Anatomy of Skeletal Muscles
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are Prime movers - Agonists
The muscle that contracts and produces the primary movement
Biceps brachii is the prime mover, contracting to flex the elbow
What are antagonists
The muscle that opposes the prime mover's action, helping to control or slow down the movement.
Triceps brachii is the antagonist, lengthening and relaxing to allow the elbow to flex
What are Synergists
Muscles that assist the prime mover in performing a joint action, either by adding force or by stabilizing the joint.
Brachialis and brachioradialis are synergists that help to flex the elbow
What are Stabilizers - Fixators
Muscles that stabilize the origin of the prime mover, allowing the prime mover to contract more effectively.
Muscles of the shoulder and scapula act as fixators, stabilizing the shoulder joint to allow the biceps to contract effectively
Gross Anatomy
Each skeletal muscle is a discrete organ made up of hundreds to thousands of muscle fibres (muscle cells)
Muscle fibres are bundled into groups called fascicles
Fascicles are then
grouped together to
form the whole
muscle
Also, within each muscle are substantial amounts of connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerve fibres
What are Connetive Tissue layers
Each muscle is held together by several different layers of connective tissue
Connective tissue is used to protect and support the soft and fragile muscle fibres, reinforce the muscle as a whole, and provide elasticity to the muscle tissue
Blood vessels and nerve fibres enter and exit through the connective tissue layers
What is the Epimysium
Epimysium = surrounds all of fascicles = entire muscle
What is the Perimysium
Perimysium = surrounds fascicles (muscle fibres bundled together)
What is the ENdomysium
Endomysium = connective tissue that surrounds individual muscle fibre
More abt connective tissue
Connective tissue gets coarser the further out it goes from the muscle fibre
All these connective tissue sheaths are continuous with each other as well as with the tendons that join the muscles to bones
When muscles fibres contract, they pull on these sheaths, which then transmit the force to the bone to be moved
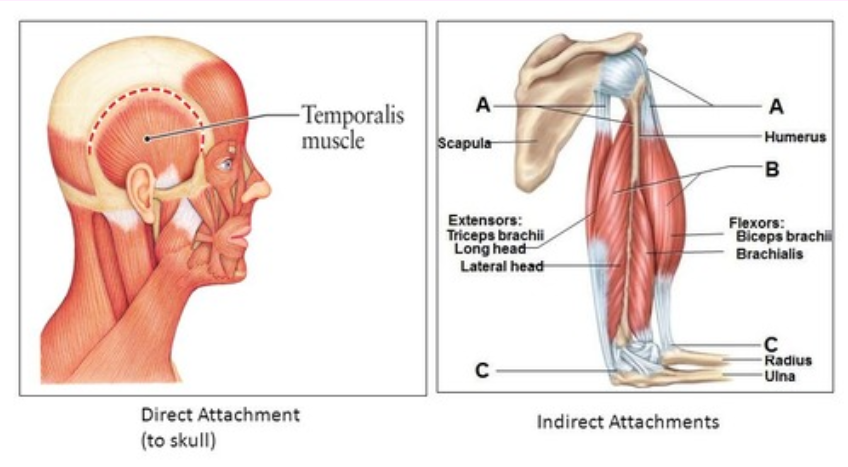
Muscle attatchment to bone
Attaches directly or indirectly
Direct - epimysium adheres to and fuses with periosteum (outer membrane that covers bone)
Indirect - epimysium extends past muscle as a tendon and then attaches to periosteum of bone (most common type)
Direct vs. Indirect
(muscle attachment to bone)
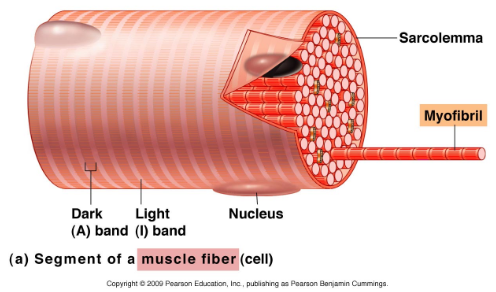
One Muscle fiber(cell)
Contains myofibrils (contractile units)
Surrounded by plasma membrane called sarcolemma (just below endomysium) and contains sarcoplasm (muscle cells cytoplasm)
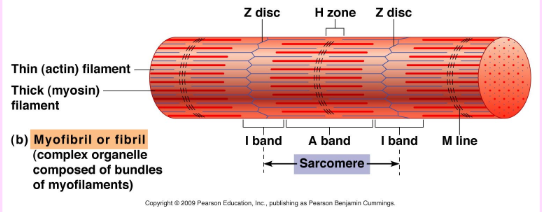
What are Myofibrils
Thread-like (or rod-like) structures that run along entire length of muscle fibre
Contractile elements of skeletal muscle cells
Contain even smaller contractile units called sarcomeres
Think of one myofibril as a train – then picture hundreds to thousands of these myofibrils/trains running side by side in one muscle fibre
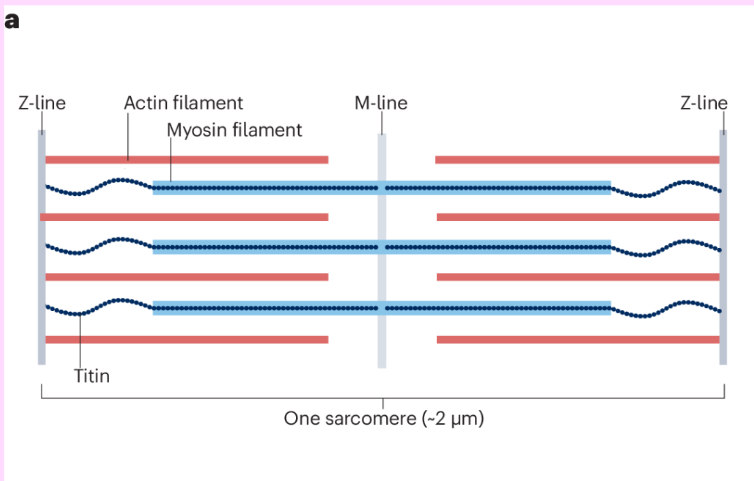
What are Sarcomeres
Compartments along the myofibrils that contain filaments (actin & myosin)
Allow for muscle contraction
Picture sarcomeres as the cars in the train
What are Filaments
Delicate fibres that are found within each sarcomere
These are what slide past each other to contract (shorten) the muscle
actin – thin filament
myosin = thick filament, has heads and tails