plate tectonics + rocks
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
wegener’s five arguments
fit of the continents, locations of past glaciations, distribution of climate belts, distribution of fossils, matching geologic units
how does new ocean floor form?
continents rift apart, upwelling of magma reaches the surface and pushes continental plates apart
young ocean floor is located [closer to/farther away from] the MOR
closer to
the farther away you are from the MOR, the [younger / older] the ocean floor
older
common bathymetric features to identify an MOR
high point in elevation at the MOR, symmetrical decrease in elevation on either side
where is the MOR?
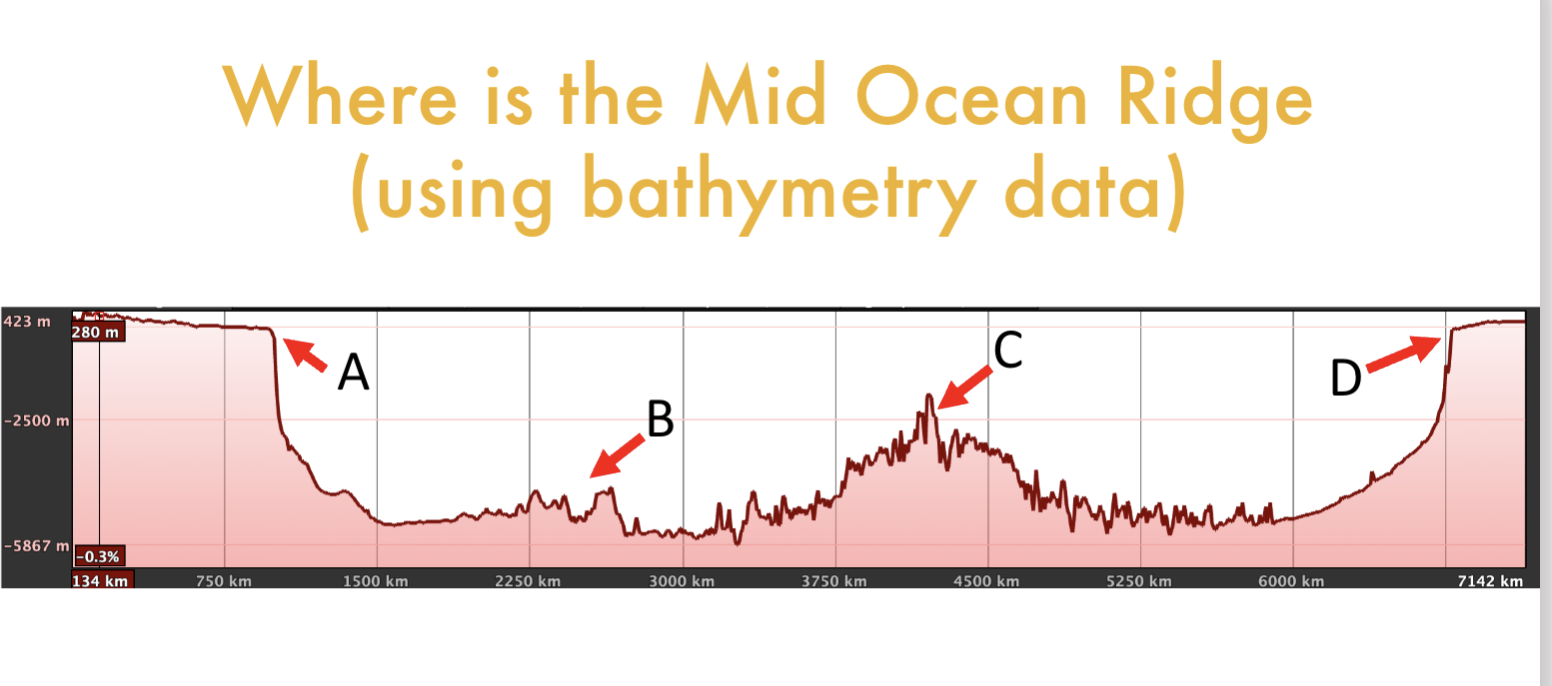
C
positive anomalies
magnetic north aligned with geographic north
negative anomalies
magnetic north aligned with geographic south
Where is the MOR
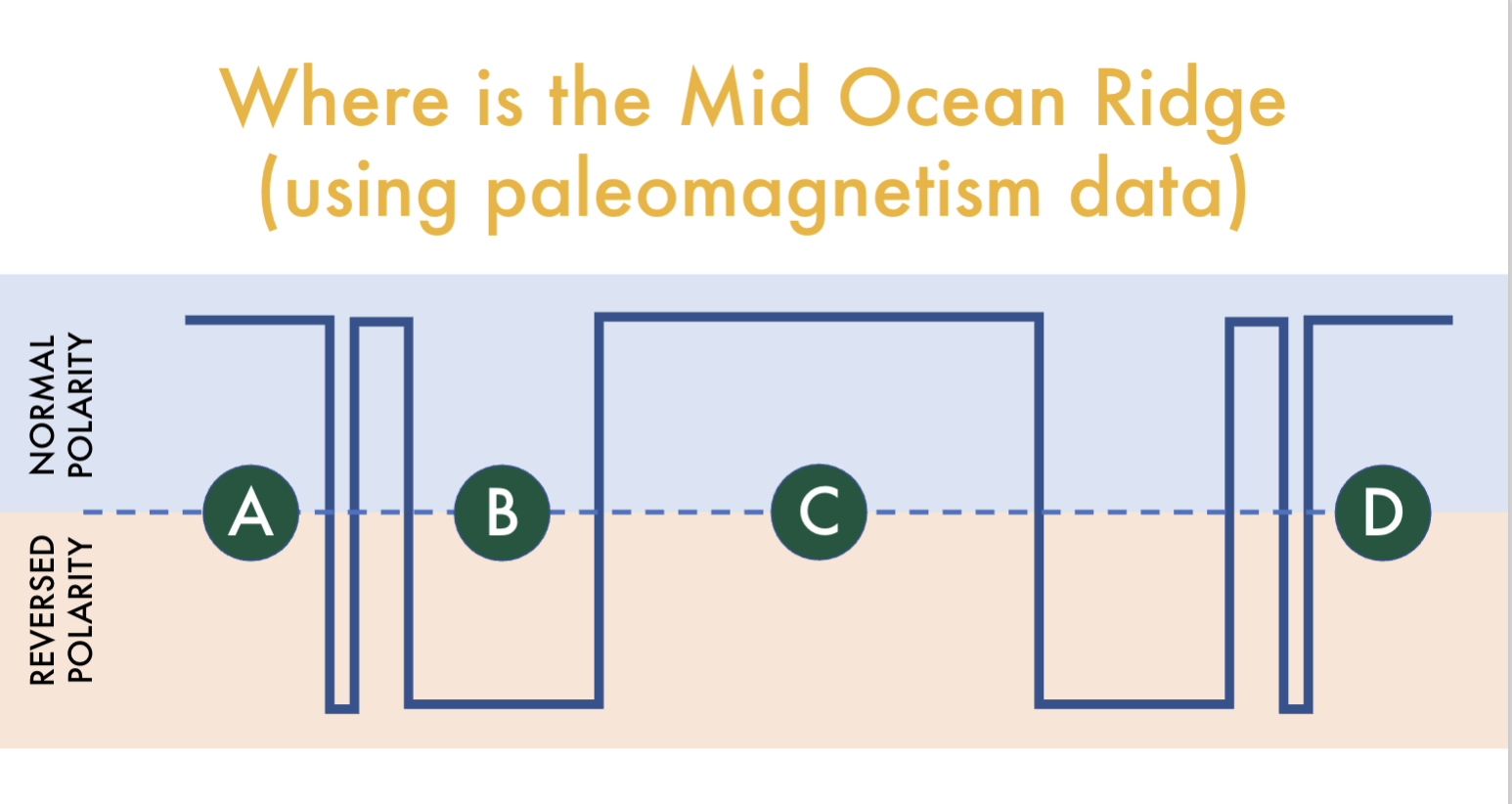
point C
common paleomagnetic features to identify MOR
normal polarity, symmetrical banding on either side
newest seafloor corresponds to [upper/lower] rock in the geometric polarity timescale
upper
divergent boundary
two or more plates are spreading apart from each other
what force acts at divergent boundaries?
ridge-push
convergent boundary
when plates collide with each other
what happens at an ocean-continental boundary?
oceanic lithosphere subducts under continent
force during convergent boundaries
slab pull forces
what features emerge at a convergent boundary
trenches and volcanic arcs
hot spot
fixed spot in the mantle that forms volcanoes as lithospheric plates move across it
ridge push
gravity forces push new crust downwards, away from divergent boudary
slab pull force
dense ocean slab is pulled down by gravity, bringing ocean plate into the mantle and facilitating pulling oceanic lithosphere from MOR
true/false: slab pull forces also work on divergent boundaries
true
how do slab pull forces affect divergent boundaries
they facilitate movement of plates
true/false: youngest seafloor is at convergent boundaries
false
where are earthquakes found at divergent boundaries
concentrated at the boundary
where are earthquakes found at convergent boundaries
along the boundary and inland on continental plate
fit of the continents
continents look like they can fit like puzzle pieces
evidence for fit of the continents
maps, geography, edges, of the continents
locations of past glaciations
glaciations appear to have been originally connected in Pangaea
evidence for locations of past glaciations
striations, glacial till
striations
scratch marks left by glacier
distribution of climate belts
continents once occupied different climate zones
evidence for distribution of climate belts
specific flora/fauna
distribution of fossils
same fossils found in South Africa and South America
evidence for distribution of fossils
fossils
matching geologic units
same precambrian rocks found in multiple continents
evidence for matching geologic units
rocks, mountain ranges
minerals
naturally occuring (formed by a geological process), solid, orderly arangement of atoms and a definable chemical composition (inorganic)
crystalline
regular internal geometric shape
ways to form minerals
solidification, precipitation from water, diffusion, biomineralization, precipitation from gas
solidification
when minerals crystalize out of a fish
precipitation from water
when minerals crystalize from water
diffusion
atoms migrate and build mineral structures
biomineralization
when minerals crystalize from organisms
precipitation from gas
when minerals crystalize from a gas
how many classes are minerals grouped into
seven
where is the anion in the chemical formula
the end of the formula
where is the cation in the chemical formula
the beginning of the formula
silicates
SiO4/4 anionic group
sulfides
metal cation bonded to sulfide anion (S2)
oxides
metal cation bonded to oxygen aniona
halide
halogen or salt producing ion
carbonate
CO2 is anionic group
native metals
pure masses of a single metal
sulfates
metal cation bonded to SO4/2 anionic group
ways to identify minerals
color, streak, luster, hardness, fracture & cleavage