Exocrine Pancreas (Hyperglycemia)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Alpha
Which pancreatic cells secrete glucagon?
Beta
Which pancreatic cells secrete insulin?
Delta
Which pancreatic cells secrete somatostatin?
Yes
Should animals be fasted 8-12 hours prior to sampling to avoid post-prandial increases of glucose?
Decrease
Will glucose values in samples decrease or increase by 5-10% per hour in unseparated serum? Increased leukocytes or platelets will also alter it in this direction.
Sodium Fluoride
What tubes used for glucose samples are hypertonic and cause lysis of RBCs, release intra-erythrocyte water, dilute the glucose concentration, and generally have lower values than in promptly separated serum samples? Lipemia and hemolysis may interfere with methodology also.
Whole blood
Is whole blood, serum, or plasma used in house glucose meters (glucometers)? They usually read a few units lower than commercial analyzers.
No
Is the value of glucose in serum and plasma equal to that in whole blood? As hematocrit increases, there is less water in the sample and therefore less glucose.
Hyperglycemia
Excitement, epinephrine, stress/steroids, and post-prandial states are physiologic causes of what blood glucose condition?
Hyperglycemia
Diabetes mellitus and some other endocrine diseases are pathologic causes of what blood glucose condition?
Dog
In which animal does the glucose seldom exceed 150 mg/dL when due to excitement?
Cat
In which animal can excitement and fear increase glucose over 300-400 mg/dL?
Fructosamine
The serum what level is used to differentiate stress from DM when hyperglycemia is present in both dogs and cats?
Duodenum
A proximal obstruction of what GI tract component in cattle can cause hyperglycemia (250-1000 mg/dL), while insulin levels will remain normal? Stress will increase the glucose, decreased uptake will lead to shock and dehydration, and animals with abomasal volvulus will have lower levels (100-200 mg/dL).
Colic
What condition in horses will cause hyperglycemia due to stress and decreased peripheral use, and the hyperglycemia will be prognostic? Over 200 mg/dL will indicate severity, and over 300 mg/dL will indicate poor prognosis.
Cushing’s
What disease in small animals will cause hyperglycemia due to steroids, leading to increased gluconeogenesis and glucagon release?
PPID
What disease in horses will cause hyperglycemia due to secreting excess GH or ACTH, causing increased insulin resistance and increased cortisol?
Hyperthyroidism
What condition of many animals will cause hyperglycemia due to decreased insulin secretion?
Yes
Will fluids with glucose/dextrose, ketamine, ovarid, thyroxine, and xylazine/detomidine cause hyperglycemia?
I
Dog breeds like keeshond, malamute, doberman, miniature schnauzer, poodle, retriever, and greyhounds, among others, are all prone to which type of diabetes mellitus?
Amyloidosis
Type II diabetes in cats is usually due to feline pancreatic what protein condition? Insulin resistance will result, leading to increased glucagon production and hyperglycemia. The amount of this protein deposited will correlate directly with the degree of glucose intolerance seen.
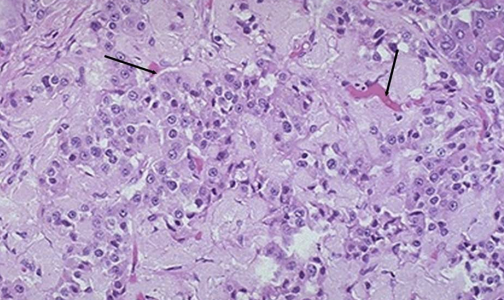
Yes
Is insulin resistance/hyperglycemia in obese cats reversible?
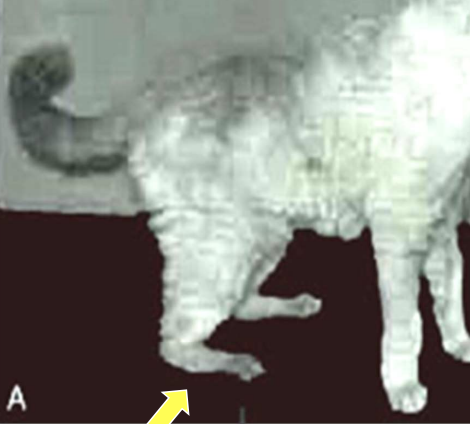
Plantigrade
What type of stance in the hind limbs can be observed in cats with diabetes mellitus?

Ketoacidosis
What complication resulting from diabetes mellitus/hyperglycemia will involve anorexia, vomiting, coma, dehydration, shock, Kussmaul respiration, and an acetone smell?
Stress
What type of leukogram, as well as an inflammatory leukogram, can be seen in animals with diabetes mellitus? Increased PCV and proteins will be seen, as well as increased MCV as an artifact due to the hyperglycemia.
Heinz Bodies
What CBC abnormality will be seen in cats with diabetes mellitus?
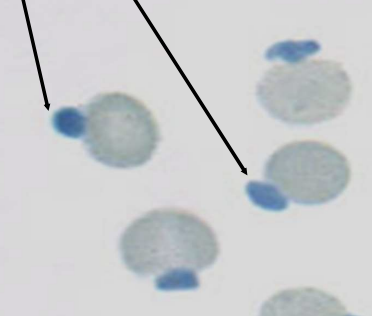
Acetoacetate, Acetone
Which two ketone bodies are measured on a dipstick?
Yes
Are persistent hyperglycemia and glucosuria diagnostic for diabetes mellitus?
Increase
Will ALT, AST, ALP, GGT, cholesterol, and triglycerides all increase or decrease in diabetes mellitus/hyperglycemia? This is often secondary to hepatic lipidosis, and less commonly can occur to bile acids and bilirubin as well.
Hypokalemia
What blood ion condition can develop due to hyperglycemia, due to insulin administration? Administration drives K into cells, can cause total body K deficiency, excretion of K with ketones bodies, and can lead to a namesake myopathy.
Prerenal
What type of azotemia can occur in diabetes mellitus/hyperglycemia?
Hypo
Will hyper- or hypo- -natremia, -chloremia and -phosphatemia occur in diabetes mellitus/hyperglycemia? This can lead to intravascular hemolytic anemia.
Serum
A red-top or what tube is required for clinical chemistry in a diabetes mellitus/hyperglycemia patient when testing for fructosamine?
Yes
Can hypoproteinemia and hypoalbuminemia cause decreased fructosamine values?
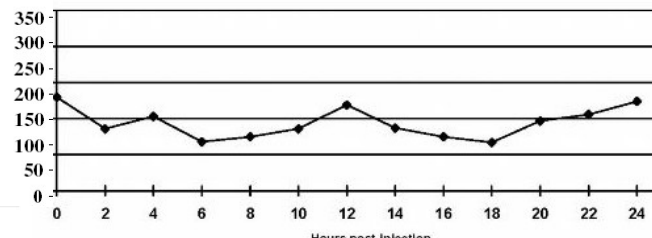
Good
Does the curve indicate good or poor glycemic control?
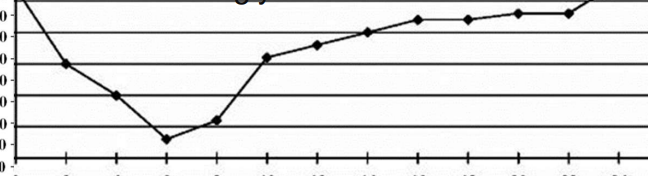
Poor
Does the curve indicate good or poor glycemic control?
No
Is fructosamine useful in differentiating DM from stress hyperglycemia in cats with hyperthyroidism? It can be low due to accelerated protein turnover.
HHNKS
What syndrome (five letters) occurs as an uncommon complication due to untreated DM? It is an emergency and has poor prognosis, is characterized by extremely high blood glucose, and results in hyperosmolality with minimal ketosis.
Somogy
What effect occurs due to administration of too much insulin? It causes marked hypoglycemia, then increased glucagon release, gluconeogenesis, and glycogenolysis, then hyperglycemia.
Insulin Resistance
Animals requiring over 1.5-2 U of insulin per day or with fructosamine over 700 umol/l should be evaluated for what condition? This can be due to glucocorticoids, catecholamines, progestagens, and thyroid hormones. Acromegaly in cats, and other conditions can also cause it.
60
In the intravenous glucose tolerance test in dogs, normal blood glucose should occur within how many minutes post glucose/dextrose administration?
Equine Metabolic Syndrome
What condition, abbreviated EMS, occurs in horses with chronic insulin resistance without PPID? Obesity and regional adiposity will be seen. They will also show hypertension, hyperleptinemia, and increased risk of laminitis.
