Structure and Functions of Living Organisms Exam Style Qs
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Explain why no droplets are seen after bile and lipase solution is added to the oil and water mixture (4)
m1: (bile) emulsification
m2: smaller drops → increased SA
m3: optimum pH
m4: lipase is an enzyme and will break down fatty acids into glycerol
Explain how the villi is adapted to absorb glucose (5)
m1: large SA → m2: microvilli
m3: one cell thick → shorter diffusion distance
m4: diffusion occurs
m5: concentration gradient
Describe the role of chloroplasts in leaf cells (2)
m1: absorb light
m2: contains chlorophyll
m3: photosynthesis
Explain what happens to a leaf when it’s destarched (2)
m1: starch removed m2: converted to glucose m3: respiration/energy
A student is given two samples of carbohydrates
He tests to see if one is glucose and one is starch
Describe the two chemical tests he should use to identify each carbohydrate (4)
m1: use iodine m2: blue → black means starch is present
m3: Benedict’s solution, use water bath red → green means glucose is present
The small food molecules can be absorbed into the blood by villi in the small intestine.
Give three ways in which villi are adapted to absorb small food molecules (3)
m1: large SA: microvilli
m2: thin, short diffusion distance
m3: blood/capillaries
m4: permeable
Describe how the green pigment in leaf cells is removed safely before testing a leaf for the presence of starch (3)
m1: boil in m2: ethanol m3: water bath
Cholesterol is a fatty substance found in the blood that can increase the risk of heart disease.
Statins are drugs thought to lower blood cholesterol levels.
Design an investigation to find out the effect of statins on blood cholesterol levels.
Your answer should include experimental details and be written in full sentences and paragraphs (6)
m1: range the statin levels
m2: ensure the people are the same gender/age - CONTROL
s1+s2: same diet, same stress, same exercise, same smoking
m3: of several people/group
m4: measure cholesterol level m5: at start and end → measure change
Wasps defend themselves from predators by using a sting.
This means that predators avoid attacking wasps. Ash borers look very similar to wasps.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to explain why ash borers have evolved to look like wasps. (4)
m1: variation in Ash borers
m2: mutation means they are not eaten m3: increases chance of survival m4: they reproduce/breed
m5: they pass on genes/alleles m6: process continues over time
Gazelles cannot maintain their top speed for a long time because a change in the type of respiration takes place in their muscle cells.
Explain how this change in respiration stops gazelles from running at a top speed for a long time. (3)
m1: anaerobic respiration m2: means less oxygen m3: which produces lactic acid m4: which affects the pH of enzymes m5: causing them to denature m6: meaning there is less energy in the form of ATP
Zebras also try to avoid being caught by lions.
It was thought that the striped coat of zebras helps to camouflage them.
A new theory suggests the striped coat evolved because it reduces the number of biting flies that feed on zebra blood.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to explain how a striped coat that reduces the number of flies feeding on zebra blood may have evolved. (4)
m1: variation m2: mutation m3: survival of the fittest m4: produce offspring m5: which pass on gene
On a hot day there is less water in urine.
Explain how the kidney is able to reduce the water content of urine produced on a hot day (3)
m1: more ADH m2: increased permeability m3: collecting duct m4: reabsorption of water
Some people do have glucose in their urine. These people have diabetes.
Suggest why a person with diabetes has glucose in their urine. (2)
m1: not enough insulin m2: causes the glucose levels to be too high m3: and the kidney is unable to reabsorb all the glucose
Describe the process of digestion in the mouth (3)
m1: chemical digestion using amylase m2: which breaks down starch m3: into glucose m4: physical/mechanical digestion as the teeth churn the food
Describe how white blood cells are used by the body to defend against infection (5)
m1: phagocyte engulfs pathogens m2: enzymes m3: breakdown m4: lymphocyte produce m5: antibodies m6: and make specific m7: antigens m8: memory cells
State two ways in which a bacterium differs from a virus (2)
m1: bacterium has a cell wall and no protein coat
m2: viruses do not have a cell membrane
Listeriosis is an illness caused by eating food containing the bacterium Listeria
Explain how the immune system protects most people from becoming ill with listeriosis. (5)
m1: the immune system kills/destroys bacteria m2: white blood cells m3: phagocytes m4: engulf a pathogen m4: lymphocytes m5: antibodies m6: bond to antigens m7: produce memory cells
Another characteristic shown by animals is the ability to respond to their surroundings.
For example, a person may withdraw their hand from a hot object.
Describe the sequence of events that cause this response. (5)
m1: receptor m2: sensory neurone m3: impulse m4: CNS spinal cord m5: synapse m6: relay neurone m7: motor neurone m8: muscle/effector m9: contract
Fully grown penguins are large, often weighing up to 30 kg. Most other birds are much smaller.
Explain how being large helps the penguin to survive at very low temperatures. (2)
m1: smaller SA:V ratio m2: less heat loss
Penguins also have soft downy feathers and a thick layer of fat just below the skin.
Suggest how these features help penguins to survive. (2)
m1: insulation m2: trap warm air m3: less heat loss
One part of the penguin that is especially exposed to the cold is their feet.
The muscles that operate the feet are located in the penguin’s body rather than in the feet themselves.
Suggest how this benefits the penguin.
m1: muscle kept warm m2: respiration m3: enzymes
Farmers use bird scarers that make a sudden loud noise to frighten birds away from their crops.
Design an investigation to find out if noise affects the amount of crops birds eat.
m1: range noise and no noise m2: ensure the species is controlled → same species m3: mass eaten/number eaten → count birds m3: replication evident m4: time period stated m5: control weather → same time of day
Describe how the growth hormone could be destroyed in the stomach. (3)
m1: hydrochloric acid m2: enzyme m3: breakdown m4: acid denatures growth hormone
The growth hormone used in this investigation was obtained from genetically modified bacteria.
Describe how bacteria can be genetically modified and used to produce growth hormone. (4)
m1: gene/allele m2: restriction (endonuclease) m3: ligase m4: plasmid m5: vector m6: recombinant
Describe how the levels of blood glucose are kept constant in human plasma after eating a meal. (5)
m1: pancreas m2: insulin m3: lower levels m4: glycogen
Describe the effects of ADH in the body. (3)
m1: collecting duct m2: more permeable m3: more water reabsorbed into blood m4: osmosis m5: urine concentrated
Plant roots also respond to external stimuli. Describe the response of roots to gravity and explain how this response benefits the plant. (3)
m1: positively geotropic m2: hold plant m3: mineral ions
Describe how the growth hormone could be destroyed in the stomach (3)
m1: hydrochloric acid m2: enzyme m3: breakdown m4: acid denatures growth hormone
The growth hormone used in this investigation was obtained from genetically modified bacteria
Describe how bacteria can be genetically modified and used to produce growth hormone. (4)
m1: gene m2: restriction m3: ligase m4: plasmid m5: vector m6: recombinant
Many seeds contain starch.
Suggest what happens to starch in the gut of a parakeet. (3)
m1: digested m2: amylase m3: maltose
Describe how the levels of blood glucose are kept constant in human plasma after eating a meal. (3)
m1: pancreas m2: lower levels m3: glycogen
Describe how structures B and D help a person to breathe in. (5)
m1: diaphragm m2: moves down m3: ribcage moves up and out m4: increase in (thorax) volume m5: decrease in (thorax) pressure
Smoking can increase the risk of developing coronary heart disease.
Explain how coronary heart disease can cause death (5)
m1: blocked m2: coronary artery m3: clot m4: fat/cholesterol m5: less blood to heart m6: less oxygen m7: muscle cells m8: less respiration → anaerobic respiration m9: lactic acid m10: heart attack
Explain why the cells in distilled water look different when compared to the cells in salt solution. (4)
m1: water into cells m2: outside solution/distilled water more dilute m3: cell membrane against cell wall m4: turgid m5: water leaves cell m6: outside solution
Explain how the rate of transpiration is affected by changes in the environment. (5)
m1: high humidity decreases rate m2: reduced concentration gradient m3: high wind increases rate m4: increased concentration gradient m5: high temperature increases rate m6: more kinetic energy m7: high light increases rate
Explain how the structure of the leaf is adapted for its role as the organ of photosynthesis. (6)
m1: upper epidermis/cuticle is transparent m2: which lets light through as light intensity increases the rate of p/s m3: contains chloroplasts m4: palisade mesophyll layer m5: close to surface which allows it to m6: absorb light m7: stomata/guard cells open when m8: carbon dioxide levels are high
Explain how the rate of photosynthesis is affected by changes to abiotic (non-living) factors throughout the day (4)
m1: temperature m2: tends to rise in the daytime which increases the rate of p/s
m3: light intensity m4: tends to rise in the daytime which increases the rate of p/s
Explain how very high temperatures might reduce the growth of plants. (4)
m1: less photosynthesis m2: more transpiration m3: stomata closed m4: less CO2 absorbed m5: enzymes denature
Explain why reducing the blood supply to the heart muscle cells can cause a heart attack (3)
m1: less oxygen m2: anaerobic respiration occurs m3: lactic acid produced which lowers pH level m4: enzymes denature
During the production of beer the number of live yeast cells initially increases, but then decreases towards the end of the process.
Explain why the number of live yeast cells decreases towards the end of the process. (2)
m1: less food/less maltose m2: increase in ethanol/alcohol
Explain why breathing rate is higher after exercise. (4)
m1: muscles m2: respiration m3: oxygen required m4: remove lactic acid m5: oxygen debt m6: remove carbon dioxide
Describe how smoking damages the lungs. (5)
m1: bronchitis m2: ciliated cells anaesthetised m3: harmful bacteria m4: cancer m5: tar produced m6: emphysema m7: smaller SA of damaged alveoli
If a pregnant woman smokes cigarettes it will increase the risk of her producing a smaller baby. This is because cigarette smoke contains carbon monoxide.
Suggest how carbon monoxide will increase the risk of producing a smaller baby (3)
m1: red blood cells m2: oxyhaemoglobin m3: less oxygen m4: baby has less metabolism and energy in the form of ATP therefore they are smaller
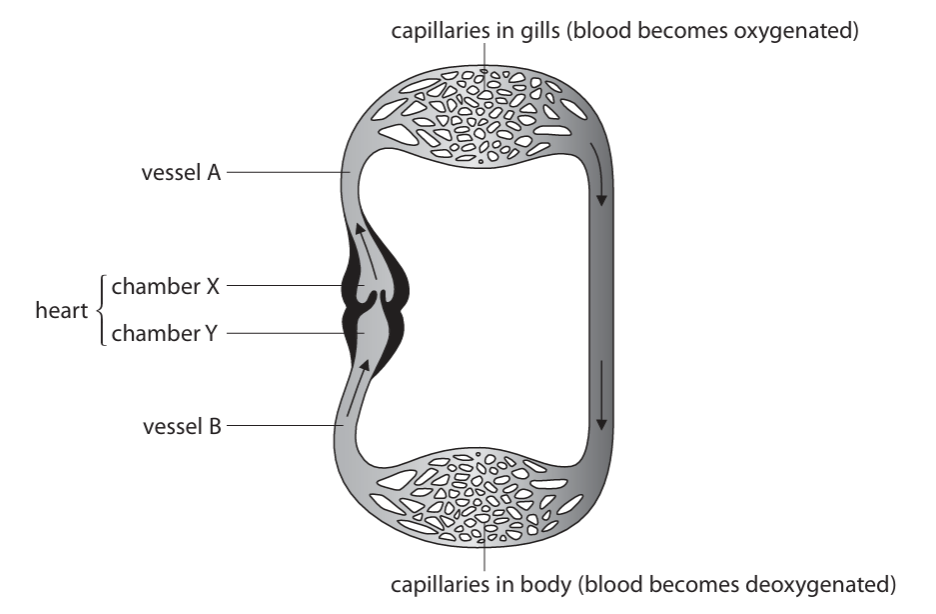
Describe how the structure of a fish heart differs from that of a human heart.(3)
m1: two chambers, one atrium one ventricle m2: less valves m3: no septum m4: chamber walls have smaller sides m5: only two blood vessels
The concentrations of the gases in the blood leaving the fish heart are different from the concentrations of the gases in the blood leaving the human heart in the aorta.
Explain the differences in the concentrations of gases. (4)
m1: less oxygenated m2: more carbon dioxide in fish heart m3: oxygen used in respiration m4: carbon dioxide produced by respiration m5: blood oxygenated in human lungs m6: carbon dioxide removed in human lungs