6- epidemiology
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is epidemiology?
Study of distribution and determinants of health related events in specified population
How it can be applied to health problems
In what 5 ways can epidemiology be applied?(objectives)
Describe distribution and magnitude of diseases
Identify causes
Study natural history and prognosis
Evaluate new preventative and therapeutic approaches
Allow development of public policies
Smokers have a …. greater risk of developing lung cancer compared to non smokers
9
1958- 44% tobacco linked to cancer
1968- 78%
Why is epidemiology and health promotion important?
People should have control over their health
Correct design of epidemiological research
Proper interpretation of research
Avoid misinformation so no public confusion
What is incidence and what type of studies is it useful in?
Number of new cases in a disease free group
Causality studies
increases when more intense risk factors (smoking, perio disease)
What is the difference between cumulative incidence and incidence rate or density?
Proportion of individuals developing the disease during follow up period- fixed cohort
Vs ratio between number of new cases during follow up period and total observation time- dynamic cohort- allows new entries
What is prevalence?
Proportion of individuals suffering from a disease at a given time
What is an epidemiological index?
Numerical value specifying health status through a graded scale
Standardises data collection
Can have individual or population indices
What are the 5 characteristics of an epidemiological index?
Validity
Clarity
Reliability
Sensitivity- detect small variations
Acceptability- no discomfort
What is the prevalence of gingivitis?
Global- 50%
Children- 70-80%
Adults- 90%
Depends on socioeconomic status, access to dental care, education
What are 8 risk factors for gingivitis?
Poor oral hygiene
Age
Genetic factors
Tobacco use
Pregnancy
Systemic diseases
Medications
Stress
What is the prevalence of periodontitis?
Global- 45%
Increases with age- severe in 40-60
65yrs- 70-80%
Adults- 30%
What are 7 risk factors of periodontitis?
Poor oral hygiene
Smoking
Genetic factors
Systemic diseases
Stress
Socioeconomic
Medications
How do you measure periodontal disease?
Calibrated probe
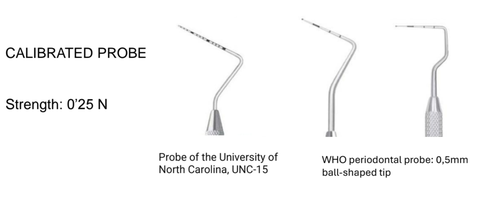
What does the Silness and Loe index measure?
Plaque thickness along gingival margin
Dry with a light air jet
No plaque disclosing agent
Examined in 4 units- B, P/L, M, D