Aldehydes and Ketones
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Nucleophilic Addition
Nucleophile initiates the reaction and the aldeyhde/ketone add together during the reaction
Using NaBH4
Provides hydride ion as a nucleophile (:H-)
Causes reduction of the aldehyde/ketone into an alcohol
Using HCN
HCN formed via NaCN in acid
Provides :CN- as a nucleophile
Mechanism for NaBH4
First is hydride ion
Second is hydrogen from the solvent
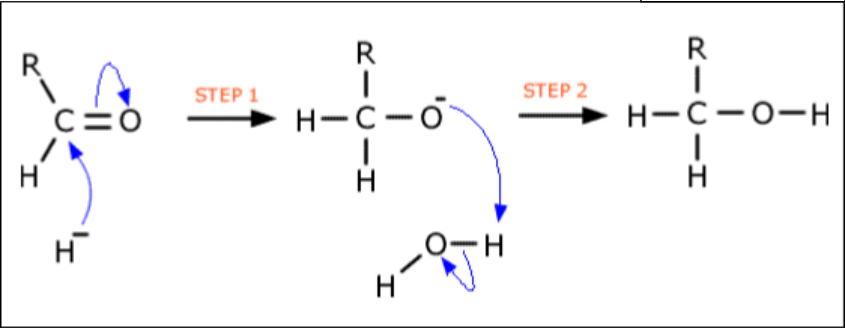
Forming racemate
In aldehydes and ketones the atoms are planar
Nucleophile has an equal probability of attacking from either side
From above, leads to the enantiomer and from below leads to the other enantiomer
Forms a racemic mixture
Using HCN
Forms hydroxynitriles
Image does not show lone pair on oxygen (this needs to be in mechanism!!!)
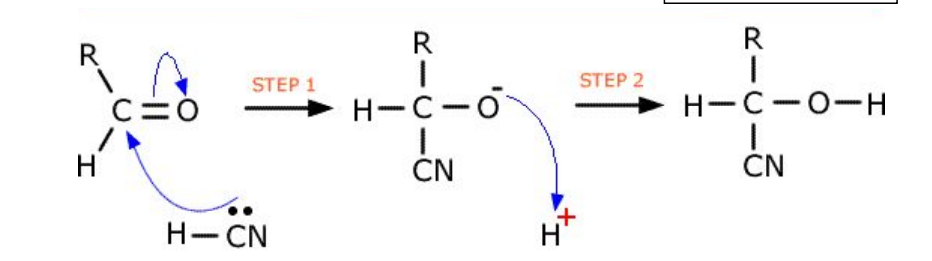
Problems with HCN
HCN used to form hydroxynitriles is toxic and so is generated in situ (in the reaction flask) using aqueous acid and an excess of NaCN or KCN
Why are Hydroxynitriles important
Important intermediate molecules
Can be reacted further through acid catalysed hydrolysis or catalytic reduction
Acid catalysed hydrolysis converts -CN nitrile into -COOH carboyxlic acid
Catalytic reduction converts -CN nitrile into -CH2NH2 amine