Biology: 2G Gas exchange in Humans
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Name all the structures in the gas exchange of humans.
External and internal intercostal muscles, Pleural Membrane, ribs, trachea, alveoli, bronchiole, right lung, left lung, diaphram, right main bronchus, left main bronchus,
What is the function of the trachea?
Supported by rings of cartilage that prevent it from collapsing. It brings air to the lungs.
What is the function of the bronchus?
They are supported by rings of cartilage. It branches off the trachea to bring air into each of the lungs.
What is the function of the bronchiole?
Branch off the bronchi
What is the function of the alveoli?
Small air sacs that are the site of gas exchange
What is the function of the lung?
The organ where gas exchange occurs
What is the function of the ribs?
Protect internal organs (heart and lungs) of the thorax
What is the function of the Intercostal muscles?
Muscles between the ribs that aid breathing by moving the ribs.
What is the function of the diaphragm?
Sheet of muscle below the ribs that aid breathing. Its movements increase and decrease the volume of the thorax
What is the function of the pleural membranes?
Thin layers that reduce friction between the lungs and the inside of the chest wall during breathing.
How do gases enter the bloodstream?
1) Air enters via the mouth and nose.
2)It will then enter the trachea.
3)The trachea branches into two bronchi, one going into each lung.
4)The bronchus branches into small tubes called bronchioles.
5)At the end of each bronchiole are millions of alveoli where gaseous exchange takes place.
6)In the alveoli, oxygen will enter the blood and carbon dioxide will leave the blood
What happens in the alveoli during the gas exchange?
Oxygen diffuses into the red blood cells from the alveoli
Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the red blood cells into the alveoli
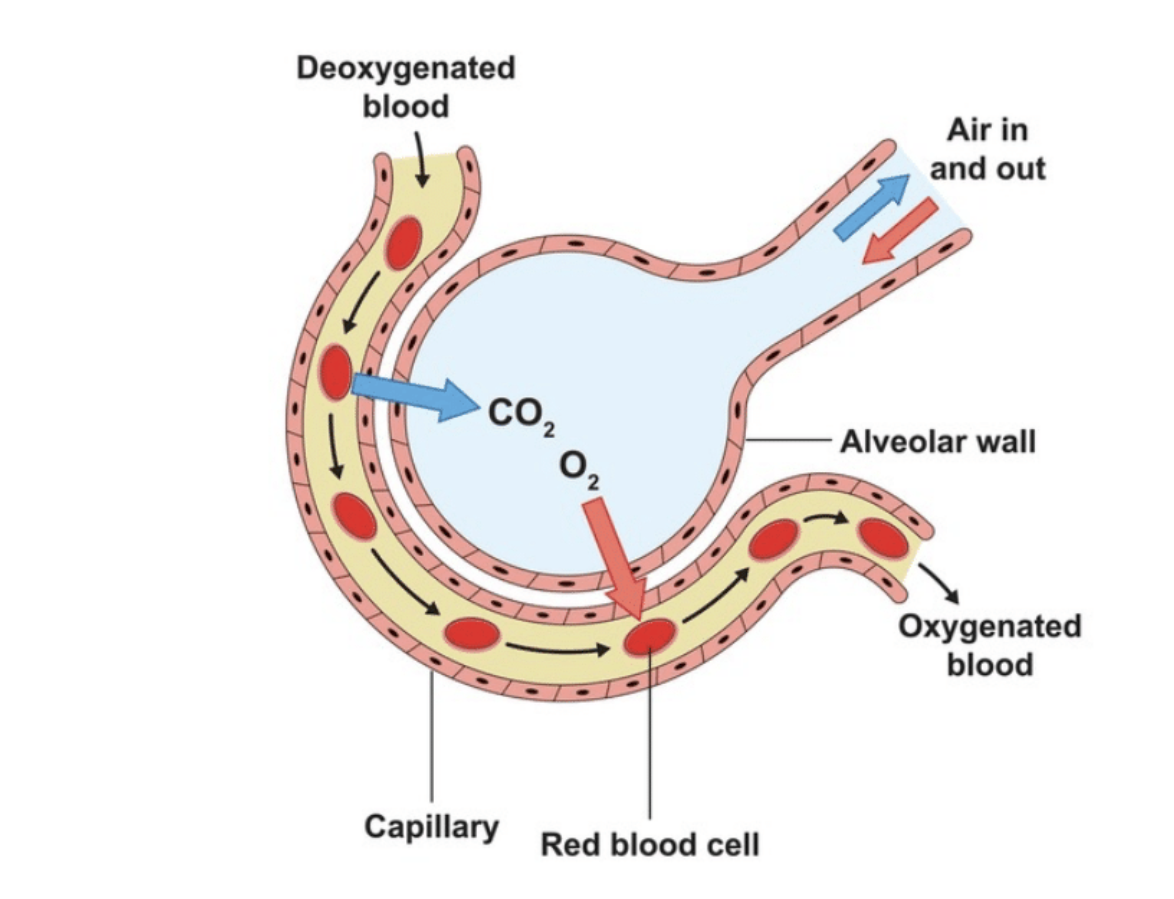
What are the Adaptations of Alveoli for Gaseous Exchange?
One-cell thick wall to reduce the diffusion distance.
Large Surface area to Increase the rate of exchange of gases by diffusion.
Moist walls to allow the gases to dissolve and easily pass through the alveolar walls.
Rich supply of blood capillaries to ensure oxygen-rich blood (oxygenated blood) is taken away from the lungs and carbon dioxide-rich blood (deoxygenated blood) is taken to the lungs.
Concentration gradient for oxygen as breathing ensures that the oxygen concentration in the alveoli is higher than in the capillaries, so oxygen moves from the alveoli to the blood. Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood to the alveoli
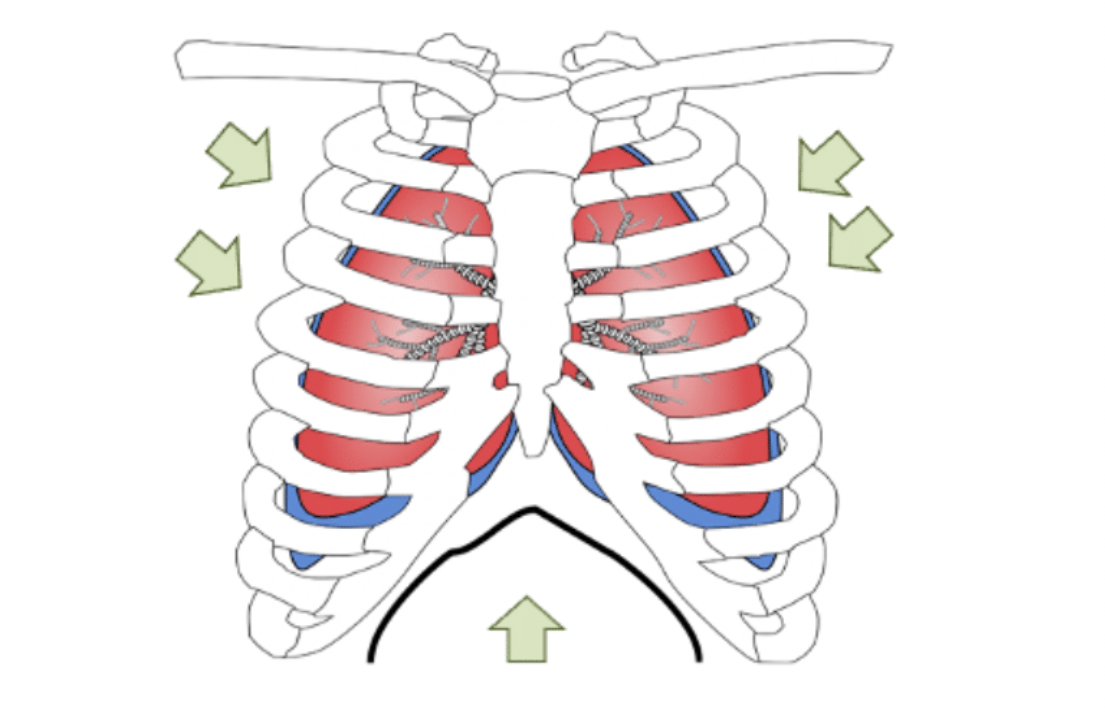
What happens to all the structures and air during inhalation?
1) The internal intercostal muscles relax and the external intercostal muscles contract.
2)This pulls the ribcage upwards and outwards.
3)The diaphragm contracts, and moves downwards.
4)Lung volume increases. Air pressure inside decreases.
5)Air is pushed into the lungs
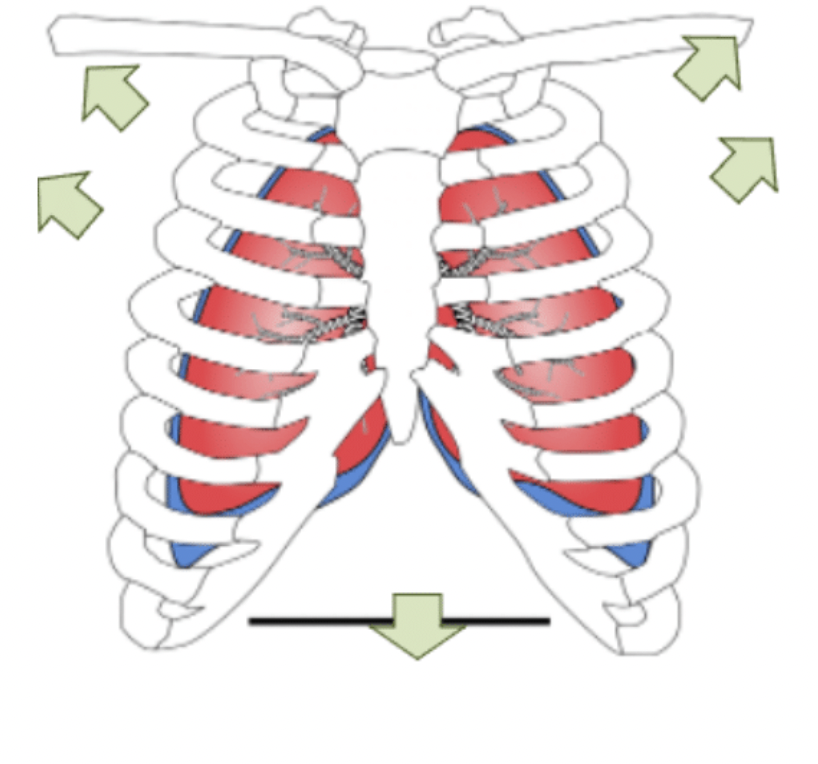
What happens to all the structures and air during exhalation?
1)The external intercostal muscle relax and the internal intercostal muscles contract.
2)This pulls the ribcage downwards and inwards.
3)The diaphragm relaxes, and moves upwards.
4)Lung volume decreases.Air pressure inside increases.
5)Air is pushed out of the lungs.
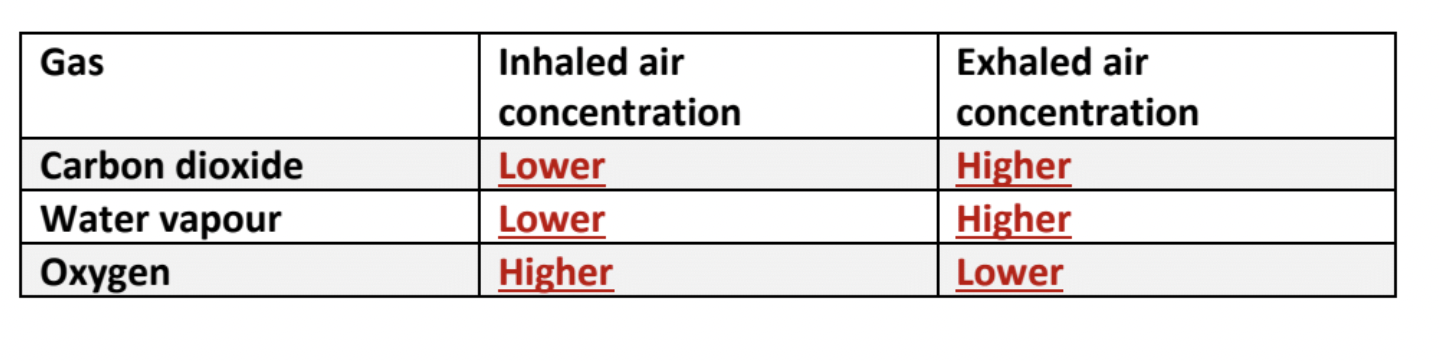
What is the Comparison of gas composition between inhaled and exhaled air
Look at the photo.
What are the effects of nicotine in tobacco?
An addictive substance that increases dependency to smoking.
Increases the heart rate and blood pressure and makes blood vessels narrower than normal. This can lead to heart disease.
What are the effects of tar in tobacco?
A sticky substance that can lead to the cancer of the mouth, throat and lungs.
It reduces gas exchange by coating the lungs including the alveoli.
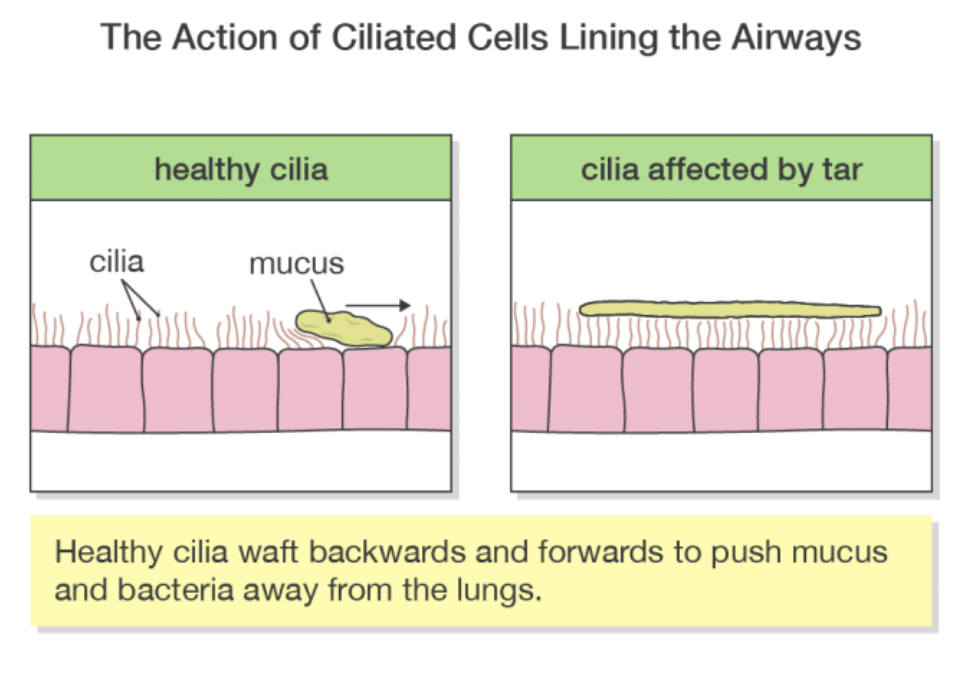
What are the effects of carbon monoxide in tobacco?
It has a greater affinity than oxygen to bind to the red blood cells.
It reduces the levels of oxygen in the body.
What is smoker’s cough?
Cilia are tiny hair-like structures on the surface of the cell. These hairs sweep hair, mucus, trapped dust and bacteria up to the back of the throat where it can be swallowed.
When a person smokes, the cilia stop moving which leads to a build-up of mucus, bacteria and dirt producing a ‘smokers cough.
What is cardiovascular disease?
The lining of the arteries, including the coronary arteries, are damaged during smoking. This damage leads to the build-up of fatty material in the arteries causing a heart attack or a stroke.
Chemicals in cigarette smoke can also increase the likelihood of blood clotting, resulting in a heart attack or stroke