Lecture 7: PTSD
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
There are different clusters of symptoms in PTSD. What is cluster A?
Trauma
Exposure to a traumatic event, by either directly experiencing / witnessing, learning it happened to a close person, experiencing repeated exposure to aversive details (e.g. coding a scary video game)
Trauma can be various things
Violence
Accidents, Disasters
Illness, death
Is criterion A even relevant for PTSD, since people who have trauma in other ways also get treated?
Not particularly. It's not a predictor. Better predictors are how often the events occurred, and whether you experienced the event yourself
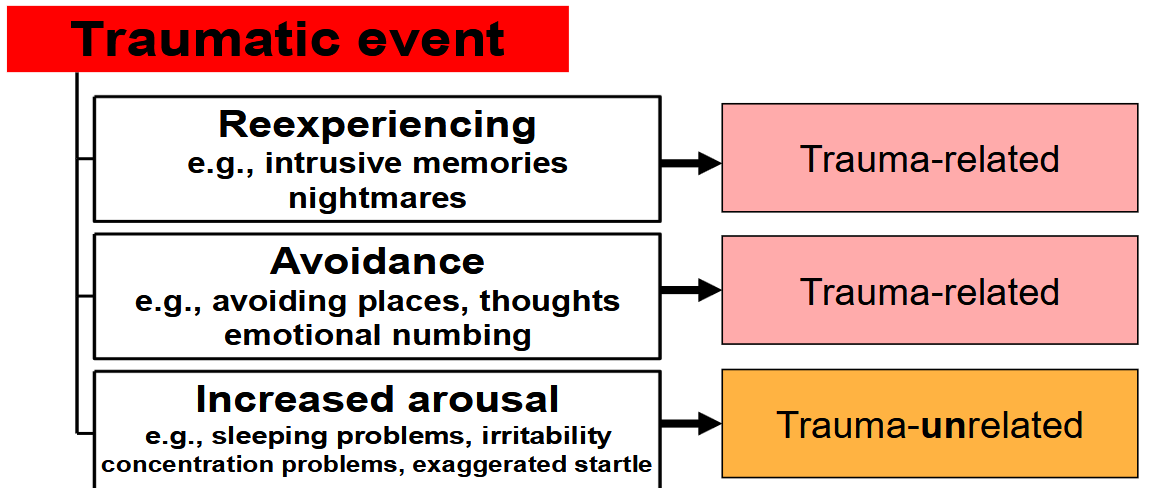
What are Clusters B-G?
B - Re-experiencing
C - Avoidance (Avoiding situations that could be triggering, but also avoid thinking about the traumatic event)
D - Arousal (constant alertness)
E - Cognitions and mood
F - Impaired functioning
G - Duration
Is having flashbacks after a traumatic event an indicator of PTSD?
No, almost everyone has flashbacks in the beginning of a traumatic event, so this is not a good predictor of PTSD
What pre-trauma risk factors exist?
* Psychiatric disorder
* Previous trauma
* Neuroticism
* IQ
What peri-trauma risk factors are there for PTSD?
* Trauma type and severity
* Emotion
* Dissociation
What post-trauma risk factors are there for PTSD?
* Social support
* Life stress
* Negative cognitions
Being blamed for the trauma by the environment
Maintaining an emotional relationship to the trauma
What does the cognitive model by Ehlers and Clark posit?
* PTSD is caused by
* Negative appraisal of the trauma and the consequences thereof
* Disordered autobiographical memory (too little elaboration and context and strong associative memory)
* Chronic perception of acute threat (feel in danger all the time)
What does the cognitive model by Foa posit?
Trauma undermines 2 basic assumptions
* The world is safe
* I am competent
* Chronic perception of acute threat
What is the nature of the neuroticism-PTSD relationship?
Why is it a problem to misinterpret trauma memories as causing PTSD?
Memories are fluid, unreliable and can be changed (e.g. “cars touched vs. hit vs. smashed” video)
PTSD treatment
* Psychoeducation and advice to reduce avoidance
* No severe comorbid depression - Trauma focused behaviour therapy (imaginal exposure therapy - Expose them to traumatic memories, expectancy violation). You have to force them to be exposed even if they don't want to
* Exposure can be combined with cognitive restructuring
* or EMDR - efficacy has been shown for trauma
* Severe co-morbid depression or non-response: SSRI
* Combined CT (cognitive restructuring) and exposure: not more effective than exposure only
* Not a phase-based approach
Can PTSD be prevented? For example by debriefing after the traumatic event?
PTSD is not preventable
* Debriefing can be harmful
* Better: info about trauma, empathy and short CBT session after trauma
What is imaginal exposure therapy?
A type of exposure where you re-imagine the traumatic event with the addition of new information
Are there any exclusion criteria for exposure therapy?
If someone has trauma but no PTSD, potentially if someone is using drugs/alcohol