MCAT: DNA Replication: The "speed" of DNA polymerase
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
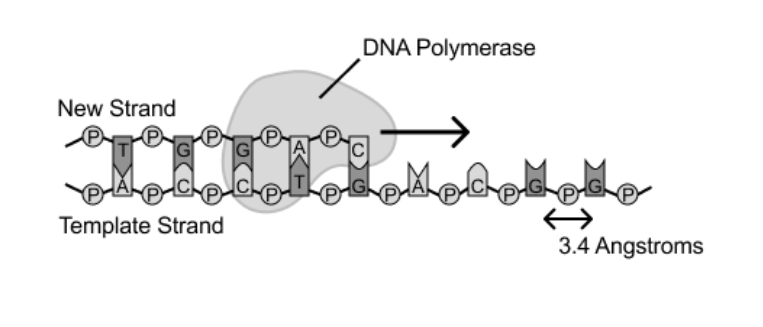
If a single stranded DNA template is 6.8 micrometers in length and a single DNA polymerase requires ~4,000 seconds to replicate it what is the average replication rate of the polymerase?
5.0 bp/s
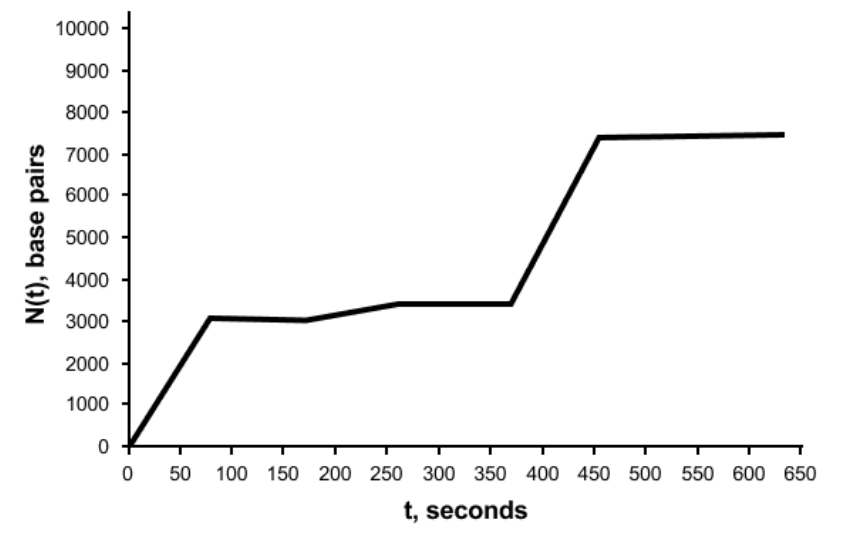
A scientist allows a single-stranded DNA molecule of known length to undergo replication with a DNA polymerase for a known time interval. At the end of this interval, she records the elasticity of the DNA molecule. Based on the method described in the passage, which quantity can be calculated for the DNA polymerase molecule?
Average speed of base pair generation
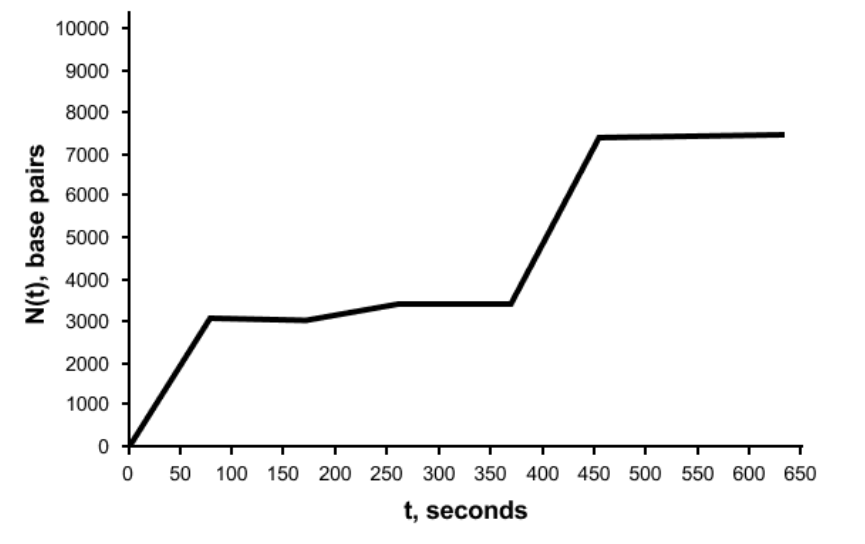
Which feature of Figure 2 represents the maximum replication rate of a single DNA polymerase molecule?
highest N(t) value
highest t value
highest slope value
highest plateau length
highest slope value
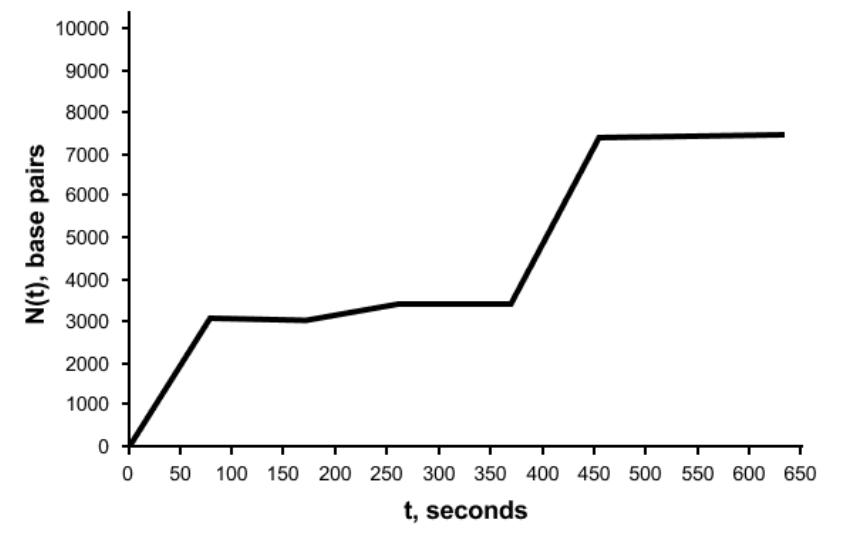
Which of the following would best explain the plateaus seen in Figure 2?
A. DNA structure is highly regular, allowing the polymerase to move at a constant speed.
B. DNA polymerase has reached its maximum velocity and can no longer acceleration
C. The replication rate of DNA polymerase depends on the surrounding concentrations of nucleotides.
D. Certain sequences in the DNA form secondary structures, such as hairpins, which impede the progress of DNA polymerase.
D
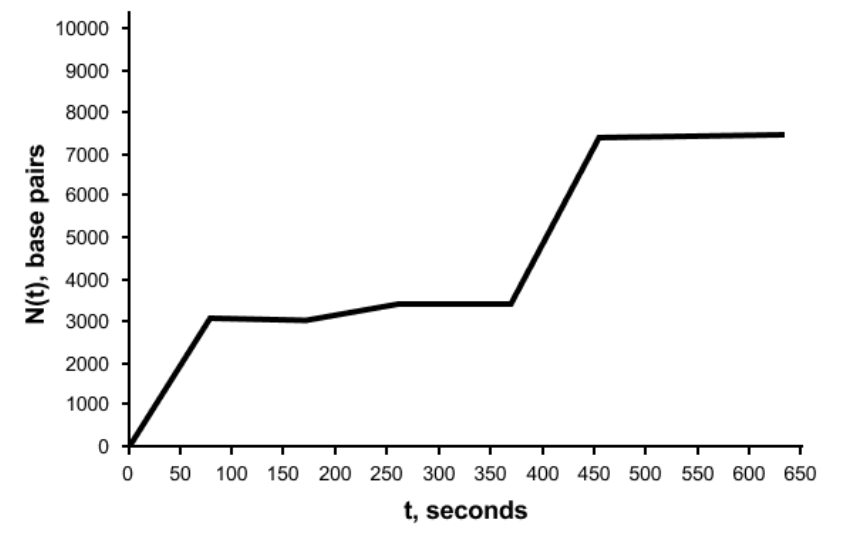
At approximately what time does the DNA polymerase molecule in Figure 2 experience the greatest positive acceleration in its rate of base pair generation?
375 s
In prokaryotes, which DNA polymerase is primarily responsible for DNA replication (i.e. elongating a growing strand of DNA)?
A. DNA polymerase I → removing and replacing
B. DNA polymerase II → repairing
C. DNA polymerase III → replication
D. DNA polymerase V → translation synthesis
C