Chapter 6 - Proteins and Nucleic Acids
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins.
A chiral carbon (a carbon bonded to 4 different things) bonded to 4 different groups: amino (-NH2), carboxyl (-COOH), a hydrogen (H) atom, and an R group (varies from protein to another)
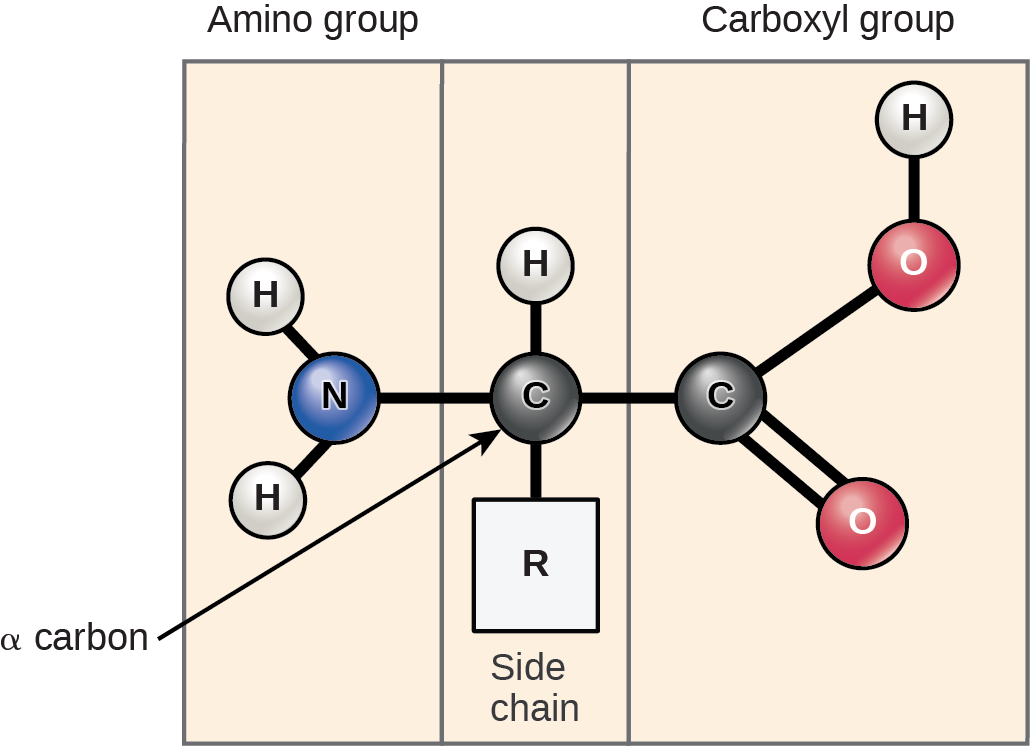
Classification of amino acids based on side chains (R-group)
Non-polar: hydrophobic side chains (have hydrogen and carbon only)
Polar: hydrophilic but uncharged side chains (have hydrogen, carbon, AND oxygen)
Acidic: negatively charged side chains
Basic: positively charged side chains
How are polypeptides formed?
Amino acids are linked together through peptide bonds.
These peptide bonds are formed through dehydration synthesis (a water is removed) and involve the carboxyl group of an amino acid reacting with the amino group of another.
Levels of protein structure (4)
Primary: linear sequence of amino acids
Secondary: regular structures like alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets are stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
Tertiary: 3D shape due to interaction between side chains (R groups of amino acids)
Quaternary: association of multiple polypeptide subunits.
Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA
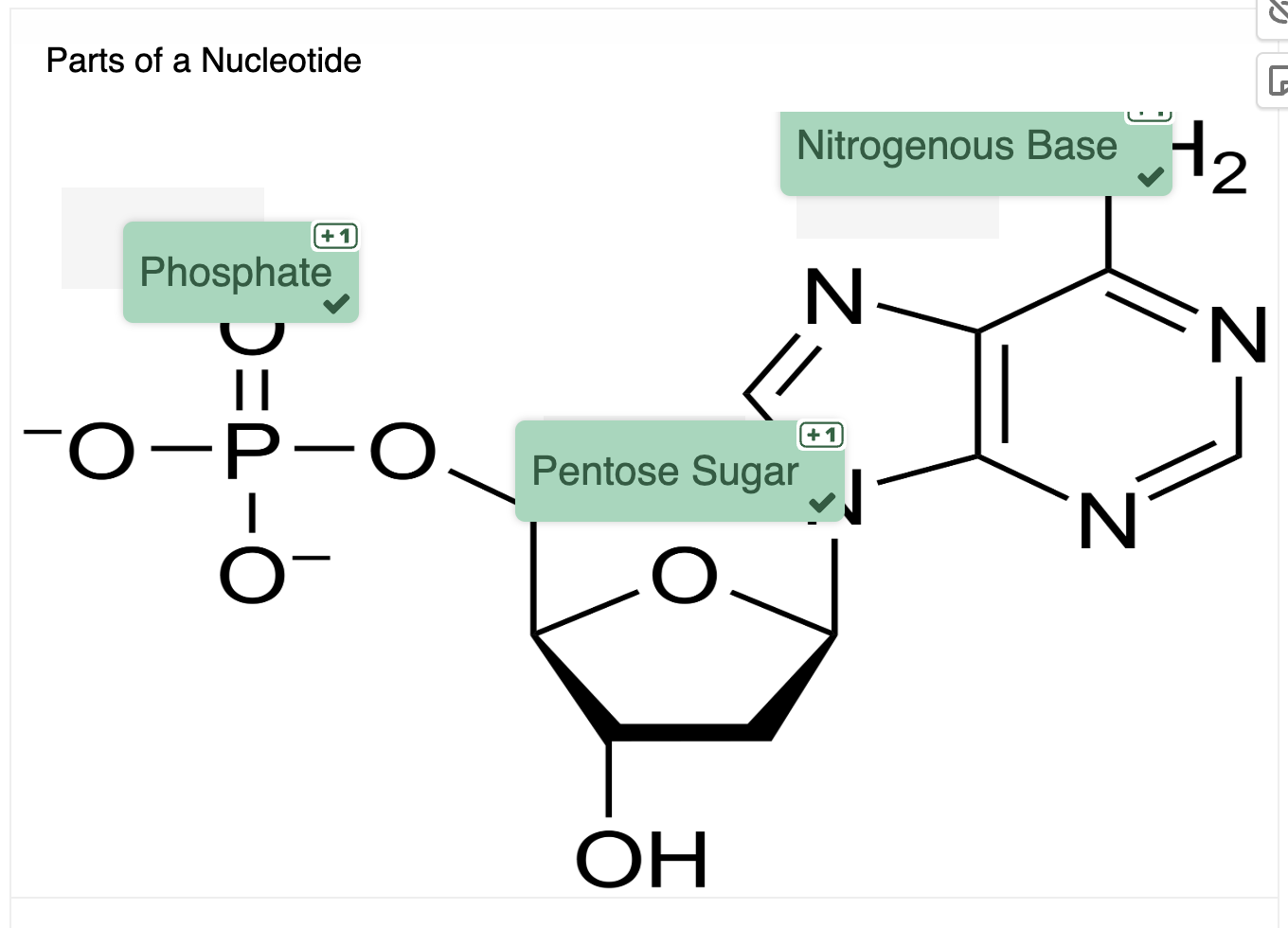
Nucleotides
Building blocks (monomers) of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
Composed of a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
DNA vs RNA function
DNA: stores genetic information.
RNA: translates genetic information into proteins.
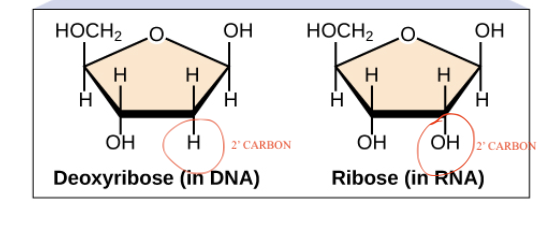
Five-carbon (pentose) sugar in DNA vs RNA.
DNA: Five-carbon sugar is deoxyribose. Has an extra -H on ‘2 carbon
RNA: Five-carbon sugar is ribose. Has an extra -OH on the ‘2 carbon.
Polynucleotides
Nucleotides bonded together.
Bonded through phosphodiester bonds.
the 3’ hydroxyl group of the sugar of a nucleotide interacts with the 5’ phosphate group of another nucleotide.