Social perception and attribution
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
born to attend faces
Evolved predisposition to respond selectively to faces ➢Innate and universal
Attentional biases to faces provide the foundation for social and cognitive development

social perception
We form impressions of what other people are like based on their perceived characteristics
Zero acquaintance: people we have never met (Kenny, 1994)
Thin-slices of behavior: based on
limited information within a brief period of time
Judgements based on brief exposure to the teacher’s behaviour in the classroom predicted students’ end of semester evaluations
Primary function of social perception
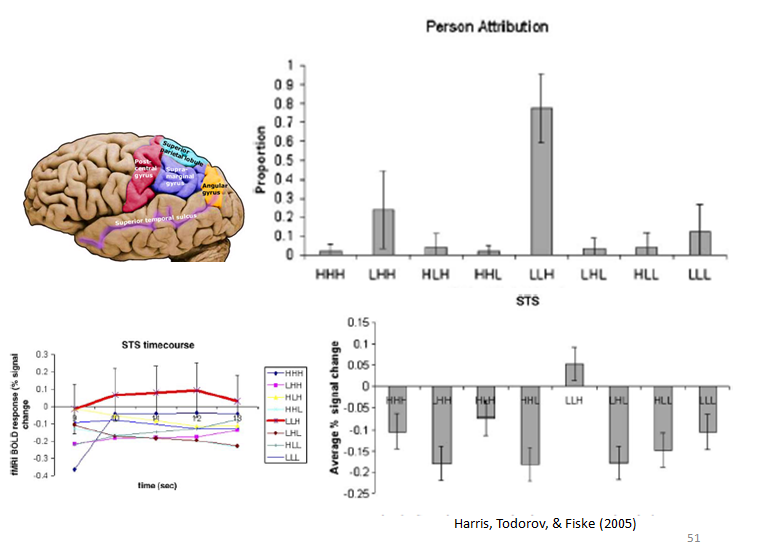
LIKING: warmth, friendliness, trustworthiness, empathy, kindness
RESPECTING: competence, power, efficacy, dominance, intellect, skill
Perceptions of warmth and competence account for 82% of variance in evaluative judgements of others
Fiske, Cuddy, & Glick (2006
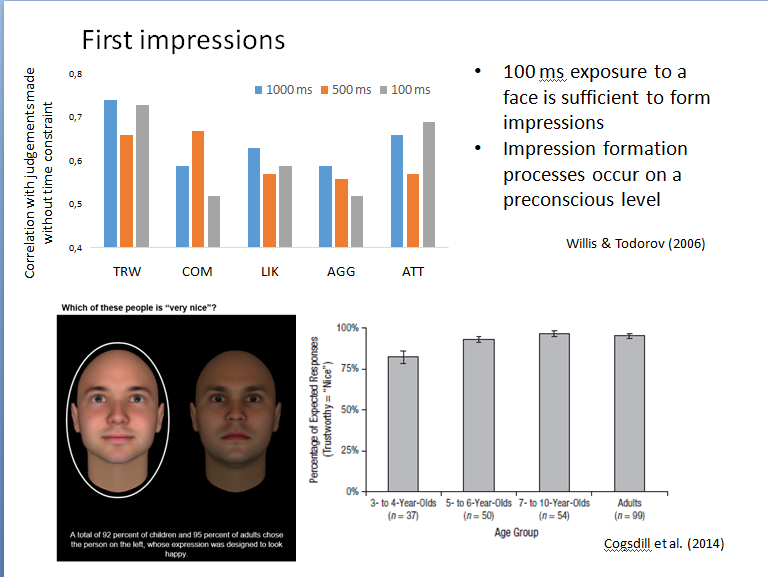
first impressions
100 ms exposure to a face is sufficient to form impressions
Impression formation processes occur on a preconscious level
Facial features
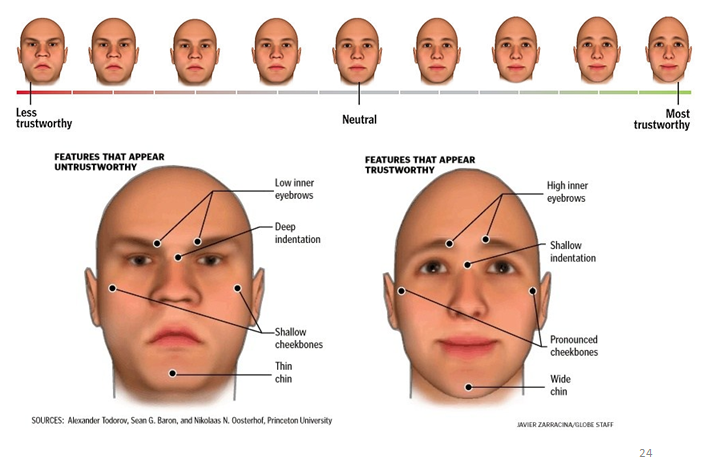
Warmth (facial expression)
definition: Features resembling expressions signalling approach or avoidance behaviour
Attempt to infer behavioural intentions
Evaluation is an overextension of the ability to read emotional expressions
Anger & Sadness: neg. correlated
Smiles: pos. correlated with trustworthiness ratings (Winston et al 2002)
Compentence (facial expression)
Features signalling physical strenght
Facial maturity and masculinity serve as the basis of dominance evaluation
Babyfacedness:
judged to be warmer, more honest, more naïve, weaker, and less competent
more likely to be recommended for jobs calling for submissiveness and warmth
less likely to be found at fault for intentional actions
Zebrowitz & Montepare (2008)
REAL-WORLD OUTCOMES OF SOCIAL ATTRIBUTIONS
Political Voting
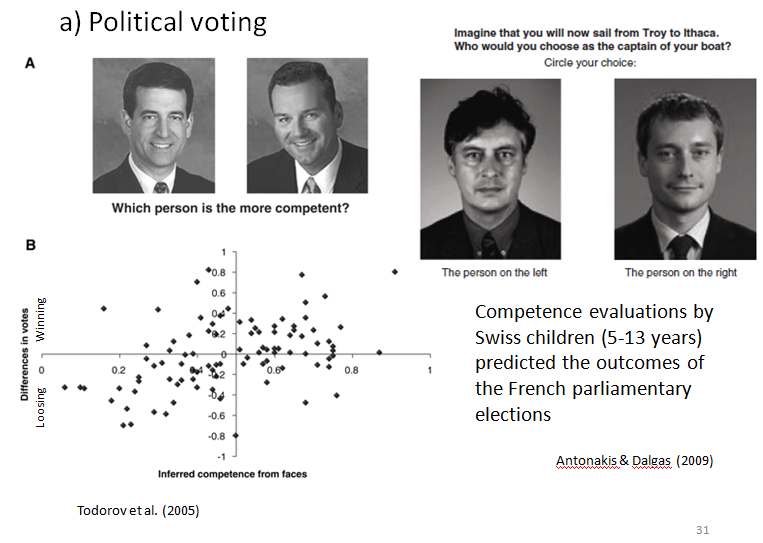
AL-WORLD OUTCOMES OF SOCIAL ATTRIBUTIONS
financial success
Competent- and dominant-looking CEOs are hired by more successful companies and receive larger salaries (Rule & Ambady, 2009)
Professional success within the military is predicted by facial dominance (Mueller & Mazur, 1996)
Trustworthy-looking people given better credit ratings on real credit websites
More likely to have loans funded (Duarte et al 2012)
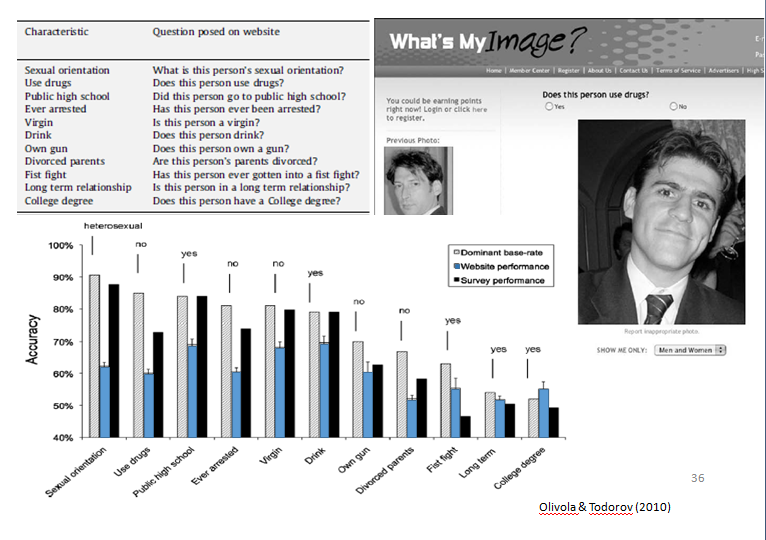
criminal justice
Trustworthiness ratings of inmates predicted whether they were on the death row
Race did not predict trustworthiness

who can catch a liar
Meta-analysis of 108 studies: Presumed lie experts who routinely assess credibility in their professional life do not perform better than lay judges
Higher confidence does not correlate with accuracy in detecting lies
Aadmodt & Custer (2006), Ekman & O’Sullivan (1991

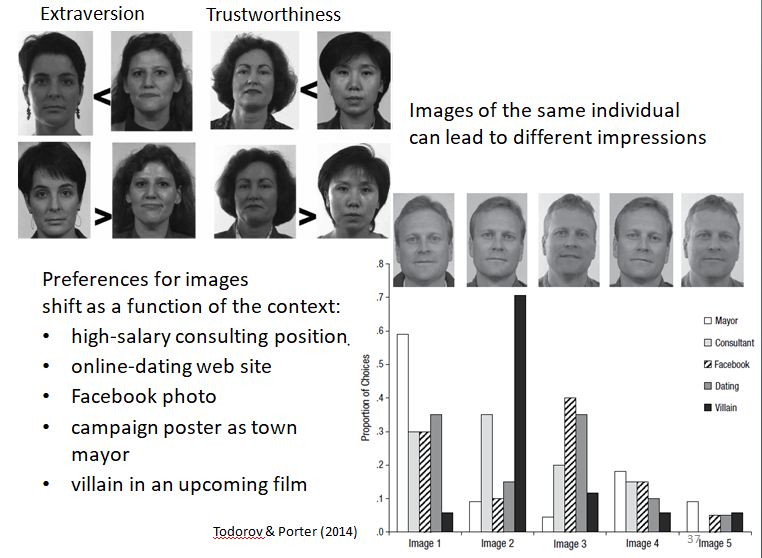
extraversion/trustworthiness
Preferences for images
shift as a function of the context:
high-salary consulting position
online-dating web site
Facebook photo
campaign poster as town mayor
villain in an upcoming film
Images of the same individual
can lead to different impressions
CAUSAL ATTRIBUTIONS: Why first impressions often last
Primacy effect:
Information presented early in a sequence has more impact on impressions than information presented later
Why? Once we think we have formed an accurate impression of someone…..
we pay less attention to subsequent information (attention bias)
we start to interpret inconsistent information in light of the initial impression (confirmation bias)
Person A
Intelligent
Industrious
Impulsive
Critical
Stubborn
Envious
Person B
Envious
Stubborn
Critical
Impulsive
Industrious
Intelligent
Person a liked more
confirmation bias study
same info opposite view

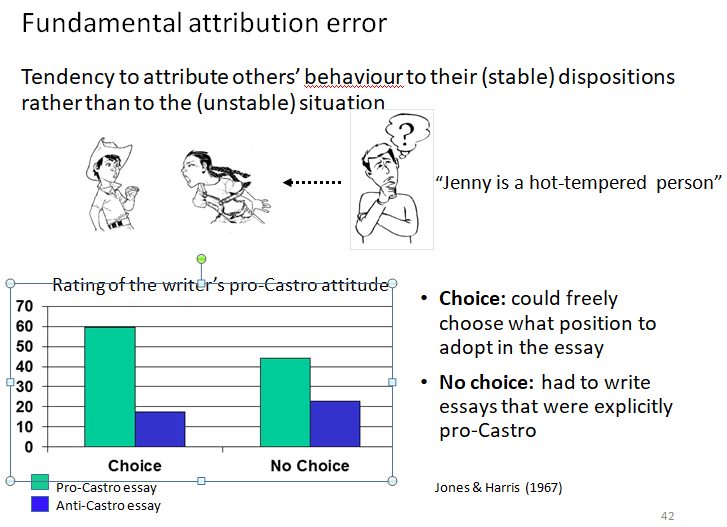
Foundamental attriution error
Tendency to attribute others’ behaviour to their (stable) dispositions rather than to the (unstable) situation
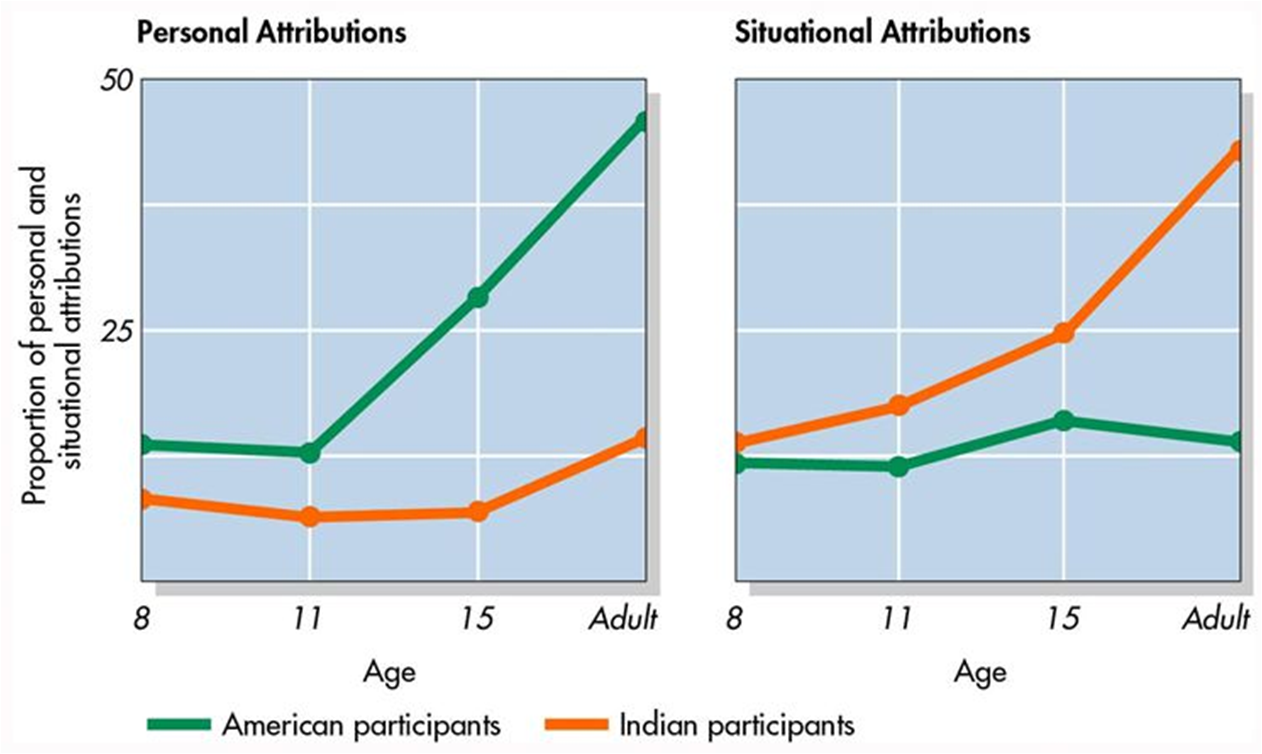
is the fundamental attribution error a western bias?
Why first impressions last (salience)
Situation: often not physical, observable or concrete
People and their behaviour are salient
Actors and actions form perceptual units
Initial salience of situation wanes over time
Behavior has a stronger memory trace than the transient and pallid situation
Sleeper effect: advantage of dispositional explanations increases with time
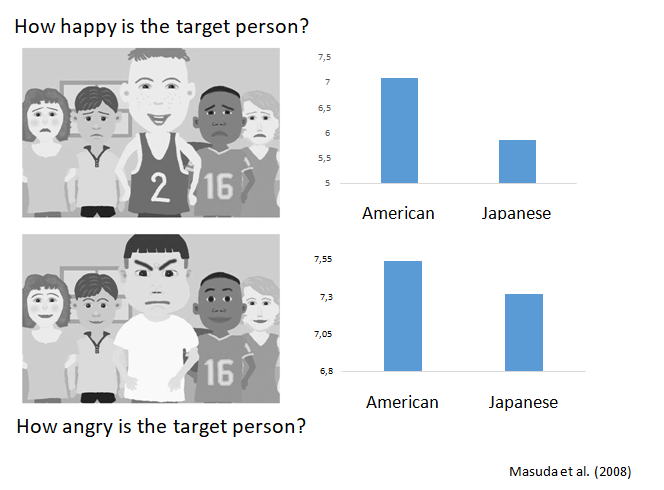
salience study
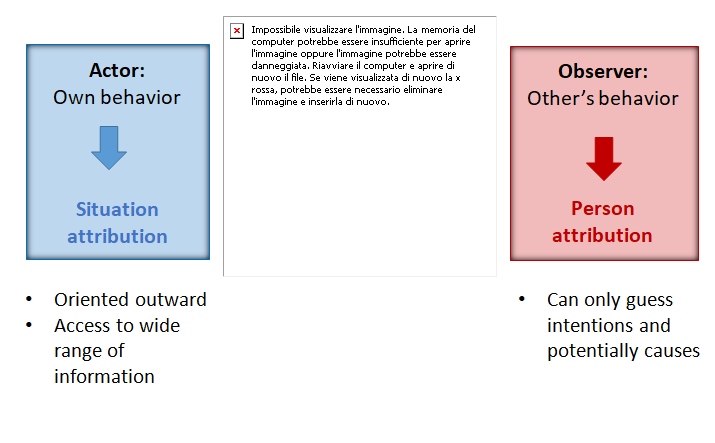
why first impressions last: Actor-observer difference
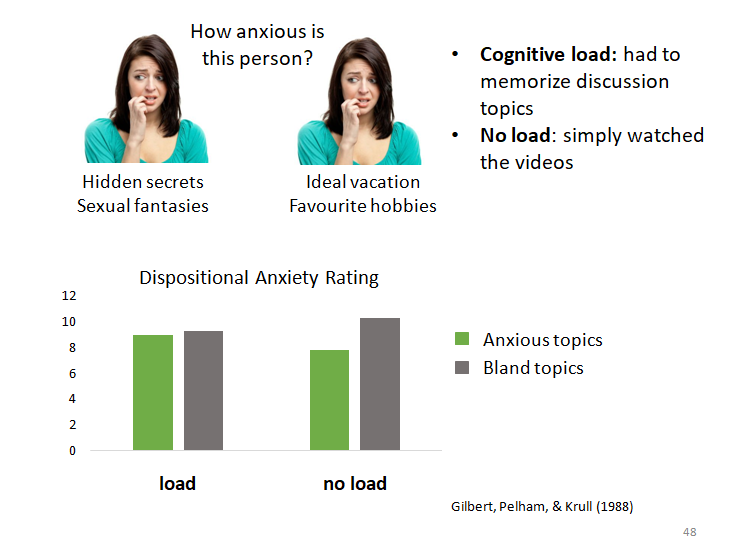
why first impressions last: cognitive resources
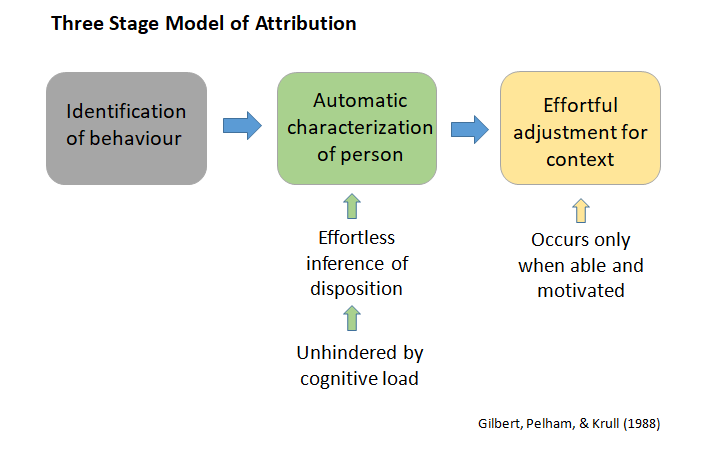
cognitive resources study
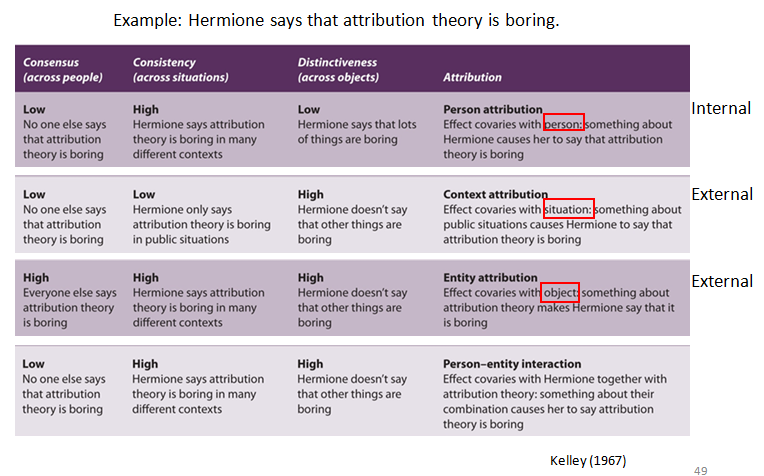
covariation theory
covariation theory study (comedian)
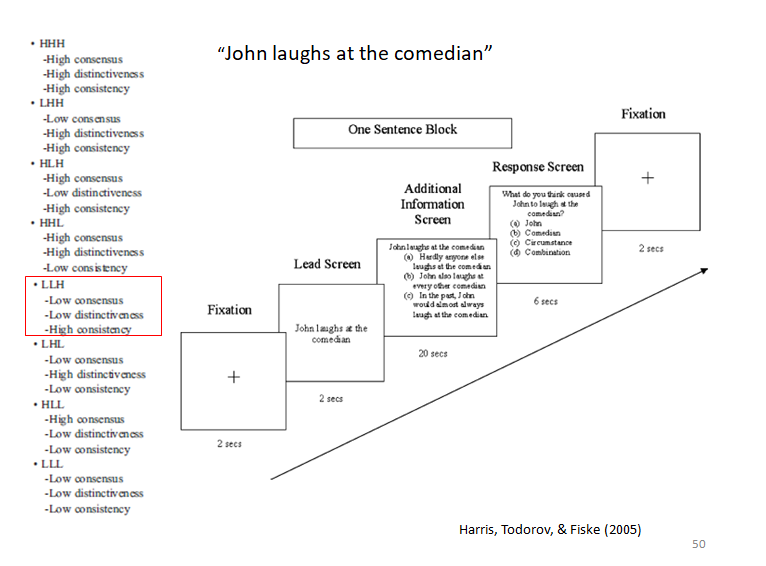
covariance study pt 2