ib econ- 2.3: equilibrium
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://www.econinja.net/microeconomics/2-3-equilibrium
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
what is the point where supply and demand meet called?
market equilibrium: the exact amount of goods demanded is supplied, we assume markets are at this point unless stated otherwise.
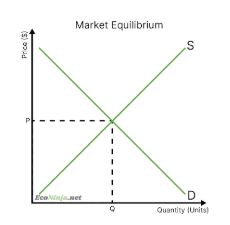
what happens to equilibrium if there is an increase in supply?
supply curve shifts to the right
prices decrease (more goods/services available but the same demand)
since prices decrease, more consumers are willing and able to buy the good/service
this means equilibrium meets at a new point with a lower price and higher quantity
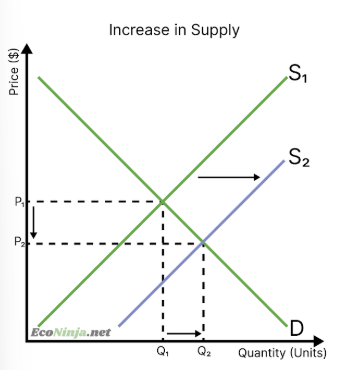
what happens to equilibrium if there is a decrease in supply?
supply curve shifts leftwards
prices increase (less goods/services available but the same demand for them)
when prices increase, fewer consumers are willing and able to buy the good/service
equilibrium meets at a new point, with a higher price and lower quantity
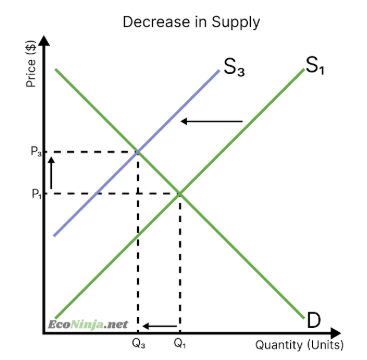
what happens to equilibrium if there is an increase in demand?
demand curve shifts to the right
prices increase (more consumers are willing and able to buy the good or service, but supply as remained the same)
as prices increase, more firms are willing and able to sell their good or service
equilibrium meets at a new point, with higher price and quantity
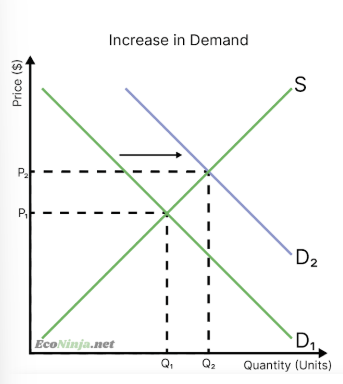
what happens to equilibrium if there is a decrease in demand?
demand curve shifts to the left
prices decrease, as less people are willing and able to consume at the original price
when prices decrease, less firms are willing to sell their good or service
equilibrium meets at a new point (lower price, lower quantity)
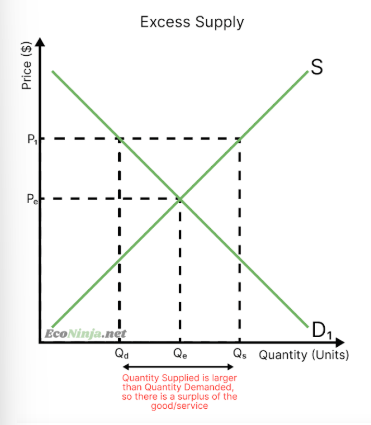
what is excess supply?
when the price is higher than the equilibrium price, so firms are more willing to produce and consumers are less willing to consume (surplus)
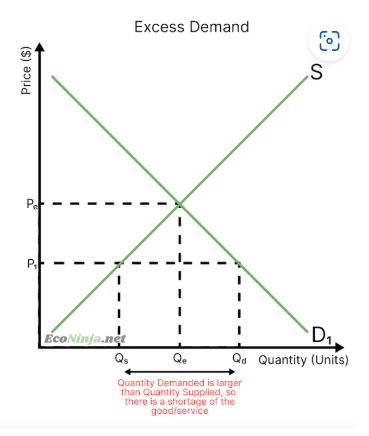
what is excess demand?
when the price is lower than the equilibrium price, so consumers are more willing to consume and firms are less willing to produce (shortage)
what is the price mechanism?
the forces of supply and demand determining the price and quality of goods and services. has two functions: resource allocation (signalling and incentive) and rationing.
what is the signalling part of the resource allocation function?
if the price of a good or service increases, it signals to producers that there is high demand for it, and they will produce and supply more of it.
what is the incentive part of the resource allocation function?
if prices increase, firms can now earn more money by supplying their good or service, meaning they are incentivised to produce and supply more of it
what is the rationing function?
if there is more quantity demanded than quantity supplied of a good/service, the price will increase, as producers can earn more from the same number of customers. this helps ration the limited supply of the good/service.
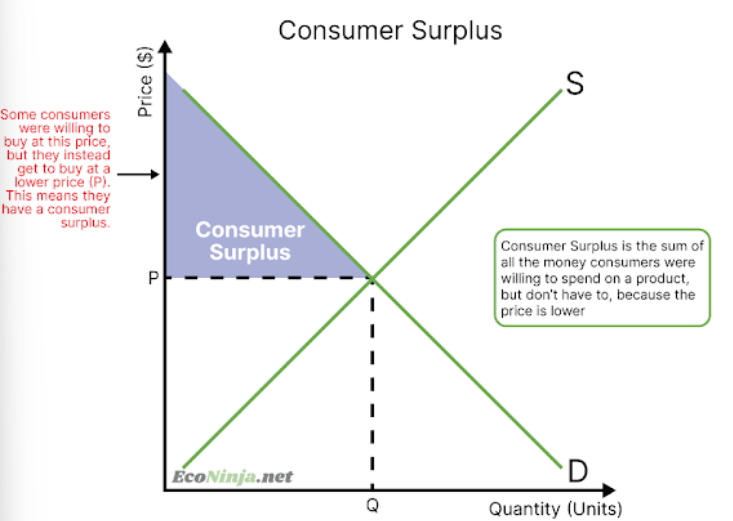
what is consumer surplus?
the gain of all customers who get to consume a product at a lower price than what they were willing and able to pay.
what is producer surplus?
the gain of all producers who get to supply a product at a higher price than what they were willing and able to earn.
draw the diagram of consumer surplus.
draw the diagram of producer surplus
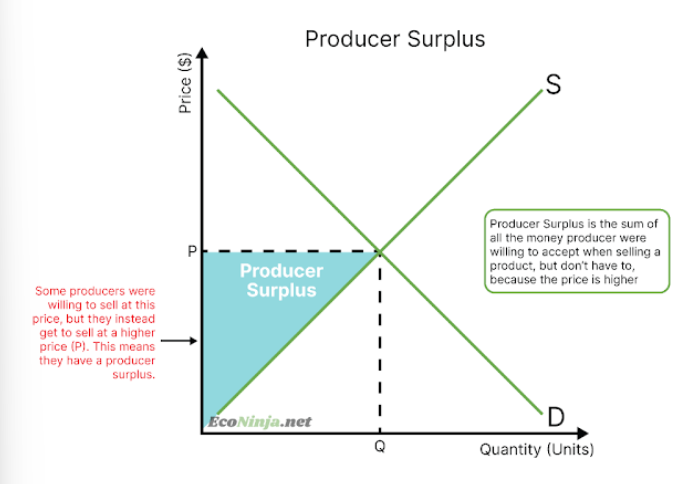
what is the social/community surplus?
the sum of consumer and producer surplus. maximised when there is no excess supply or demand- the market is allocatively efficient.
what is allocative efficiency?
the situation where the social surplus is maximised- no one (producers or consumers) can be better off without others being worse off.
when does allocative efficiency occur?
when the price mechanism works to create a market equilibrium- at this point, the additional marginal benefit that one more good or service brings equals the additional marginal loss.