Functions of the skeleton
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
functions of the skeleton
support - supports softer tissue and provides points of attachment for most skeletal muscles
protection - reduces risk of injury by providing mechanical protection for the body’s organs
movement - muscles are attached to bones and when they contract the bones move
blood production (haematopoiesis) - red blood cells (erythrocytes), which carry oxygen, and white blood cells (leucocytes), which protect against infection, are produced in the bone marrow of some bones
storage of minerals - bones store minerals, including phosphorus (P) and calcium (Ca), which are released into the blood when required
haematopoiesis
blood production
another name for red blood cells
erythrocytes
another name for white blood cells
leucocytes
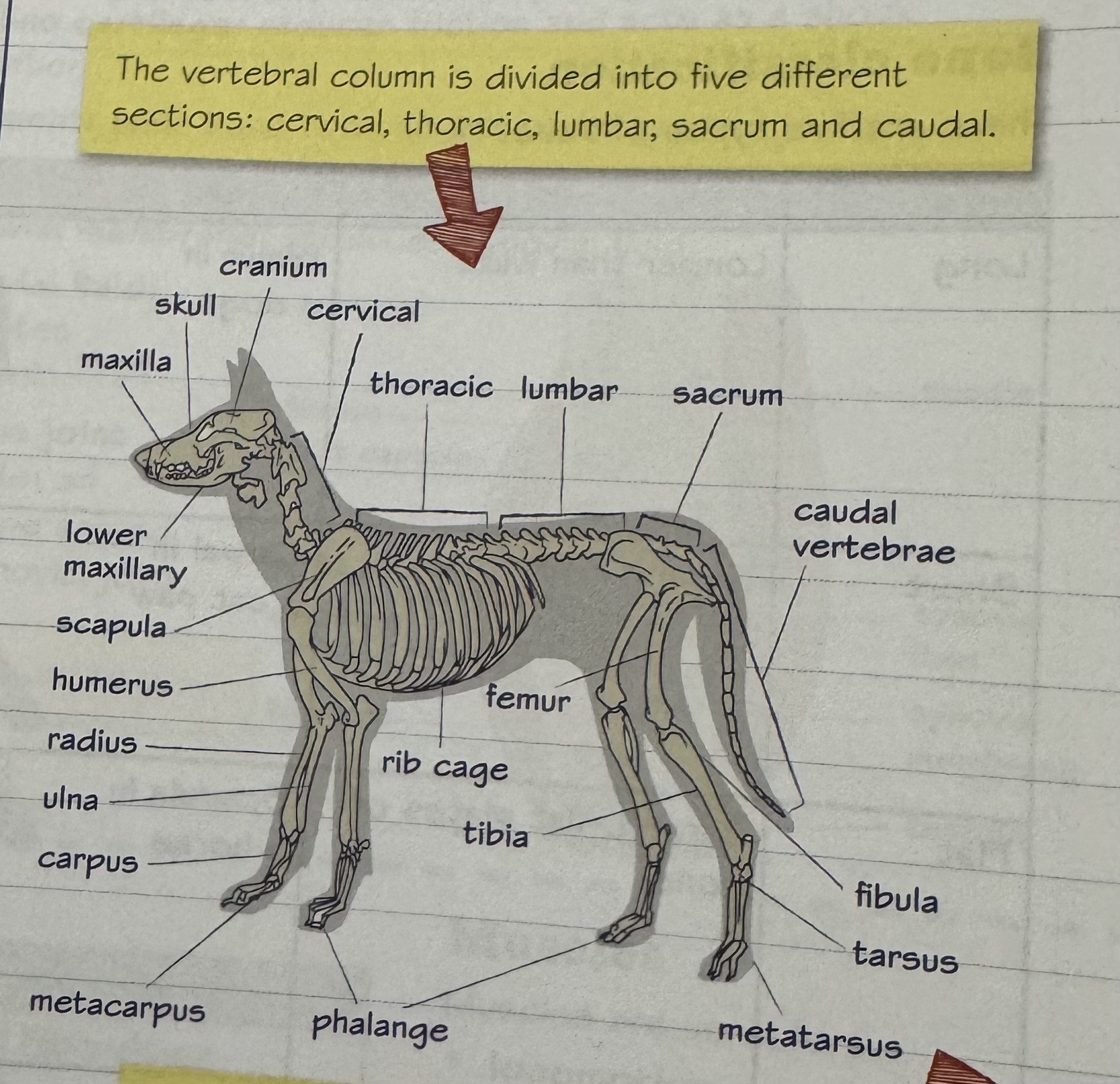
components of a basic four-legged mammal skeleton
cranium, skull, maxilla, lower maxillary, scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, carpus, metacarpus, phalange, rib cage, femur, tibia, metatarsus, tarsus, fibula, vertebral column (caudal vertebrae, lumbar, thoracic, cervical, sacrum)
divisions of the vertebral column
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, caudal vertebrae
four-legged mammal skeleton diagram
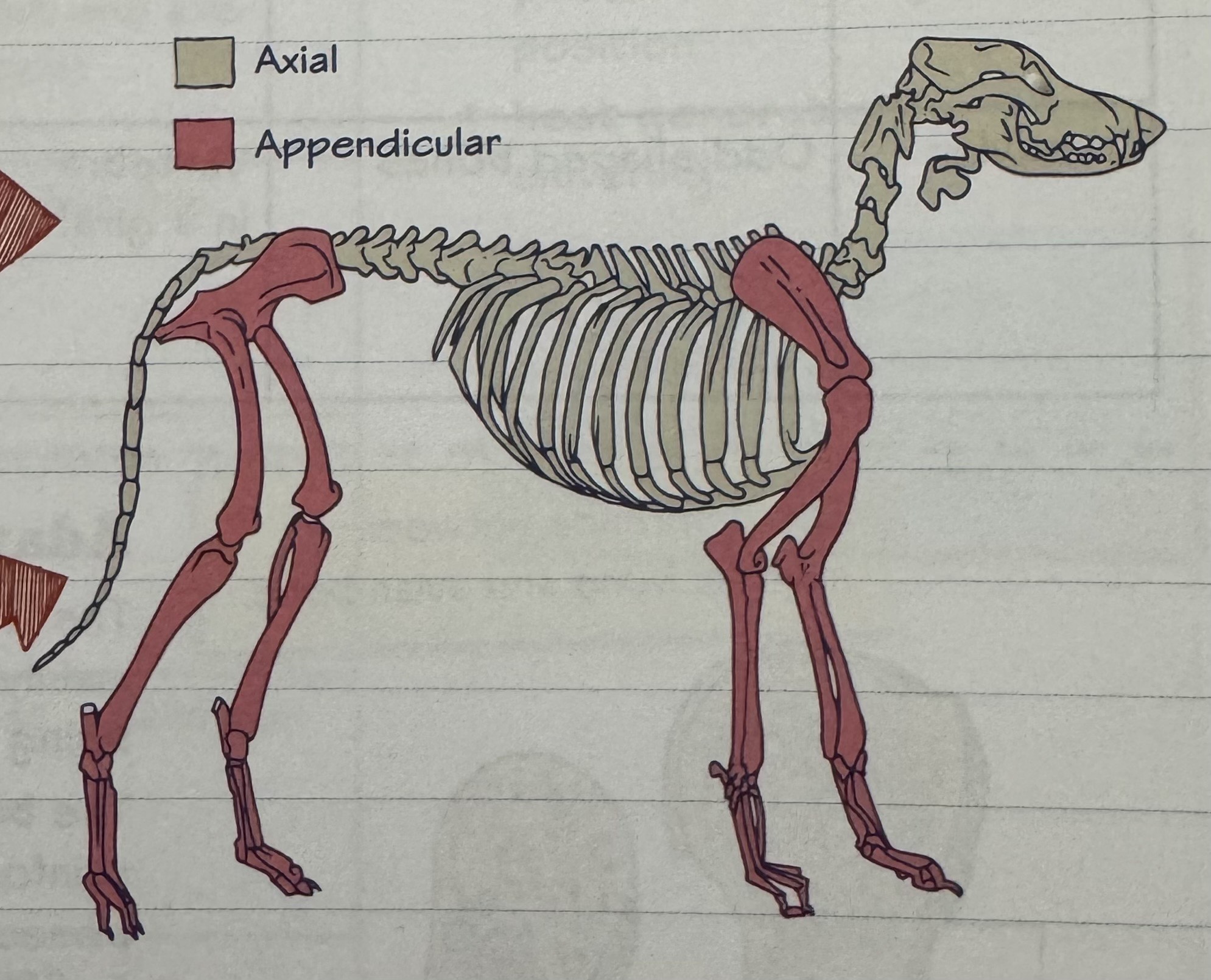
axial skeleton
bones that make up the head and trunk of the body
appendicular skeleton
appendage bones - called this because they are appendages of the axial skeleton
consists of the bones of the upper and lower limbs (limb bones), and the bony girdles that support them on the body trunk
appendicular skeleton function
the bones enable the body to move and protect some organs
what are the bones of the appendicular skeleton called?
appendage bones
why are appendage bones called that?
because they are appendages of the axial skeleton
axial and appendicular skeleton of a four-legged mammal diagram