Chemistry 2 Exam 3 Chapter 17
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Strong Acids

Hydrochloric acid: (HCl)
Hydrobromic acid: (HBr)
Hydroiodic acid: (HI)
Sulfuric acid: (H₂SO₄)
Nitric acid: (HNO₃)
Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
Perchloric acid: (HClO₄)
Chloric acid: (HClO₃)
pH, Ka, strength
The higher Ka value, lower PH, stronger the acid
Weak Acids

Acetic acid: CH3COOH (organic) or
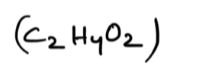
Hydrofluoric acid: HF
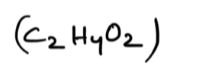
Strong Bases

Sodium Hydroxide: NaOH
Potassium Hydroxide: KOH
Ammonia: NH3
Amine (organic): R [any organic compound] -NH2
Aniline (organic):C6H5NH2
Pyridine (organic):C5H5N
Sodium Bicarbonate: NaHCO3
Sodium Carbonate: Na2CO3
Weak bases

Binary Acids
molecular compounds composed of hydrogen and one other nonmetal element



Sulfuric Acid
(H2SO4)

(
Nitric Acid
(HNO3)

Acetic Acid
(CH3COOH)

Phosphoric Acid
(H3SO4)

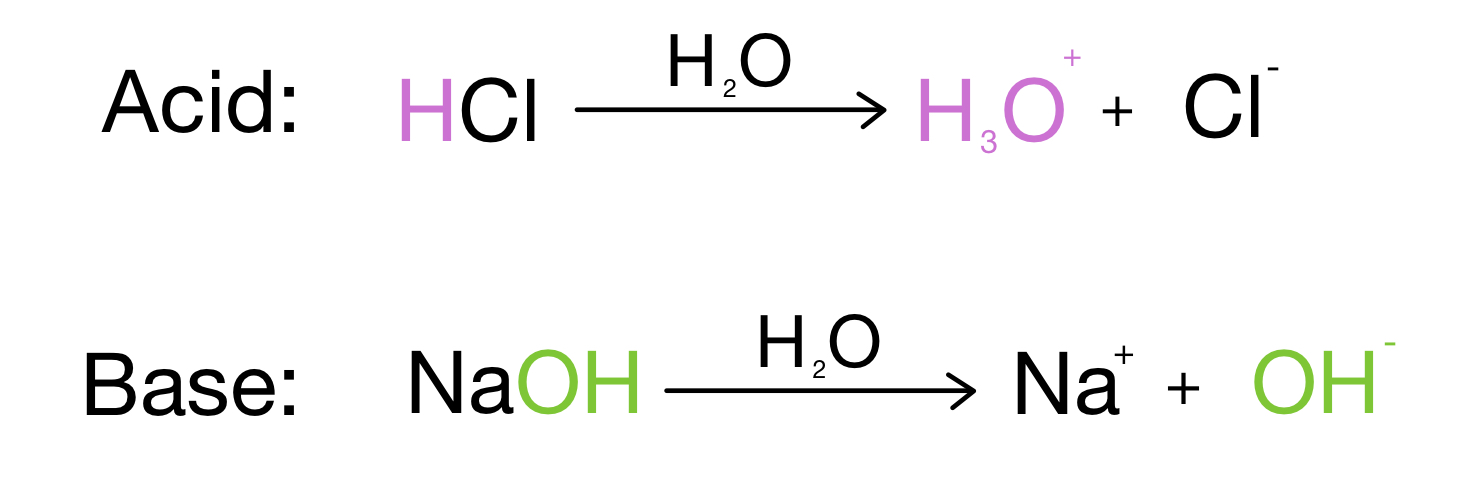
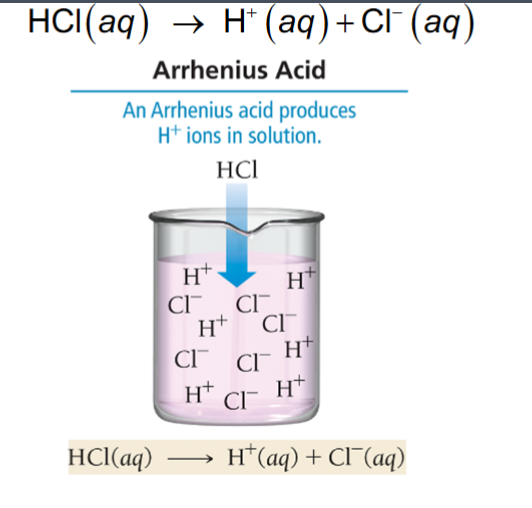
Arrehnius Acid-Bases
Acid: Produces H+ in a solution
H+/H2O
HCl/H2O
H+ +H2O = H3O+
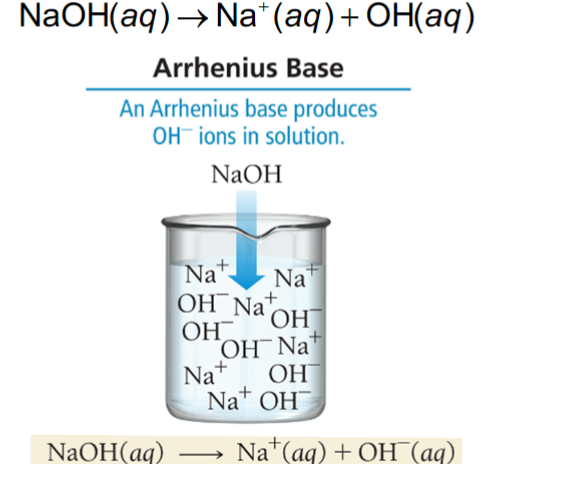
Base: Produces OH- in a solution
-OH (aq)
-OH/H2O
NaOH/H2O

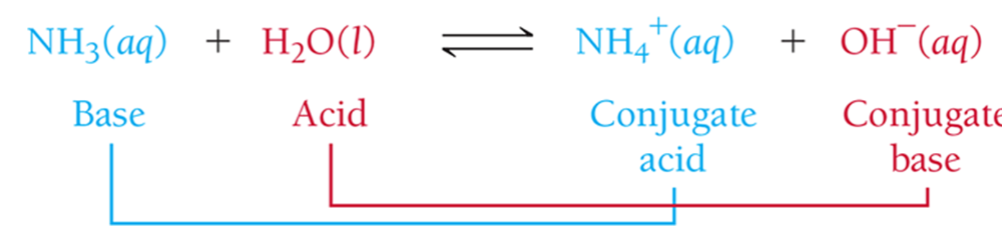
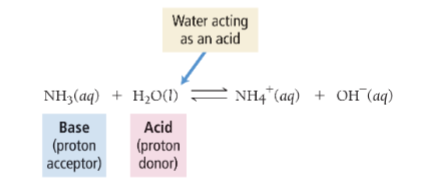
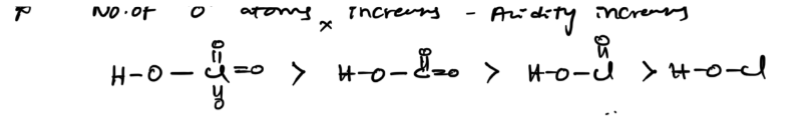
Bronsted Lowry Acid Base
an acid as a proton (H+) donor and a base as a proton (H+) acceptor

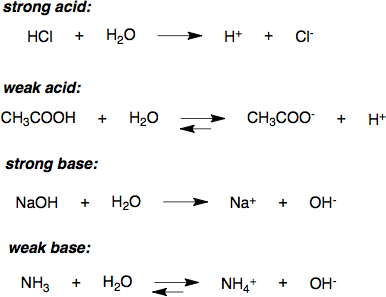
Strength of Acid Bases
STRONG Acid/Bases—> Strong electrolytes (forms ions) + COMPLETLY ionizes (weak bonds)

WEAK Acids/Bases—> Weak electrolytes + PARTIALLY ionizes (strong bonds)
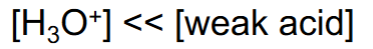
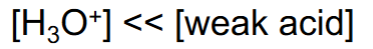
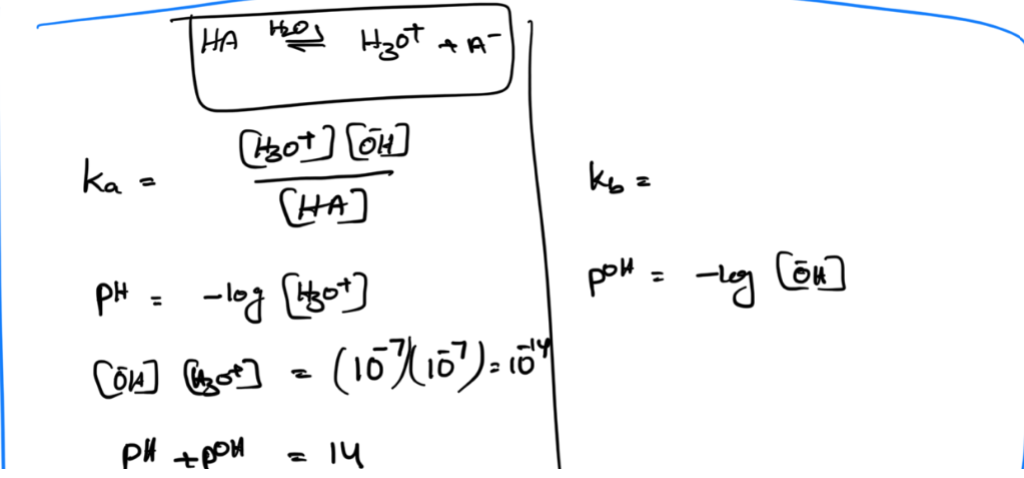
Ionization constant (Ka or Kb)
ignore solids or liquids
[products]/[reactants]
The higher the Ka or Kb value= the stronger the acid/base—> the more it dissociates or breaks down in a solution
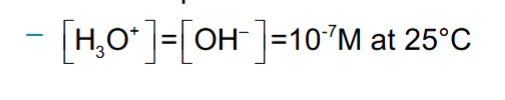
![<ul><li><p>ignore solids or liquids</p></li><li><p>[products]/[reactants]</p></li><li><p>The higher the Ka or Kb value= the stronger the acid/base—> the more it dissociates or breaks down in a solution </p></li></ul><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c603f933-ec61-422f-a731-d0641c35cd31.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center" alt=""><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/22664b10-4f82-4396-8cab-e199ff6a2029.png)
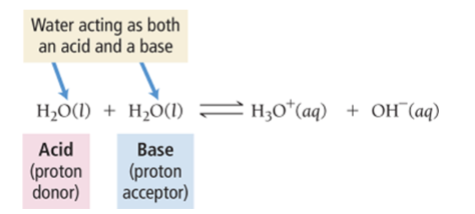
Autoionization of Water

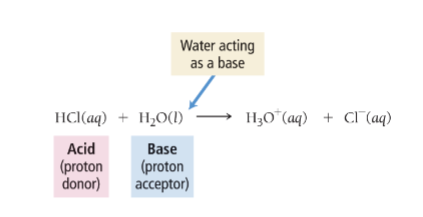
water acts with itself as an acid
and a base to form ion
Kw
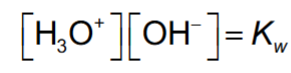
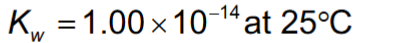
acid vs base


ph scale + equation


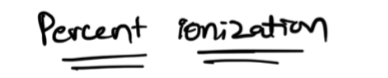
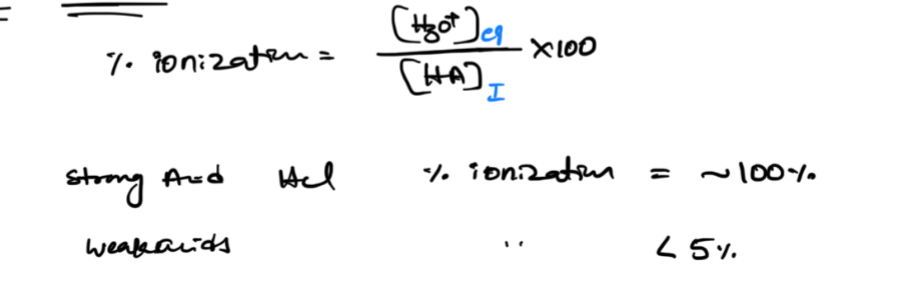


x small
x small does not work if it is similar/close to initial and K values of a weak acid
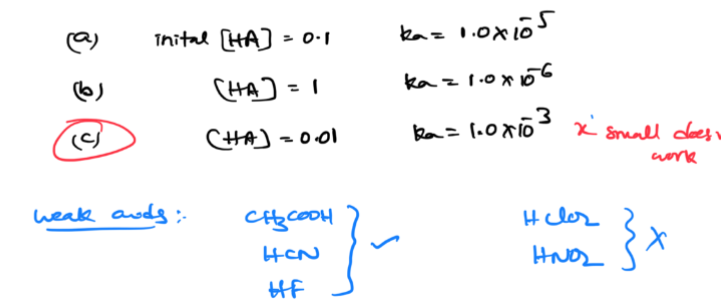
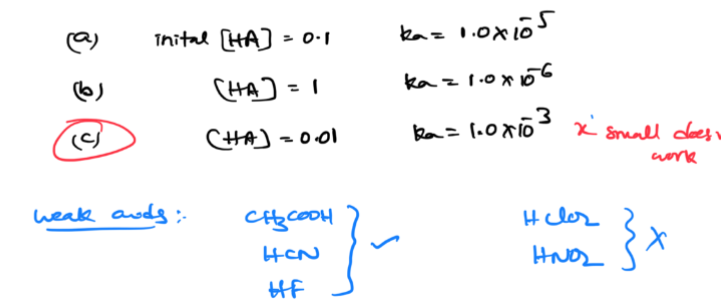
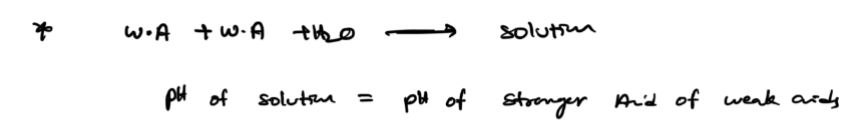
acids /bases equations


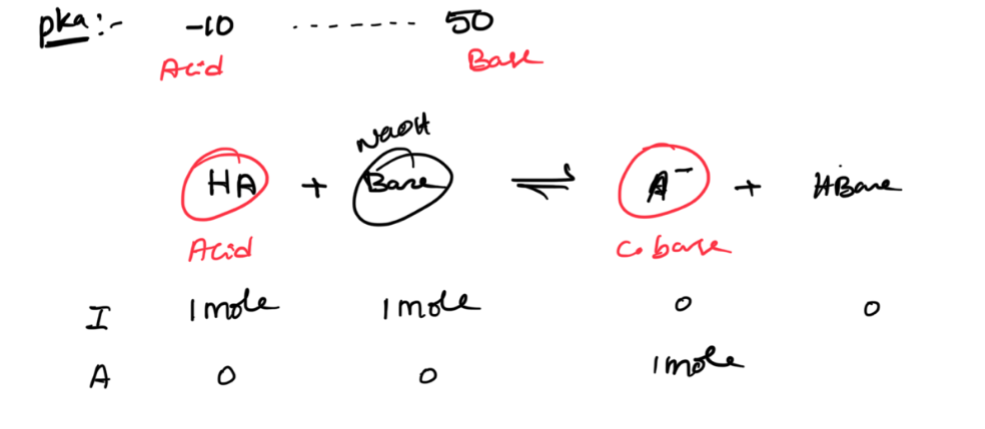
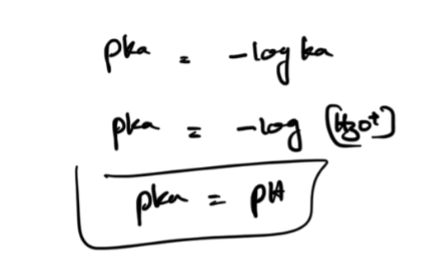
Pka



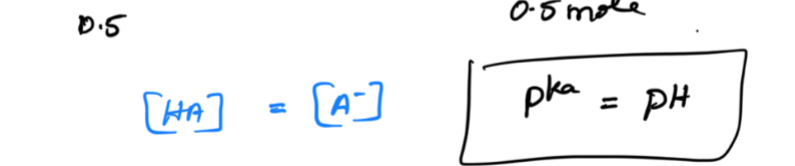
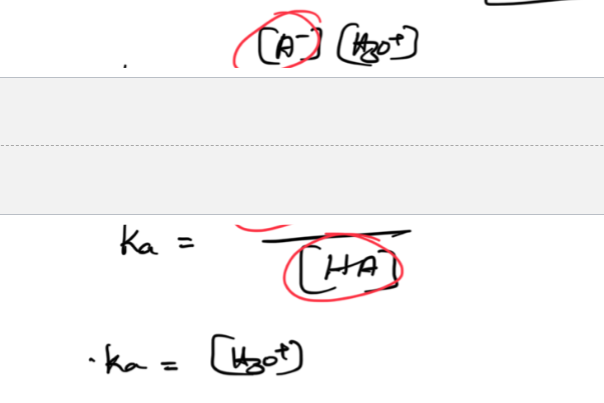



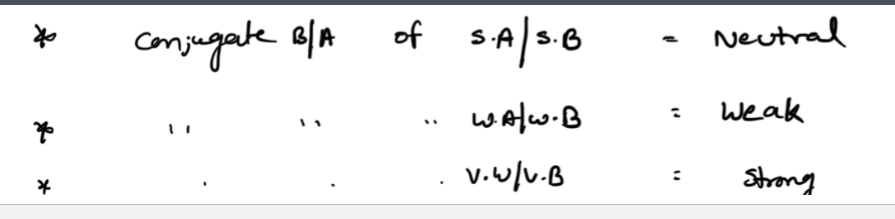






polyprotic acid




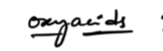

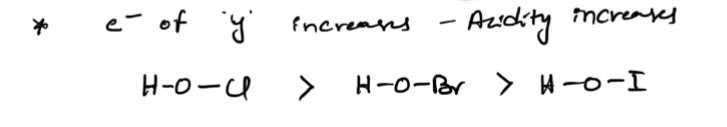



both donates and gains
only lewis acid
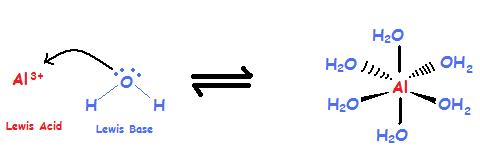


Bastosity
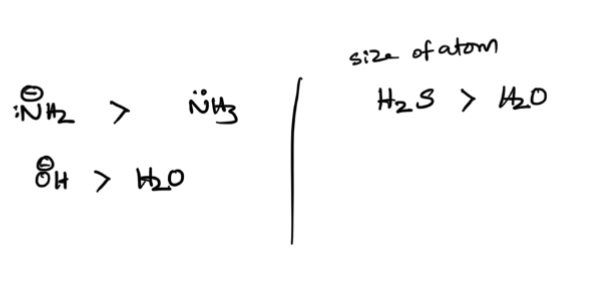
number of atoms + size of the atom

summary of all of them
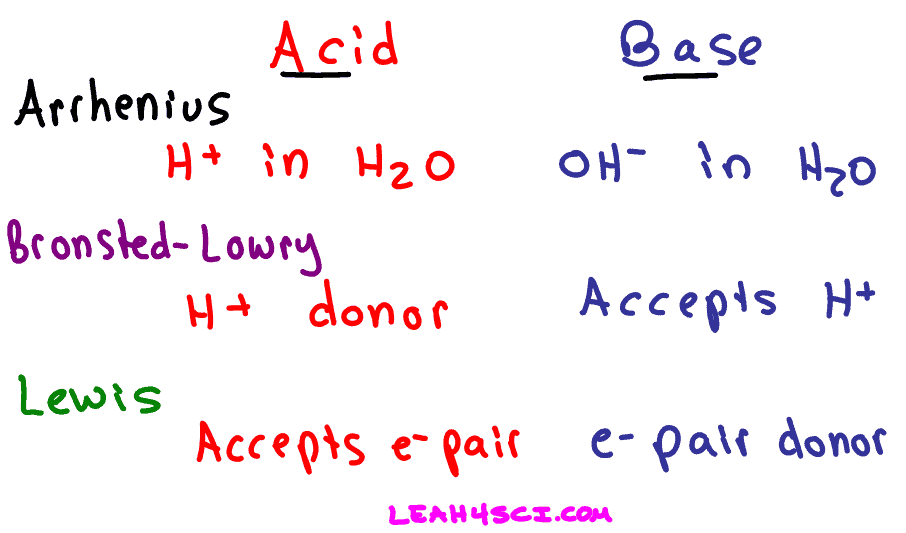
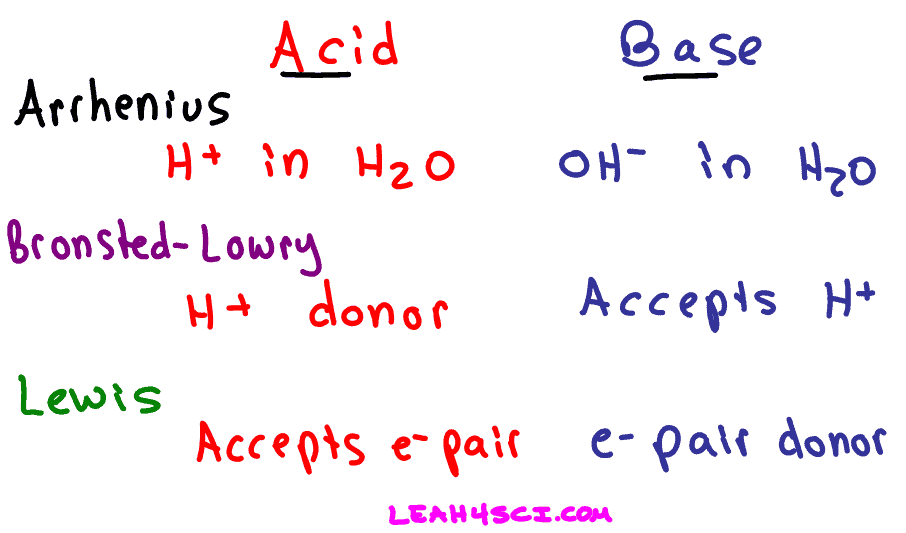
just a lewis acid
anything that has these C+,Fe, Al, and B
because they all accept e-
lewis bases

