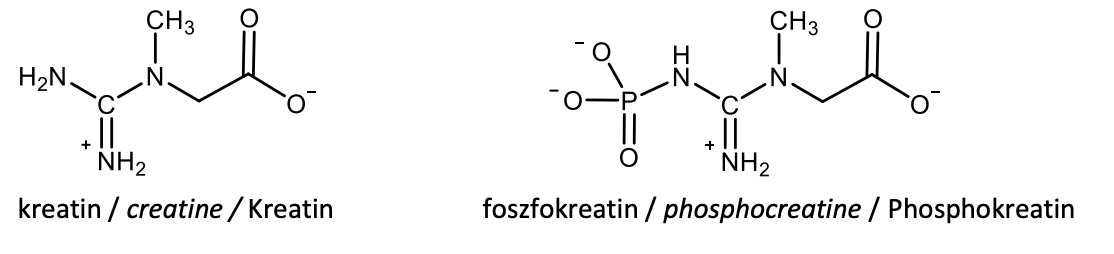
Draw with structural formulas creatine and creatine phosphate (phosphocreatine).
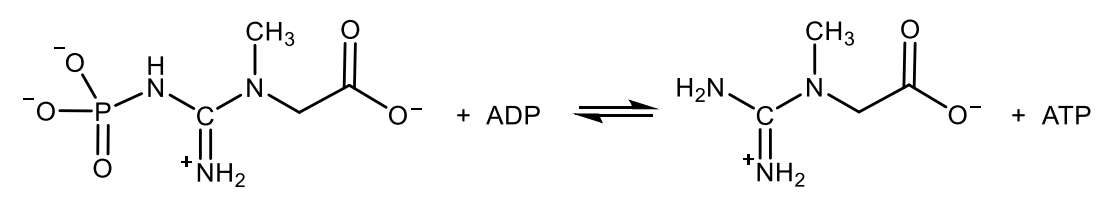
Write with structures the reaction catalysed by creatin kinase
Draw the structural formula of creatinine and give its most important medical relevance.

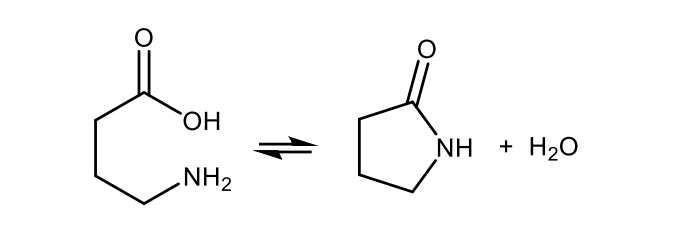
Write with structures the equation of a lactam formation.
Draw the structural formulas of pyrrole and imidazole.

Draw the structural formulas of pyridine and pyrimidine, characterize their acid-base properties.

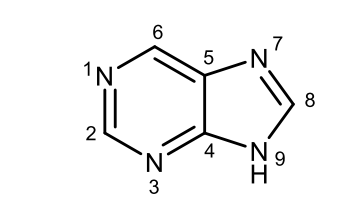
Give the structural formula of the purine and number the atoms in the ring.
Draw with structural formulas nicotinamide and indole.

Draw with structural formula uric acid and give its most relevant physiological importance.

Define the term: alkaloid.
Alkaloids are a group of naturally occurring compounds that contain mostly basic nitrogen atom and possess strong physiological activities.
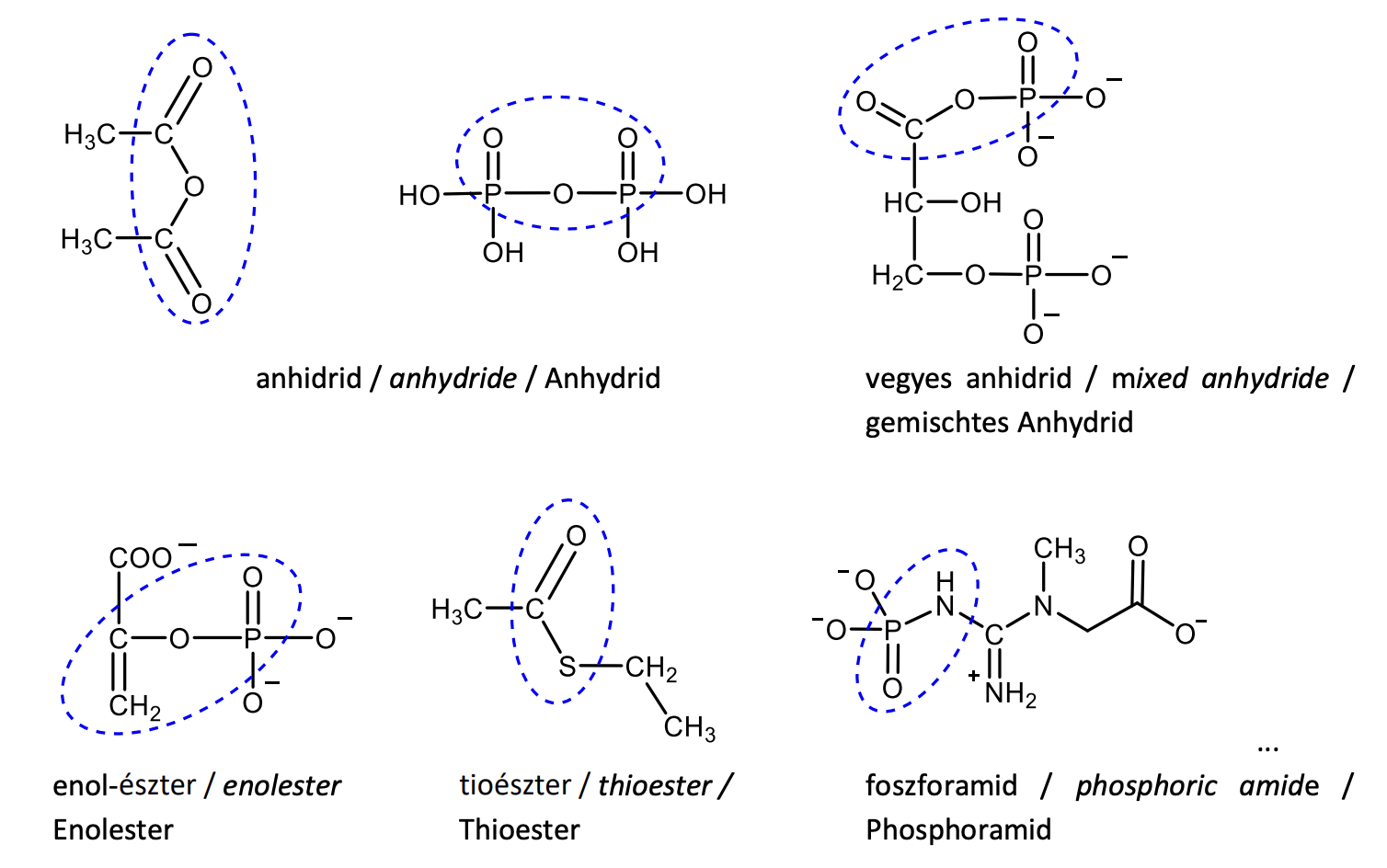
Draw the structural formula of three compounds containing a high-energy bond, indicate and name the type of the high-energy bond.
Give the full names and biological roles of the following compounds: NAD+ , FAD, CoA-SH, ATP.
NAD+ : nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, oxidizing agent, coenzyme
FAD: flavin adenine dinucleotide, oxidizing agent, prostetic group
CoA-SH: coenzyme-A, transfer of acyl groups
ATP: adenosine triphosphate: phosphorylating agent (a phosphoryl group donor), energy storage
Draw the structural formulas of cytosine, and thymine.

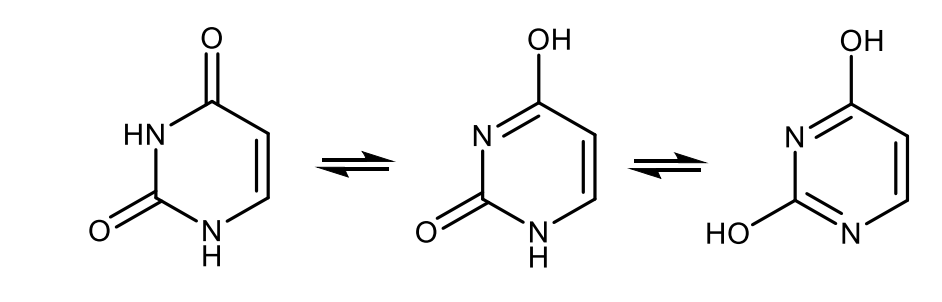
Draw with structures the tautomerisation of uracil.
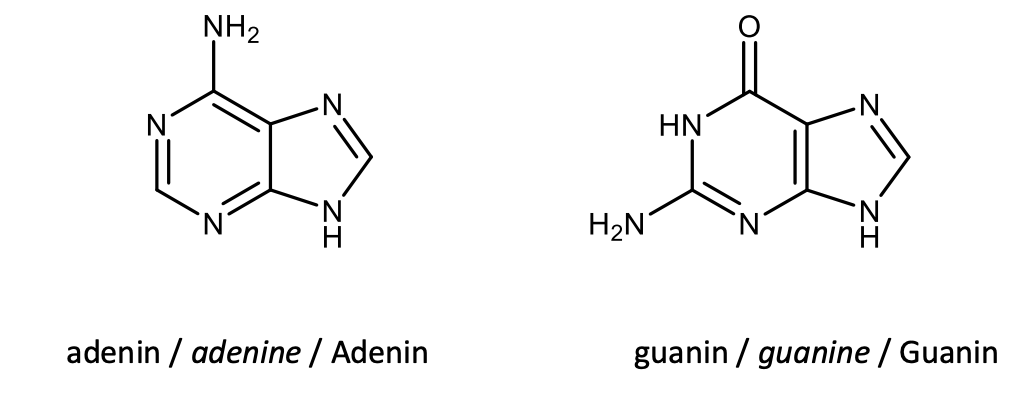
Draw the structural formulas of adenine and guanine.
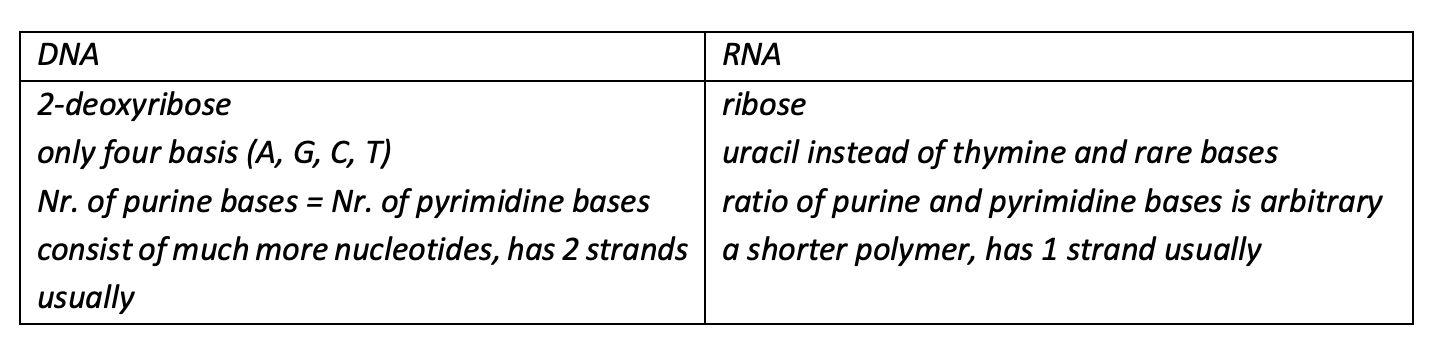
List of differences in the structures of DNA and RNA (min. 3).
Draw the general structural formulas of the α-amino acids in non-ionic and in zwitterionic (dipolar ion) forms.

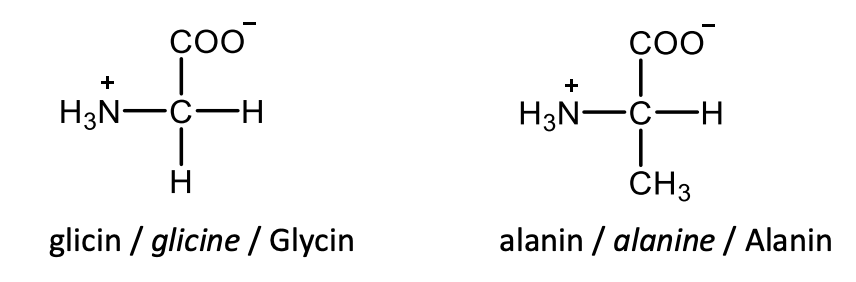
Draw the structural formulas of glycine and L-alanine.
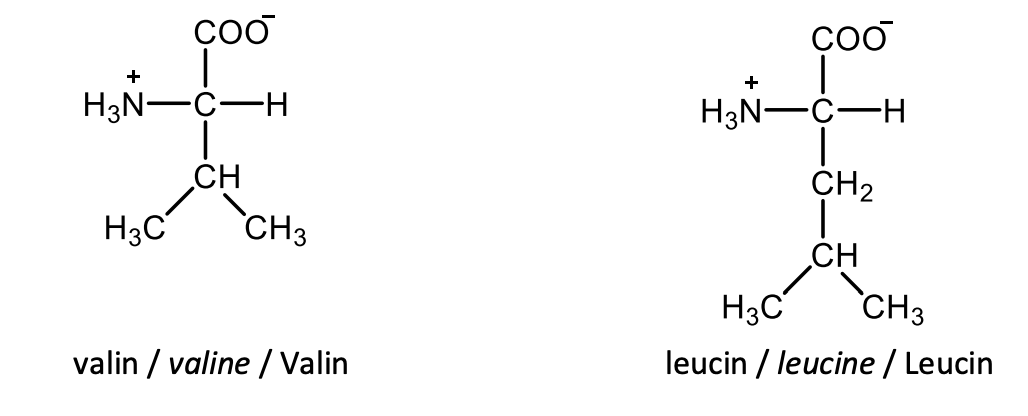
Draw the structural formulas of L-valine and L-leucine.
Draw the structural formulas of L-tyrosine and L-phenylalanine.
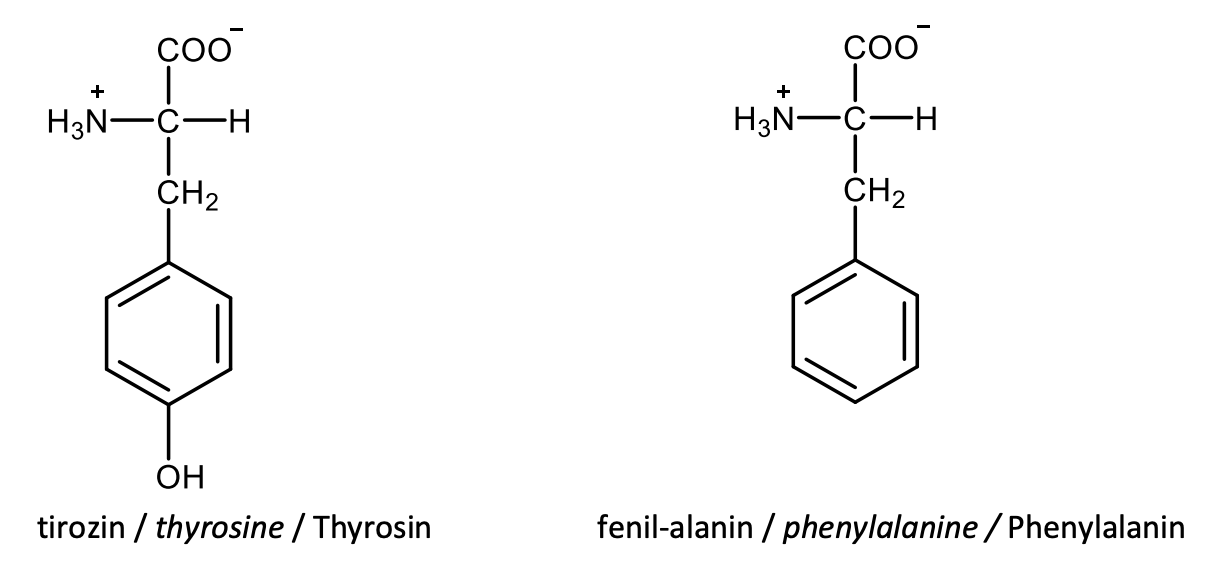
Draw the structural formulas of L-methionine and L-cysteine.
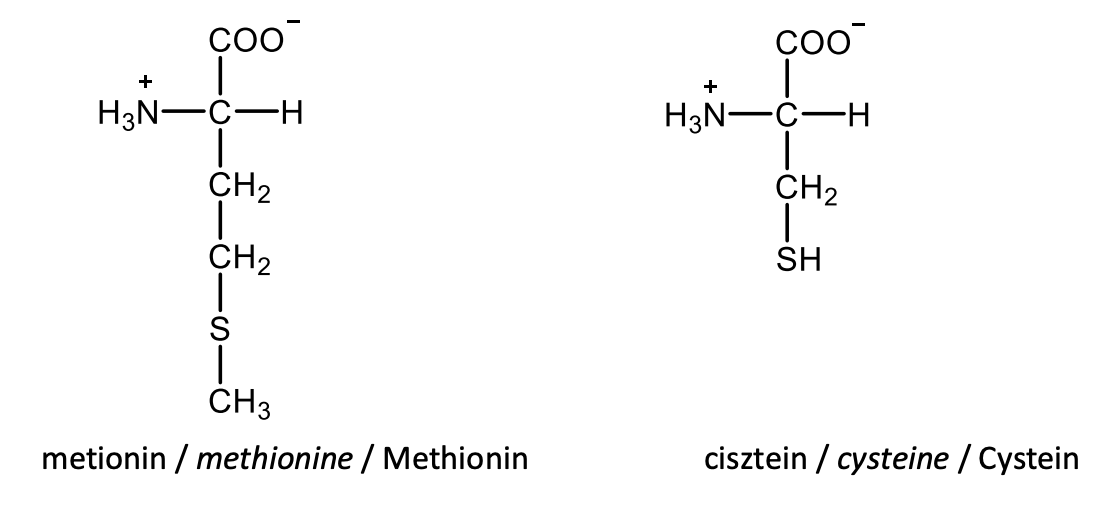
Draw the structural formulas of L-serine and L-threonine.
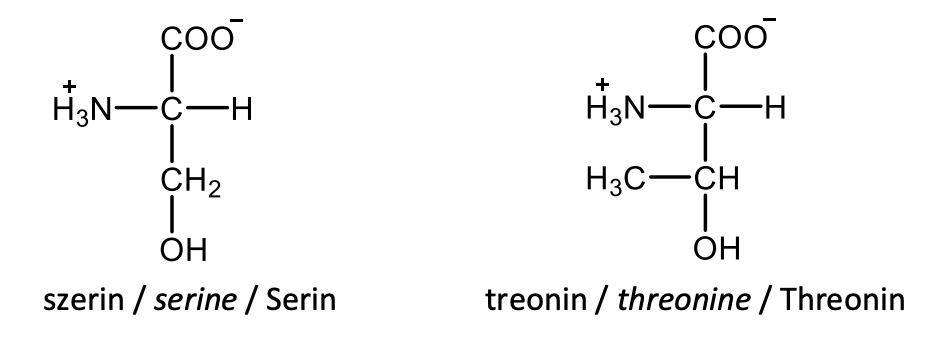
Draw the structural formulas of L-aspartate and L-glutamate.
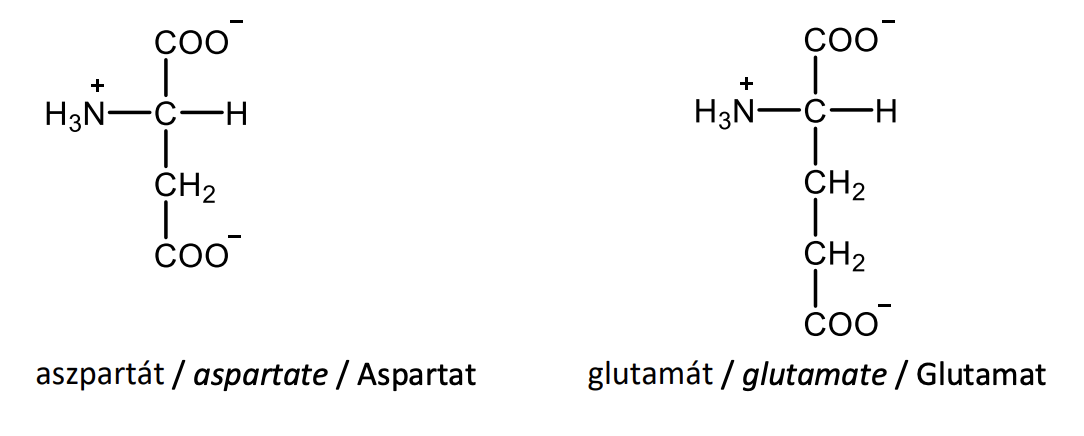
Draw the structural formulas of L-asparagine and L-glutamine.
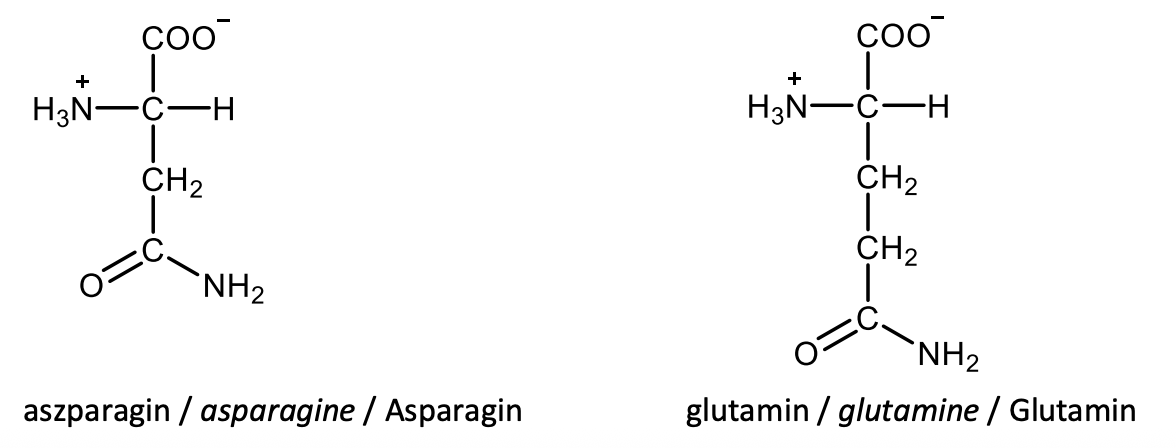
Draw the structural formulas of L-lysine and L-arginine.
Draw the structural formulas of L-tryptophane and L-histidine.

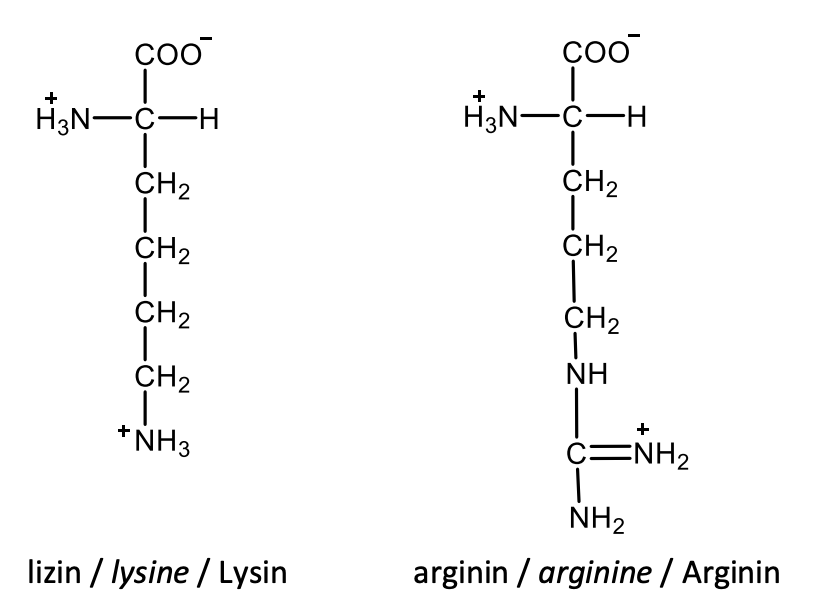
Draw the structural formulas of L-proline and L-isoleucine.
Define the term isoelectric point of amino acids.
The pH at which the amino acid has no overall charge is called isoelectric pH or isoelectric point (pI).
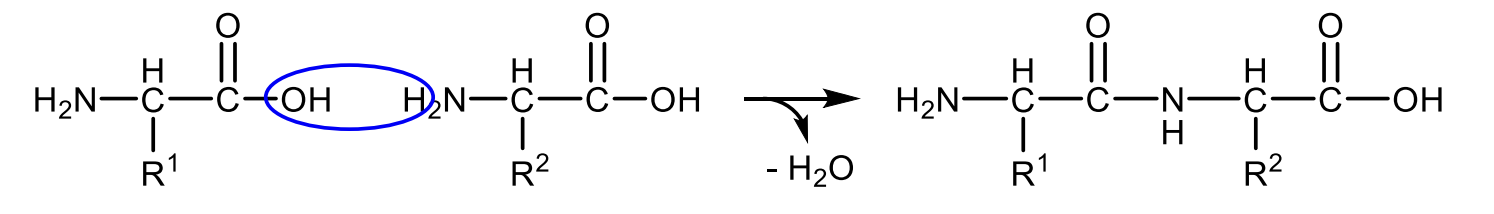
Write with general structural formulas the equation for peptide-bond formation.
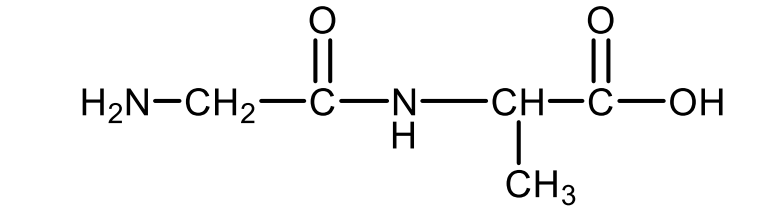
Draw the structural formula of the dipeptide alanyl glycine.
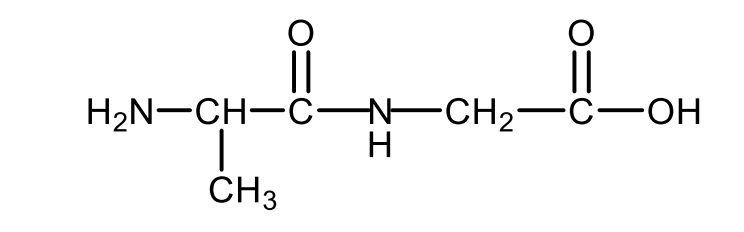
Draw the structural formula of the dipeptide glycyl alanine.
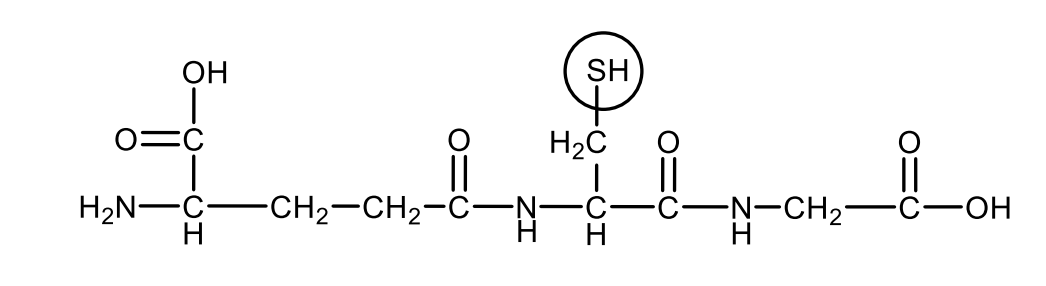
Draw the structural formula of the reduced glutathione. Circle the part of the molecule responsible for the antioxidant property.
Define the secondary structure of proteins.
The secondary structure means the relative arrangement of the nearby amino acids in the polymer chain, e.g.: α-helix, β-sheet, β-turn.
List the most important types of interactions responsible for maintaining the tertiary structure of proteins!
Hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bond, ionic bond, disulphide bridge.
Write the CO2 binding reaction of hemoglobin. Give the structure of the involved functional group of hemoglobin.

Write the carbonic anhydrase reaction.
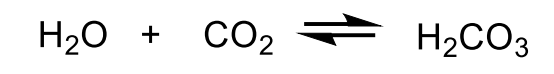
Define the concept of a heterotropic modulator and give an example.
Heterotropic modulation means that a molecule other than the ligand acts as an allosteric modulator. This effect can be positive or negative. For example, the negative heretotropic modulator of hemoglobin is 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate, which reduces the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.
Define the concept cooperaticvity and give an example.
It is the characteristic of an enzyme or other protein in which the binding of the first molecule of a ligand changes the affinity for the second molecule. In positive cooperativity, the affinity for the second ligand molecule increases, in negative cooperativity it decreases. e.g. hemoglobin and oxigen, positive cooperation.
Give the model of enzyme function according to Michaelis and Menten with reaction equations. Indicate the rate determining step.
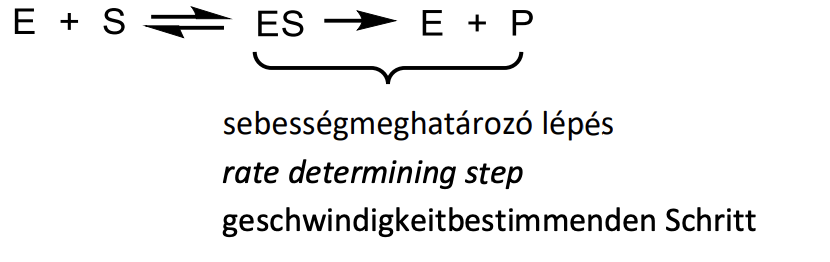
Give the Michaelis-Menten equation with the explanation of the denotations.

Give the definition and two most frequently used units of enzymatic activity.
The activity of an enzyme equals to the amount of substrate transformed by the enzyme within a unit of time. Units: Unit (U): μmol/min; katal: mol/s
Define the KM (Michaelis-Menten) constant. Which property of the enzyme is characterized by this value?
KM is a substrate concentration (mol/dm3 ), at which the catalysed reaction occurs with the half of its maximal rate (Vmax). It measures the affinity of the catalytic protein towards the substrate.
What does the allosteric modulation of enzyme activity mean?
A non-covalent interaction between the enzyme and the effector molecule at a specific regulatory site (allosteric binding site), which leads to a conformational change of the enzyme and thus changes the enzyme activity.
What does the covalent modulation of enzyme activity mean?
A reversible, covalent, post-translational modification of an enzyme that results in a change in enzyme activity.
Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by hexokinase.
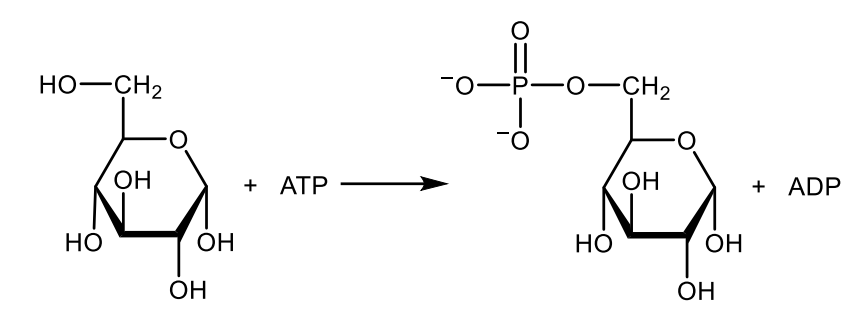
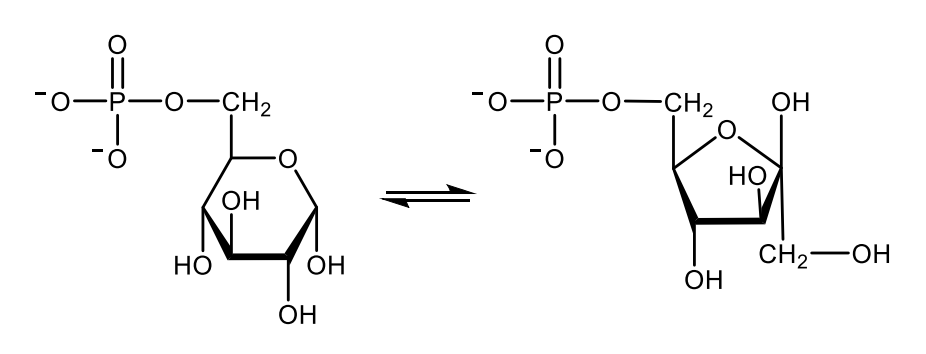
Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by phosphohexose isomerase.
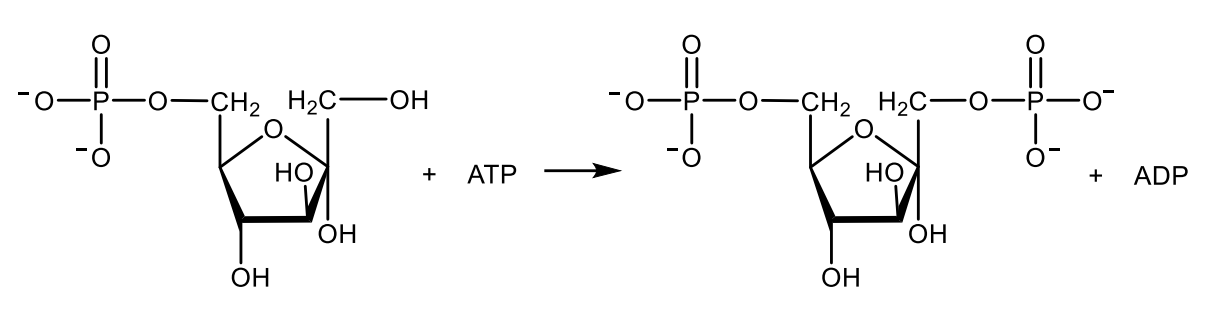
Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by phosphofructokinase-1.
Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by aldolase.
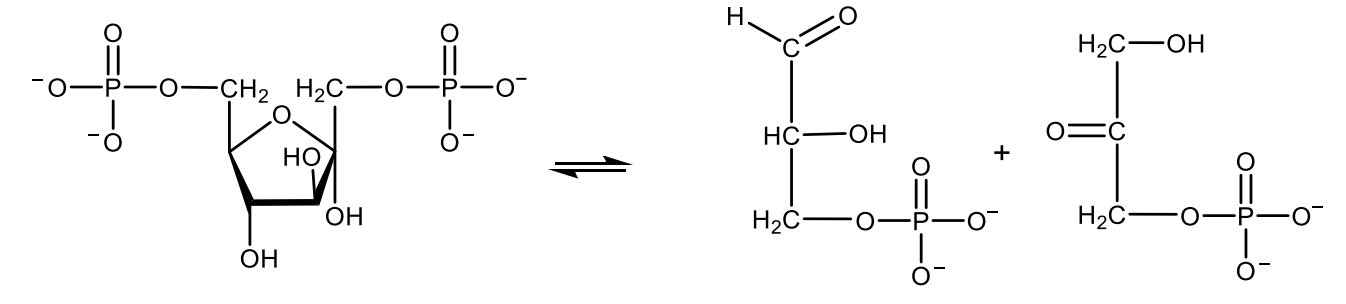
Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
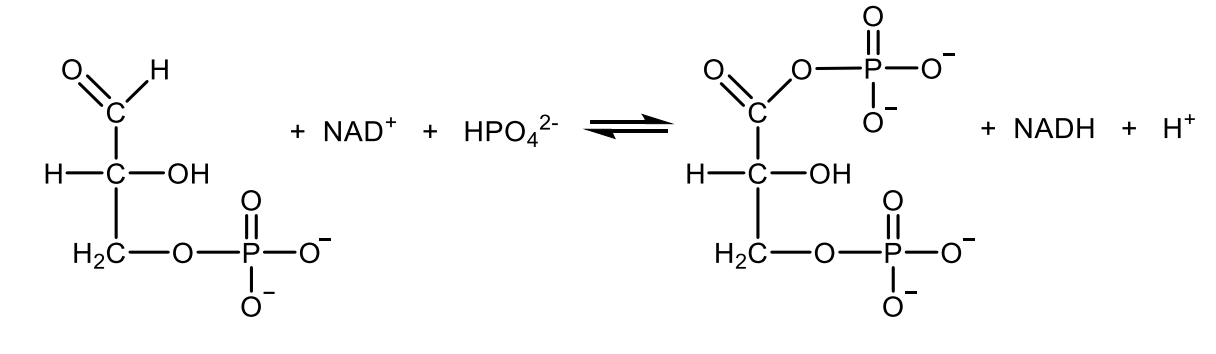
Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by phosphoglycerate mutase.
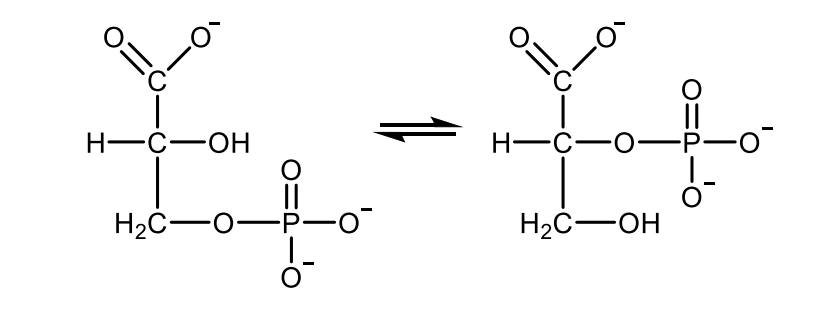
Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase.
Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by citrate synthase.
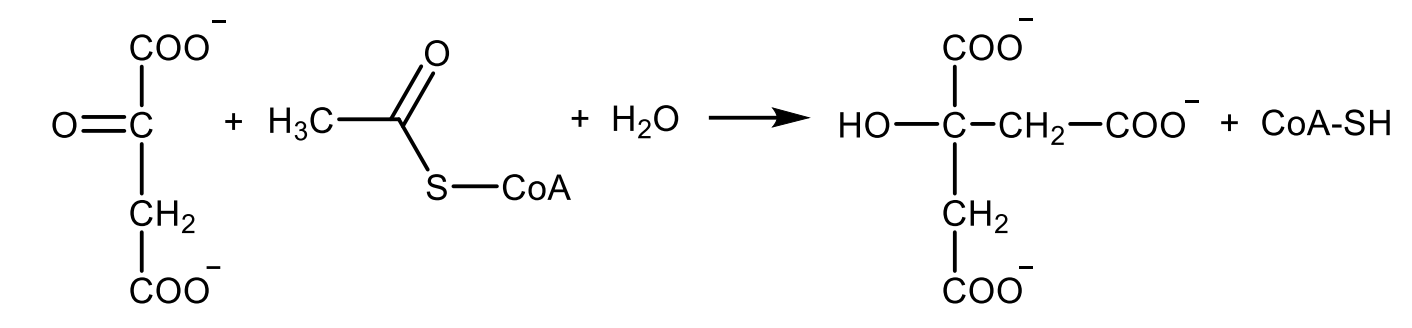
Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by succinyl CoA synthetase (a.k.a. succinate thiokinase).
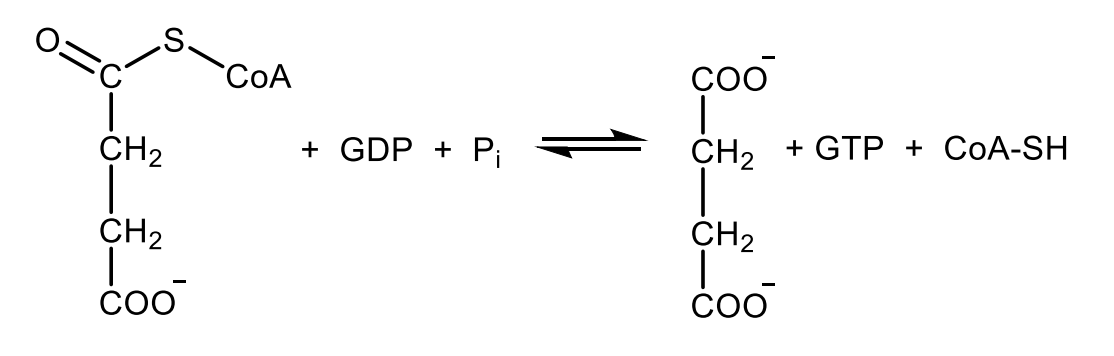
Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase.
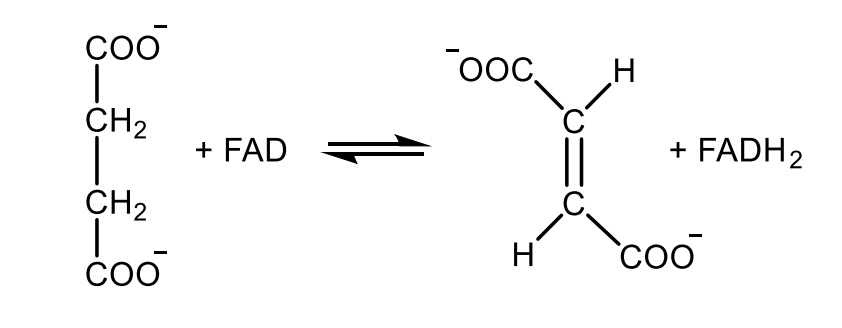
Draw the structural formula of an aldotriose and a ketotriose. Give also their names
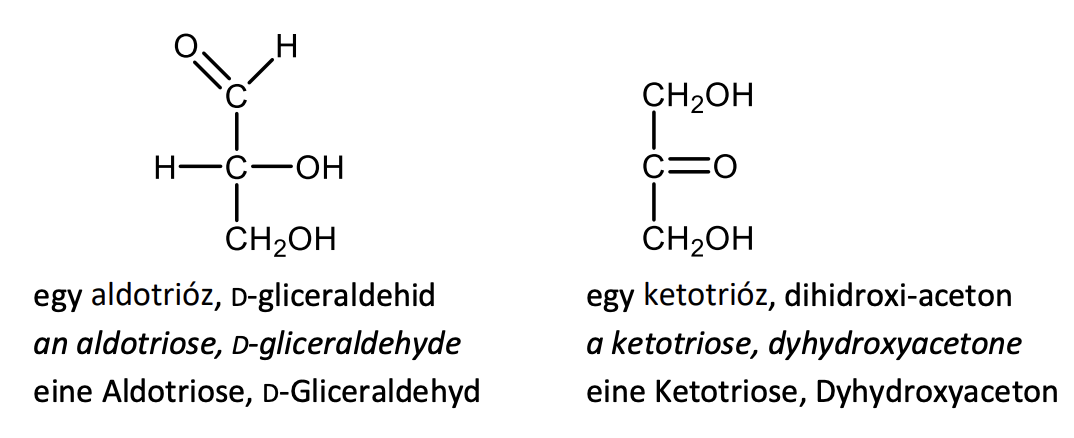
Draw the Fischer-projection of the open-chain structure of D-glucose with the indication of the carbon atom referring to the D configuration.
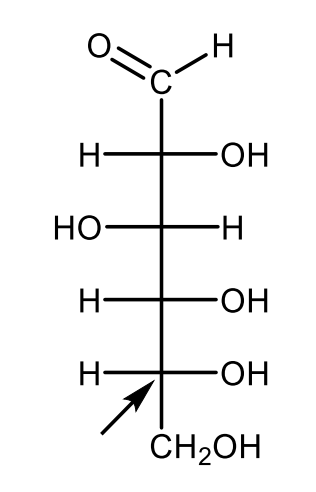
Define the term of epimers.
Epimers are diastereomers which have different configuration around only one carbon atom.
Draw the projective formulas of open-chain and a furanose ring structure of D-fructose.
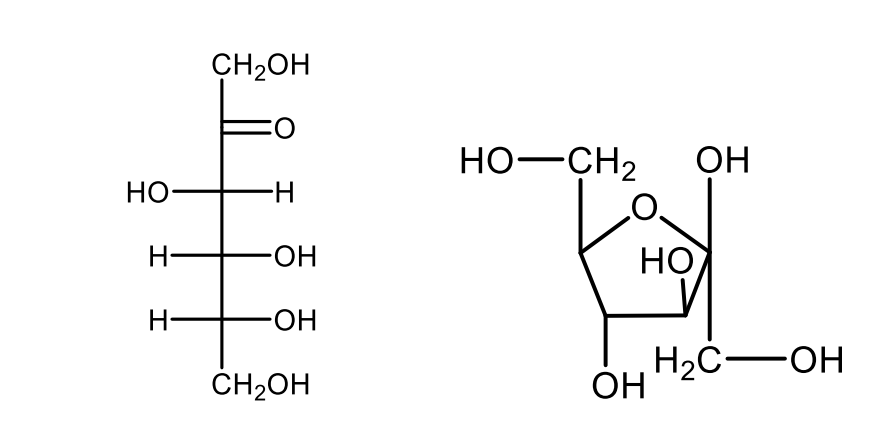
Draw the projective formulas of open-chain and a furanose ring structure of D-ribose.
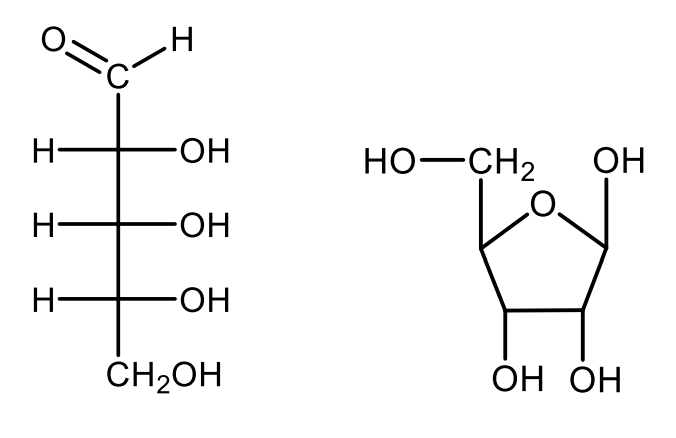
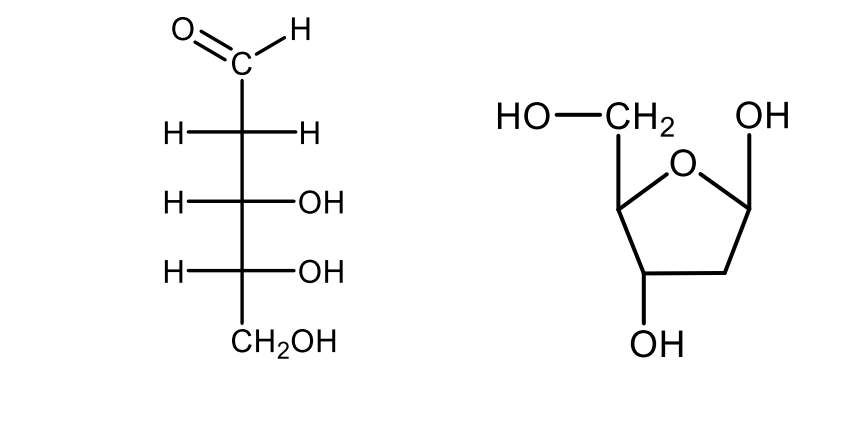
Draw the projective formulas of open-chain and a furanose ring structure of 2-deoxy-D-ribose.
Draw the Haworth's perspective formulas of β-D-glucopyranose and α-D-glucopyranose with the indication of the glycosidic hydroxyl groups
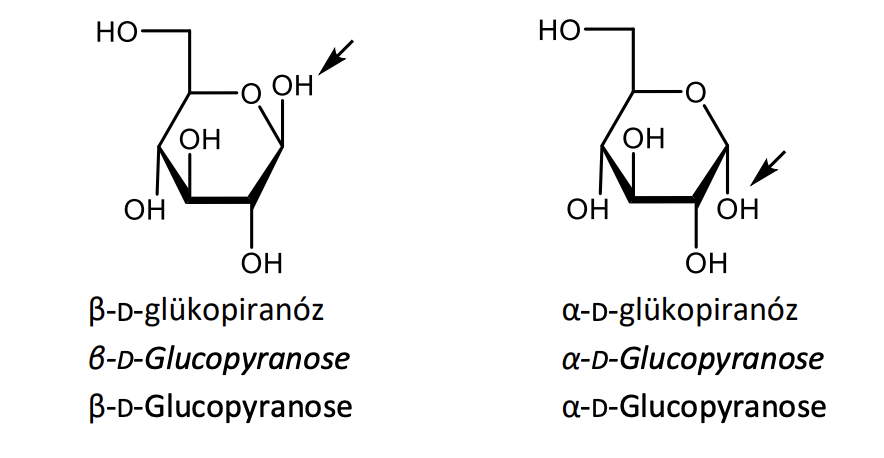
Write with projective formulas the equilibrium of the mutarotation of glucose.
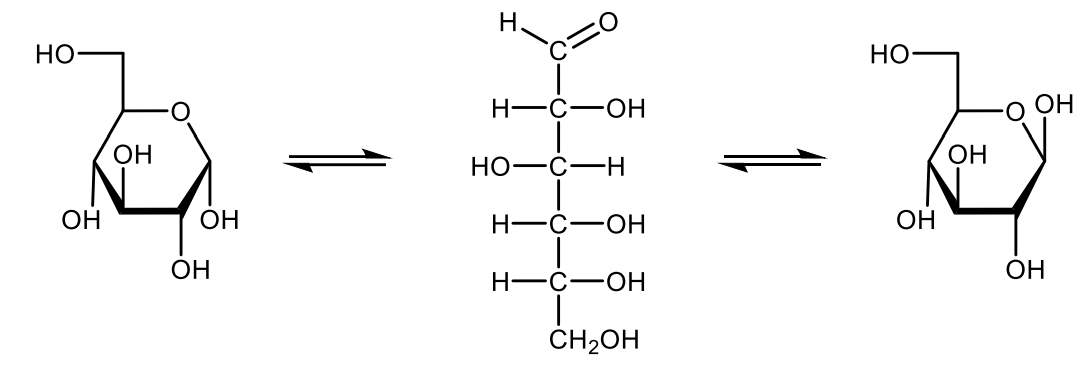
Draw with projective formulas the oxidation of D-glucose under mild and drastic conditions and name the products
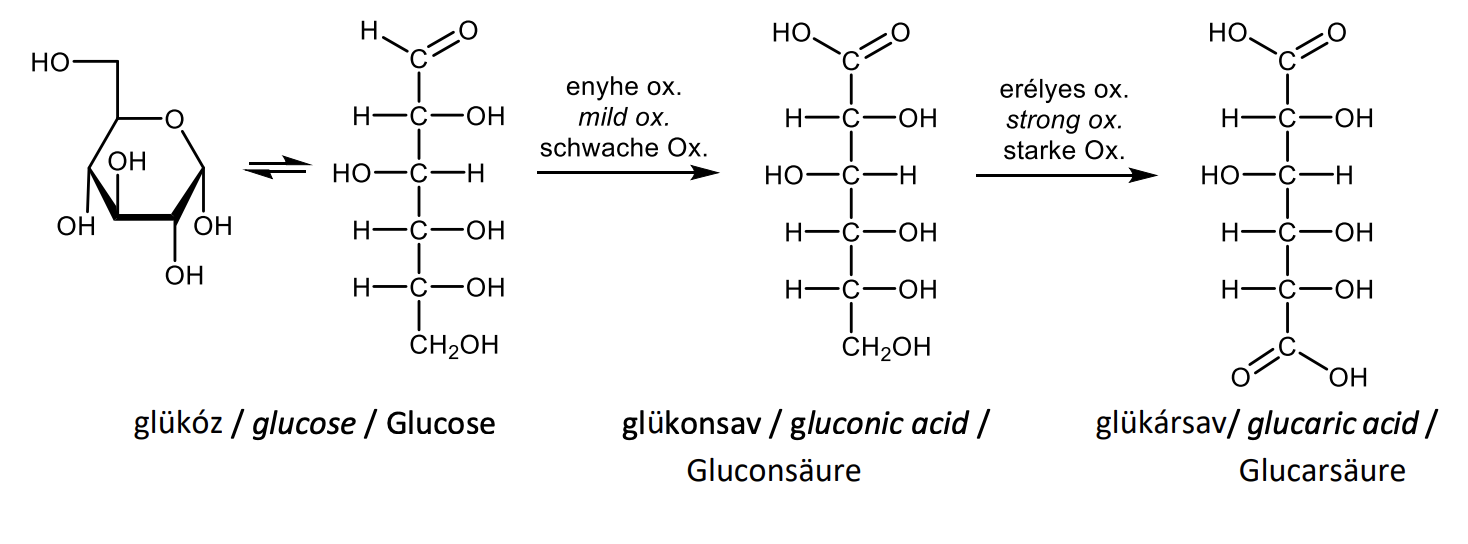
Draw with structural formulas the formation of an O-glycoside.
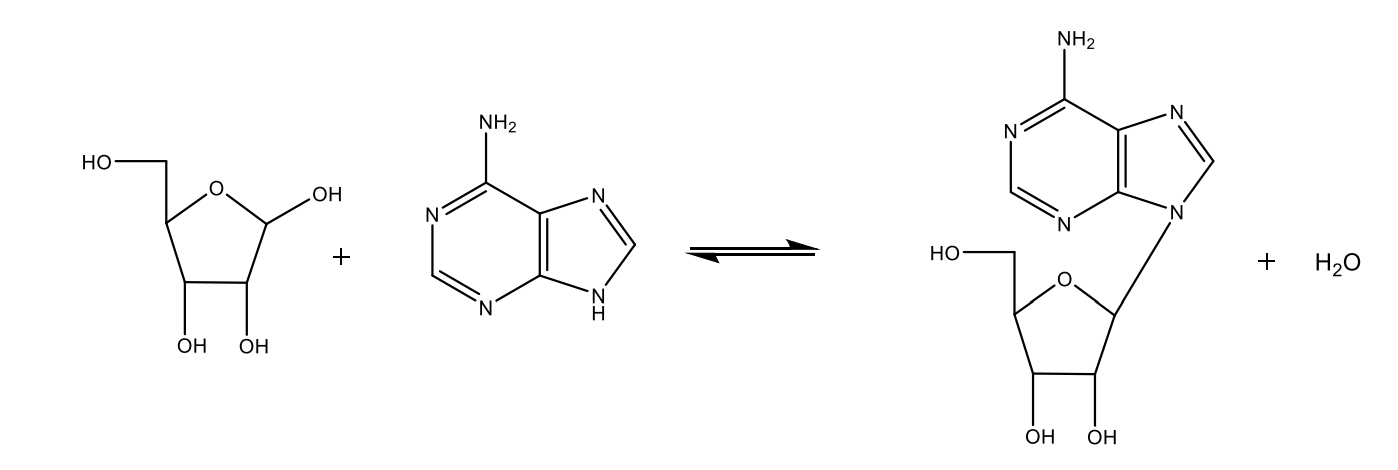
Draw with structural formulas the formation of an N-glycoside.
Draw the structural formula of glucuronic acid and give its most important physiological role.

Give the definition of sialic acids (without formulas) and their biological role.
Monosaccharides, acetylated derivatives of neuraminic acid, they are negatively charged at physiological pH. Common components of receptors and other oligosaccharides involved in recognition processes.
Describe the build-up and structural features of glycogen (without formulas).
Branched-chain polysaccharide, D-glucose units in (α1→4) glycosidic bonds, with (α1→6) branchpoints pe r8-12 glucose units.
Describe the build-up and structural features of glycosaminoglycans (without formulas), and their biological role.
Non-branched heteropolysaccharides with negative charges, consisting of repeating disaccharide units. They form a highly hydrated, gel-like structure. Components of the extracellular matrix.
Schematically describe the built-up of the bacterial cell wall (no formulas).
Non-branched heteropolysaccharide strands of aminosugars are linked by peptide bridges (peptidoglycan network).

List the types of saponifiable lipids.
Waxes, triacylglycerols, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids.
List the types of unsaponifiable lipids.
Terpenes, steroids, eicosanoids
Give the general formula and biological role of triacylglycerols (triglycerides).

Draw the general formula of phosphatidic acid.
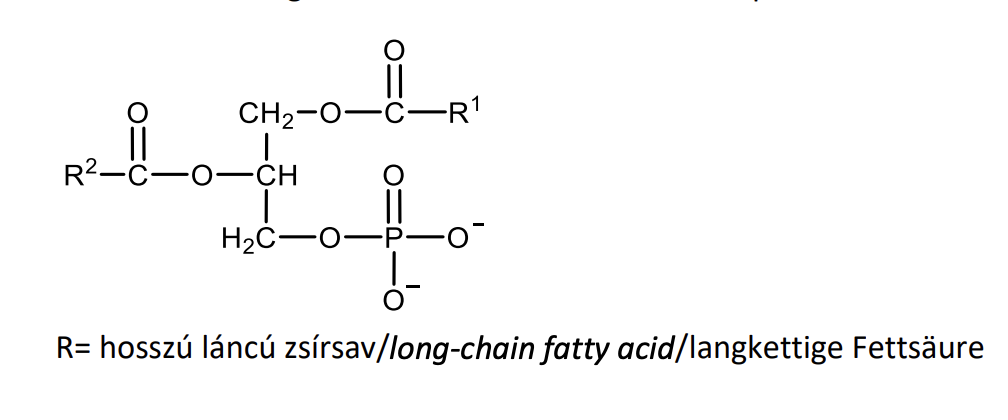
Give the general structural features and biological role of phosphoglycerides.
Esters of glycerol with long-chain fatty acids and phosphoric acid, to which additional hydrophilic parts are linked by an ester bond. They have an amphipathic structure and are membrane constituents.
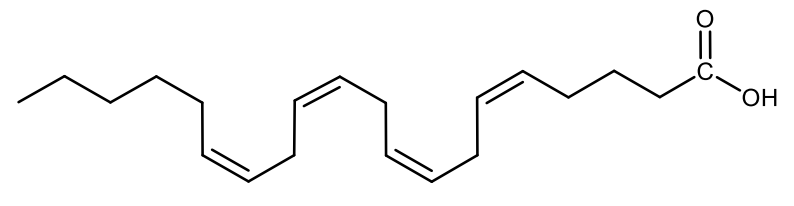
Draw the structural formula of arachidonic acid.
List the four main groups of steroids.
Sterols, steroid hormones, bile acids, steroid alkaloids.
Draw the structural formula of cholesterol and give the numbering of the atoms of the sterane skeleton.

Define the general structural features and biological role of prostaglandines.
20-carbon long carboxylic acids with a substituted cyclopentane ring. Paracrine hormones.
Write with names the schematic biosynthesis of prostaglandins and thromboxanes and name the key enzyme.
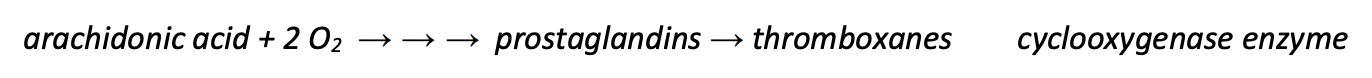
Write with names the schematic biosynthesis of leukotrienes and name the key enzyme.

Characterize the structure and physiological roles of retinoids.
Hydrophobic (fat soluble) diterpenoids. Retinol (alcohol) = Vitamin A, retinal (aldehyde) is involved in light perception, retinoic acid is a hormone.
Describe the structure of the membranes and name their main components.
A phospholipid bilayer with asymmetrical composition, cholesterol, proteins.
List the characteristics of the channels.
- specific
- no conformational change
- not saturable
- the speed reaches its unhindered diffusion
- movement takes place along an electrochemical gradient
List the characteristics of the transporters.
- specific
- kinetics typical for enzymes
- conformational change
- saturable
Classify the transport processes.
passive transports:
- simple diffusion
- facilitated diffusion
active transports:
-primary active transport
- secondary active transport
List the groups of ATPases.
- P-type ATPases
- F-type ATPases
- V-type ATPases
- ABC transporters
Briefly describe the central dogma, by drawing and naming possible ways of information flow.
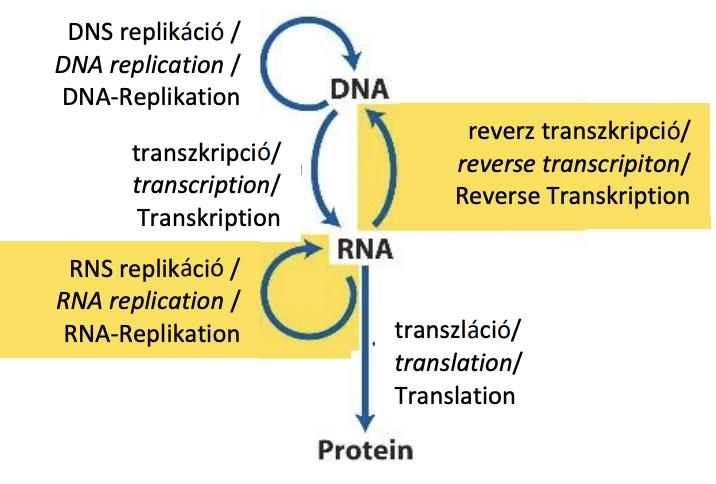
List the characteristics of DNA replication.
Semi-conservative, bidirectional, semi-discontinuous, template and primer dependent
Define what proofreading in replication means.
Recognition and cleavage of the incorrectly incorporated base by 3'-5 'exonuclear activity before proceeding with the polymerization.
Define what processivity means.
The average number of nucleotides added before the DNA-polymerase dissociates.
List the types of DNA repairs.
Mismatch repair, Base-excision repair, Nucleotide-excision repair, Direct repair
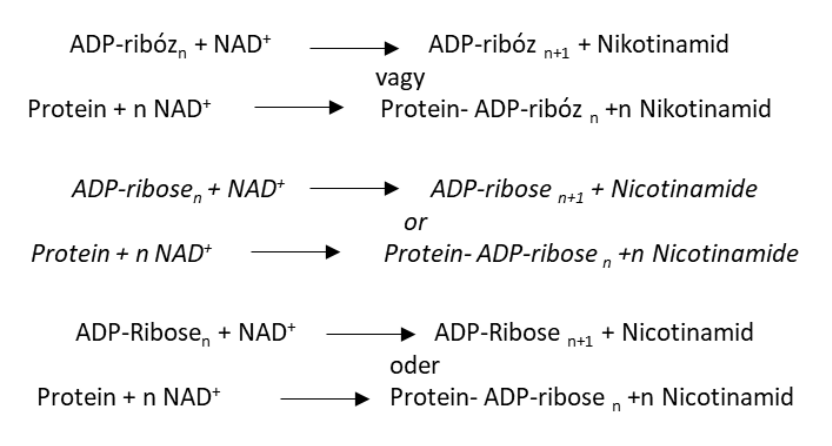
Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase PARP.
List the processes involved in RNA maturation.
- CAP synthesis
- Poly (A) tail synthesis
- Splicing
- Editing
Define the concept of ribozyme, give an example.
Ribonucleic acid molecules with catalytic activity e.g. peptidyl transferase in large ribosomal subunit.
List the characteristics of the genetic code.
- degenerated
- does not overlap
- conserved
- universal
Define, what does the wobble hypothesis mean?
The first two bases of a codon are always strongly bound to the anticodon. "Wobble" is the possibility of non-complementary base pairing between the base at the 3 'end of the codon and the base at the 5' end of the anticodon, providing optimization between the accuracy and speed of the process.
Write with names the equation for aminoacid activation.
