Geography Rivers and Coasts Paper 1.
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Describe how waves form.
wind blowing over the ocean creates friction with the water surface causing ripples to form.
Faster moving ripples merge with slower ones. Waves become bigger and more organised.
The longer the waves travel for, the larger and more organised they become
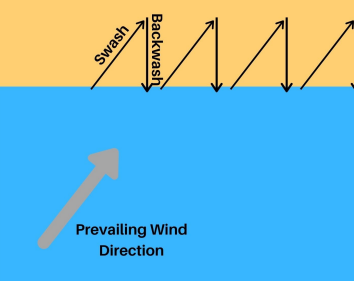
What is backwash?
movement of the wave down the beach
What is swash?
movement of the wave up the beach
Describe the features of a constructive wave.
wave crests are far apart
wave spills forward
gentle sloping wave front
strong swash and weak backwash
results in gentle beach
Describe the features of a destructive wave.
wave crests are close together
steep wave front
wave plunges downwards
strong backwash which pulls pebbles and sand out to sea
results in steep beach
What is weathering?
The breaking down of rocks by mechanical, chemical or biological processes.
What is freeze thaw action?
mechanical weathering
where rain fills up in cracks in rocks, freezes overnight and expands which pushes the crack outwards
What is mechanical weathering?
The break up of rocks by physical force.
e.g. freeze thaw and biological weathering
What is biological weathering?
weathering when living things like animals and plants burrow into a crack which eventually weakens the structure.
What is chemical weathering?
Where rainwater which contains carbon dioxide, reacts with the calcium carbonate in rocks such as limestone and chalk. This dissolves and is washed away in the solution, weakening the rock.
What are the types of mass movement?
mudflows
rockfalls
landslides
rotational slip
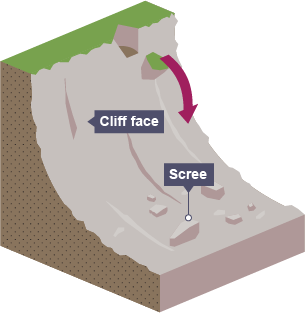
What is rockfall?
fragments of rock break away from the cliff face often due to freeze thaw weathering.
piles of rock called scree form at the bottom
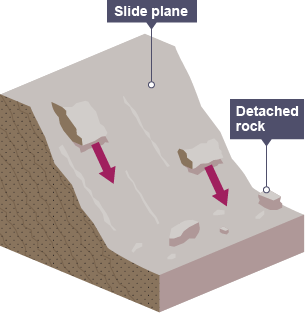
What is a landslide?
Where blocks of rock slide downhill because the bedding of the rock sloops downwards and makes it more likely that large blocks will shear out.
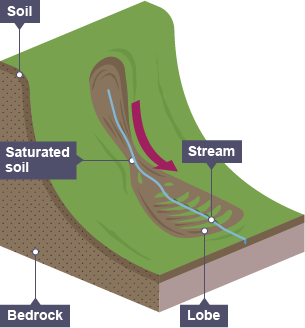
What is a mudflow?
soil or weak rock becomes saturated
occurs on slopes over 10 degrees tilt
rapid sudden movement occurs when there is not enough vegetation to hold the soil in place.
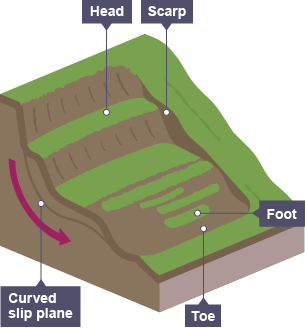
What is rotational slip?
occasional rapid movement of a mass of earth or rock sliding along a concave plane. They can occur over periods of heavy rain, when the water saturates overlaying rock, making it heavy and liable to slide.
What do processes end in?
ION
e.g.
erosion
abrasion
solution
What are the processes or erosion?
hydraulic action
abrasion
attrition
solution
What are the processes of transportation?
traction
saltation
suspension
solution
What is erosion?
The process of seawater wearing away land
What is hydraulic action?
type of errosion
The power of the waves as they smash against the cliff
trapped air is forced to make holes in the rock
this forces the rock to eventually break apart
What is corrasion?(abrasion)
type of erosion
fragments of rock, pebble and sand are picked up by waves and hurled at cliffs, acting is sandpaper
What is attrition?(it doesn’t wear the cliff down)
type of erosion
Where rocks and pebbles under the water knock against each other continuously, which chips fragments off.
What is solution?(corrasion)
type of erosion
acids in the seawater erode rock.
What is suspension?
type of transportation
particles are suspended in the flow of the water
What is solution?
type of transportation
rocks are being transported as dissolved chemicals, often from chalk
What is traction?
Type of transportation
large pebbles are rolled along the seabed by currents
What is saltation?
Type of transportation
Currents lift up pebbles which bounce along seabed.
What is deposition?
Where sediment is dropped due to less wave energy.
What is long shore drift (LSD)
pebble moves up the beach at an angle due to swash
backwash carries the pebble down the beach at a straight line
this happens continuously at the general direction of the prevailing wind.