Biomechanics Week 1
1/236
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
237 Terms
kinesis
to move
logy
study of
Kinesiology
study of movement
Biomechanics
A discipline that uses principles of physics to quantitatively study how forces interact within a living body
The study of forces applied to the outside and inside of the body and the body's reactions to those forces
biomechanics
Biomechanics branches
kinematics and kinetics
Kinematics
Describes the motion of a body WITHOUT regard to the forces/torques that may produce the motion
Kinematics includes
osteokinematics and arthrokinematics
Kinetics
study of forces associated with the motion of a body
kinetics includes
forces, torques and physics principles
Translation
linear motion
Translation definition
All parts of a rigid body move parallel to and in the same direction as every other part of the body
rectilinear
moving in or forming a straight line; having many straight lines

curvelinear
curved lines
Translation is measured in
meters or feet
Translation can cause
linear displacement
Accessory movement
movement that could occur at a joint that's passive
linear displacement
change in location, or the directed distance from initial to final location in the same direction
Excessive translation of a bone relative to the joint indicates
injury
Abnormal laxity in translation may indicate
pathological stiffness in surrounding connective tissue
distraction
pulling apart-separated
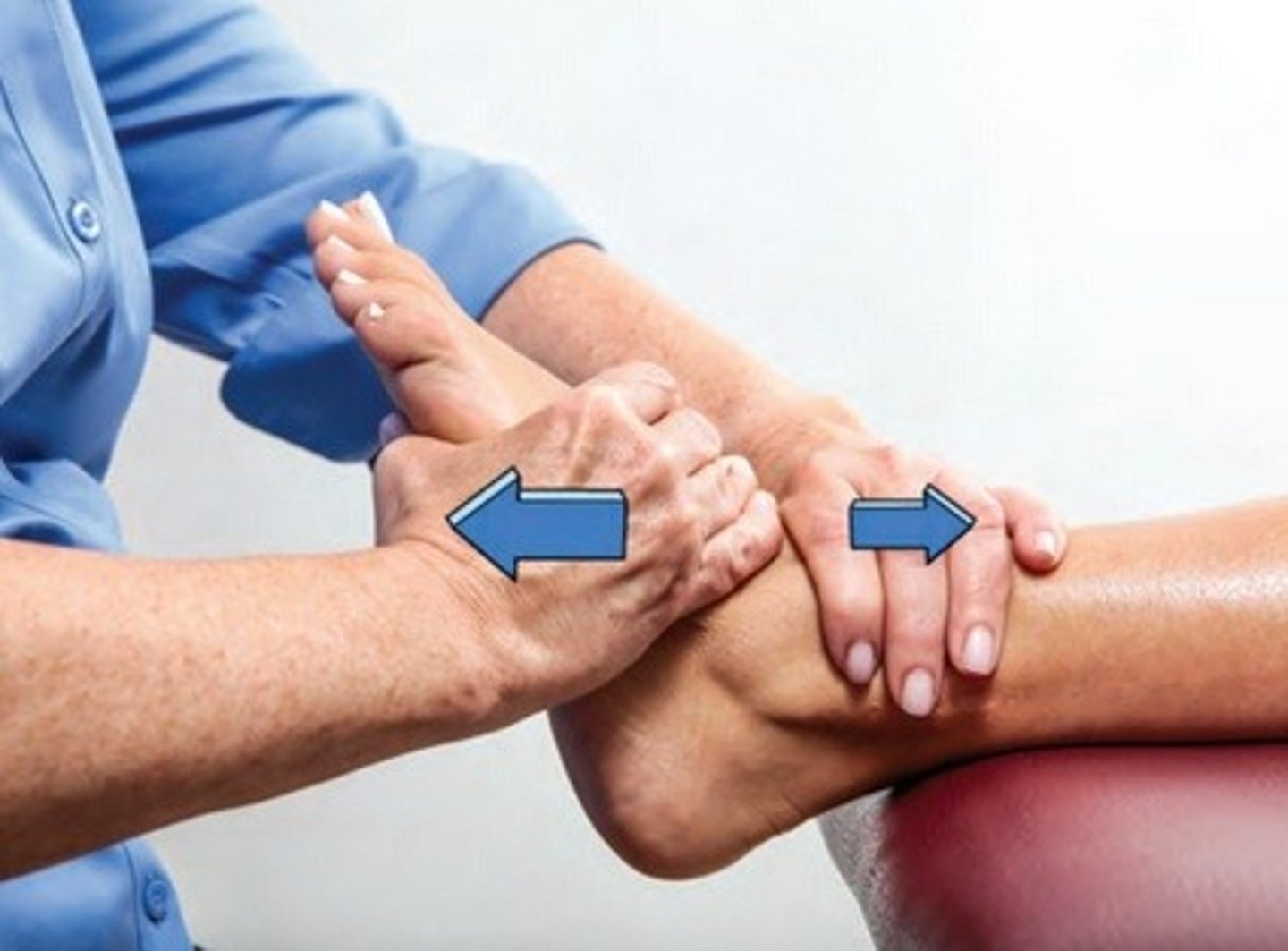
compression
joint surfaces pulled towards each other
rotation
Rigid body moves in a circular path around a pivot point
All points in the body simultaneously rotate in the same
angular direction
All points in the body simultaneously rotate across the same
# of degrees
rotation is measured in
degrees or radians
angular displacement
All points on the body segment rotate in the same direction and same distance
Axis of rotation
the point around which a body rotates
Does an axis rotate
no
2 multiple choice options
Axes are usually located
near the joint
Axes run through
the convex partner of a joint.
Evolute Axis of Rotation
migrating axis of rotation, the axis changes throughout the ROM
Sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
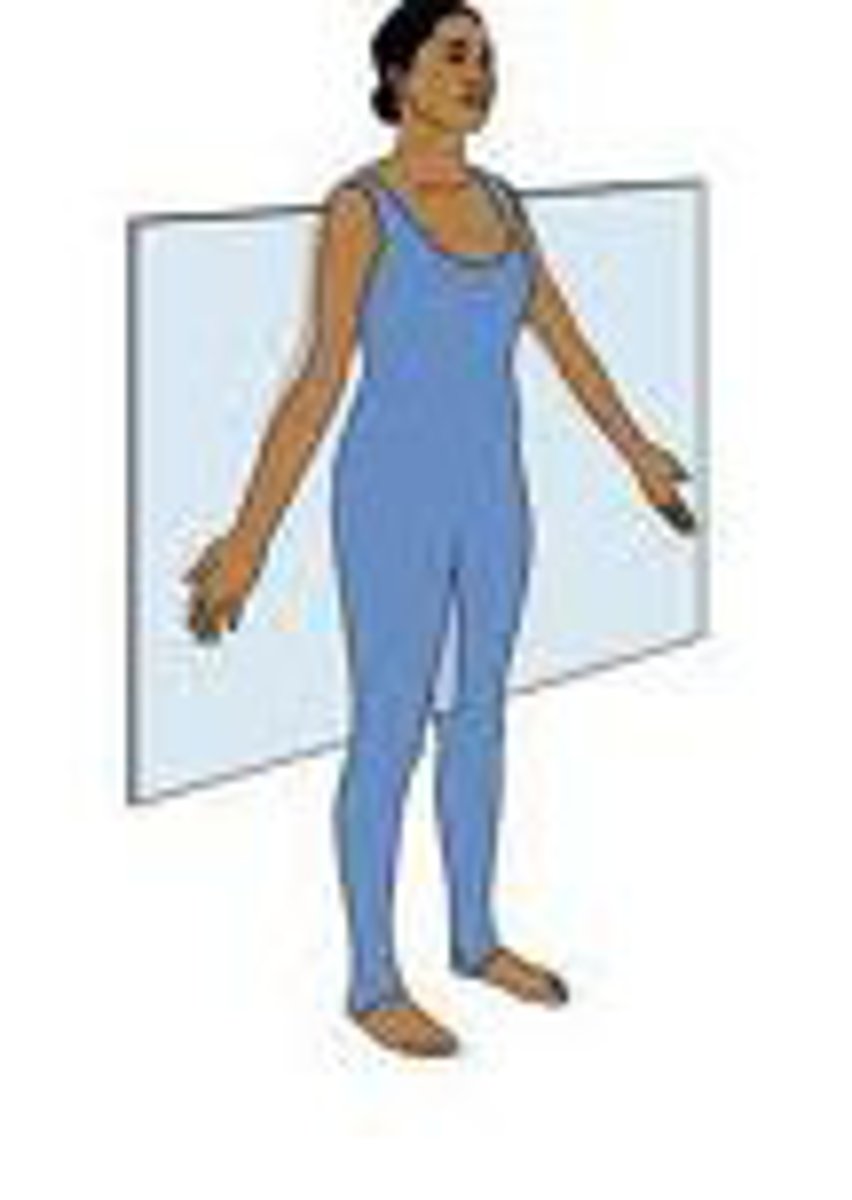
Frontal plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior portions

horizontal or transverse plane
Any plane dividing the body into superior and inferior portions.
Sagittal axis
medial and lateral
frontal axis
anterior and posterior
horizontal axis
vertical/ longitudinal
The Axis of rotation is perpendicular to
The cardinal plane of motion
Degrees of freedom
Number of independent directions of movements allowed at a joint
Uniaxial
movement in one plane and 1 axis and 1 degree of freedom
biaxial
joints that move in two planes around 2 axis and have 2 degrees of freedom
biaxial joints
condyloid, ellipsoid, saddle
Uniaxial joints
hinge, pivot
Triaxial
joints that move in all 3 planes abouts 3 axes and 3 degrees of freedom
Triaxial joints
ball and socket joints
Is naming the plane of motion considered part of kinetics or part of kinematics
Kinematics because it doesn't deal with the forces
Translation vs. Rotation
Translation: linear motion in which all parts of a rigid body move parallel to and in the same direction as every other part of the body
Rotation: motion in which an assumed rigid body moves in a circular path around some pivot point (axis of rotation)
Active movement vs passive movement
Active is controlled by the pt, while passive is controlled by an external force
Lumbar flexion plane
sagittal
shoulder abduction plane
frontal
Hip IR plane
horizontal
Knee flexion plane
sagittal
Cervical rotation plane
transverse, horizontal
finger abduction plane
frontal
Shoulder ER Axis of Rotation
vertical
elbow flexion Axis of rotation
medial lateral
hip abduction AoR
Anterior-posterior
Ankle DF AoR
Medial lateral
2 multiple choice options
Cervical rotation AOR
vertical
MCP Flexion AOR
Ant-post
Coxafemoral joint degrees of freedom
3
Tibiofemoral joint degrees of freedom
1
1st MTP joint degrees of freedom
3 it's a ball and socket
Uniaxial joint example
knee
biaxial joint example
wrist
triaxial joint example
hip
Osteokinematics
motion of bones relative to the 3 cardinal planes of the body
osteokinematic Movement the occurs between
the shafts of 2 adjacent bones as they move with regard to each other
Osteokinematics concern with
the movements of bony partners or segments that make up a joint
Goniometry is an example of
osteokinematics
Arthokinematics
Motion that occurs between the articular surfaces of joints
Arthrokinematics focuses on
minute movements occurring within the joint and between the joint surfaces
Arthrokinematics can be
Can be rotary or translatory
example of arthokinematics
joint mobilization
end feels
Joint's resistance to further movement; sensation perceived by clinician when assessing passive range of motion at the end of a joint's ROM
Soft end feel
(soft tissue approximation) ex: elbow flexion, knee flexion
Firm end feel
muscular stretch
capsular stretch
ligamentous stretch
Hard end feel
(bone to bone) ex: elbow extension
empty end feel
movement is beyond anatomical limit
- pain occurs before end range (complete lig rupture)
end feels are abnormal when
they appear where they shouldn't
Kinematic chains
combination of several joints uniting successive segments
Open kinematic chain
distal segment is free to move
Open kinematic chain movement
Distal segment moves on a fixed proximal segment (bicep curl)
Closed kinematic chain
distal segment is fixed
Closed kinematic chain movement
Proximal segment moves on a fixed distal segment (Push up)
convex
curved outward
concave
curving inward
most joints are a mix of
convex/concave
Arthrokinematics can include
Rolling, sliding and spinning
Rolling
rotary or angular motion
slide (glide)
translatory motion, sliding of one joint surface over another
spin movement
One joint surface rotates on another (ie: forearm is rotate from the hand facing down to the hand facing up).
Convex-Concave Rule
determines the direction of decreased joint gliding and the appropriate direction for the mobilizing force
Convex on concave
roll and slide in opposite directions
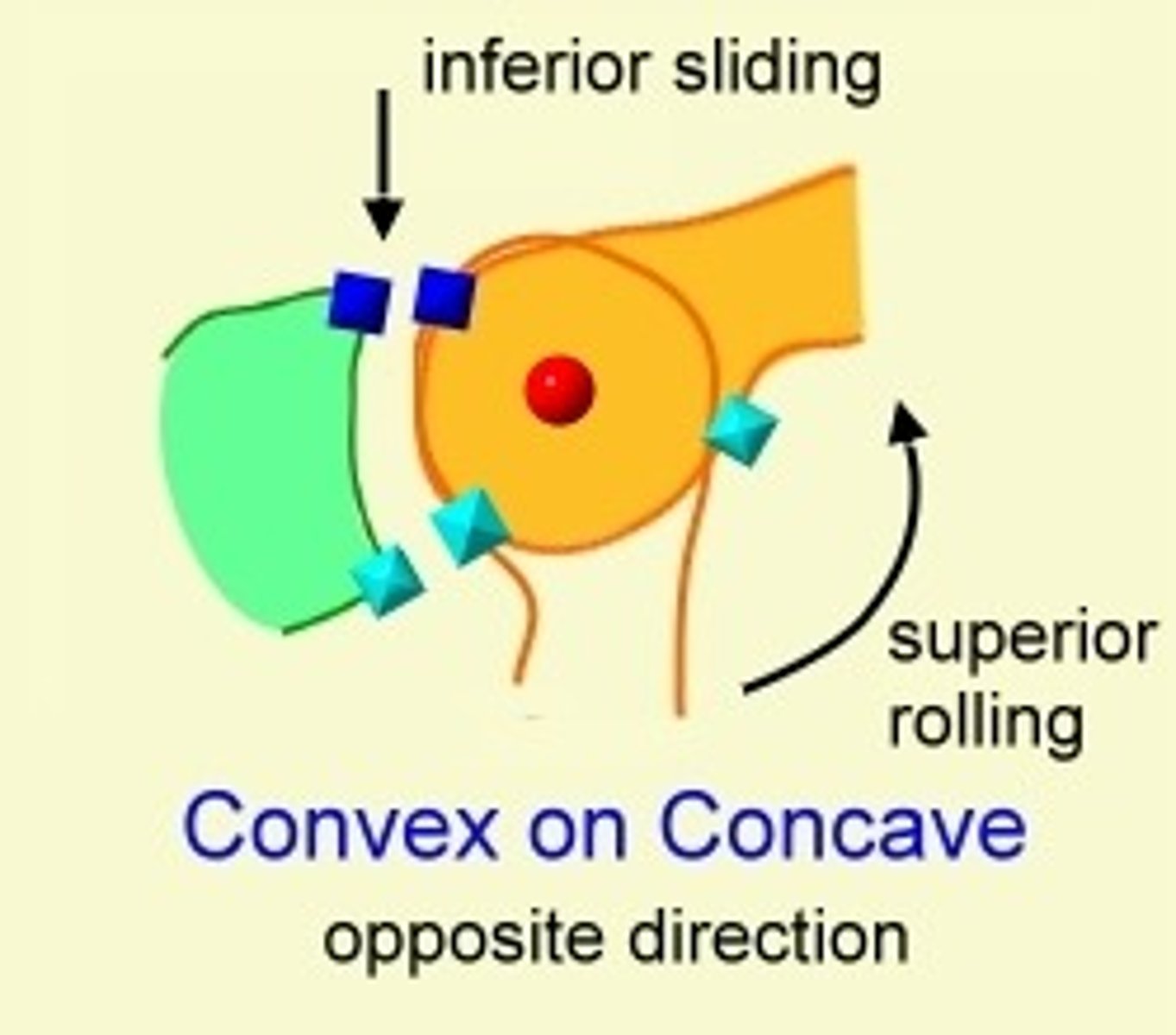
concave on convex
roll and slide in same direction
Spin joint example
Radial head spins as it attaches to the capitulum.
Close-packed position
joint orientation for which the contact between the articulating bone surfaces is maximum
Very stable
Reduced need for muscle forces
Accessory movements are minimal
Near end range
open packed position
minimal stress on joint, minimal congruency of joint, great laxity in ligament position, no volitional separation of joint surface, increased accessory movement, preferred during long periods of immobilization
Kinetics
study of forces associated with the motion of a body