Anatomy and Physiology: Chapter 2 section 1 Atoms, Molecules, and Compounds
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Chemistry is a science that
studies the structure of matter
Matter
Anything that takes up space and has mass
Atoms
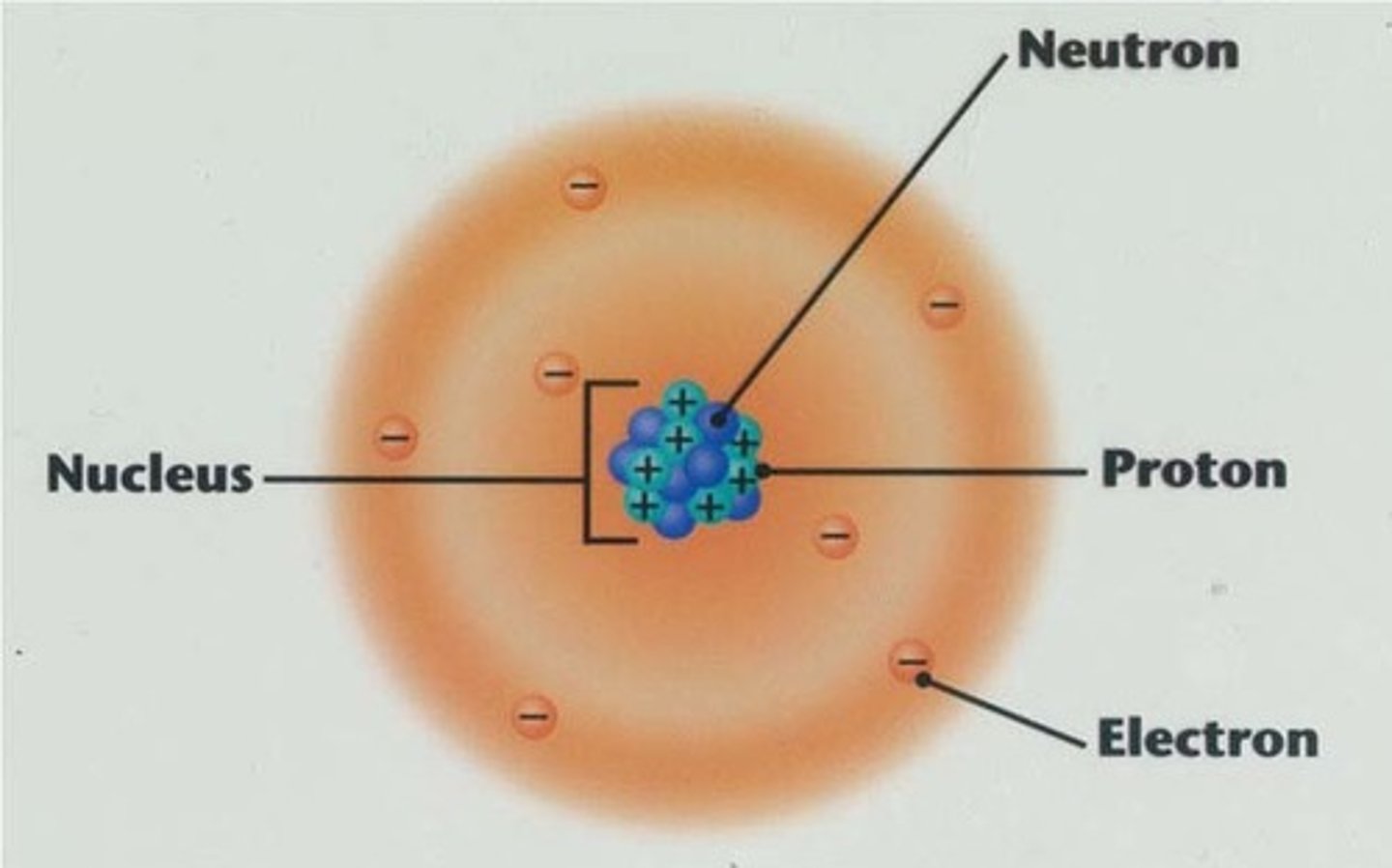
Smallest stable unit of matter, composed of three important subatomic particles. (p = n = e-)
What are the three important subatomic particles of an atom?
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
What is the charge of the three subatomic particles?
Protons - Positive (p+) +1
Neutrons - Neutral/uncharged (n or n^o) 0
Electrons - Negative (e-) -1
What determines the mass of an atom and why?
Protons and neutrons because electrons are very light
What is the relationship between an atom and matter?
An atom is the smallest stable unit of matter, and matter is anything that takes up space and has mass.
Atoms can be subdivided into
the nucleus and the electron cloud.
The nucleus in an atom
Lies at the center of the atom, it contains one or more protons and may contain neutrons as well
The electron cloud is
A spherical region/space around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are likely to be found orbiting around the nucleus often shown as an electron shell
Valance electrons
the number of electrons in the outermost energy level
Valance electrons determine
An atoms stability and chemical reaction
Atomic number
= number of protons in an atom
Mass =
protons + number of neutrons (in an atom)
Element is a
Pure substance composed only of atoms with same
atomic number
Isotopes
are atoms whose nuclei contain the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons.
atomic mass (amu)
The average mass of all the isotopes of an element
Principal Elements of the Human Body
Thirteen most abundant elements by body weight
1. Oxygen, O (65 % of total body weight)
2. Carbon, C (18.6 % of total body weight)
3. Hydrogen, H (9.7 % of total body weight)
4. Nitrogen, N (3.2 % of total body weight)
5. Calcium, Ca (1.8 % of total body weight)
6. Phosphorus, P (1.0 % of total body weight)
7. Potassium, K (0.4 % of total body weight)
8. Sodium, Na (0.2 % of total body weight)
9. Chlorine, Cl (0.2 % of total body weight)
10. Magnesium, Mg (0.06 % of total body weight)
11. Sulfur, S (0.04 % of total body weight)
12. Iron, Fe (0.007 % of total body weight)
13.Iodine, I (0.0002 % of total body weight)
Trace elements
Fourteen other elements present in the body in very
small amounts
Atoms are electrically neutral because
they contain equal numbers of protons and electrons
(Cl, O, Na etc... contains no charge)
Valence shell (atom's surface)
The outermost energy level of electrons. The amount of electrons in this energy level determines the chemical properties of the element
Atoms with unfilled outer shells are
reactive
How many electrons can the first three energy levels hold?
First level - 2
Second level - 8
Third level - 8
inert (nonreactive)elements
are stable elements with filled valence shells that do not readily react with other elements because they already have 8 valence electrons, these elements are called "Noble gases"
Reactive elements
are elements with unfilled valence shells that readily interact or combine with other atoms
In Two ways:
Sharing electrons
Gaining or losing electrons
chemical bonds form
molecules and compounds
Ions are
charged atoms that have gained (cation) or lost (anion) electrons
Cation (metals)
An ion with a positive charge, formed by losing electrons
- Fewer electrons (negative) than protons (positive)
such as Na+
Anion (nonmetals)
An ions with a negative charge, formed by gaining electrons
- More electrons (negative) than protons (positive)
such as Cl-
Compound
Chemical substance made up of atoms of two or more
different elements in a fixed proportion, regardless of
type of bond joining them.
Ionic bonds (compounds formed by metals bonded to nonmetals)
Occur when the valence electrons of atoms of a metal (cation) are transferred to atoms of a nonmetals (anion).
For example, sodium atoms lose electrons and chlorine atoms gain electrons to form the ionic compound NaCl.
Covalent bonds (molecules formed only by nonmetals bonding)
Occurs when atoms of nonmetals (anions) share valence electrons equally, and there is no electrical charge on the molecule
For example, In the molecular compounds H2O and C3H8, atoms share electrons.
Molecules
chemical structure consisting of one or more elements held together by covalent bonds (nonmetals).
Single covalent bond
sharing 1 pair of electrons
Double covalent bond
sharing 2 pairs of electrons
Free radical
Ion or molecule that contains unpaired electrons in its outermost energy level. They are highly reactive
nonpolar molecule (formed by a nonpolar covalent bond)
Equal sharing of electrons between atoms (no electrical charge)
- such as O2 and CO2
Polar molecule (formed by polar covalent bonds)
Unequal sharing of electrons between atoms (electrical charge)
- such as H2O
Hydrogen bond
H attache to a F, O or N
What are the three states in which matter can exist?
Solid - Maintains volume and shape
Liquid - Constant volume but indefinite shape (container determines shape)
Gas - Indefinite volume and shape ( can be compressed or expanded and fill a container of any size)
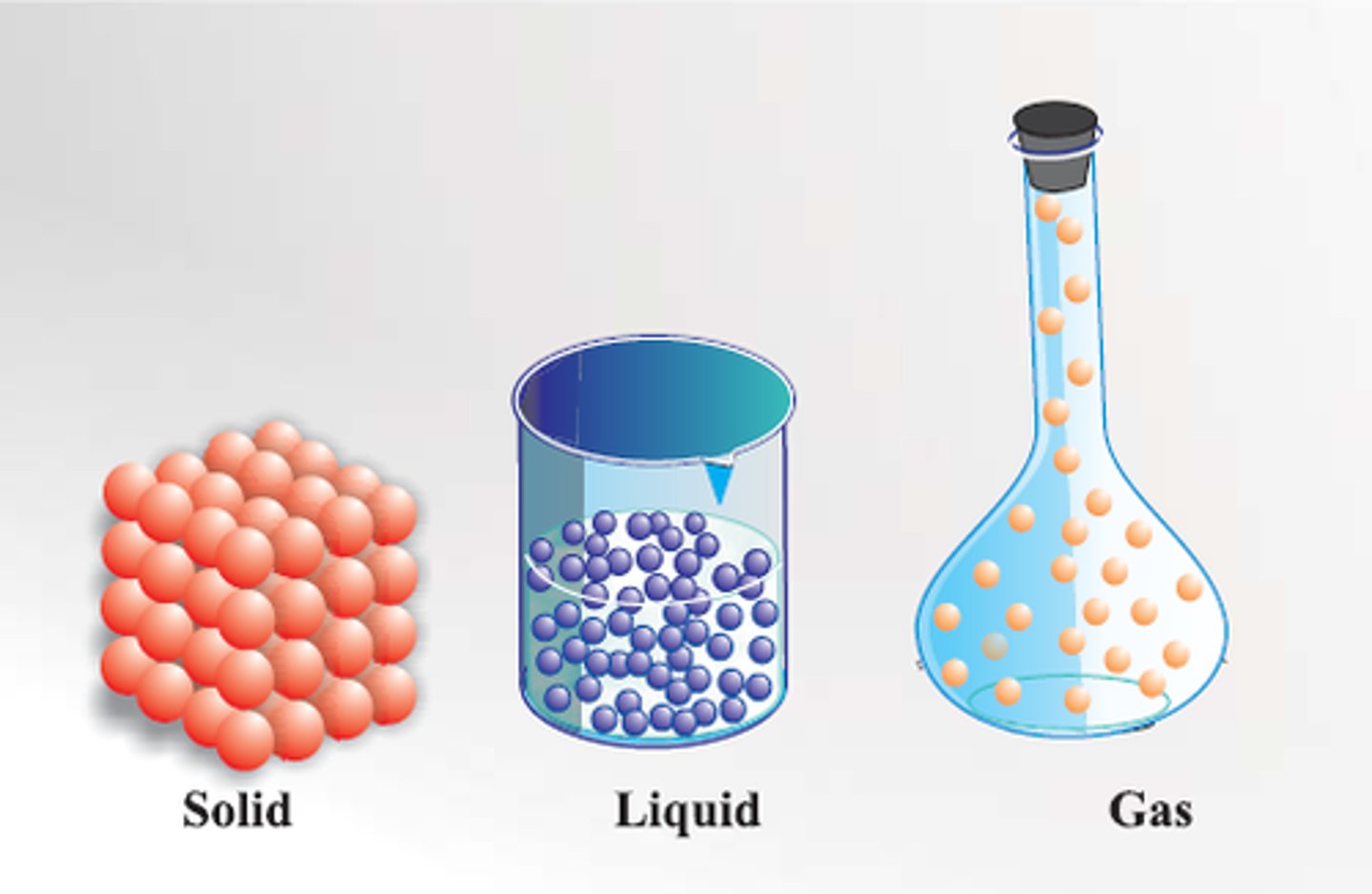
State of Matter: Solid
Maintains volume and shape at ordinary temperatures and pressure
- such as a brick
State of Matter: Liquid
Constant volume but indefinite shape (container determines shape)
-
State of Matter: Gas
• Has neither a constant volume nor a fixed shape
• Can be compressed or expanded
• Will fill a container of any size
Only substance that exists in all three states of matter at temperatures compatible with life
Water:
- Solid (ice)
- Liquid (water)
- Gas (water vapor)
Surface tension
Barrier that keeps small objects from entering the water
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in their number of which particles?
A. protons
B. neutrons
C. daltons
D. electrons
B
By weight, the two most common elements in the human body are _________.
A. calcium and phosphorus
B. sodium and chlorine
C. carbon and hydrogen
D. oxygen and carbon
D
Which of the following is a characteristic of ionic bonds?
A. The participating atoms share their electrons unequally.
B. The participating atoms bond asymmetrically, forming polar molecules in which one atom carries a slightly positive charge and the other atom carries a slightly negative charge.
C. The electrical attraction between the participating atoms involves the transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another atom.
D. The participating atoms share their electrons equally.
C
Which characteristic is true of liquids?
A. It can be compressed or expanded.
B. Its shape is determined by the shape of its container.
C. It does not have a constant volume.
D. It has a fixed shape.
B
Which principal element of the human body functions as a cofactor for many enzymes?
A. Mg (magnesium)
B. K (potassium)
C. Na (sodium)
D. N (nitrogen)
A
The loss of electrons from the outer energy level results in:
A. an atom with a net positive charge.
B. no electrical charge to the atom.
C. an atom with a net negative charge.
D. an electrically neutral atom.
A
Which of the following is a trace element of the human body?
A. magnesium
B. phosphorus
C. manganese
D. sulfur
C
An atom that has a net positive charge is called a positive ion, or cation, whereas an atom that has a net negative charge is called a negative ion, or
anion
The polar charges on water molecules give water the ability to disrupt the _______________ bonds of a variety of inorganic compounds.
ionic
In a typical ___________________ bond, the participating atoms share the electrons equally, and there is no electrical charge on the molecule.
covalent
H2O forms what type of bond
A. Ionic bond
B. Single covalent bond
C. Double covalent bond
D. Two double covalent bonds
E. Polar covalent bonds
E
O2 forms what type of bond
A. Ionic bond
B. Single covalent bond
C. Double covalent bond
D. Two double covalent bonds
E. Polar covalent bonds
C
H2 forms what type of bond
A. Ionic bond
B. Single covalent bond
C. Double covalent bond
D. Two double covalent bonds
E. Polar covalent bonds
B
CO2 forms what type of bond
A. Ionic bond
B. Single covalent bond
C. Double covalent bond
D. Two double covalent bonds
E. Polar covalent bonds
D
NaCl forms what type of bond
A. Ionic bond
B. Single covalent bond
C. Double covalent bond
D. Two double covalent bonds
E. Polar covalent bonds
A
The loss of electrons from the outer energy level results in:
A. an electrically neutral atom.
B. an atom with a net negative charge.
C. an atom with a net positive charge.
D. no electrical charge to the atom.
C
Which type of bond is formed when one oxygen atom bonds with a second oxygen atom?
A. peptide bond
B. double covalent bond
C. single covalent bond
D. ionic bond
B
Which statement regarding matter is true?
A. Nitrogen exists in a liquid state over a wide range of temperatures due to polar interactions.
B. Gas has neither a constant volume nor a fixed shape.
C. Liquids have a constant volume and a fixed shape.
D. Almost all naturally occurring elements are found dissolved in body fluids.
B
Which of the following implies that the atom has lost one electron?
A. H
B. Ca2+
C. K+
D. Cl-
C
Molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structures are called _______________.
isomers
Neutrons
Subatomic particles that bear no electrical charge
Protons
Subatomic particles that bear a positive electrical charge
Electrons
Subatomic particles that bear a negative electrical charge
Mass number
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom
Molecular weight
the sum of the atomic weights of all the atoms in a molecule
Atomic weight
The actual mass of an atom
Mole
A quantity with a weight in grams equal to an element's atomic weight