Chapter 4: Aerobic Cellular Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Refers to the reactions that occur within a cell through which energy is released from nutrient molecules, such as glucose, and made available for cellular use.
Cellular respiration.
Specifically refers to the breakdown of nutrients in the presence of oxygen to provide energy.
Aerobic cellular respiration.
What is the formula for aerobic cellular respiration?
C6 H12 O6 → 6 CO2 + 6 H20 + 32-36 ATP + HEAT.
What is step #1 of aerobic cellular respiration?
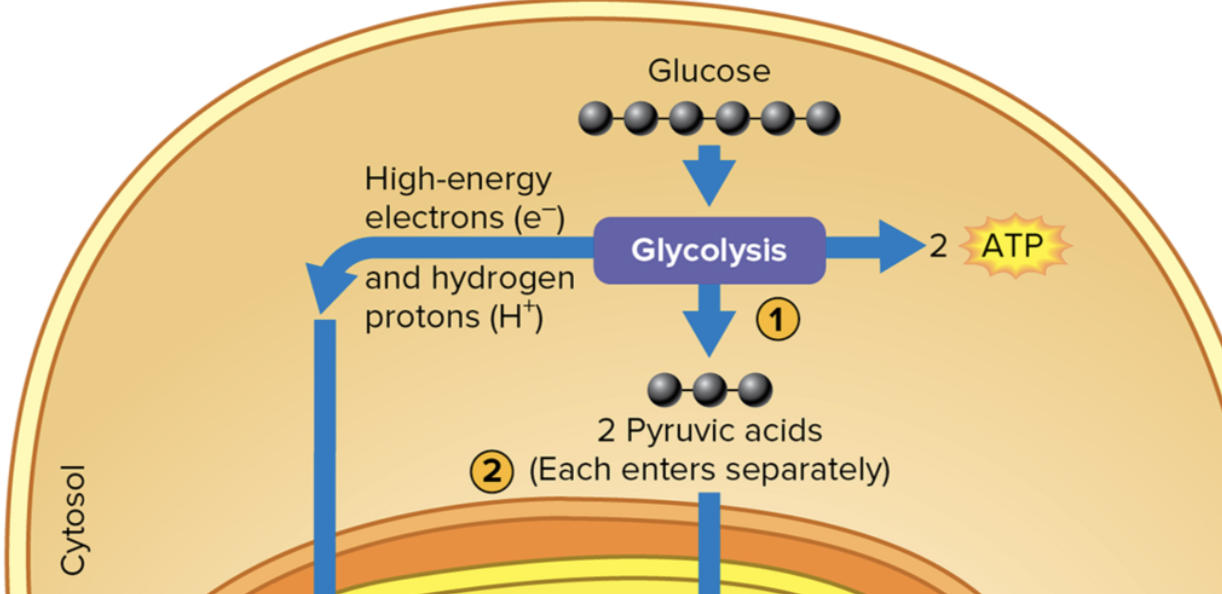
Glycolysis
What is glycolysis?
Series of 10 reactions that take place in cytosol.
Where does the reactions of glycolysis take place in?
Cytosol.
Phase 1 of Glycolysis: Priming
2 ATP are used to transfer phosphate groups to the glucose molecule.
Phase 2 of Glycolysis: Cleavage
The BC (B: Phosphate, C: Carbon) molecule split. Basically, 6 molecules are being split into 2*3C (Two 3 carbon molecules) molecules.
Phase 3 of Glycolysis: Oxidation reduction reaction
Production of ATP, and release of hydrogen atoms.
2*3C molecules are oxidized/lose energy → Energy transferred to the produced ATP and reduce NAD+ and NADH through the transfer of H.
State the net products of glycolysis based on the input of one original glucose:
Two molecules of pyruvic acid (2 * 3C pyruvic acid molecules); two molecules of ATP (net gain); 2 molecules of NADH.
What happens after the glycolysis?
Prep/conversion of pyruvic acid
What is the first step of the prep/conversion of pyruvic acid?
Each pyruvic acid loses C (carbon) atom in the form of CO2 (carbon dioxide).
What is the second step of the prep/conversion of pyruvic acid?
Redox reaction produces a reduced NADH, it temporarily accepts the energy (H).
When each pyruvic acid loses C (carbon) atom in the form of CO2 (carbon dioxide) and the redox reaction produces a reduced NADH (temporarily accepts the energy (H)), then it would result in:
Acetic acid.
How is CAC (Citric Acid Cycle) made?
Acetic Acid combines with coenzyme A producing acetyl coA.
What does the prep/conversion of pyruvic acid result in?
2 * 1 CO2 = 2CO2
2* NADH = 2 NADH
2 * 1 Acetyl coA = 2 Acetyl CoA (2c)
What is step #2 of aerobic cellular respiration?
Citric Acid Cycle (CAC).
At the beginning of the citric acid cycle, ___ combines with oxaloacetic acid to produce citric acid.
Acetyl coA.
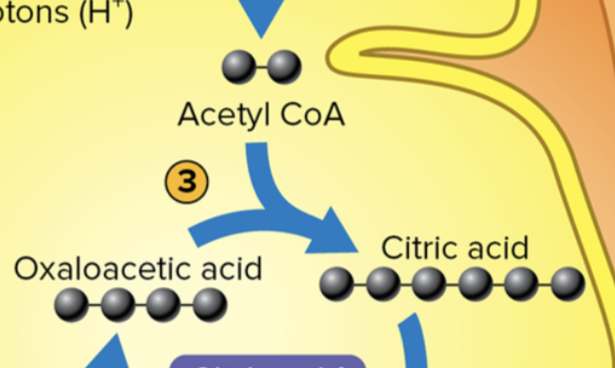
What is the citric acid cycle?
A cycle of 8 metabolic reactions.
The reactions of the citric acid cycle take place in the ___ of a eukaryotic cell.
Matrix of the mitochondria.
How many times does the citric acid cycle turn for every original glucose? (This one)
The cycle turns twice for every original glucose.
What are the results for one turn of the citric acid cycle?
Production of 2 CO2.
Production of 1 ATP molecule.
Production of 3 NADH
Production of 1 FADH2
Last reaction regenerates oxaloacetic acid.
What is the result for two turns of the citric acid cycle?
2 * 3 NADH = 6 NADH
2 * 1 ATP = 2 ATP
2 * 1 FAHD2 = 2 FADH2
2 * 2 CO2 = 4 CO2
How many reduced NADH are produced during ONE TURN of the citric acid cycle?
3 NADH.
How many times does the citric acid cycle turn for every one original glucose molecule?
2 times.
How many ATP molecules are directly produced during ONE TURN of the citric acid cycle?
1 ATP molecule.
At the point that one original molecule of glucose has proceeded through glycolysis, oxidation of pyruvate, and the citric acid cycle, how many reduced NADH total have been produced?
10 reduced NADH.
At the point that one original molecule of glucose has proceeded through glycolysis, oxidation of pyruvate, and the citric acid cycle, how many reduced FADH2 total have been produced?
2 reduced FADH2.
What is step #3 of aerobic cellular respiration?
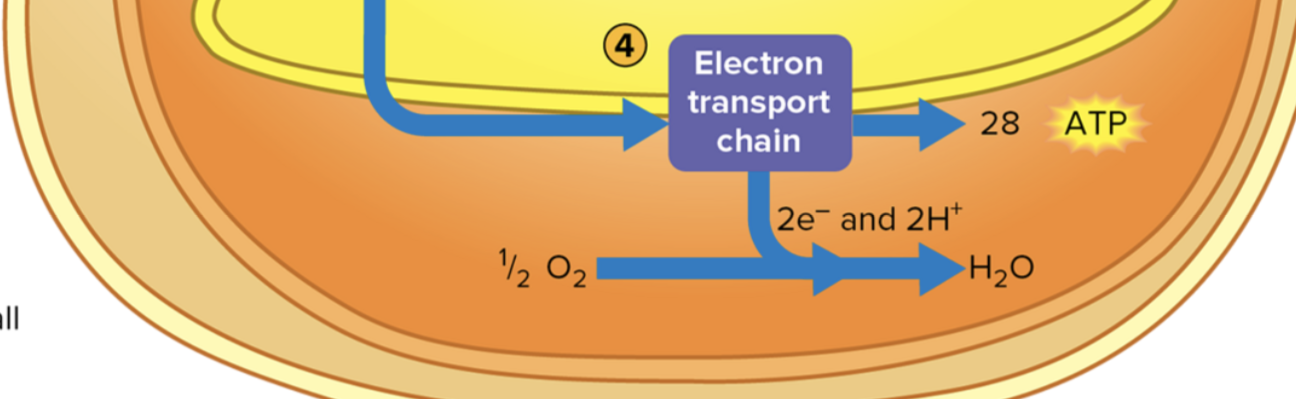
Electron transport chain.
What is the electron transport chain?
A series of proteins embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
The molecules that composed the electron transport chain of eukaryotic cell are located:
Embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Transfer of electrons among proteins generates energy. This energy is used by a molecule called ?
ATP Synthase.
Which molecule is powered by the flow of electrons through the electron transport chains to phosphorylate ADP to ATP?
ATP Synthase.

ADP + Pi = ATP.
How does the formula for ATP look like?
How are electrons delivered?
Electrons are delivered to the ETC by NADH and FADH.
O2 (Oxygen).
Which of the following acts as the final electron acceptor at the end of the electron transport chain?
What is the result of the electron transport chain?
For every NADH = 2.5 ATP
For every FADH2 = 1.5 ATP
Approximately, how many total ATP molecules are produced from the complete aerobic respiration of one molecule of glucose all the way through the ETC?
32-36.
Written Result for ETC:
In total per glucose: 10 NADH (2.5ATP/NADH) = 25 ATP
+ 2 FADH2 = (1.5/FADH2) = 3 ATP = 28ATP
+ 2 ATP (Glycolysos) = 30 ATP
+ 2 ATP (CAC) = 32 ATP
= 32 ATP
34.
How many net molecules of ATP molecules are produced when one original molecule of glucose is completely metabolized in the presence of O2 (oxygen)? (HW Question)
During aerobic cellular respiration, which molecule acts as a temporary electron acceptor during REDOX reactions?
NAD+.
Lactic acid/lactate
NADH from glycolysis reduces pyruvic acid and produces lactic acid/lactate.
How much capacity do skeletal muscles have?
Skeletal muscles have some capacity.
Limited capacity.
Certain skeletal muscle cells are able to convert nutrients to energy in the absence of oxygen for a limited amount of time. Which of the following describes that process?
Glycolysis followed by reduction of pyretic acid to lactate (lactic acid).
How many net ATP molecules are produced when one molecule of glucose undergoes anaerobic respiration? (Think of in the absence of oxygen O2).
2.