cell-cell junctions and ECM
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
describe the lateral domain of cell-cell junctions
epithelial cells are joined tightly by cell-cell junctions categorized using molecular technique:
tight junctions
desmosomes/hemidesmosomes (anchoring junctions)
gap junctions
all apprear as a darkly staining structure reffered to an “terminal bar”
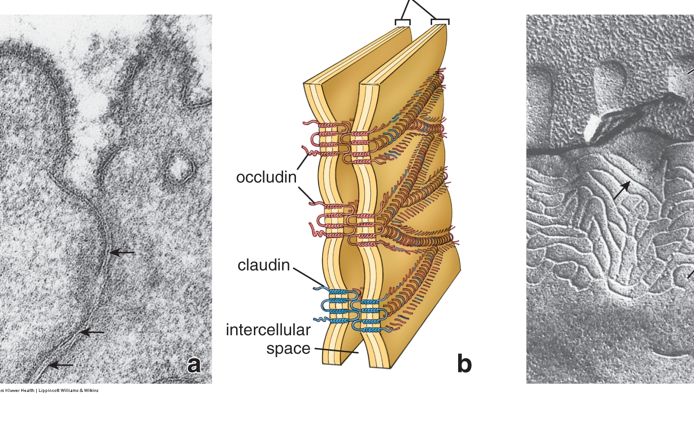
describe tight junctions
form barrier that limits water and other molecules from passing
any molecule that pass must either diffuse/be transported through the epithelial cell
OR
diffuse through the occluding junction (varies based on tightness and number of extracellular aqueous channels present)
located at most apical point of lateral domain
prevent apical lipids and proteins from moving to the lateral domain
is limiting to the “fluid mosaic” PM
what do tight junctions do?
seals the PM of adjacent cells by forming “focus fusion”
transmembrane proteins occludin and claudin
the extracellular portions of the transmembrane proteins form a “zipper”
a group of zone occludens (ZO) proteins regulate formation of the zona occludens
the ZO proteins (and others) localize here due to a recognizable amino acid sequence in the cytoplasmic domains
what are anchoring junctions?
lateral adhesions between epithelial cells
use proteins that link into the cytoskeleton of adjacent cells
main types of anchoring junctions
zonula adherens - interact with actin filaments
macula adherens (desmosomes) - interacts with intermediate filaments
adtl. anchoring junctions, attach the epithelial cells at the basal domain to connective tissue, 2 types
focal adhesions and hemidesmosomes
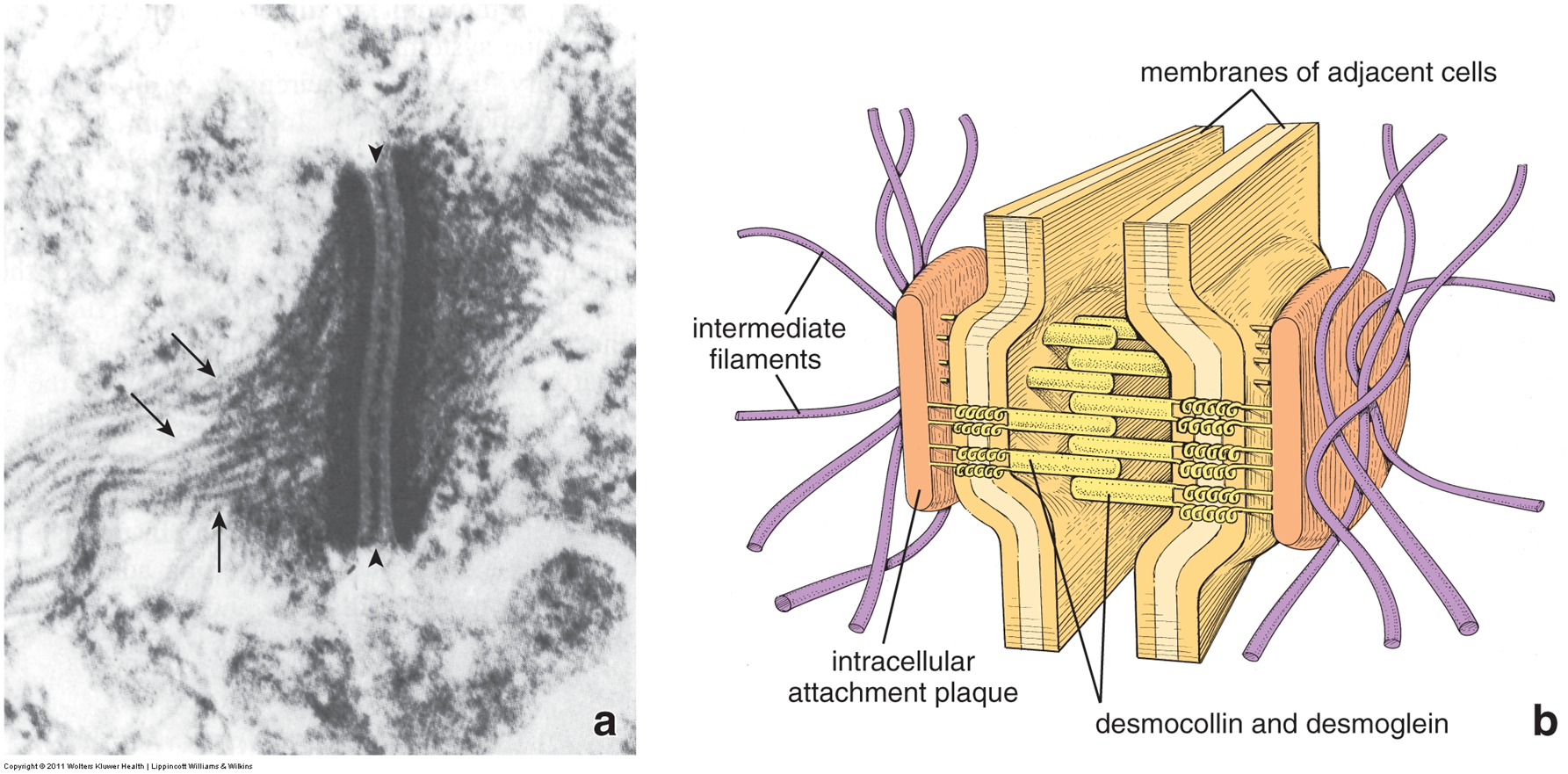
describe desmosomes and hemidesmosomes
cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) of neighboring cells interact:
homotypic binding
heterotypic binding
adhesion of anchoring junctions dep on attractions of CAMs from neighboring cells
easier to dissociate than tight junctions

desmosomes are ___ and hemidesmosomes are ___
cell to cell
cell to basal lamina junctions
what do cadherins do?
control cell-cell interactions
participate in cell recognition
participate in embryonic cell migration
E-cadherin is important tumor suppressor
what do desmosomes do?
provide very strong cell-cell attachment by anchoring to intermediate filaments
analogous to series of “spot welds” along lateral domain
not sufficient as a barrier alone but in conjunction with occluding junctions and zonula adherens strengthen cell-cell contact
what anchors intermediate filaments in desmosomes? members of attachment plaque?
desmosomal attachment plaque on cytoplasmic side of PM anchors intermediate filaments
desmoplakins and plakogolbins = members of attachment plaque
describe gap junctions
structures allow passage of molecules and ions between cells
present in many tissue types
each communicating junction = an accumulation of transmembrane channels or pores
connexins are a family of proteins that function to create the channels that comprise the communicating junction
communicating junctions can open and close via conformation changes in response to stimulus
basement membrane
epithelial cells’ basal domain contacts basement membrane
BM is a specialized structure that lies between the epithelial tissue and the CT
amorphous, difficult to preserve and stain
within the basement membrane — a thin, electron dense layer termed basal lamina
what is the basal lamina? what does it contain?
basal lamina = fine network of sticky molecules like:
laminins, collagen (type IV), proteoglycans, glycoproteins
what are three major components of the ECM?
fibrous proteins (collagen, elastin)
glycosaminoglycans (GAGS) and proteoglycans
glycoproteins (fibronectin and laminin)
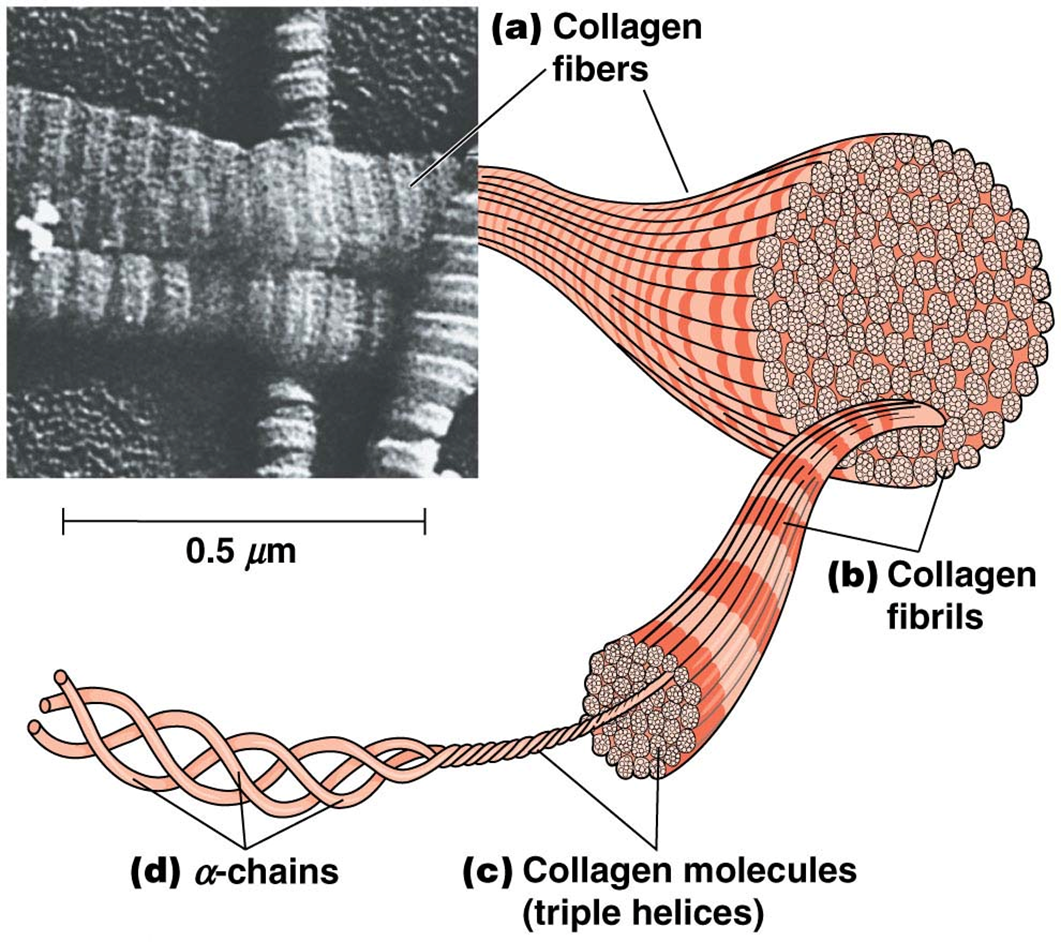
collagen fibers
resist tensile force
alpha-chains
collagen molecules (triple helices)
collagen fibrils
collagen fibers
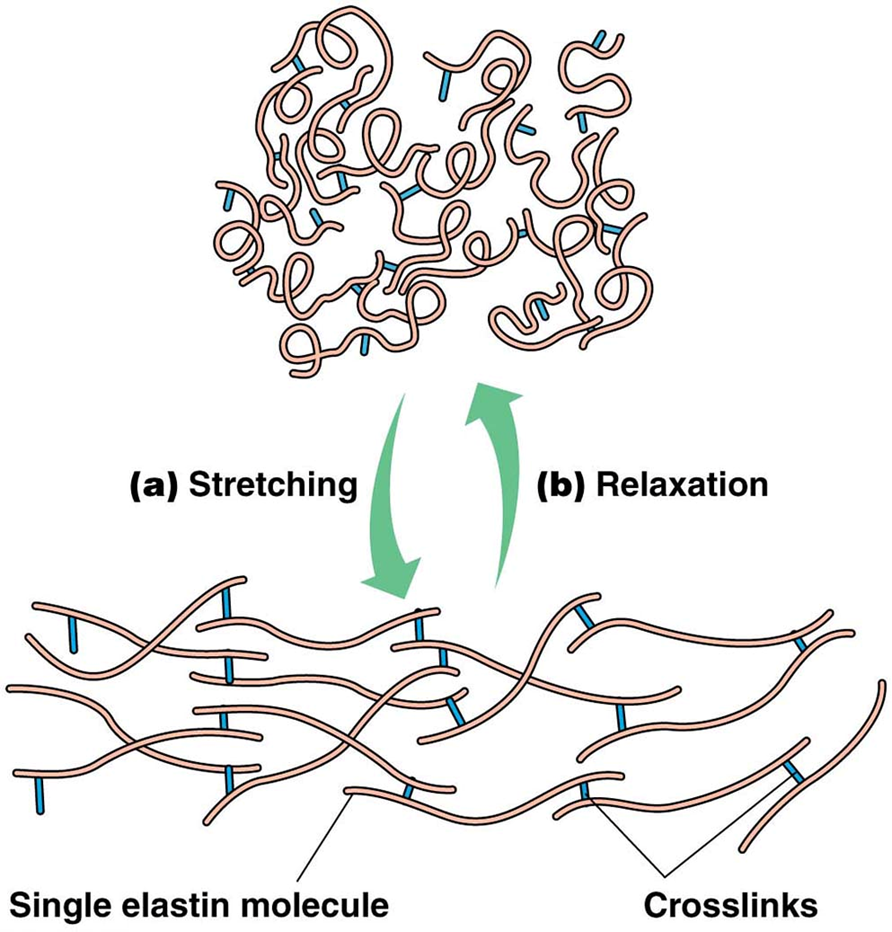
elastic fibers involved in…
stretching and relaxation
single elastin molecule and crosslinks
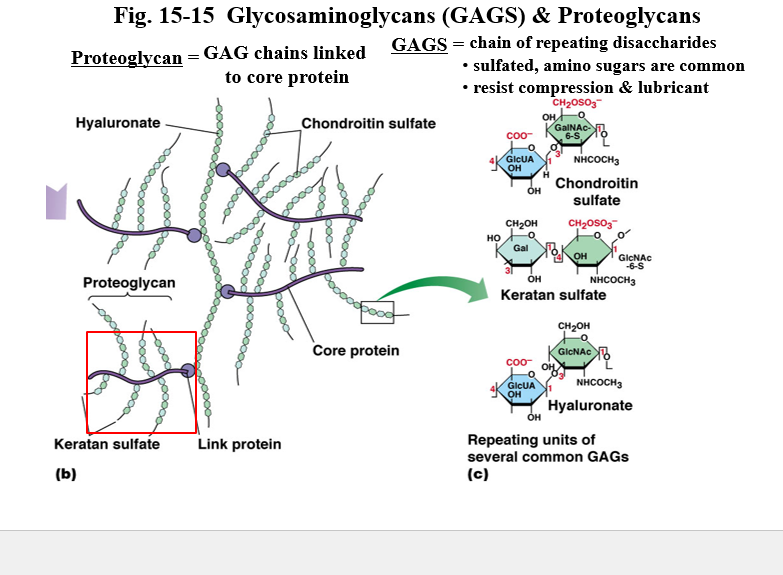
what are GAGS? what are proteoglycans?
GAGS = chain of repeating disaccharides
sulfated, amino sugars are common
resist compression and lubricant
proteoglycan - GAG chains linked to core protein
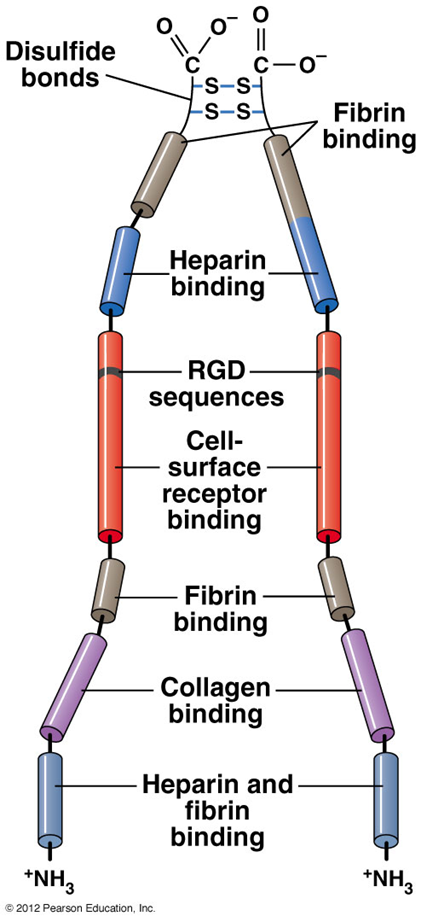
ECM glycoproteins
fibronectin
laminin
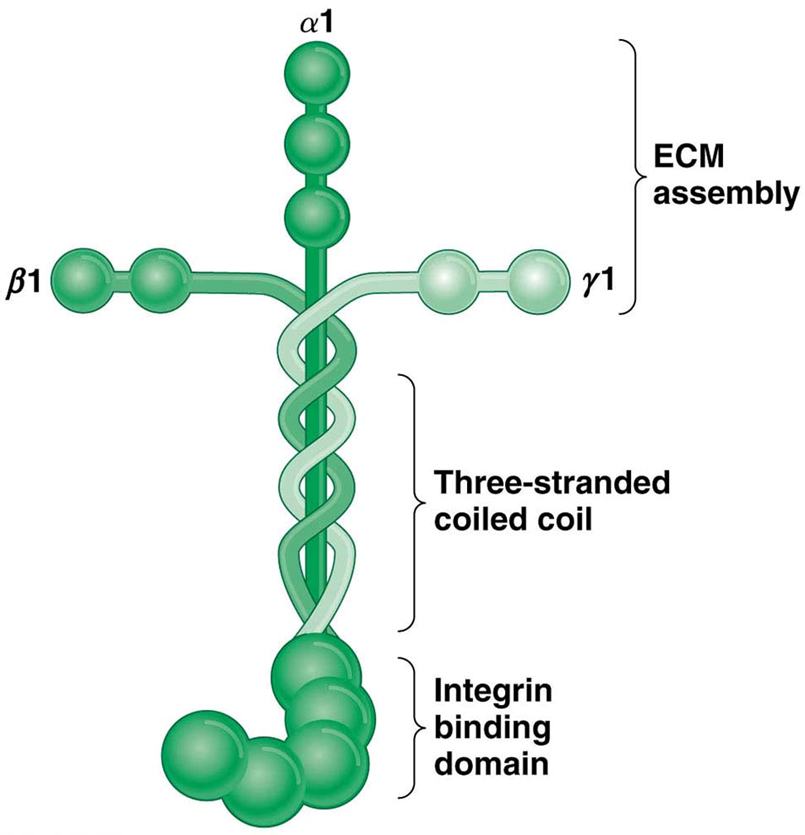
what is an integrin?
it goes through the membrane — fibronectin and laminin receptor
