Humanism, Self-Actualization, and Self-Determination
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
What did Maslow describe as the “third force” of psychology?
Humanism
If humanism is the third force of psychology, what were the first two forces?
Psychoanalysis and Behaviorism
Self-Actualization
Full use of exploitations of talents, capabilities, potentialities.
Need for Positive Regard
Innate human need for love, affection, acceptance
Who was Maslow’s advisor?
Harry Harlow
What was Maslow’s view on health?
Health isn’t the absence of disease. Any theory of motivation must deal with highest capacities of the healthy and strong man as well as the defensive maneuvers of one.
Maslow’s examples of self actualized individuals (4)
Harriet Tubman
Thomas Jefferson
Ben Franklin
George Washington Carver
What is the most central characteristic of self-actualized individuals?
Creativity
Peak Experiences
Brief experiences, often involving self transcendence or a state of awe, where the individual is no longer concerned with deficiency needs but more concerned with things like intrinsic values or things that are true and good
(T/F) There are 15 central characteristics to self-actualization. A self-actualized individual must possess all of them.
False; one doesn’t need to have all 15 characteristics, but it’s important to keep in mind that creativity is the most central characteristic.
Understanding what it means to be self-actualized makes one (more/less) likely to become self-actualized.
More
What percent of individuals does Maslow believe to be self-actualized?
2%

15 Characteristics of Self-Actualized Individuals
Efficient Perception of Reality
Problem Centered
Acceptance of self and others
Spontaneous
Detached
Independence from environment
Resistance to enculturation
Freshness of appreciation
Creative
Unhostile sense of humor
Democratic
Gemeinschaftsgefuhl
Intimate interpersonal relationships
Discrimination of means from ends (Intrinsic Motivation)
Peak Experiences

Gemeinschaftsgefuhl
Taking care of and looking out for the wellbeing of others
Prepotency
When we need something, we are focused on it because it demands our attention
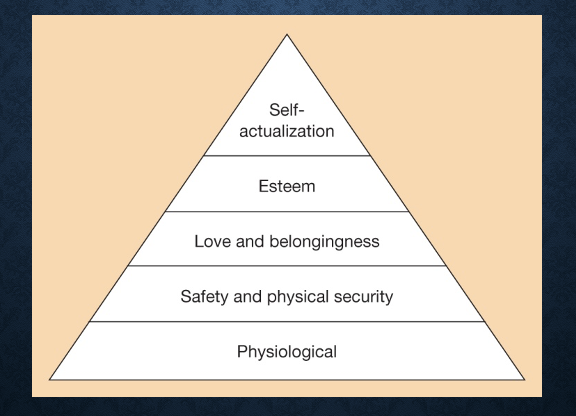
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Prepotency
We have different types of needs and they change in prepotency
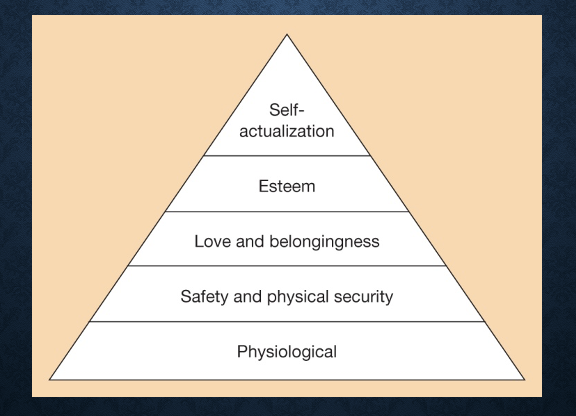
5 levels of needs in Maslow’s Hierarchy (lowest to highest)
Physiological → Safety and Physical Security → Love and Belongingness → Self-Esteem → Self-Actualization
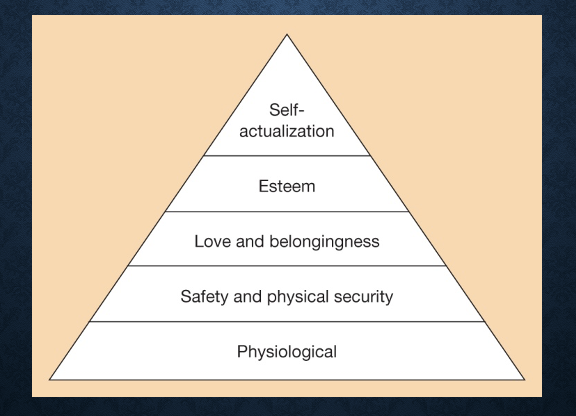
Deficiency Needs
When they are not met, they demand our attention. This includes all lower needs besides self-actualization
Growth Based Motives
Seeking growth, rather than being motivated out of deprivation of something. Self-Actualization is an example of this.
What state are peak experiences similar to?
William James’s Mystical State
William James’s Mystical State Features (4)
Ineffability
Noetic Quality
Transiency
Passivity
Ineffability
Can’t be put into words
Noetic Quality
Involves insight, revelation, or truth finding
Transiency
Is fleeting or brief
Passivity
Unwilled; it happens to you, it’s not a moment of self expression or exertion
Being Values (definition)
Occur when someone has a peak experience or is self actualized
Being Values (examples)
Truth
Goodness
Beauty
Aliveness
Completion
Meaningfulness
Self-sufficiency
Actualizing Tendency
The natural tendency of an organism to maintain or enhance itself and move in the direction of self-actualization.
Who termed actualizing tendency, need for positive regard, and the therapeutic approach?
Carl Rogers
What happens if positive regard is unconditional?
Then one has the freedom to be themselves, leading to higher congruence and higher actualizing tendency
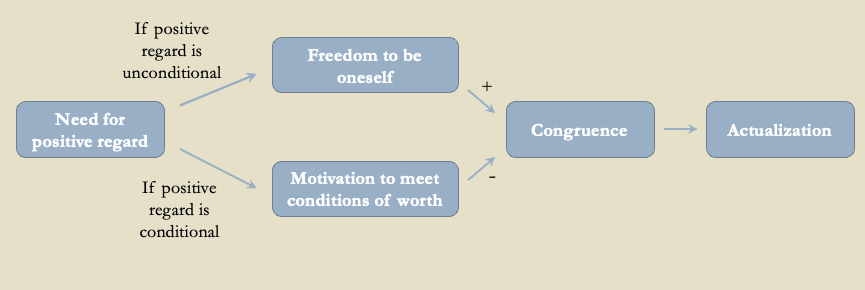
What happens if positive regard is conditional?
Then they have motivations to meet those conditions of worth, leading to lower congruence and lower actualizing tendency
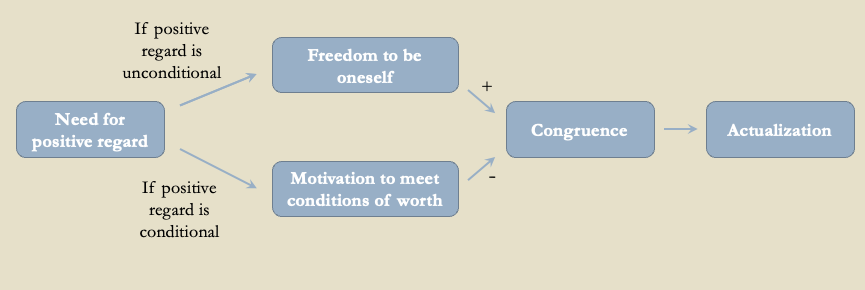
What is congruence the basis of?
Congruence is the basis of moving towards actualizing tendency
Therapeutic Approach (3)
Be accepting
Be empathetic
Be genuine
Which aspect of the therapeutic approach best predicts the outcomes of therapy?
Being empathetic
Which two psychologists created Self-Determination Theory?
Ed Deci and Richard Ryan
What 4 mini-theories go into self-determination theory?
Cognitive Evaluation Theory
Organismic Integration Theory
Causality Orientations Theory
Basic Needs Theory
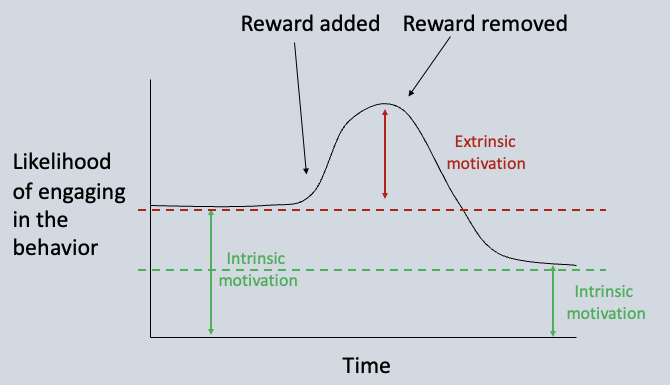
Cognitive Evaluation Theory
The likelihood of engaging in a behavior increases after a reward contingency system is in place, but when the reward is removed the likelihood of engaging in that behavior goes lower than the original baseline. This shows that intrinsic motivation decreases after a reward is introduced and then taken away because one misattributes the reason the did the action in the first place.
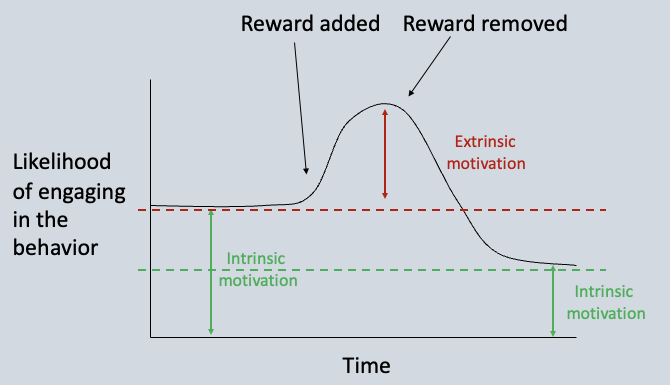
Intrinsic Motivation
Engaging in a task for its own sake (interest, enjoyment)
Extrinsic Motivation
Engaging in a task because of its consequences (reward that follows)
Can extrinsic motivation be healthy?
Yes (but not always)
Why do rewards often undermine intrinsic motivation?
Being controlled by others leads to a more external locus of causality
T/F: Rewards can increase or decrease intrinsic motivation.
True; if a reward makes you feel like you are being controlled, then it will likely increase your external locus of control and decrease your intrinsic motivation. However, if a reward increased your sense of autonomy, that may increase your intrinsic motivation by getting some positive confidence feedback.
Internal Locus of Causality
Person as “origin” of own behavior; free choice
External Locus of Causality
Person is “pawn”; rewards often make people feel this way
Organismic Integration Theory
External motivation can be healthy or unhealthy, depending on how it’s regulated.
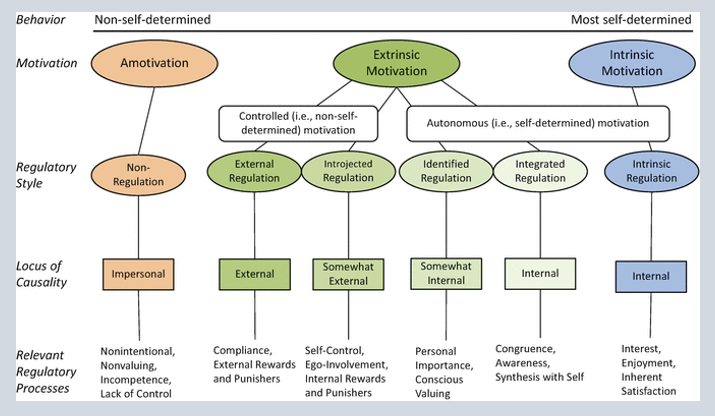
Two types of motivation for extrinsic motivation
Controlled Motivation
Autonomous Motivation
4 types of Extrinsic Motivation
External Regulation
Introjected Regulation
Identified Regulation
Integrated Regulation
External Regulation
External; compliance, external rewards and punishers (most controlled motivation)
Introjected Regulation
Somewhat external; self control, ego-involvement, internal rewards and punishers, feeling pressured by yourself (more controlled then autonomous)
Identified Regulation
Somewhat internal; personal importance, conscious valuing
Integrated Regulation
Internal; congruence, self awareness, synthesis with self
Performance is better when you have which type of extrinsic motivation?
Internalized form of extrinsic motivation (integrated regulation)
What is necessary to carry out the natural tendency to internalize extrinsic motivation?
A supportive environment
Causality Orientations Theory
Concerns individual differences in motivation styles; there are three orientations that play a role in intrinsic and extrinsic motivation.
Three Orientations of Causality Orientations Theory
Autonomy
Controlled
Impersonal
Autonomy (orientation)
Intrinsically motivation, internalized form of extrinsic motivation
Which type of orientation has people that are self-determined?
Autonomy
People who fall under the autonomy orientation have (better/worse) performance and well-being.
Better
Controlled
No intrinsic motivation, externalized form of extrinsic motivation
People who fall under the controlled orientation have (higher/lower) self-determination than people under the autonomy orientation.
Lower
Impersonal
Absence of motivation
Which orientation is related to anxiety?
Controlled
Which orientation is related to depression?
Impersonal
Basic Needs Theory
Human well being and growth are facilitated by satisfaction of three needs:
Autonomy
Competence
Relatedness
Autonomy (need)
Feeling free to make your own choices
Competence
Feeling of capability of high self efficacy and effectance motivation
Relatedness
having close, caring, intimate relationships with others
Humanistic Psychology
Everyone has potential for growth, no one is inherently bad
Phenomenological
Emphasis of importance of one’s own experiences
Organismic Valuing Process
Automatically evaluating experiences to tell if they promote actualization. If they don’t, you have a nagging sense.
Fully Functioning Person
Someone who is self-actualized: they are open to experiencing their feelings and are not threatened by them.
Conditions of Worth
Conditions under which people are judged worthy of positive regard
Conditional Self-Regard
Behaving to fit conditions of worth you’re applying to yourself; this interferes with self-actualization
Contingent Self-Worth
Use performance n some area of life as condition for self-acceptance
Self-Determination
Controlling ones own life; necessary for life of growth
Self-Concordant
Consistent with core values; important aspect of goals
Stereotype Threat
When there is a negative stereotype about a group, people are scared of being identified with that threat and thus tend to misidentify with the stereotyped group.
Transcendent Self-Actualizers
Self-Actualization is most important aspect of their life.
Existential Psychology
Each person must take responsibility for their choices; emphasizes individual perception of reality
Daesin
Totality of person’s experience as autonomous, separate, and evolving entity; there is no existence apart from world, and the world has no meaning apart from the people in it.
Existential Guilt
Occurs from failing to completely fulfill your possibilities
Terror Management Theory
Death leads to existential angst, and people respond to this by trying to live lives of meaning and value. This leads to increased self esteem and pushes them towards affiliation.
Content Analysis
Evaluates and organizes interview information into groupings of peoples statements.
Q-Sort
Give people a set of items on cards, person sorts cards into piles based on how life them to how unlike them the cards are. Forced self-evaluation.