Synovial Fluid
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What is synovial fluid?
ultrafiltrate of plasma between the joints
What are the 3 main functions of synovial fluid?
lubrication, nutrients, and shock absorption
Freely movable joints due to synovial fluid are called:
Synarthroses
Amphiarthroses
Diarthroses
Fibrous joints
Diarthroses
Which component of synovial fluid is primarily responsible for its viscosity and lubrication?
Lubricin
Water
Hyaluronic acid
Plasma proteins
Hyaluronic acid
What is arthritis?
pain and stiffness in the joints due to membrane damage
What are the 4 classifications of synovial fluid disorders?
noninflammatory arthritis
inflammatory arthritis
septic arthritis
hemorrhagic arthritis
Degenerative joint disorders can cause what type of synovial fluid disorder?
noninflammatory arthritis
What is an examples of a noninflammatory joint disorder that causes noninflammatory arthritis?
osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disorder)
A synovial fluid specimen has the following test results:
appearance: yellow, clear
glucose: 85 mg/dL (blood is 90 mg/dL)
WBC count: 1500/uL
differential: neutrophils 15%
culture: negative
What type of synovial disorder is this?
noninflammatory
inflammatory (immunological)
inflammatory (crystal-induced)
septic
hemorrhagic
noninflammatory
Immunologic joint disorders and crystal formation can cause what type of synovial fluid disorder?
inflammatory arthritis
What are 3 examples of immunologic joint disorders that can cause inflammatory arthritis?
Lupus erythematosus (LE)
rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Lyme disease
A synovial fluid specimen has the following test results:
appearance: yellow, cloudy
glucose: 60 mg/dL (blood is 90 mg/dL)
WBC count: 4,000/uL
differential: neutrophils 60%
culture: negative
What type of synovial disorder is this?
noninflammatory
inflammatory (immunological)
inflammatory (crystal-induced)
septic
hemorrhagic
inflammatory (immunological)
What are some examples of crystal-induced inflammatory arthritis?
gout and pseudogout
A synovial fluid specimen has the following test results:
appearance: yellow, milky
glucose: 60 mg/dL (blood is 90 mg/dL)
WBC count: 45000/uL
differential: neutrophils 75%
culture: negative
What type of synovial disorder is this?
noninflammatory
inflammatory (immunological)
inflammatory (crystal-induced)
septic
hemorrhagic
inflammatory (crystal-induced)
Microbial infections can cause what type of synovial fluid disorder?
septic arthritis
A synovial fluid specimen has the following test results:
appearance: yellow-green, cloudy
glucose: 60 mg/dL (blood is 90 mg/dL)
WBC count: 80000/uL
differential: neutrophils 95%
culture: positive
What type of synovial disorder is this?
noninflammatory
inflammatory (immunological)
inflammatory (crystal-induced)
septic
hemorrhagic
septic
The presence of blood in the joint is a characteristic of what synovial fluid disorder?
hemorrhagic arthritis
What 3 things can cause blood in the synovial fluid, leading to hemorrhagic arthritis?
trauma
tumors
coagulation deficiencies
A synovial fluid specimen has the following test results:
appearance: red/pink, cloudy
glucose: 85 mg/dL (blood is 90 mg/dL)
WBC count: 4500/uL
differential: neutrophils 40%
culture: negative
What type of synovial disorder is this?
noninflammatory
inflammatory (immunological)
inflammatory (crystal-induced)
septic
hemorrhagic
hemorrhagic
What is the normal volume of synovial fluid?
< 3.5 mL
What is the normal color and clarity of synovial fluid?
colorless - pale yellow
clear
Patients with noninflammatory or inflammatory arthritis would have what color synovial fluid?
deeper yellow
Synovial fluid from a patient with septic arthritis or some kind of infection in the fluid would be what color?
green
Patients with hemorrhagic arthritis or had a traumatic tap would have what color synovial fluid?
red
Crystals in synovial fluid would have what affect on the clarity?
it would be milky
What are 4 cause that would make synovial fluid turbid?
WBCs
cellular debris
fibrin
crystals
Synovial fluid with normal viscosity will be able form strings how long?
4-6 cm
The mucin clot test adds what fluid to a patient’s synovial fluid to test for the viscosity?
acetic acid
When combined with acetic acid to test for viscosity, should normal synovial fluid form a clot or not clot?
form a clot
How many leukocytes should be seen in 1 uL of normal synovial fluid?
< 200 leukocytes/uL
A patient with septic arthritis would have how many leukocytes per 1 uL of synovial fluid?
> 100,000 leukoctres/uL
When performing cell counts (WBC/diff.) on synovial fluid, what fluid is added to dilute the specimen?
normal saline or methylene blue
What would you add to decrease the viscosity of synovial fluid to prepare it for cell counts?
hyaluronidase
After treatment with hyaluronidase, what should you do to prepare the sample for a cell counts?
incubate at 37C for 5 minutes
After incubation with hyaluronidase, what should you do to prepare the sample for a differential count?
cytocentrifuge
What are the cells normally found in synovial fluid?
monocytes, macrophages, and synovial tissue cells
What percentage of leukocytes should be neutrophils when performing a differential on synovial fluid?
< 25%
Increased neutrophils in synovial fluid is indication of what condition?
sepsis
What percentage of leukocytes should be lymphocytes when performing a differential on synovial fluid?
< 15%
Increased lymphocytes in synovial fluid is indication of what condition?
inflammation
What are neutrophils that have phagocytized nuclear material?
lupus erythematosus (LE) cells
Reiter cells/neutrophages
ragocytes
hemosiderin granules
lupus erythematosus cells
What are vacuolated macrophages with ingested neutrophils?
lupus erythematosus (LE) cells
Reiter cells/neutrophages
ragocytes
hemosiderin granules
Reiter cells/neutrophages
What cells are neutrophils with small, dark granules containing precipitated rheumatoid factor?
lupus erythematosus (LE) cells
Reiter cells/neutrophages
ragocytes
hemosiderin granules
ragocytes
What are pigmented villonodular synovitis?
lupus erythematosus (LE) cells
Reiter cells/neutrophages
ragocytes
hemosiderin granules
hemosiderin granules
Seeing lipid droplets in synovial fluid indicates what kind of injury?
crush injury
How many crystal formations should you see in synovial fluid?
none
What are 4 causes for crystals to form in synovial fluid?
metabolic disorders
decreased renal function
degeneration of bone/cartilage
corticosteroids
What are the 2 primary crystals found in synovial fluid?
monosodium urate (MSU)
calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD)
MSU is the primary crystal found in (gout/pseudogout).
gout
What are 2 causes that could cause an increase in MSU formation in synovial fluid?
increased purines and uric acid
leukemia chemotherapy
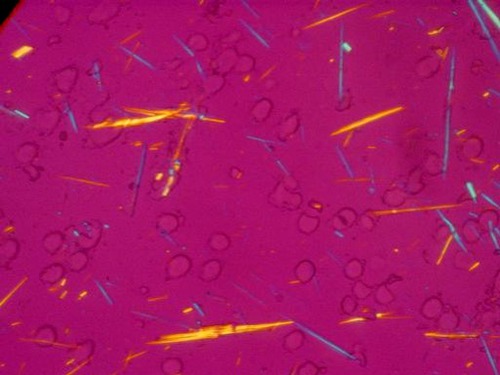
What primary crystal is this?
MSU
CPPD is the primary crystal found in (gout/pseudogout).
pseudogout
What are 2 causes that could cause an increase in CPPD formation in synovial fluid?
degenerative arthritis
increased calcium levels
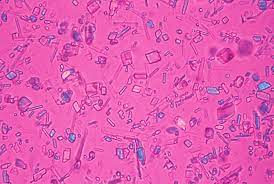
What primary crystal is this?
CPPD
Cholesterol is present in synovial fluid during what?
chronic inflammation
Corticosteroids are seen in synovial fluid after what?
injections
Calcium oxalate is seen in synovial fluid when patients have what condition?
renal failure
How long can a synovial fluid sit before examining for crystals?
should be performed ASAP
After initial viewing of synovial fluid, how find and differentiate crystals?
find crystals using polarized light
differentiate crystals using compensated polarized light
Light is allowed to pass through the polarized microscope when both fields are what?
aligned
All light is prevented from passing through the polarized microscope when both fields are what?
analyzer is perpendicular to polarizer
What is the purpose of the red/gamma compensator on a polarized microscope?
determines the type of birefringence (positive or negative)
What are the 2 identify factors of negative birefringence?
red/gamma compensator is parallel to crystal = crystal is yellow
red/gamma compensator is perpendicular to crystal = crystal is blue
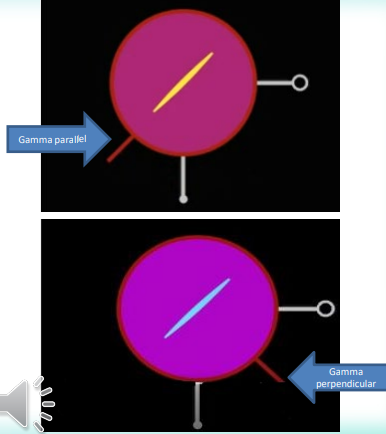
Does this image represent positive or negative birefringence?
negative
Does MSU have positive or negative birefringence?
negative
What are the 2 identify factors of positive birefringence?
red/gamma compensator is parallel to crystal = crystal is blue
red/gamma compensator is perpendicular to crystal = crystal is yellow
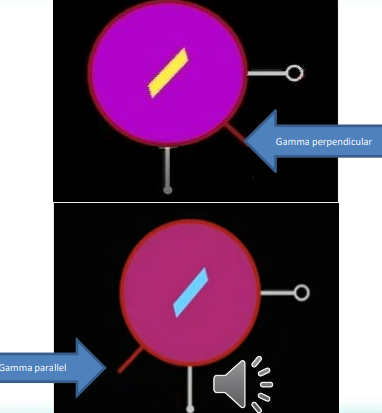
Does this image represent positive or negative birefringence?
positive
Does CPPD have positive or negative birefringence?
positive
How does the glucose value of synovial fluid relate the the glucose value of blood?
< 10 mg/dL lower compared to glucose value of blood
What is the normal total protein of synovial fluid?
< 3 g/dL
Which procedure is used to collect synovial fluid?
Arthroscopy
Arthrography
Arthrocentesis
Arthrectomy
Arthrocentesis
How many mL of synovial fluid is collected for noninflamed and inflamed joint testing?
noninflamed: 3.5 mL
inflamed: > 25 mL
Clotting of synovial fluid indicates what?
fluid is diseased
When collecting synovial fluid for microbiology testing, what are the 2 tubes you can collect the fluid in?
heparin or sodium polyanethol sulfonate (SPS)
What are the 4 main organisms tested for in synovial fluid?
Staph
Strep
H. influenza
N. gonorrhoeae
When collecting synovial fluid for hematology testing, what tube do you use to collect the fluid in?
liquid EDTA
When collecting synovial fluid for glucose testing, what 2 tubes do you use to collect the fluid in?
nonanticoagulated
sodium fluoride
When collecting synovial fluid for other types of testing, what 2 tubes can you use to collect the fluid in?
heparin
nonanticoagulated