C3 neutralisation and some electrolysis and other stuff-do both C3
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
state the overall neutralisation reaction
base + acid -> salt+ water
state the neutralisation reactions
metal oxide + acid -> salt + water
metal hydroxide + acid -> salt + water
metal carbonate + acid -> salt + water + carbon dioxide
formula for phosphoric acid
H3PO4
how do you calculate the concentration of hydrogen?
10 to the power of -(pH)
formula for hydrochloric acid
HCl
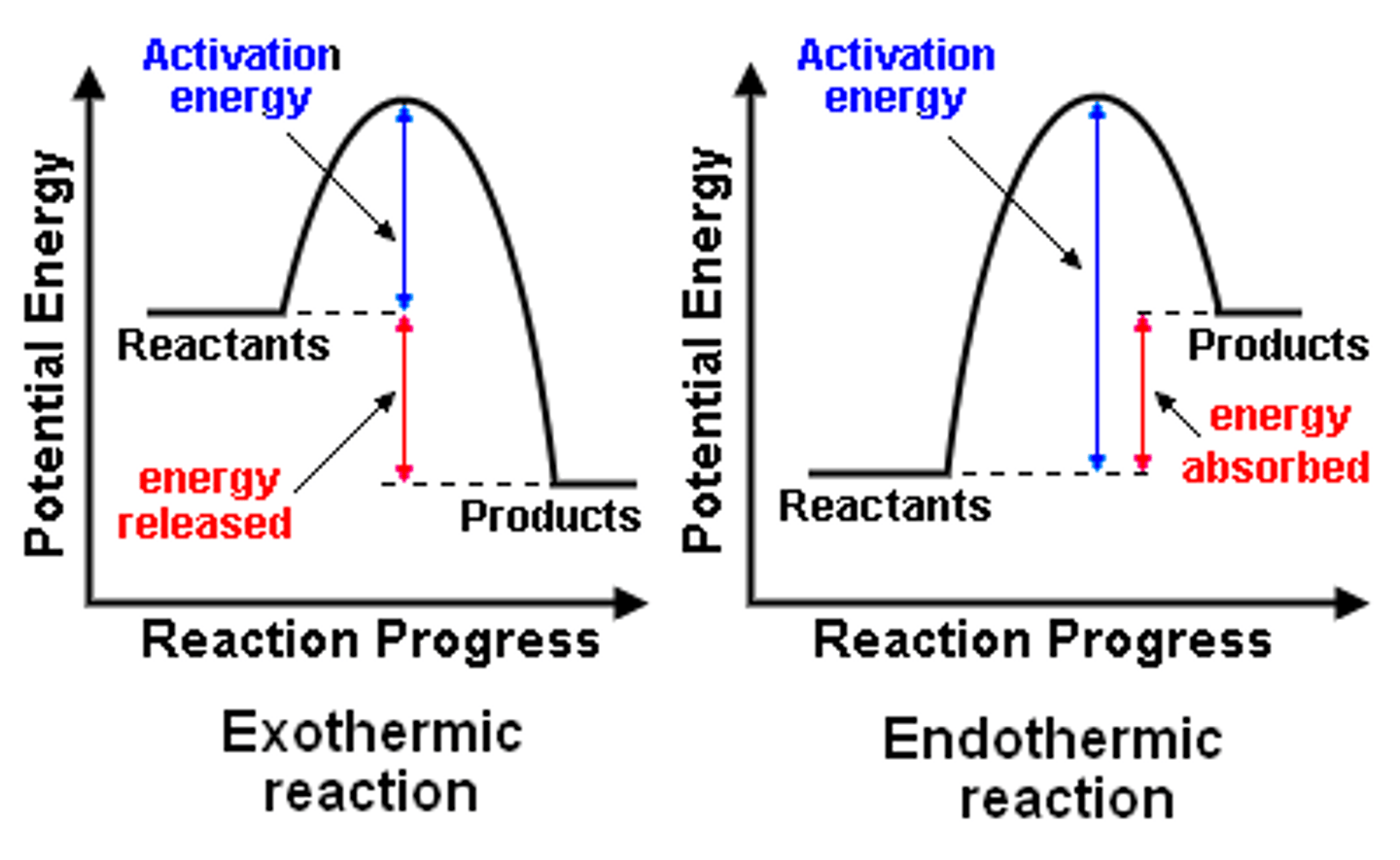
labelled reaction profiles
dont do bottom arrows
overall equation for electrolysis of aluminium oxide
2Al2O3(l) -> 4Al(l) + 3O2(g)
half equation for aluminium
[Al]3+ + 3e- -> Al
half equation for oxygen
[2O]2- = O2 + 4e-
what are halides containing?
containing group 7 (halogen) and metal ion
electrolysis of aqueous solutions rules are cathode and anode:
at cathode-less reactive element is discharged
at anode-if halide is present, it gets discharged. If not, hydroxide is discharged
when hydroxide is produced at the anode, what is formed and whtat is the equation?
forms water and oxygen
4OH- -> 2H2O + O2 + 4e-
what is the mnemonic for diatomic elements?
HOFBrINCl
what is formed at each electrode and what are the half-equations for electrolysis of sodium chloride solution?
cathode-hydrogen formed (2H+ + 2e- -> H2)
anode-chlorine formed (2Cl- -> Cl2 + 2e-)
what could you use to measure pH?
pH probe attached to pH meter, probe placed in solution and pH is given as numerical value on digital display-more accurate
universal indicator
other indicators-methyl orange, phenolphthalein, litmus
colours of methyl orange indicator:
acidic-red
neutral-yellow
alkaline-yellow
colours of phenolphthalein indicator:
acidic-colourless
neutral-colourless
alkaline-pink
colours of litmus
red litmus
acidic-red
neutral-colourless
alkaline-pink
blue litmus
acidic-red
neutral-blue
alkaline-blue
universal indicator colours:
acids-strong to weak is red to yellow
neutral is green
alkalis weak to strong is blue to purplish
titration curves:
show where neutralisation happens during a reaction
vertical point where solution is neutral- called the end point
how do you calculate overall energy change?
energy required ot break bonds-energy required to make bonds
describe technique of electrolysis using inert and non-inert electrodes:
usually use inert electrodes eg platinum of carbon if products made are reactive
non-intert electelectrodes can decompose into the electroyte eg copper elecrodes in solution of copper sulfate
mass of anode will decrease and mass of cathode will increase because copper is transferred from the anode to the cathode
EXPLAIN what happens at the cathode in aqueous solutions
less reactive one is reduced more easily/gains electrons more easily, so is discharged first