law and economics
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Law
rules of behabior for members of society to advance collective good through cooperation
Why Have Laws
people are self interested and self intererests conflict/need basic rules of the game
What do laws do
Minimize potential conflict
How work
impose cost and benefits and backed by power of government
Do they work?
Economics can help us see
Economics
study of how individuals and ssocieties choose to use their scare resources im an attempt to satisfy unlimited wants
Old Law and Economics
concerned with laws that affect the operation of the economy and markets
New Law and Economics
law is a giant pricing machine-how respond to price changes
Positive Analysis of Law
Prove true or false—-need general not just partial equilibrium analysis
Normative Analysis of Law
opinion based—recommend
equity vs efficiency
Differences Between La and Economics
1) Ex ante vs ex poste view of the law
lawyers come to problem after
econ-who bears cost is a warning to future
Judhes-after dispute but creates precent
legislatoers-after it apply to future
2) Details vs Simpliation
case law focuses on perculiarites
econom ics uses simplifed models to predict consequences of change in a variable
3) Rasonable vs Rational Man
4) Marginal vs binary
are we always ration, calculating too much?
Dehumanizing-price on life
efficiency vs equity
conservative bias
Market Failures Sources
1) Imperfect competition
2) Presence of external costs and benefits (externalities)
3) Existnece of public goods
4) Imperfect Information
5) Behaviorial Economics-assumptions about rational behavior
Imperfect Competition/Game Theory
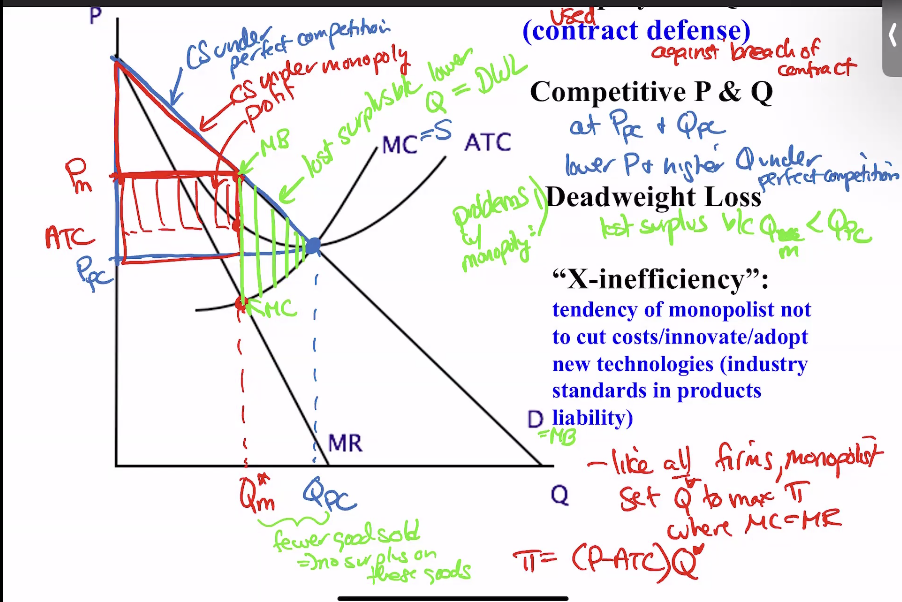
monopolies, create x-inefficiency where monopolists tend to not cut costs/innovate/adopt new techs and also dwl
also monopsony
Bilateral monopoly
monopolistic competition—many firms but each is a little monopoly
mostly an issue of antitrust policy
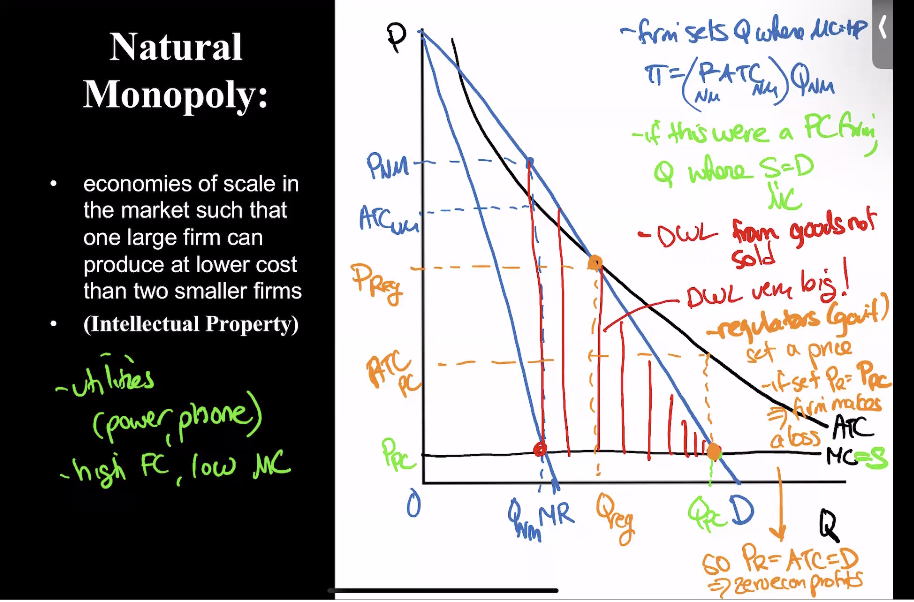
Natural Monopoly
DWL huge in these cases
Regulators come in and set a price to fix
But if set regulated price, then they make loss, have to subsidize firm
used with IPs
Game Theory
Players, strategies, and payoffs
Inefficiency caused by imperfect information
but factors can change this outcome (mafia, contract with person)
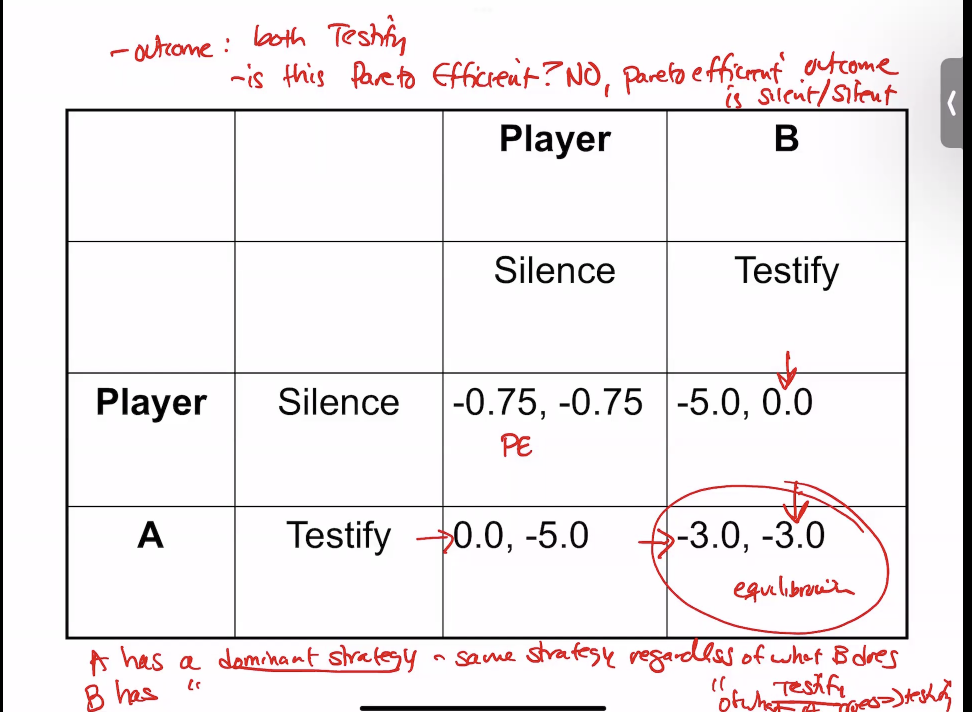
Nash Equilibrium
strategy that is optimal given knowledge of what B is doing
Pareto Optimal
can’t make anyone better off without making someone worse off
Incentive for infinitve games
cooperation based on tit for tat ability
Externalities
a consequence of an economic activity that spills over to affect third parties
(consumption or production)
Producer to Producer
Positive: apple orchard and honey bees
negative: poluution harms downstream commercial fishing
Producer to Consumer
positive: heated water for horse
negative: 3-Mile Island-water pollution
Consumer to Consumer
Positive: vaccines, fave masks
Negative: smoking, noise
Consumer to producer
Positive: unsolicited feedback
Negative: cowtipping, graffiti, vandalism
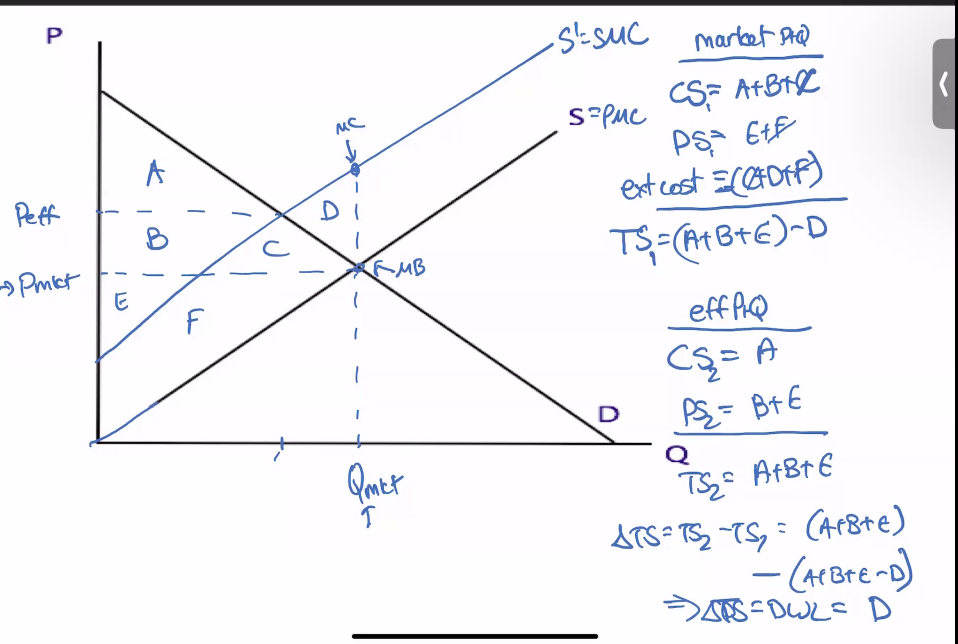
Graph of Negative Externality
production externality-use firms MC to show it
Consumption externality uses indifference curves
too much produced-loss from overproduction
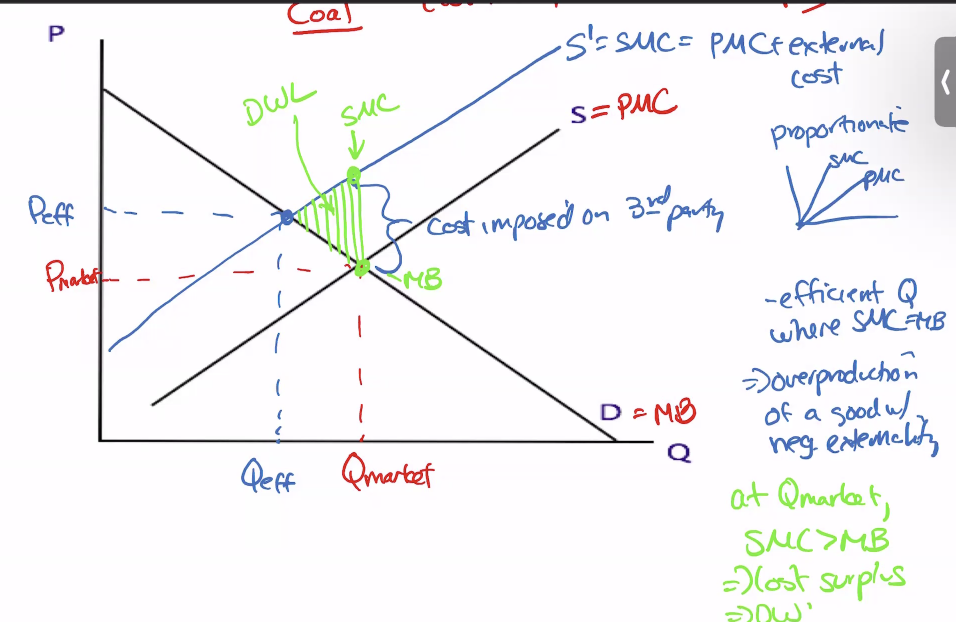
How get rid of negative externality
impose tax equal to external cost on firm producing negative externality (but if tax > external cost, then could drive them out of business or if tax< true external cost—still over production)
1) Pigovian tax
2) Pollution permits
3) Regulation
4) lawsuits-legal compensation-impose cost on polluter
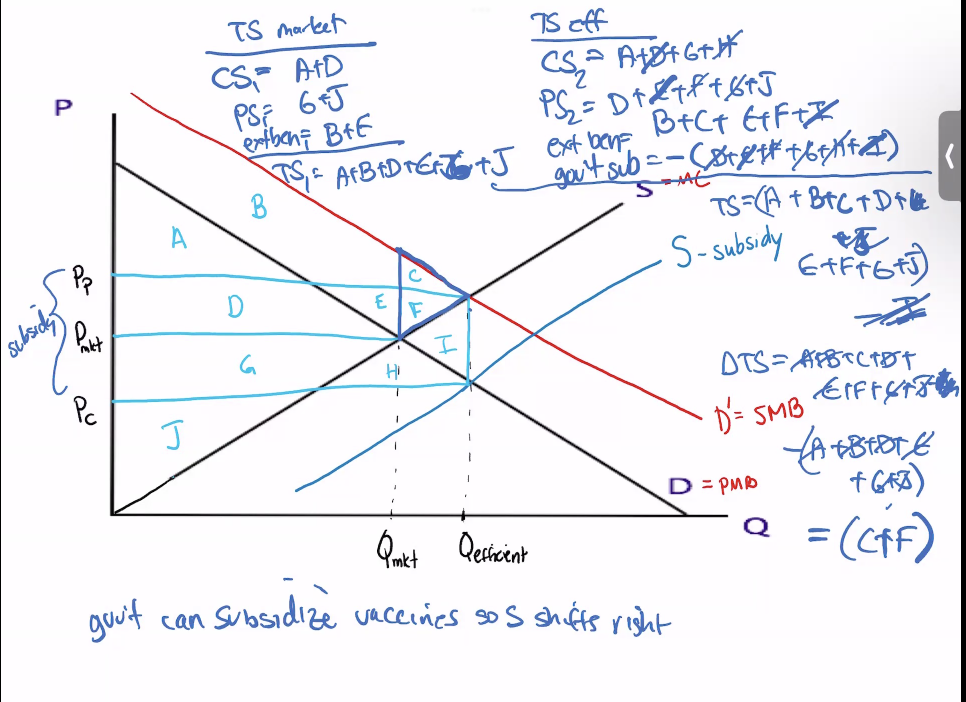
Positive Externality (vaccines)
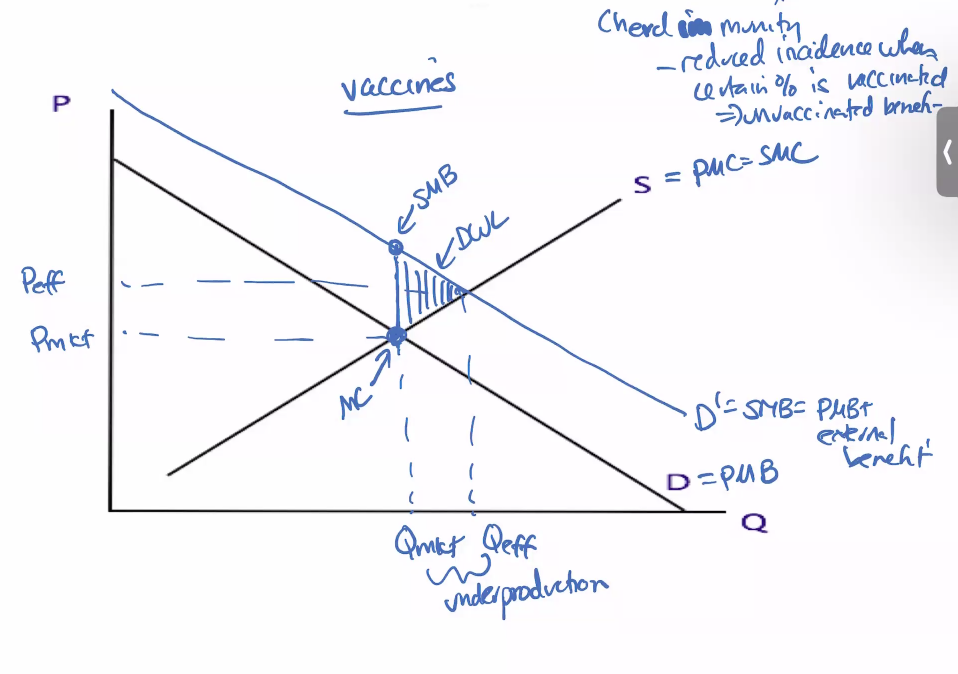
How eliminate positive externality
1) Subsidize
2) Government provision
3) Regulation
Private Goods
rival(less of it to consume for others) if i consume it) and exclusive (can exclude others from using it)
Public Goods
Non-rivalious (my consumption doesn’t decreasr the amount that others can consume—-national defense)
Non-excludability—costly to exclude people
Congestible Goods
initially non-rival goods but can become rivalious as lots use)
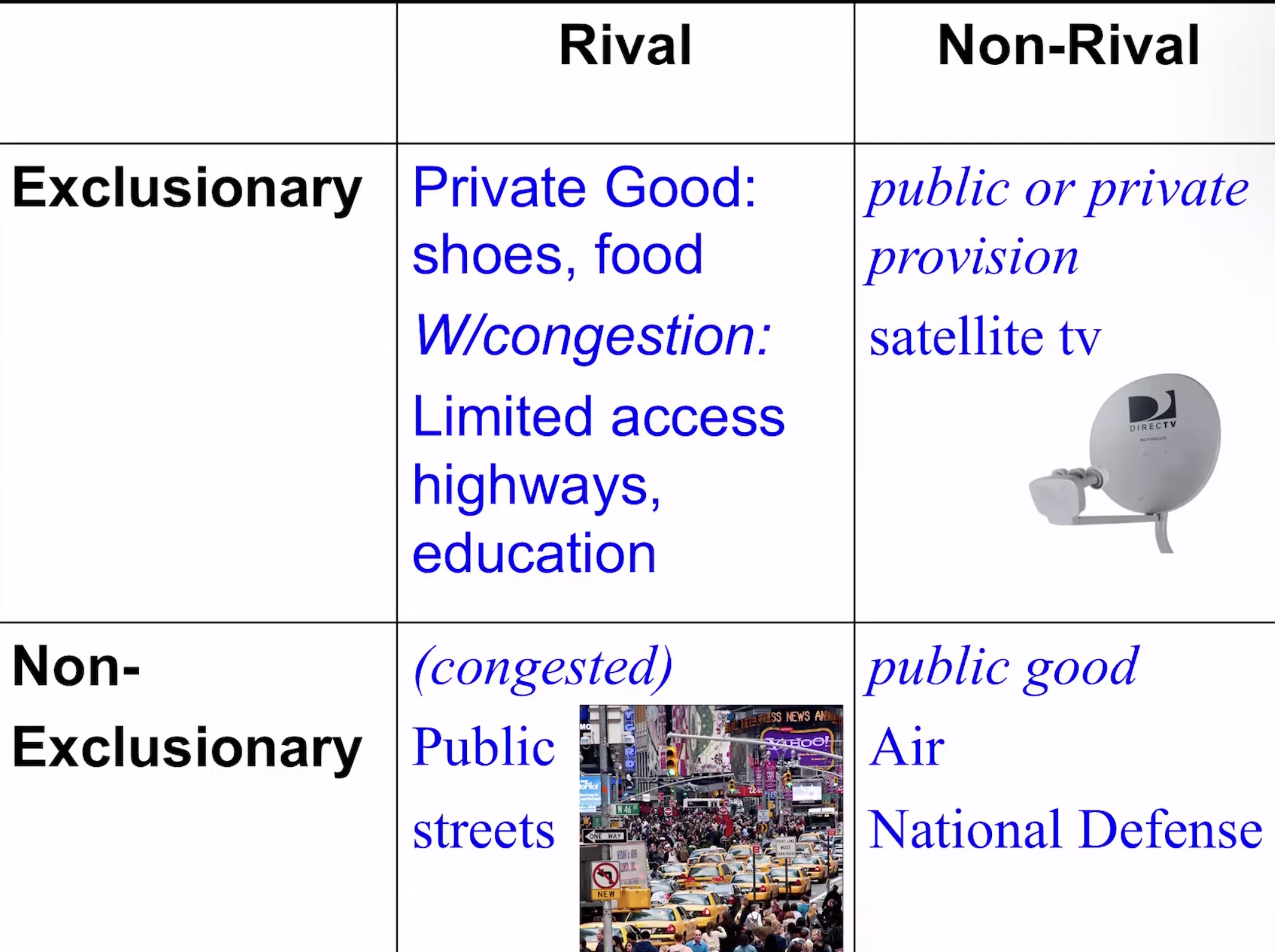
Public Goods
government provides, which either would not be provided by private markets or would be provided insufficiently
Risk averse
willing to pay more to avoid risk
risk neutral
pay expected amount
risk preferring
pay less
Free rider problem
don’t pay—-off others who are willing to pay more——problem with lack of excludability
Drop in the bucket
because a good or service is costly that its provision cannot not be provided by one person
How fix it?
Taxation
When provide public good
When benefits>costs—-there is pareto improvement to provide good when sum of WTP>cost
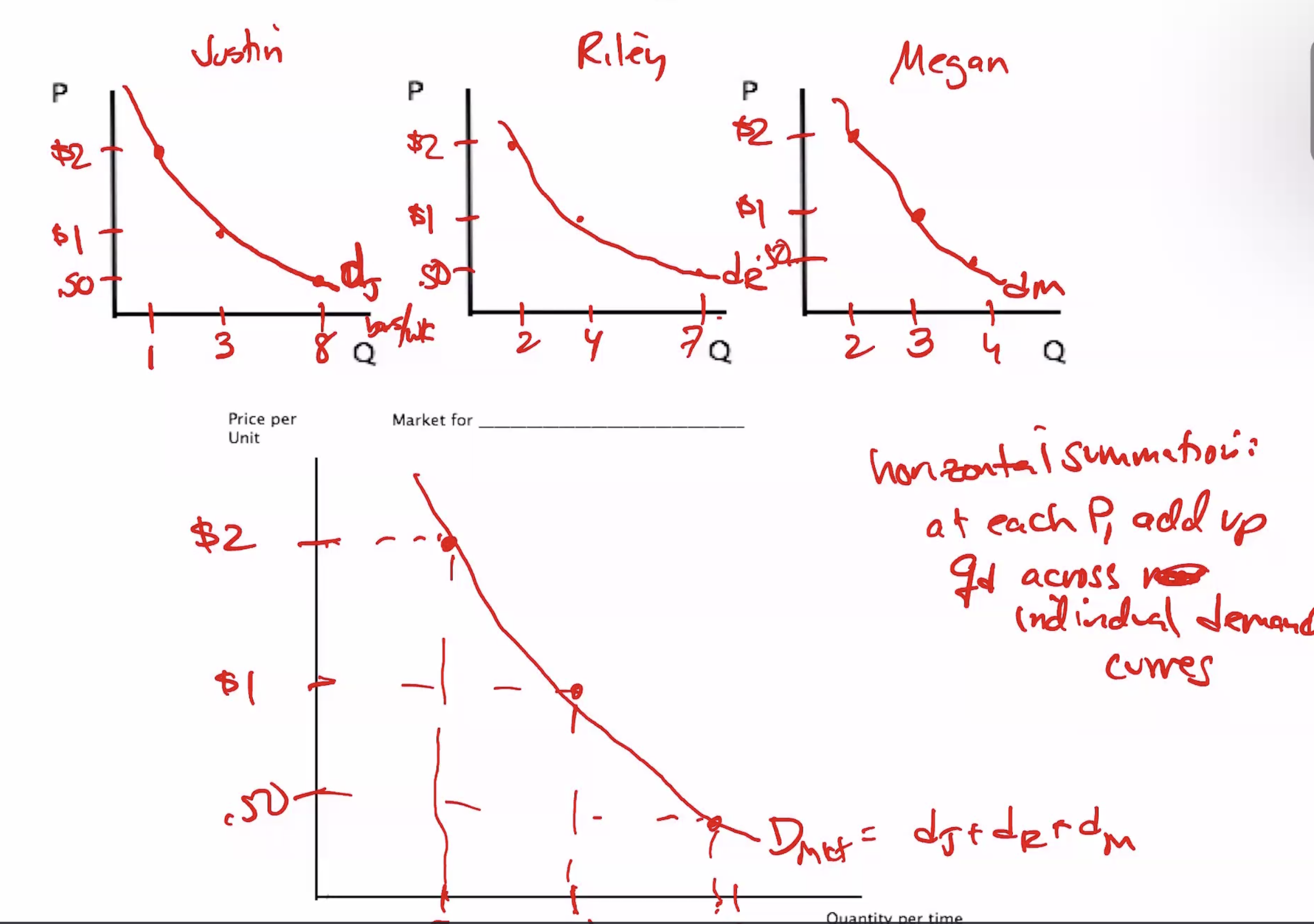
Private demand curve
horizontal sum of individual D curves
Imperfect Information Types
Incomplete and Asymmetric
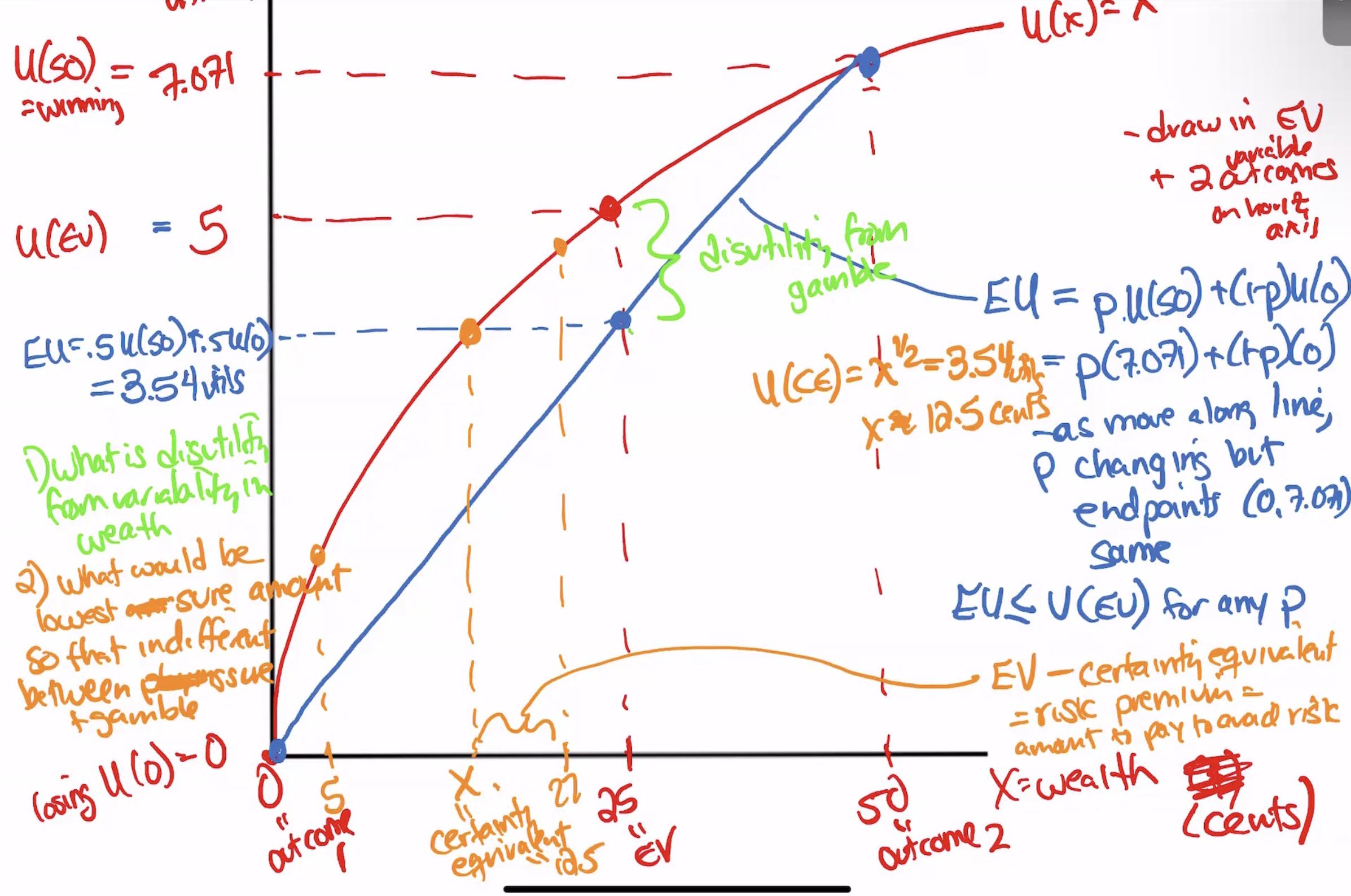
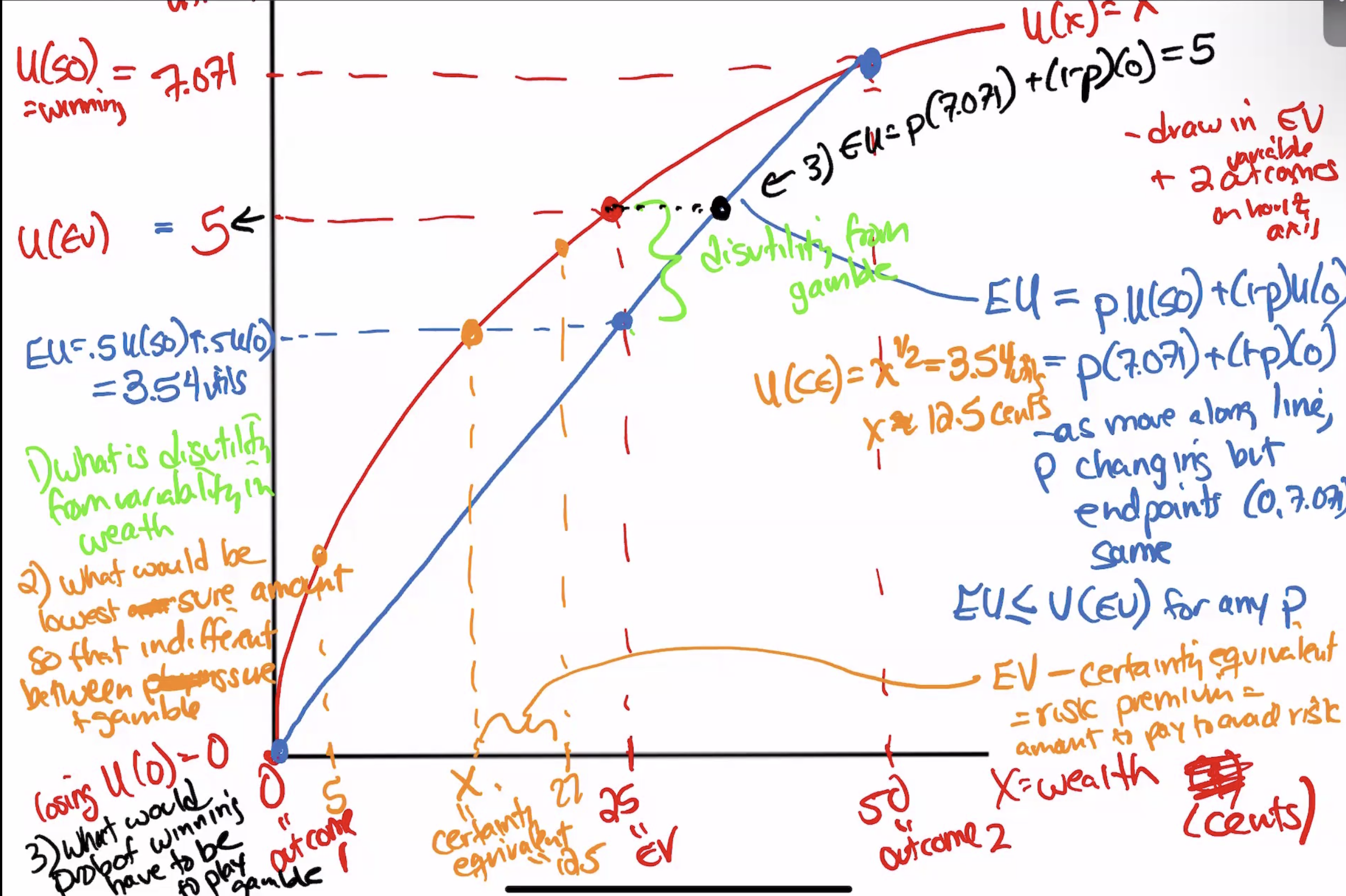
Expected Value
EV=p1O1+….
Expected Utility
the sume of pronbbilities of each outcome*the utility of each outcome
Utility of expected value
the utility from the expected value of an outcome

EU and U(EV) comparison for differnent perspectives of risk


if diminishing mu income
risk averse
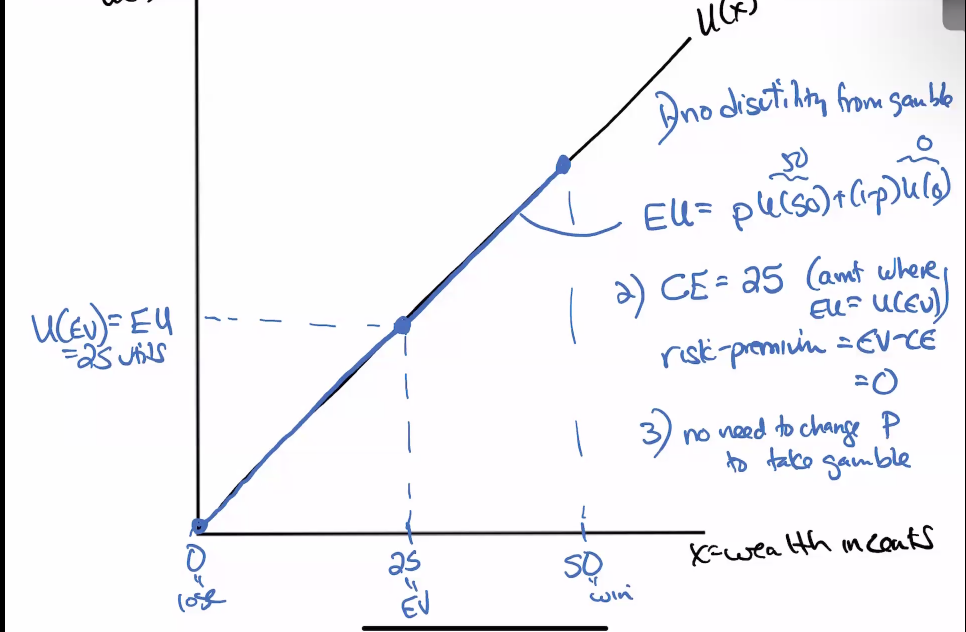
Risk neutral
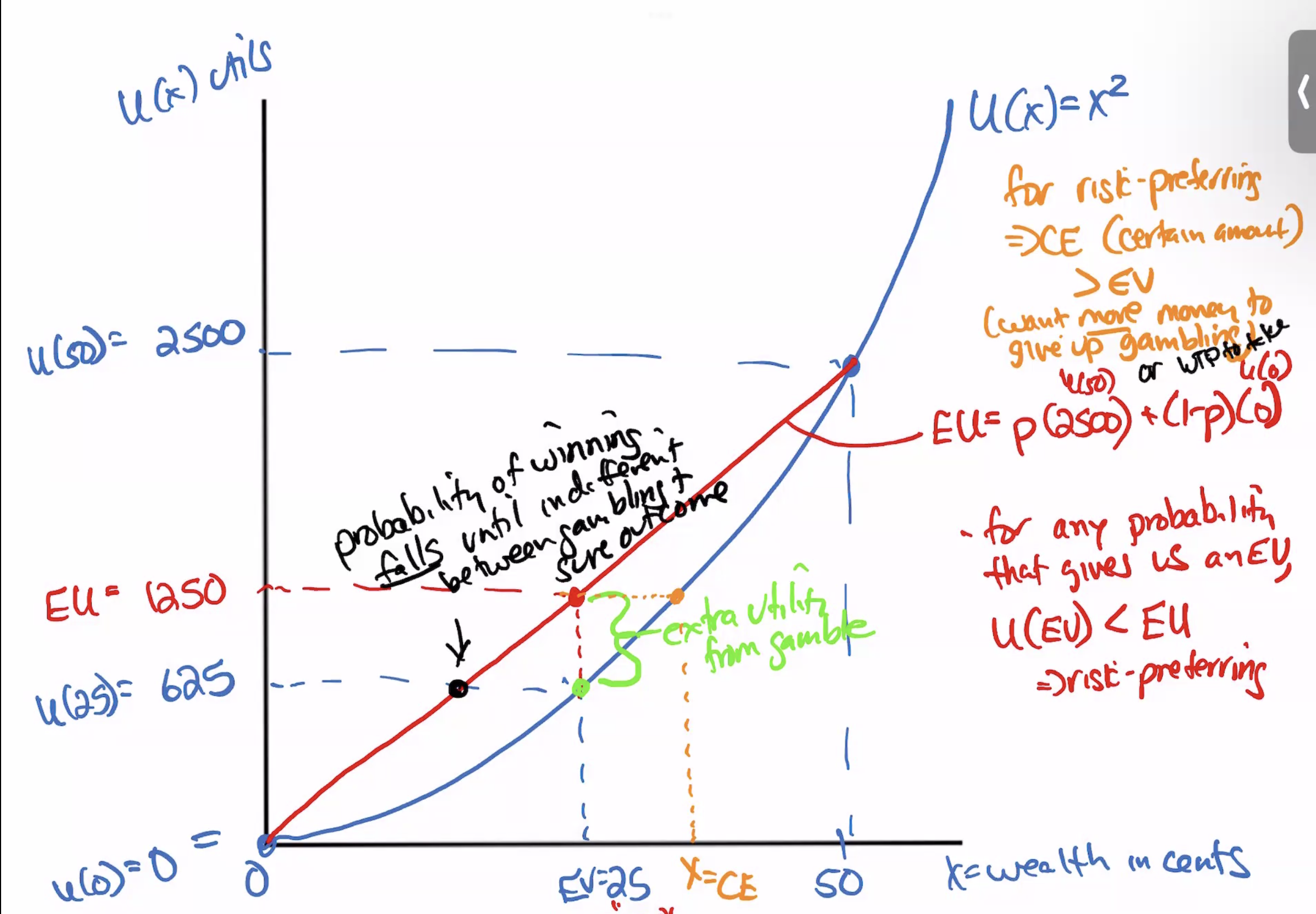
Risk preferring
Problems with asymetric info
1) Adverse selection or hidden-type problem—-one person can’t see other side of market while other can
2) Moral Hazard or hidden-action—can’t observe the actions of the other
3) Principal-Agent Problem
Lemons Cars
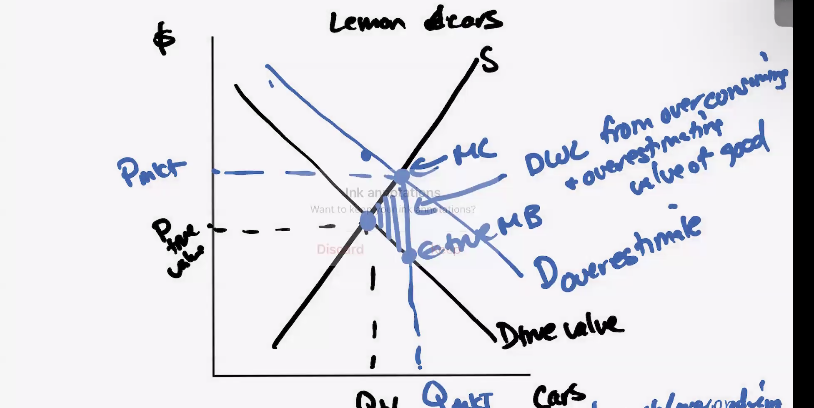
Errors in Predicting Risk
1) Hindsight Bias-because it happened, think the probability of it happening was high (things that actually happen seem, in hindsight, to have been far more Riley than they were in foresight)
2) Gambler’s Fallacy-thinking that independent outcomes are affected by past events (picking lotto numbers based on pass)
3) Overconfidence—think prob higher
4) Overestimate-low probability events
5) Underestimate high probability events
Errors in Predicting Happiness

Emotions and Changing Preferences
decision making effected by emotions and states
Time Consistency
impatient—-weigh immediate benefits more
procrastinate—weight immediate costs more
falling discount rates
Too Many Choices
decision fatigue—-parole board
Anchoring
anchor price based on other information
General Equilibrium and Government Intervention
Why should they
when market failures
redistribution of income

Pareto Efficient/Optimal
can’t make anyone better off without someone worse off
Pareto Improvement
make someone better off without making anyone else worse off
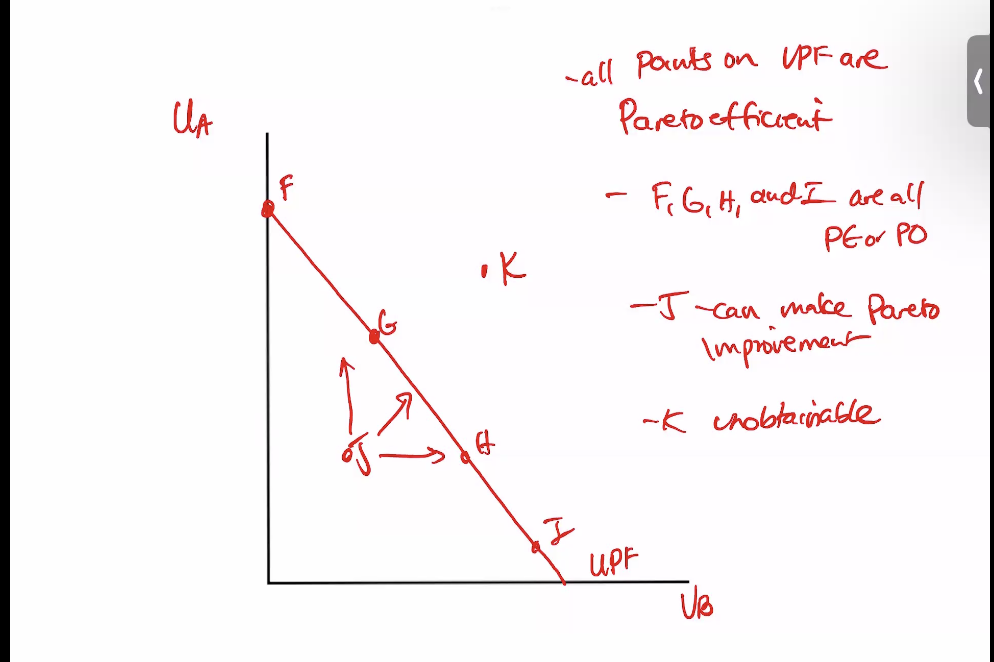
Kaldor-Hicks (potential Pareto improvement)
As long as gainers could compensate losers and benefit occurs to society, then improvement. But costly to do this
Polinsky’s efficiency
relation between aggregate benefits of a sitution and aggregate costs of a situation—size of the pie
Equity
how slice pie
Social Welfare function
function of utilities
Welfare economics
studies well being of many
Benthamite
greatest happines for greatest bymber
W=max of sum of utilities
people can have zero utility
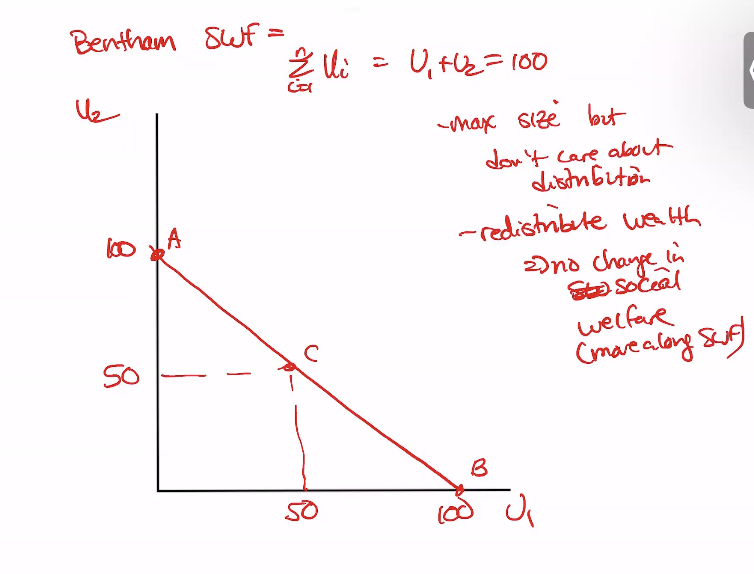
Rawlsian (minimax)
social welfare depends on wrost off
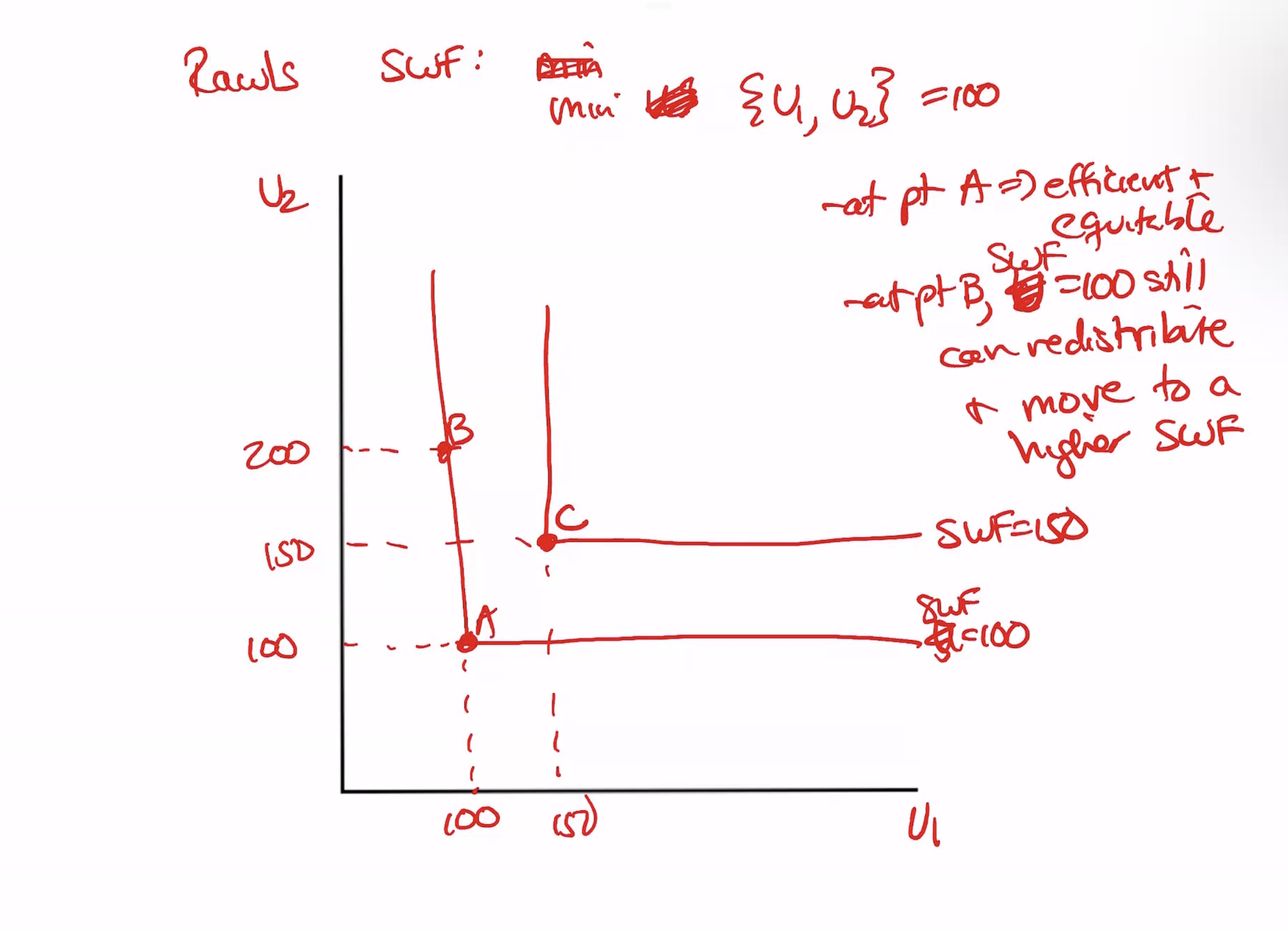
Nash
multiple utilities so that none can equal zero (balance equitable and efficient)
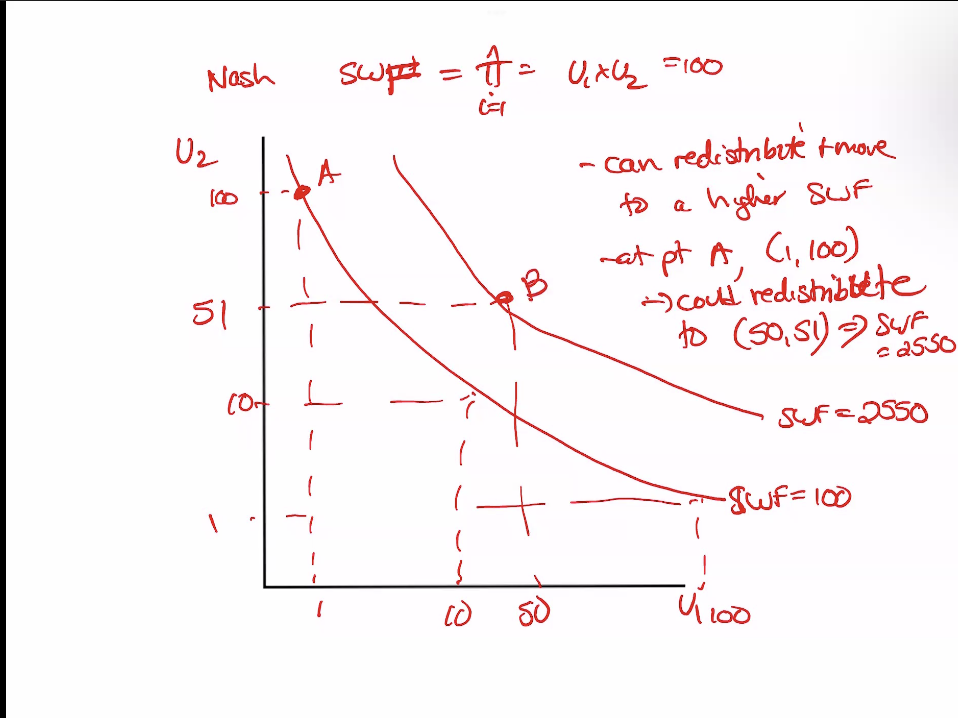
Trade off between effieicency and equity
Standard Assumptions in analyzing effiency of legal rules
1) Costs and benefits measured in terms of dollars
2) Consumer soverignty—-indivudals detrermine themselves the dollar values ro place on costs and benefits
3) Costs and benefits are stable-unchanged by public policy
4) Firms and consumers maximize benefits less costs
MEthods for Redistributing Income
1) Direct Tax and Transfer—crearetes incentive effects, distrobtions of prices—collecting and redistrubuting uses resources
2) Human investment—do they work, may not raise incomes of poor, long term to realize gains
3) Social Insurance (social security, unemploment insurance)-too expensive, adverse selection, irrational choices towards saving
4) Legal rules/outcomes—too blunt, may not target right people
assume tax and transfer is least costly—use effieicy not equity
Measuring Costs and Benefits
Diret Method—market price reflects MC and MB to society
Benefit of market existence= PS+CS
Indirect Method-
Structure of Government
Rule of law
3 branches
legislative-statutes
Mishkin
institutions are important to organizing property rights
institutions-the set of rules, organizations, and customs that govern the behavior of individuals and firms
property rights: the protection of perperty from expropriation by the government or other parties
Douglass North—-what is important ot economic growth
effective, low cost enforcement of contracts and strong property rights
Countries with english common law outperform others
Obstacles to effective propertu rights
corruption
high cost of legally establishing a business
governemtn taknig of property
wars/unstable legal systems
Epstein
accesses eastern German vs western-fall of berlin wall
don’t need to make constitutions different for each country because each country actually has same background—actuallly not different in governance—maximize utility
either paint toward culture or go to just general things
3 laws
property
contract
criminal/tort
Three questions when setting up law
Efficiency-equity question
Incenctive question —-consider care level—behavior of an individual or firm that affects costs and benefits—-and activity level
Risk-allocation question—-risk preference, access to information
Butterfield v Forrester
Butterfield driving
Forrester put log in road
Not legal to put log in road but Butterfield could see
according to precedent-negligence
create contributory negligence
broad ruling—this applies to all negligence
narrow-only car accidents
Butterfield partially responsible-so loses—-upheled by appellate
Jury role-decide the facts—butterfiled not drunk, but driving fast
Judge—instructs the jury and applies the law
appeal because incorrectly applied (cannot be on wrong facts)
new law—contributory negligence is a complete bar to recovery
Davies v Mann
davies leave donkey in road
going with precedent would incentivize accident
Last clear chance bariation of contributory negligence
Butterfield could have had last clear chance but law evolves over time
British Columbia Electric Railway v Loach
argue breaks didn’t work so didn’t have last clear chance
should have had last clear chance if maintained breaks properly
Second Civil Chamber case
drunk person on train
get to end
civil law-statute—-says train company had duty of care—-laws about contributory negligence
Flood v Kuhn
baseball—write about how important and who favorite players
reserve clause—keep salaries down, teams used 1 yr standard contracts with a clause that reserved the players for the team-players could not bargain with other teams
Flood sued-played for cardinals-traded to Phillies—-sued under Sherman antitrust act
Earlier decision-commerce vs business——limited reading that commerce needs goods not service—manufacturing economy
Baseball not subject—establish precedent
but became narrow interpretation
If courrt incorrect-overturn or law
1952 hearing—keep reserve clause
Toolsen v New York Yankees
still don’t overturn
but other supports are subject
act later passed
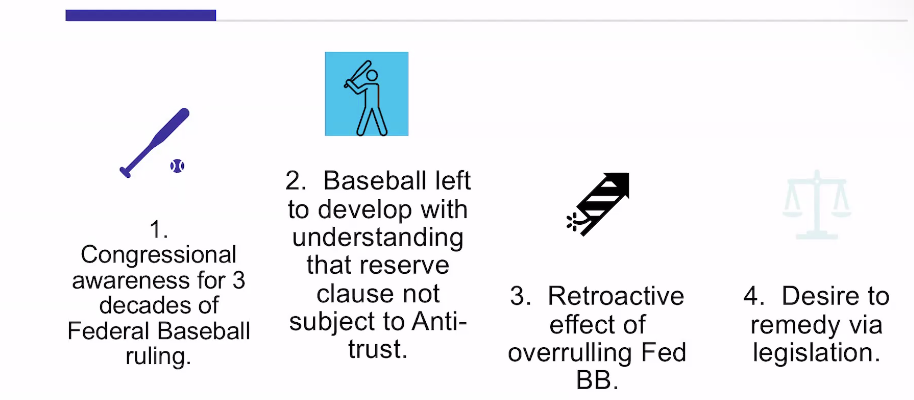
Holy Trinity Church v United States
can’t prepay for transport of alien of foreigner
exceptions
meant to cover low wage workers—protect domestic wages from cheap unskilled labor
court found only to include manual labor——narrow reading—rewrite the law
Judges make law through common law or interpretation

technical v ordinary meaning, grammar, etc, connectors