7 Ischemia & Acute Coronary Syndromes
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
ischemia results from reduction of blood flow from a combination of
fixed vessel narrowing
abnormal vascular tone
what is poiseuille’s law?
Q (flow) = deltaP(pi)(r^4) / 8nL
P : pressure
r : radius
n : viscosity
L : length
how does pressure affect flow?
greater pressure difference = greater flow
how does radius affect flow?
larger radius = larger flow ; really affects flow because it is to the 4th power
how is viscosity related to flow?
inversely related; more viscosity less flow
how is vessel length related to flow?
inversely related; increased vessel length less flow
how do vessels physiologically respond to decreased blood flow?
compensatory vasodilation of the distal vessels
what occurs in stenosis of less than 60%?
blood flow is not affected because of compensatory vasodilation
what occurs in stenosis of more than 70%
normal flow at rest; maximal blood flow reduced (so symptoms can appear when going to gym or going up stairs)
what occurs in stenosis of more than 90%
ischemia can develop at rest
how does endothelial cell dysfunction contribute to ischemia?
inappropriate vasoconstriction of coronary arteries
loss of normal antithrombotic properties (prone to thrombosis)
how does atherosclerosis affect vasoconstriction?
normally with physical activity and mentral stress → vasodilation (overtakes sympathetic influence)
in atherosclerosis there is impaired release of vasodilators → sympathetics are now unopposed and there is vasoconstriction
besides atherosclerosis what are other causes of myocardial ischemia?
hypotension (low blood pressure - not enough blood volume)
decreased blood oxygen content (anemia)
massive internal bleeding (less blood supply going to heart)
what is stunned myocardium?
transient (temp) ischemia without necrosis; systolic dysfunction
effects of ischemia reversible; contractile function recovers
what is hibernating myocardium?
persistent reduction in blood flow resulting in CHRONIC ventricular contractile dysfunction
can recover with revascularization
hibernating myocardium is usually from
multivessel CAD
what is the levine sign?
clenched fist
what are the signs of ischemia?
tightening/ increased pressure
levine sign (clenched fist)
what are the symptoms of ischemia?
tachycardia
diaphoresis
nausea
SOB
what is the gold standard in diagnosing CAD?
coronary angiography
what is nuclear imaging stress test?
radioactive dye injected that causes blood flow to be highlighted; decreased brightness when stressed
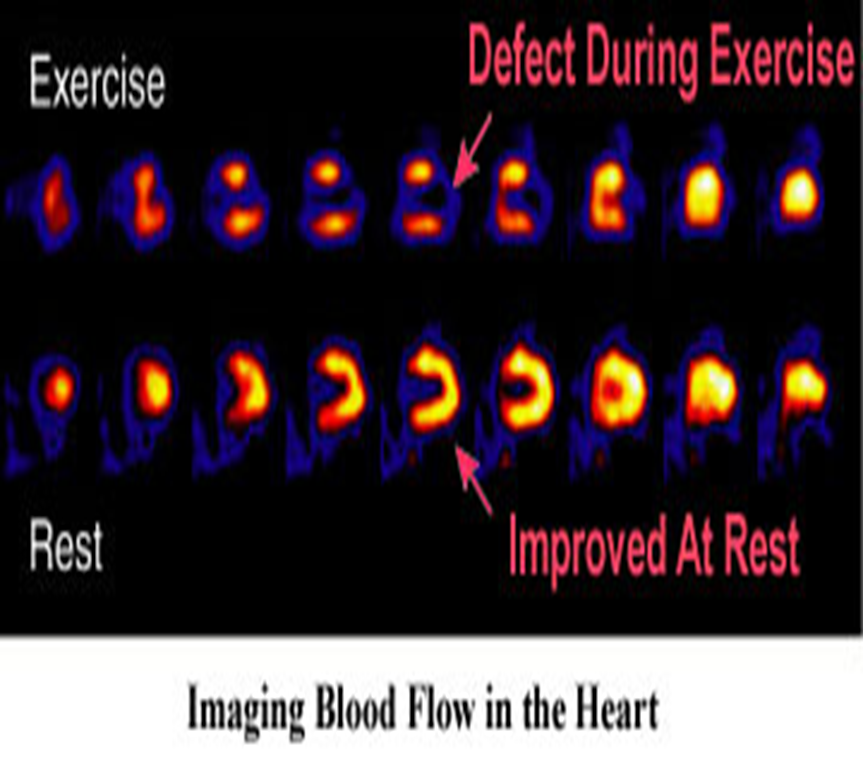
what is the first line of treatment for ischemia?
decrease risk factors such s smoking, alcohol, diet, exercise
how is acute angina treated medically?
sublingual nitroglycerin
what does nitroglycerin do?
promotes venodilation → reduces venous return (lower pressure in veins) → decreases cardiac output → decreases strain to pump large volumes of blood → decreases wall stress → decreases myocardial oxygen demand
dilates coronary arteries → increases coronary blood flow
what medical treatments are used to prevent recurrent ischemic episodes?
organic nitrates
Beta blockers
calcium channel blockers
what do beta blockers do?
reduce myocardial oxygen demand by decreasing force in ventricular contraction and heart rate
what medical treatments are used to prevent acute cardiac events?
anti-platelet therapy → antithrombotic properties
lipid regulating therapy (statins) → decreases lipid LDL to decrease vascular inflammation
angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors → treats hypertension
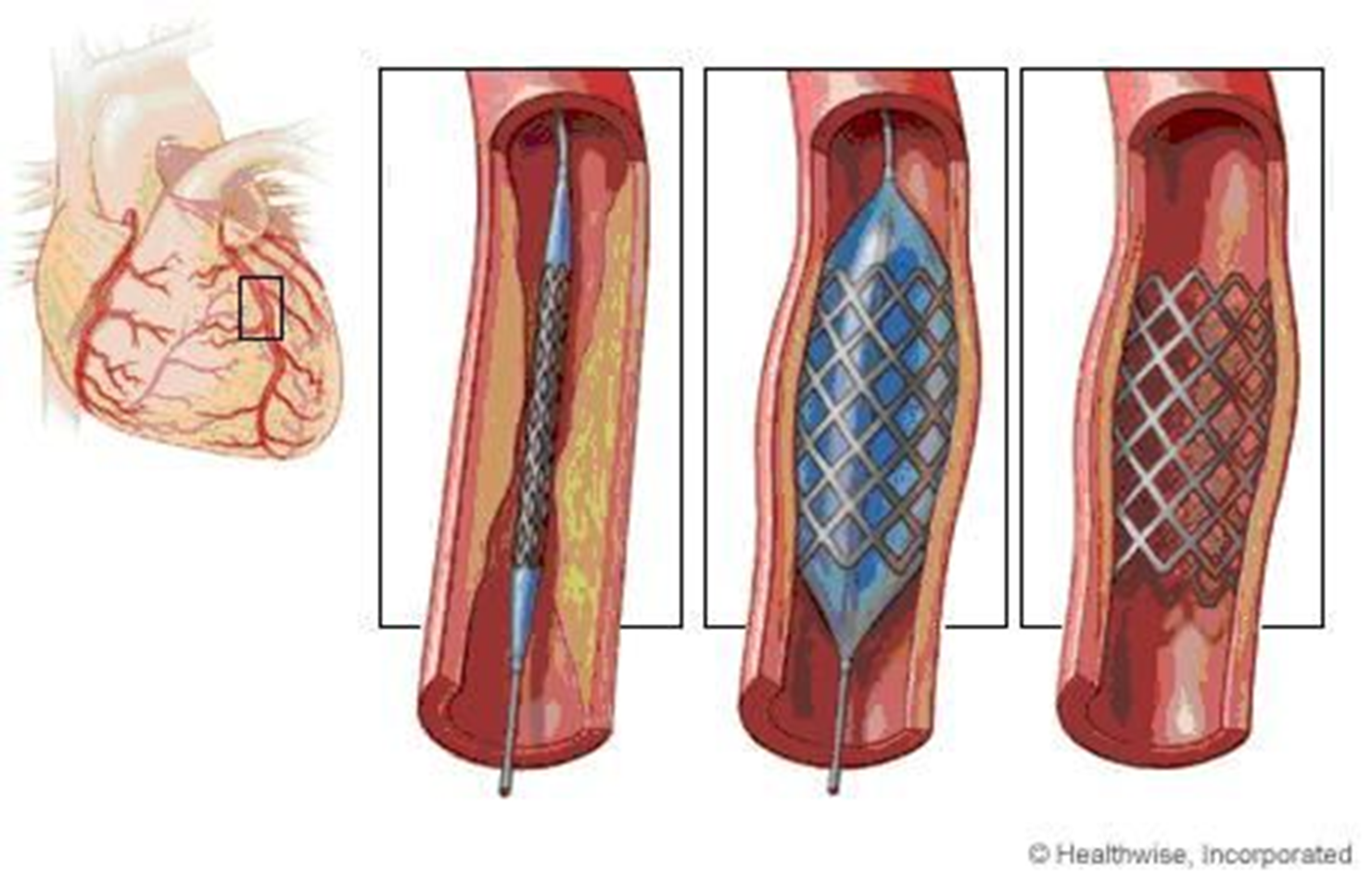
what happens if medicine does not work to treat ischemia?
mechanical revascularization methods such as
percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) → balloon tipped catheter
coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)
what is acute coronary syndrome?
ACS is an umbrella term for situatiosn where there is sudden decreased blood supply to the heart
type of ACS depends on
degree of coronary obstruction associated with ischemia (transient or permanent)
ACS is usually diagnosed as
partially occlusive thrombus
complete obstruction
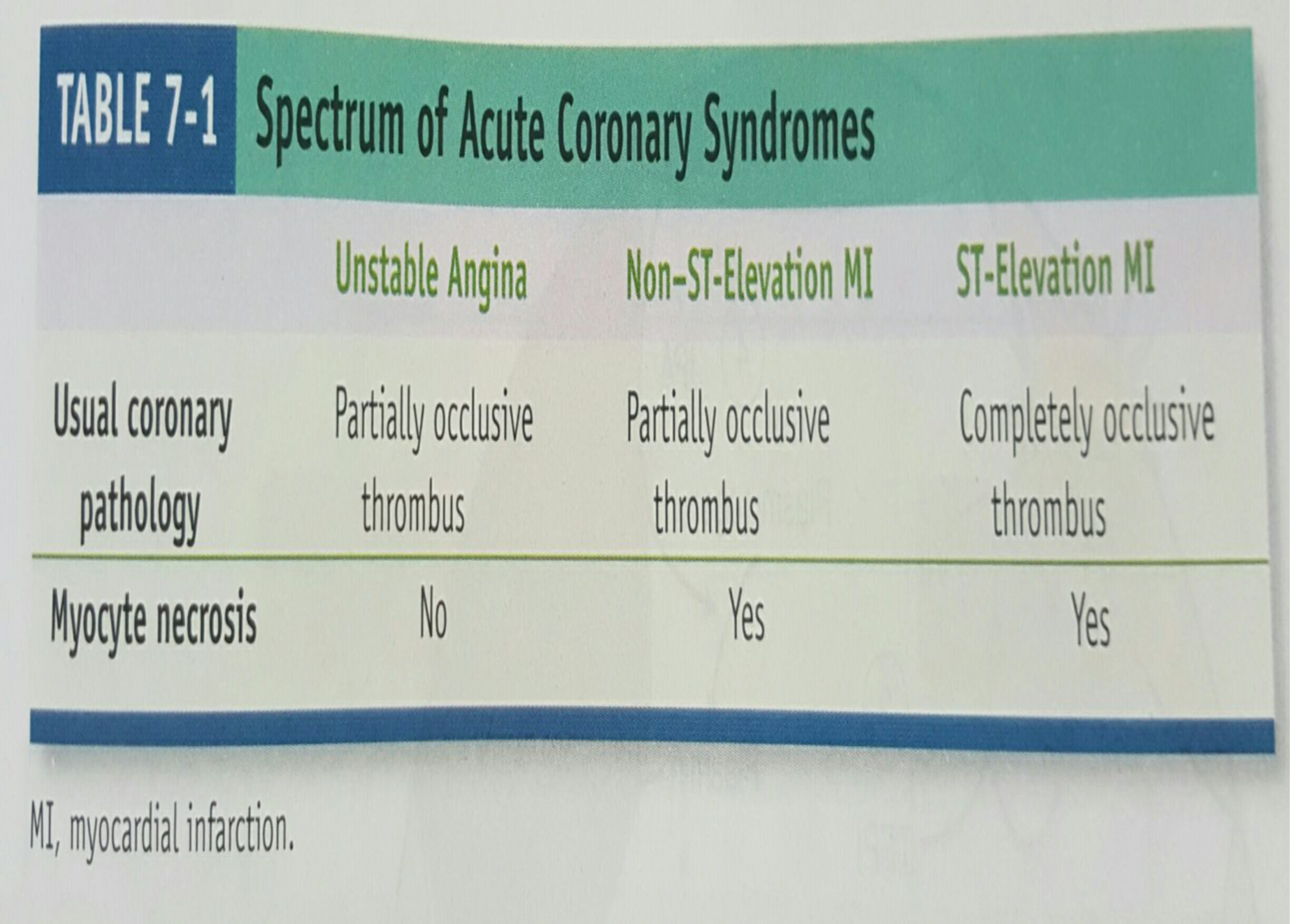
what is partially occlusive thrombus? aka?
unstable angina of angina pectoris
aka non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)
what is complete obstruction called?
ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
what kind of thrombus is seen in unstable angina? myocyte necrosis?
partially occlusive thrombus
no necrosis
what kind of thrombus is seen in NSTEMI? myocyte necrosis?
partially occlusive thrombus
yes necrosis
what kind of thrombus is seen in STEMI? myocyte necrosis?
completely occlusive thrombus
yes necrosis
know
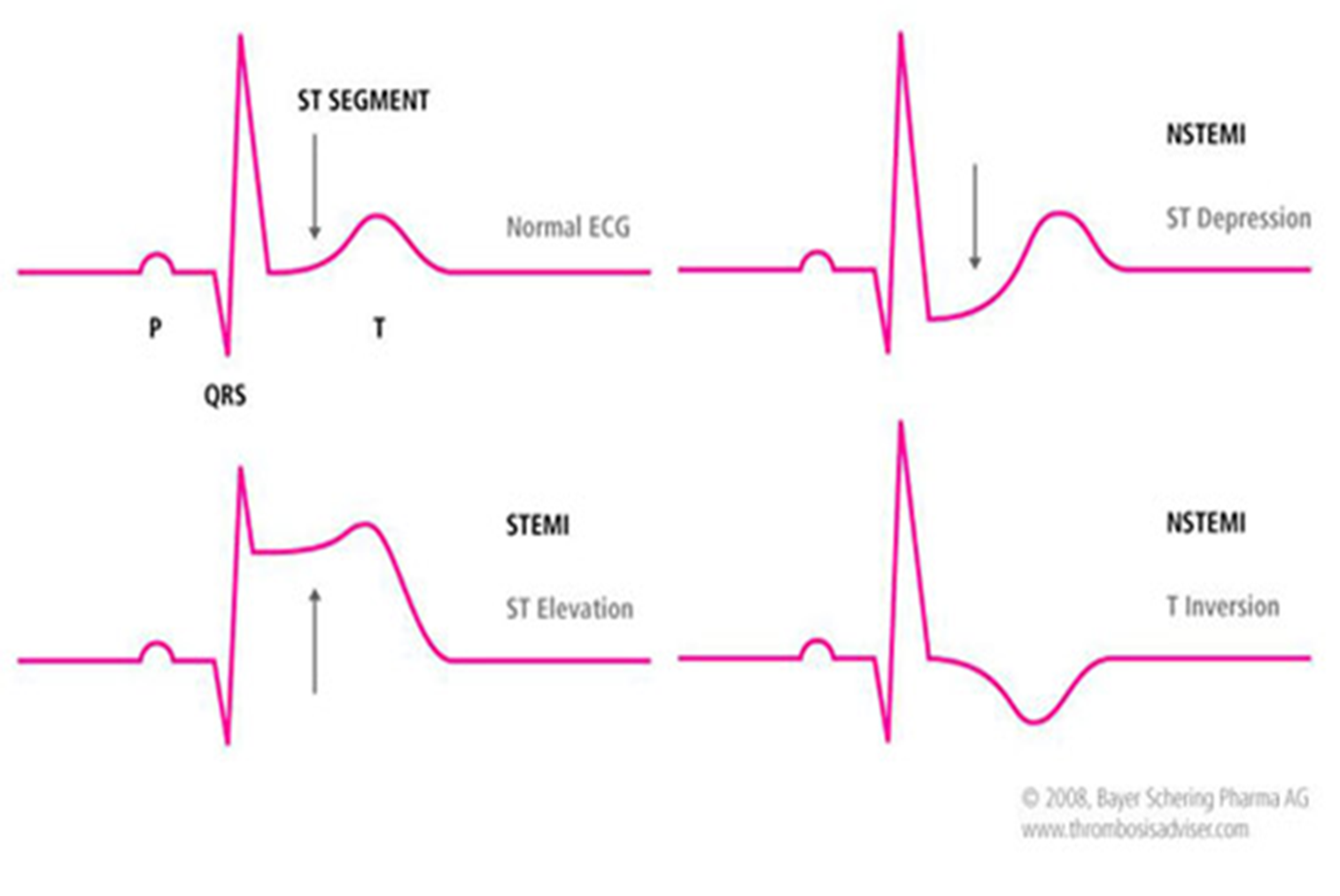
what is the difference between a STEMI and NSTEMI?
STEMI : vessel is completely blocked
NSTEMI : vessel is partially blocked
how can NSTEMI show up on EKG?
ST depression
T inversion
what are the causes of acute coronary syndrome?
90% of cases are secondary to plaque rupture and subsequent thrombosis
what are the effects of ACS?
ST changes on EKG
angina/unstable angina
+/- biomarkers detected in blood
what are the biomarkers used to detect ACS?
cardiac specific troponin
creatine kinase MB isoenzyme
myoglobulin
what is the most commonly used biomarker in diagnosis ACS? why
cardiac specific troponin because up to 80% of pts with acute MI will have elevated troponin within 2-3 hours of ED arrival
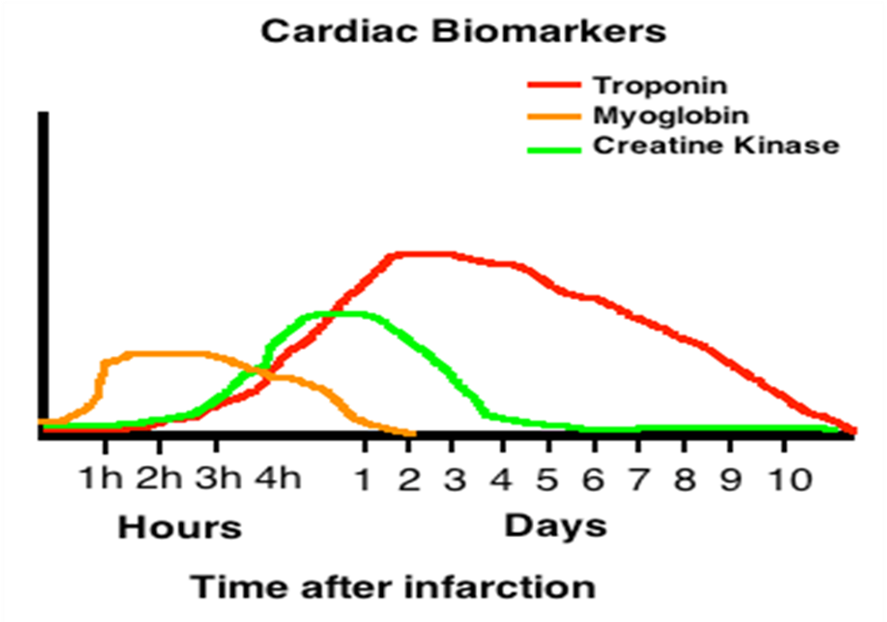
what are other causes of elevated troponin?
renal failure/insufficiency
muscular trauma
pulmonary embolism
congestive heart failure
severe septicemia
KNOW THIS
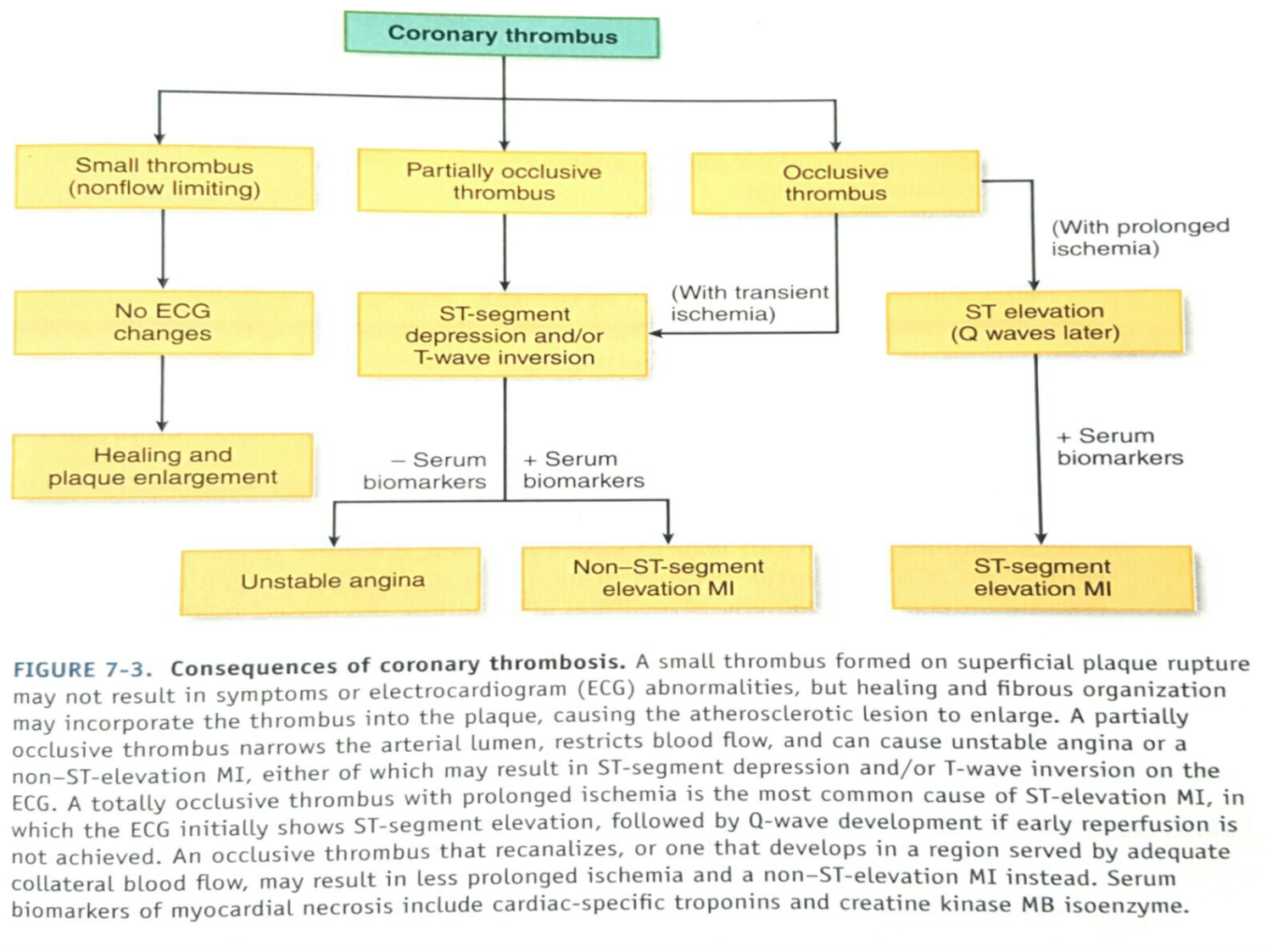
what are nonatherosclerotic causes of acute MI?
coronary emboli from mechanical/infected cardiac valves
inflammation from acute vasculitis
connective tissue disordes
cocaine abuse
what are the functional changes secondary to ACS?
systolic dysfunction (impaired ventricular contraction)
diastolic dysfunction
ventricular remodeling
what happens with systolic dysfunction?
decreased ejection fraction and stroke volume
increases systolic diameter and volume
increased wall stress
increased myocardial demand
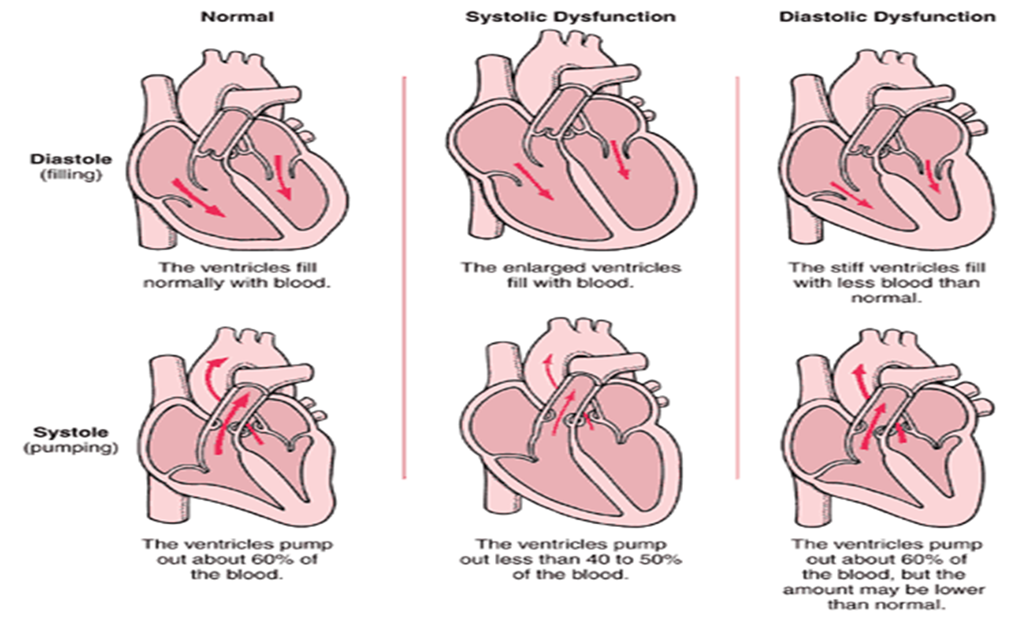
what happens with diastolic dysfunction
ventricular relaxartion is an active process and is energy dependent so when ischemia/infarction occurs there is a reduction in myocardial compliance
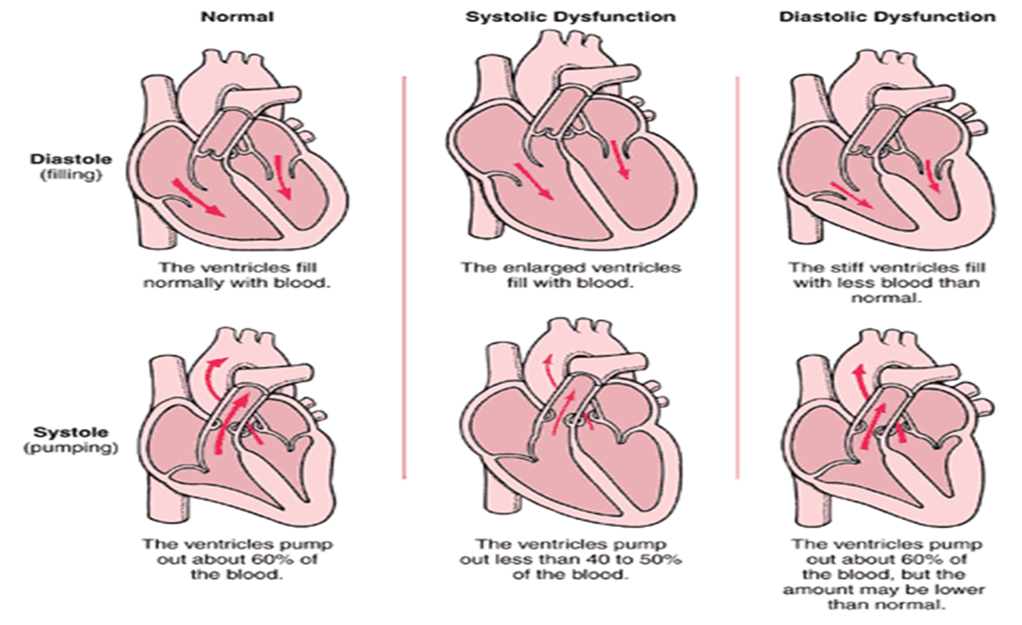
what happens with decreased compliance?
increased diastolic pressure
decreased myocardial perfusion/supply
what is ventricular remodeling?
changes in size, shape, structure and physiology of heart after injury to mycoardium
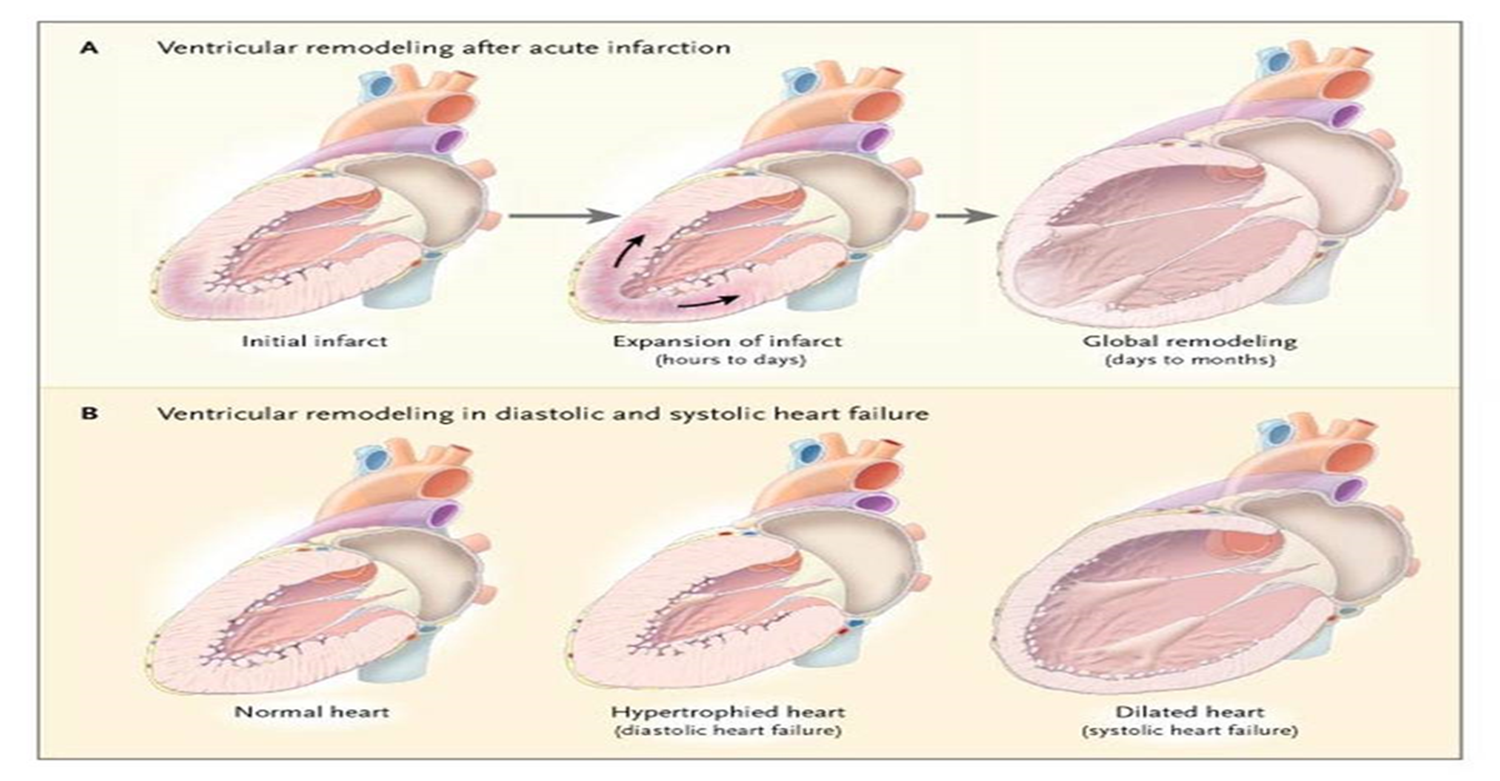
loss of effective contractile myocytes causes
wall motion abnormalities
define hypokinetic, akinetic and dyskinetic
hypokinetic : segment of decreased contraction
akinetic : segment that does not contract
dyskinetic : segment that bulges outward during contraction