Database Systems: Key Concepts, Types, and Design Principles
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What do the presentations cover?
The presentations cover the objectives found in the opening of each chapter.
Where can all chapter objectives be found?
All chapter objectives are listed in the beginning of each presentation.
Can the presentations be customized?
Yes, the presentations can be customized to fit class needs.
What additional resources are available for images from the book?
A complete set of images from the book can be found on the Instructor Resources disc.
What is the primary focus of Module 1 in Database Systems?
The primary focus is on understanding database systems, their design, implementation, and management.
What is the difference between data and information?
Data are raw facts, while information is the result of processing raw data to reveal meaning.
Why are databases considered valuable assets for decision making?
Databases provide structured data management, which is essential for making informed decisions.
What are some key topics covered in the objectives of the chapter?
The objectives include the importance of database design, types of databases, and flaws in file system data management.
How did modern databases evolve?
Modern databases evolved from file systems.
What are the main components of a database system?
The main components include the database itself, the DBMS, and the applications that interact with the database.
What is a DBMS?
A Database Management System (DBMS) is software that facilitates the creation, manipulation, and administration of databases.
Why is understanding file system characteristics important?
Understanding file system characteristics is important because databases evolved from these systems.
In what settings are databases commonly used?
Databases are used in business, research, and administration.
What is required for raw data to become information?
Raw data must be processed and formatted for storage, processing, and presentation to become information.
What is the relationship between data, information, and knowledge?
Data is the foundation of information, which in turn is the bedrock of knowledge.
What problems do databases solve in data management?
Databases address issues related to data redundancy, inconsistency, and accessibility.
What is the significance of good information in decision making?
Good decisions require good information derived from raw facts.
What is the role of context in information?
Context is necessary to reveal the meaning of information derived from data.
What is the main function of a database management system?
The main function of a DBMS is to manage data storage, retrieval, and manipulation.
What are some flaws in file system data management?
Flaws include data redundancy, inconsistency, and difficulty in data retrieval.
What is the importance of database design?
Database design is crucial for ensuring efficient data management and retrieval.
What are the building blocks of information?
Data
What is the role of information in relation to data?
Information is produced by processing data and is used to reveal meaning in data.
Why is accurate, relevant, and timely information important?
It is key to good decision making.
What is a database?
A shared, integrated computer structure that stores a collection of end-user data and metadata.
What is metadata?
Data about data, providing descriptions of data characteristics and relationships.
What is a Database Management System (DBMS)?
A collection of programs that manages the structure and controls access to data.
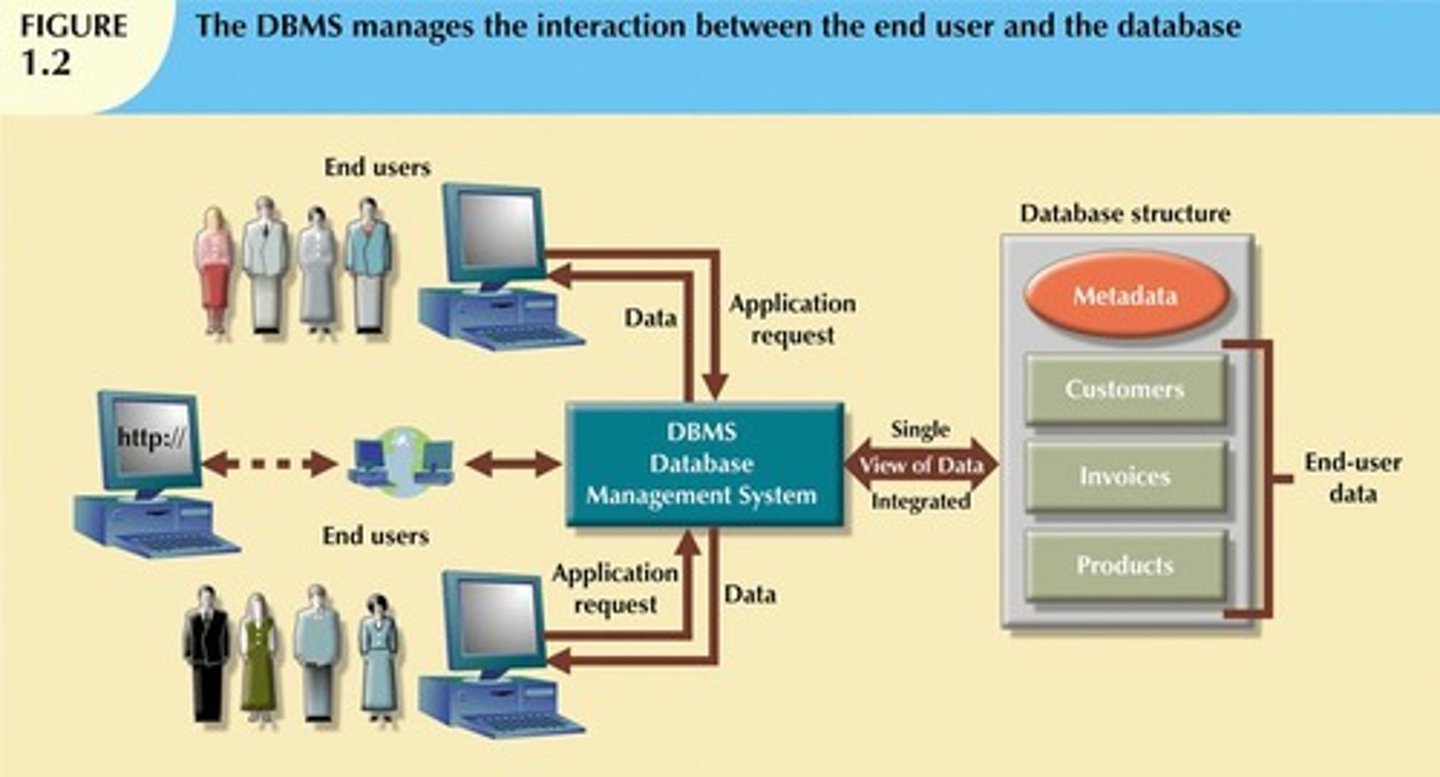
What are the advantages of using a DBMS?
Improved data sharing, security, integration, minimized inconsistency, better access, improved decision making, and increased productivity.
What distinguishes a single-user database from a multiuser database?
A single-user database supports only one user at a time, while a multiuser database supports multiple users simultaneously.
What is a centralized database?
A database where data is located at a single site.
What is a distributed database?
A database where data is distributed across several different sites.
What type of database supports a company's day-to-day operations?
Operational database, also known as a transactional or production database.
What is a data warehouse?
A database that stores data used for tactical or strategic decisions.
What are the three types of data classifications?
Unstructured data, structured data, and semistructured data.
What is the significance of database design?
It focuses on the structure used for end-user data, facilitating management and generating accurate information.
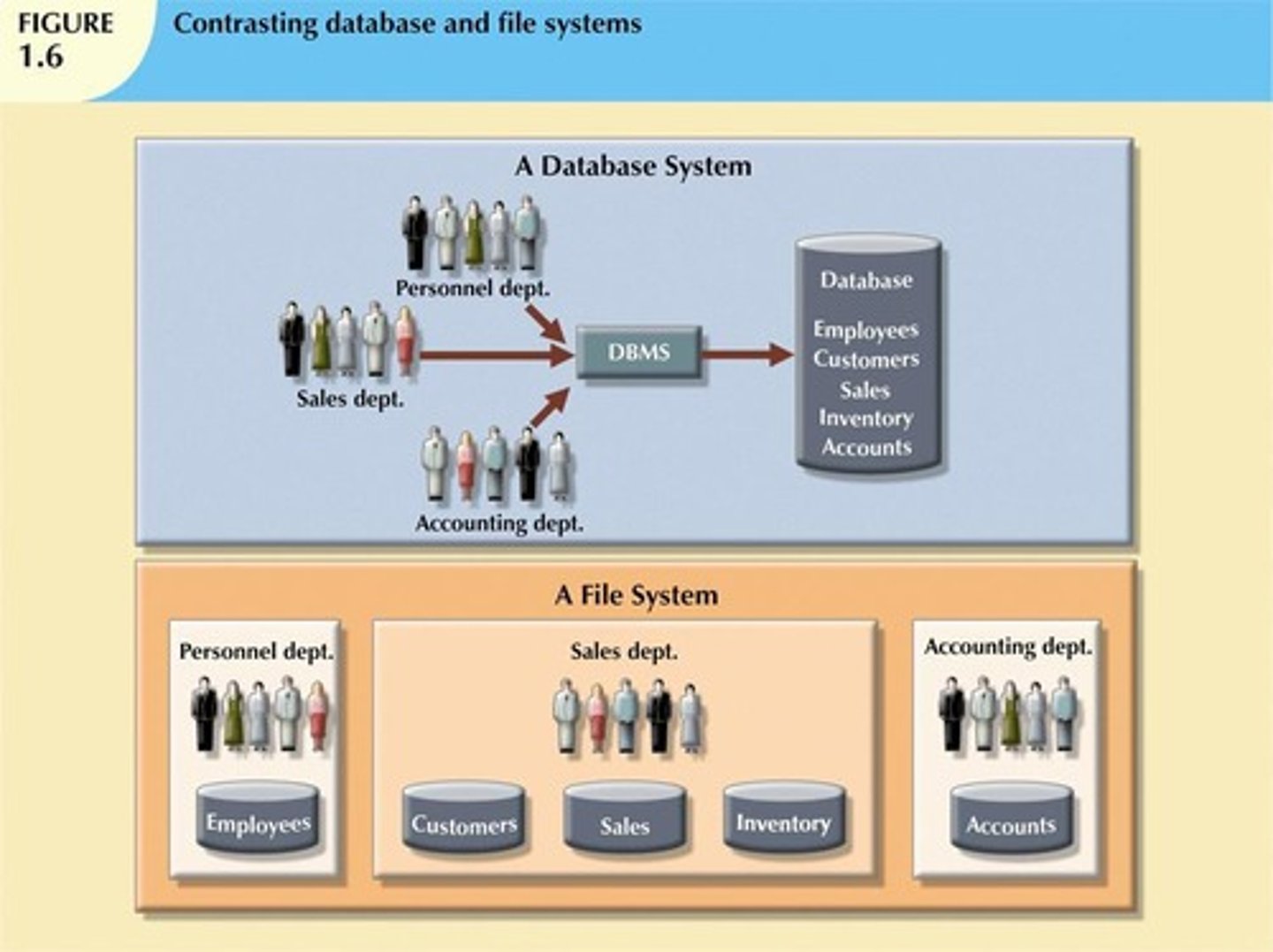
What are the problems associated with file system data processing?
Extensive programming required, inability to perform ad hoc queries, complex system administration, and inadequate security features.
What is structural dependence in database systems?
Access to a file is dependent on its own structure, requiring modifications to all programs if the structure changes.
What is data redundancy?
The unnecessary storage of the same data in different places, leading to potential inconsistencies.
What are data anomalies?
Abnormalities that occur when changes in redundant data are not made correctly, including update, insertion, and deletion anomalies.
What is the role of a data dictionary in a DBMS?
It stores definitions of data elements and relationships, providing metadata management.
What are the five major parts of a database system?
Hardware, software, people, procedures, and data.
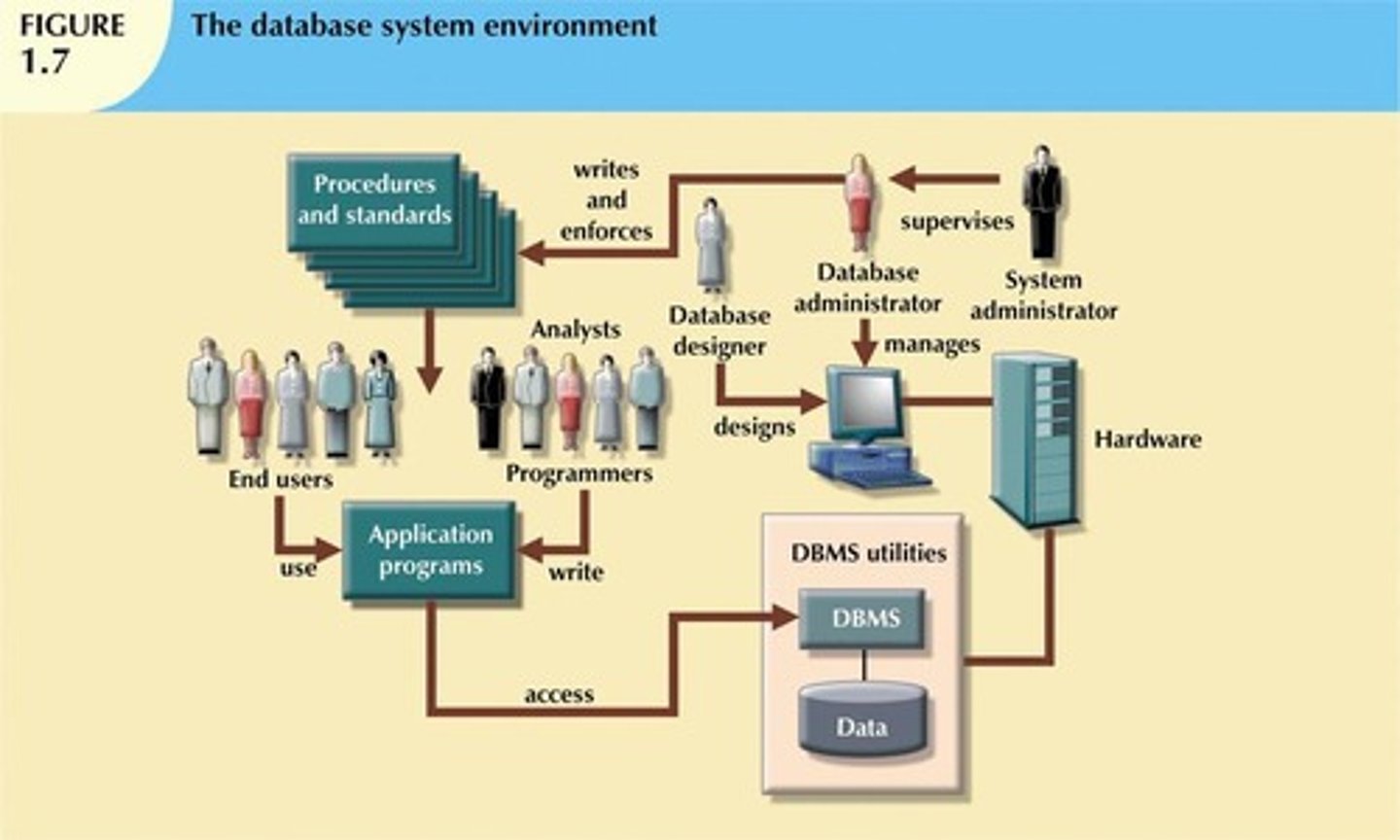
What types of software are required in a database system?
Operating system software, DBMS software, and application programs.
Who are the users of a database system?
System and database administrators, database designers, systems analysts, programmers, and end users.
What is the purpose of procedures in a database system?
They provide instructions and rules governing the design and use of the database.
What does data independence mean?
Data storage characteristics do not affect data access.
What is the practical significance of logical vs. physical data format?
Logical format is how humans view data, while physical format is how computers work with data.
What is the function of a DBMS in data storage management?
It creates and manages complex structures required for data storage.
What is the relationship between DBMS and file systems?
DBMS eliminates most of the problems associated with file systems, providing a more efficient way to manage data.
What is performance tuning in the context of a database?
Activities that make the database perform more efficiently.
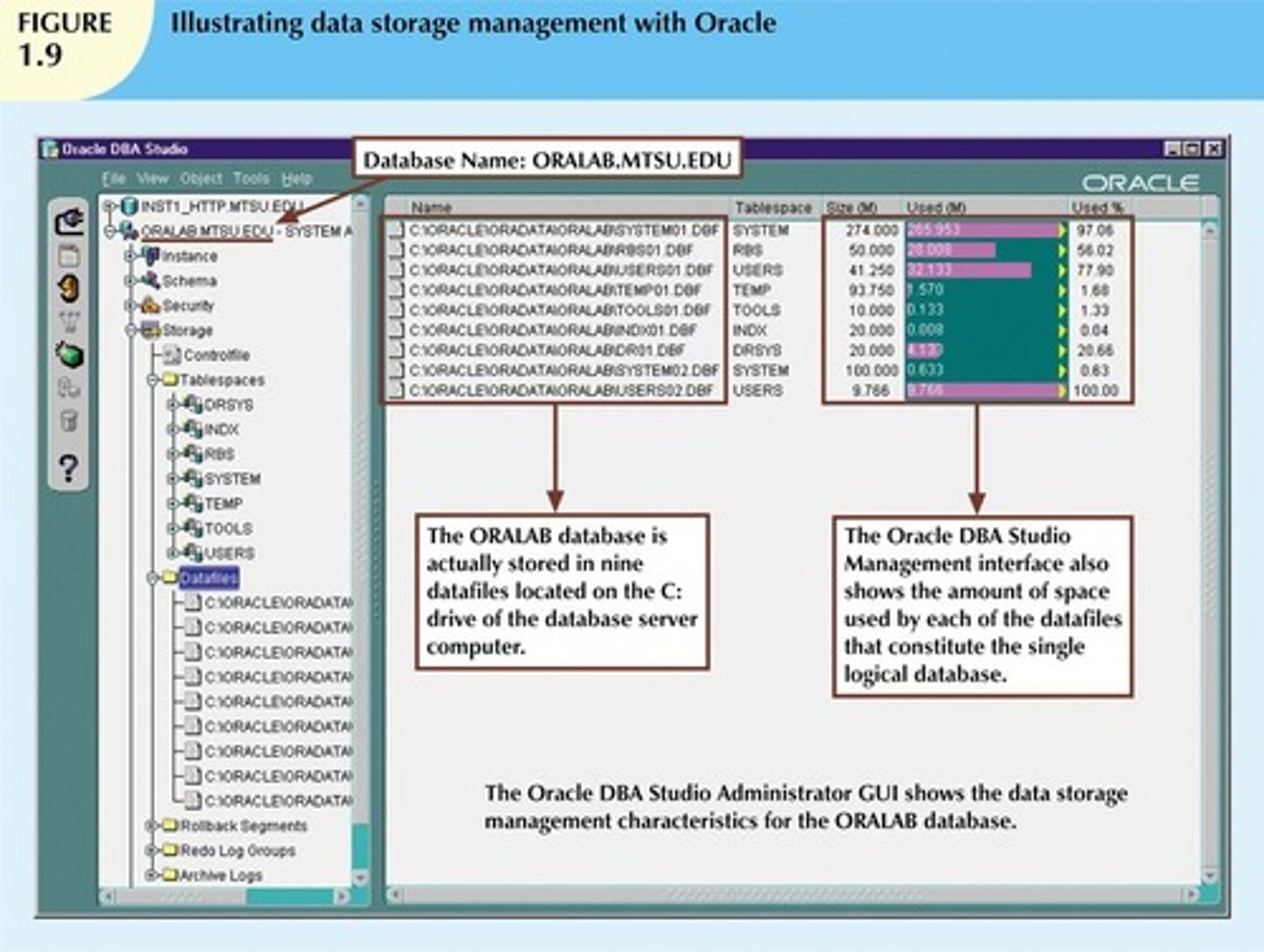
How does a DBMS store data?
The DBMS stores the database in multiple physical data files.
What is the role of a DBMS in data transformation and presentation?
The DBMS transforms data entered to conform to required data structures and transforms physically retrieved data to conform to user's logical expectations.
What is the purpose of security management in a DBMS?
The DBMS creates a security system that enforces user security and data privacy.
What do security rules in a DBMS determine?
Security rules determine which users can access the database and which items can be accessed.
What is the role of multiuser access control in a DBMS?
DBMS uses sophisticated algorithms to ensure concurrent access does not affect data integrity.
What does backup and recovery management in a DBMS ensure?
It ensures data safety and integrity by providing backup and recovery options after a failure.
Why is data integrity management important in a DBMS?
It promotes and enforces integrity rules, minimizes redundancy, and maximizes consistency, especially in transaction-oriented systems.
What is the de facto query language used in DBMS?
Structured Query Language (SQL) is the de facto query language supported by the majority of DBMS vendors.
How do current DBMSs handle database communication?
They accept end-user requests via multiple network environments, allowing users to generate answers to queries through web forms, publish reports on websites, and connect to third-party systems for information distribution.
What shift in focus occurs in managing a database system?
The role of humans changes from programming to managing the organization's resources, enabling more sophisticated use of data.
What are some disadvantages of database systems?
Increased costs, management complexity, maintaining currency, vendor dependence, and frequent upgrade/replacement cycles.
What does a well-designed database facilitate?
It facilitates data management and generates valuable information.
What are some limitations of file system data management?
Extensive programming requirements, complex system administration, difficulty in changing structures, inadequate security features, and redundancy in independent files.
How do DBMS address the weaknesses of file systems?
DBMS present the database as a single repository, promoting data sharing, eliminating islands of information, enforcing data integrity, and promoting security.
What is the importance of the data dictionary in a DBMS?
It stores data relationships used to enforce data integrity.
What is the impact of poorly designed databases?
They lead to bad decision making and organizational failure.
What is the significance of recovery management in a DBMS?
It is critical for preserving the database's integrity after a failure.
What is the primary purpose of database access languages?
They provide access to the database through a query language.
What does the DBMS framework enforce?
It enforces strict procedures and standards for managing data.
How does a DBMS eliminate redundancy?
By enforcing data integrity and presenting data as a single repository.
What are the implications of vendor dependence in database systems?
It can lead to challenges in flexibility and adaptability to new technologies.
What is the relationship between data structures and database effectiveness?
The effectiveness of a database is determined by the data structures created within it and their relationships.
What is the role of DBMS in decision making?
DBMS provides accurate, relevant, and timely information, which is key to good decision making.
What is the significance of data relationships in a DBMS?
They are essential for enforcing data integrity and ensuring consistency within the database.