Chemistry AP Review
1/432
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
433 Terms
Thermal heat equilibrium
When hot and cold molecules collide, they create an average of the two to form a temperature (or new one)
Heat capacity
Amt of heat needed to raise temp of thing by 1 C “specific” = g “molar” = 1 mole
Q = mcΔT
Allows one to calculate heat transfer (amount of heat transferred or amount needed to make a specific change). Q = joules total m = mass C = specific heat of substance. and Delta T is the change in temp
Lower specific heat value…
Higher change in temperature
What is ΔH?
The change in heat (enthalpy).
What is enthalpy?
Heat at constant pressure
What is the delta H (change in heat) of a reverse reaction?
Flip the sign of the initial
What is constant during phase change?
Temperature (plateau)
Entropy (disorganization)
Measure of how spread out atoms and molecules become during chemical processes
Calculating enthalpy
Delta H reaction = products - reactants
How do we calculate entropy?
Delta S = final - initial
Gibbs Free Energy
G = spontaneity H = enthalpy T = Kelvin S = Entropy
High heat capacity means…
Less temperature change when exposed to heat
What comes out of the q=Mc^T?
Joules! (For Q)
How to find Q with Delta H?
Q rxn divided by moles of limiting reactant bc 1:1 with rxn (Q = ΔH / n)
How to find qRxn in a calorimeter
Take the Q and make it negative (one gains, other loses)
How to find Delta H rxn?
The Qrxn divided by moles of the reaction, found through the limiting reactant (these being divided by the stoichiometry)
What does Delta H rxn tell us?
The energy per mole released in the reaction
What does reversing the equation do for Delta H?
Change its sign
For Delta H, what can we do when we change the stoichiometry?
Multiply Delta H by the new ratio. Double is 2x, ½ is 0.5x
How do we calculate the Delta H from several equations?
ADD, not multiply, their Delta Hs together
How to calculate Delta H from bonds
Reactants enthalpy minus products enthalpy
Delta S, positive and negative
Positive = More entropy (less order)
Negative = Less entropy (more order)
What’s a good way to gauge if entropy increased?
More moles, more gases and liquids (more entropy)
Delta H from Hf
Products minus reactants
How can we find the equivalence point on a titration curve?
The middle of the middle curve
What is the half equivalence point?
A weak acid and its conjugate base are equal at half the volume used to achieve the equivalence point (pH = pKa)
What are the strong acids to remember?
HCI, HBr, HI, HCIO4, H2SO4, HNO3
What is Ka/pKa?
The equilibrium of an acid. Pka is the -log of that
What occurs at the half equivalence point?
pH = pKa
pH = pKa + -log (A)/(HA)
Henderson-Hasselbach
What are the strong bases?
Mostly Group 1 and 2 metal hydroxides
How are pOH/pH correlated to OH/H?
Inversely
How can we find pOH or pH?
14 = pOH + pH
What is pOH/pH?
-log (OH) / -log (H)
How can we use pOH/pH to find H/OH?
They are equal to 10 to the power of the negative pOH/pH
What is LeChatelier’s principle?
If stress is put on an equilibrium equation, it will act to balance it out that stress.
If K is greater than 1, what does this mean?
Products are favored, and vice versa.
What do we never use in K?
Solids, nor aqueous solutions if not Keq.
What goes on top of K?
Products. Reactants on the bottom. Remember exponents!
What is Hess’s law?
Energy change will be the same if a reaction happens in one or multiple steps.
What are we trying to do when using Hess’s law for calculations?
To cancel out what we don’t want from a mixture of reactions.
How do we cancel out in Hess’s law?
We arrange an element on the products and reactants, and they subtract from each other. Remember that this may be necessary if you have too much of something in the final equation, in which case 2 H - 1.5 H = .5 H
What is molar solubility?
It’s molarity of a substance at equilibrium, and not the same as K.
Common ion effect
The solubility of an IONIC compound is decreased by the presence of a common ion (an ion that is also present!! in the compound).
ΔH and Endo/Exothermic
Positive is endo, negative is exo
Endothermic
Takes in heat
Exothermic
Releases heat
What do the coefficients in equilibrium reactions tell us?
The coefficients in equilibrium reactions show stoichiometric ratios/consumption. For example, X can be greater than 2Y at equilibrium.
How are H+ and OH- related?
Inversely.
Hess rules for reversing and doubling (EQUILIBRIUM ONLY)
Reversing = 1/K Doubling = Squared
What is NEVER part of equilibrium/chatelier?
Gases and liquids!
How does a catalyst effect equilibrium?
It does not change anything, it only speeds up the reaction (reverse and forward).
How do solids/liquids act in equilibrium?
Beyond being present at all, they don’t affect the equilibrium constant. Adding more does nothing!
Can gases be used in Kc?
Yes, just divide their moles by the liters.
How do we calculate molar solubility?
Get the x from the Ksp. ex: [Ag][CI] = x². If we take the square root of the Ksp we get it in this scenario.
What do metals do in solution?
Something like I2 becomes I- to dissolve better
What does saturated mean?
To be at equilibrium
How do we solve common ion problems?
use a rice box to account for the additional ion
How do we solve eq problems when the top is unknown and squared but we know the bottom?
Multiply bottom by Keq
If you have the total pressure, how can Dalton’s law tell you partial PR?
The number of moles is proportional to pressure, so use that to estimate
What do you NEVER need to use in Chemistry?
Quadratic equations
What must you remember when squaring/rooting?
The x coefficient is squared or rooted too
How do we solve common ion solubility problems?
Add the additional molarity to the concentration of the ion. Set M equal to Ksp. Get x!
When is a solution acidic?
When H30 > OH-
Hess law for multiplying coefficients by n
K^n (Times ½ is sq root of K as ex)
What can we do to avoid quadratics?
Ignore x if its very small or square root both sides
What do a strong acid and strong base make net ionic?
H30(aq) + OH(aq) → 2H20 (l)
What do a weak acid and strong base make net ionic?
HA(aq) + OH(aq) → H20(l)
What do a weak base and strong acid make net ionic?
B(aq) + H30(aq) → HB-(aq) + H20(l)
What do a weak acid and weak base make net ionic?
B(aq) + H30 (aq) → HB(aq) + H20(l)
How can we determine the strongest base/acid?
Equilibrium favors the side opposite to it
What is a buffer solution?
A weak acid and its conjugate base which prevent precipitious changes in the pH (neutralizes H and/or OH)
Effective buffer range
When the pH is less than -1 or +1 the pKa
[HA] = [A]
pH = pKa
[HA] > [A]
pH < pKa
[HA] < [A]
pH > pKa
How do we determine good indicators?
Their pKa should be near the pH at the equivalence point
What can we use to find Ka or Kb if we have the other?
ka * kb = kw
A solution is only acidic if..
[H30] > [OH]
What does high electronegativity do to a base/acid?
Base weaker b/c less proton acceptance (repels), acid stronger because more proton donation (repels)
What does low electronegativity do to a base/acid?
Base stronger b/c more proton acceptance (attracts), acid weaker because less proton donation (attracts)
Hydrochloric Acid (STRONG ACID)
HCl
Hydrobromic Acid (STRONG ACID)
HBr
Hyrdroiodic Acid (STRONG ACID)
HI
Nitric Acid (STRONG ACID)
HNO₃
Perchloric Acid (STRONG ACID)
HClO₄
Sulfuric Acid (STRONG ACID)
H₂SO₄
Group 1 AND 2 metal hydroxides are…
Strong bases
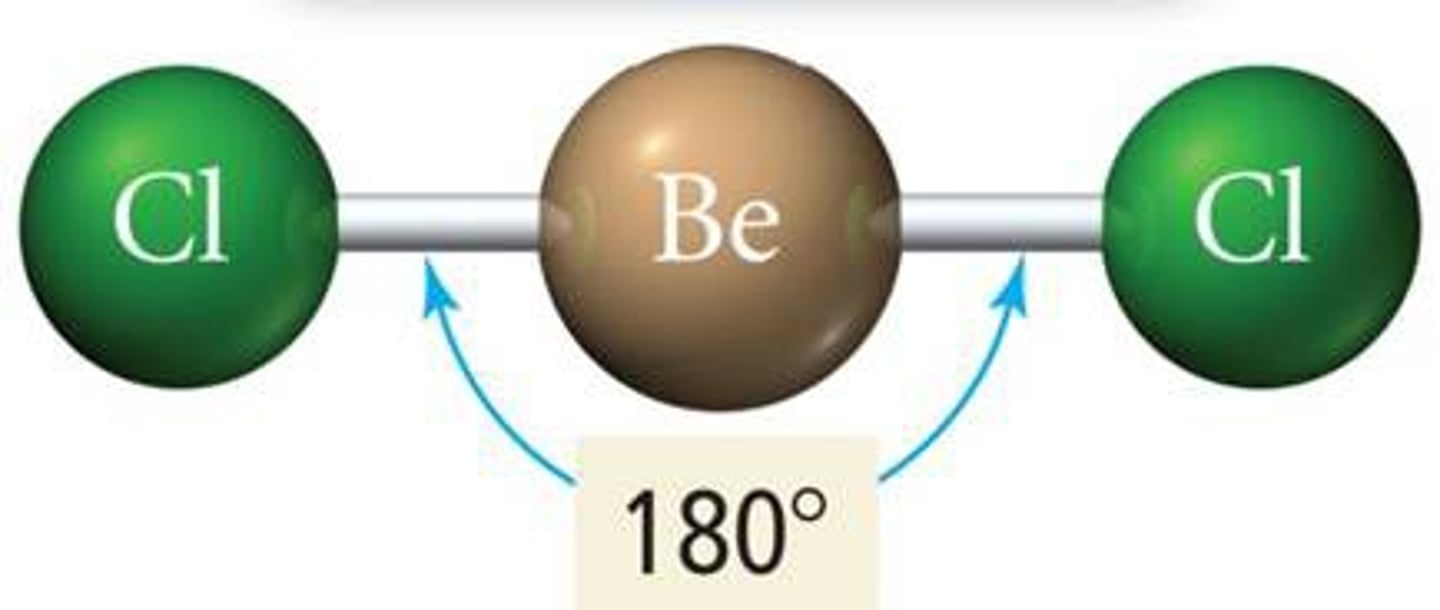
2 groups around central atom
linear (180)
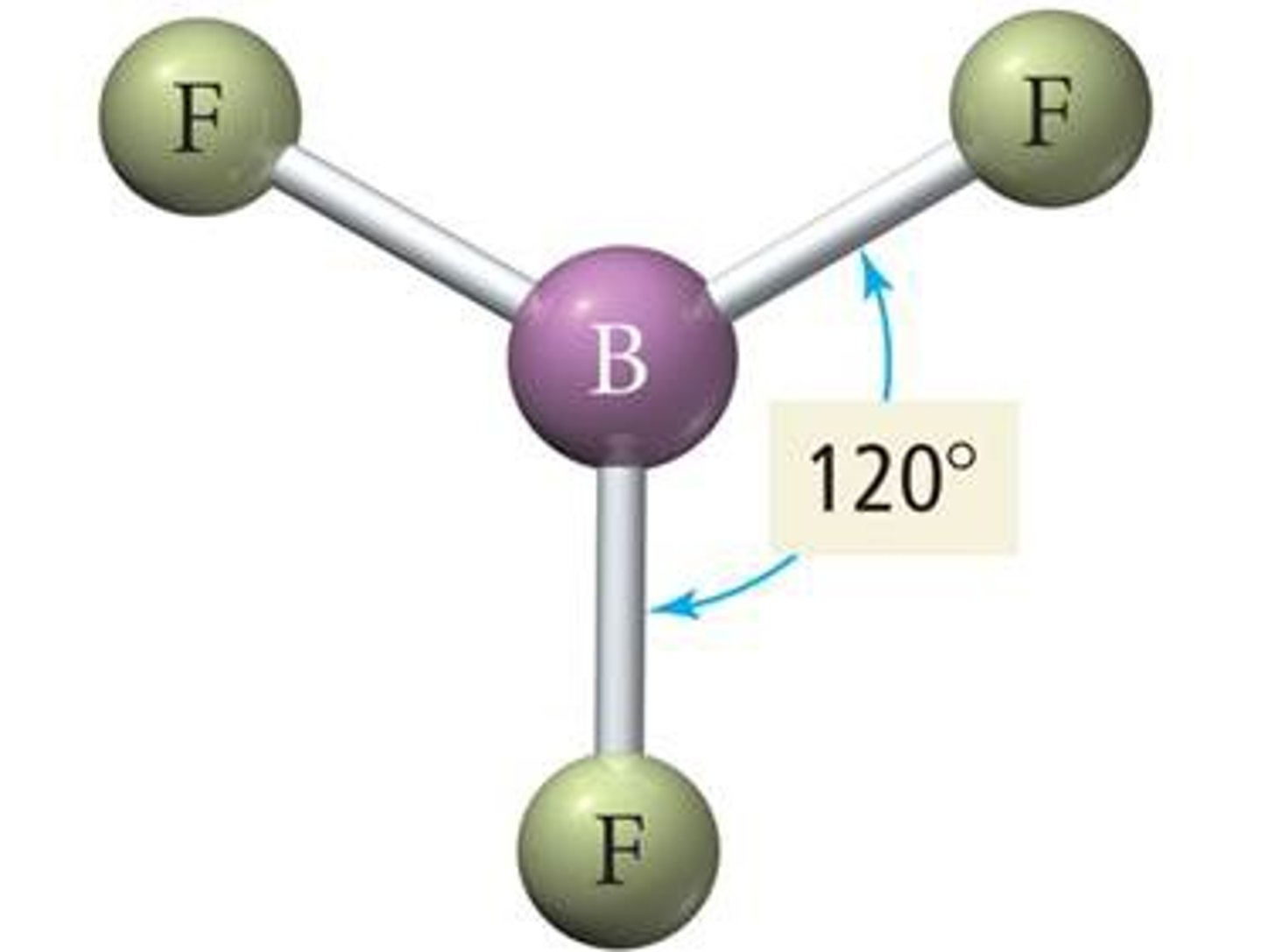
3 groups around central atom
trigonal planar (120)
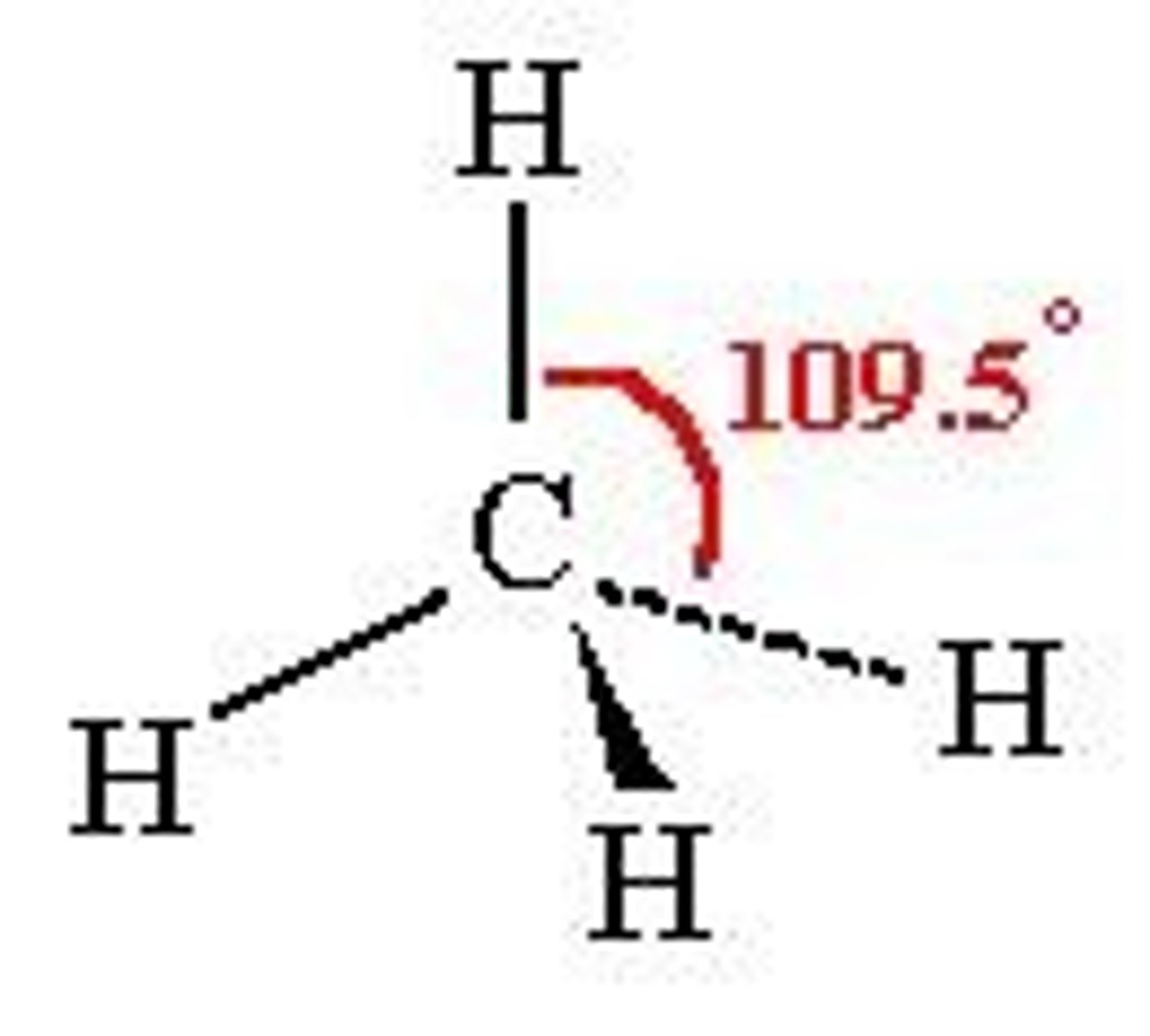
4 groups around the central atom
tetrahedral (109.5)
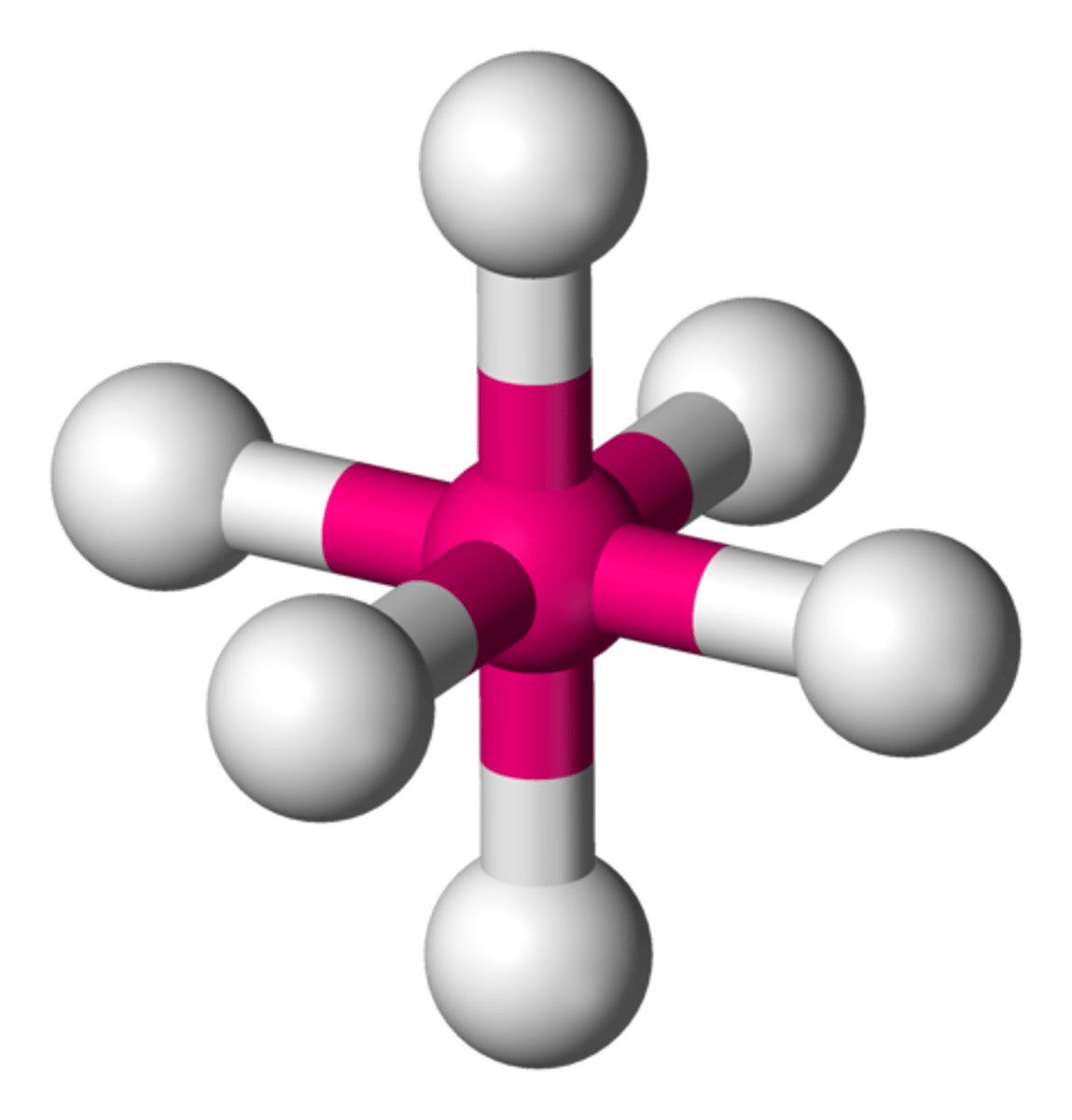
5 groups around central atom
trigonal bipyramidal (90, 120)
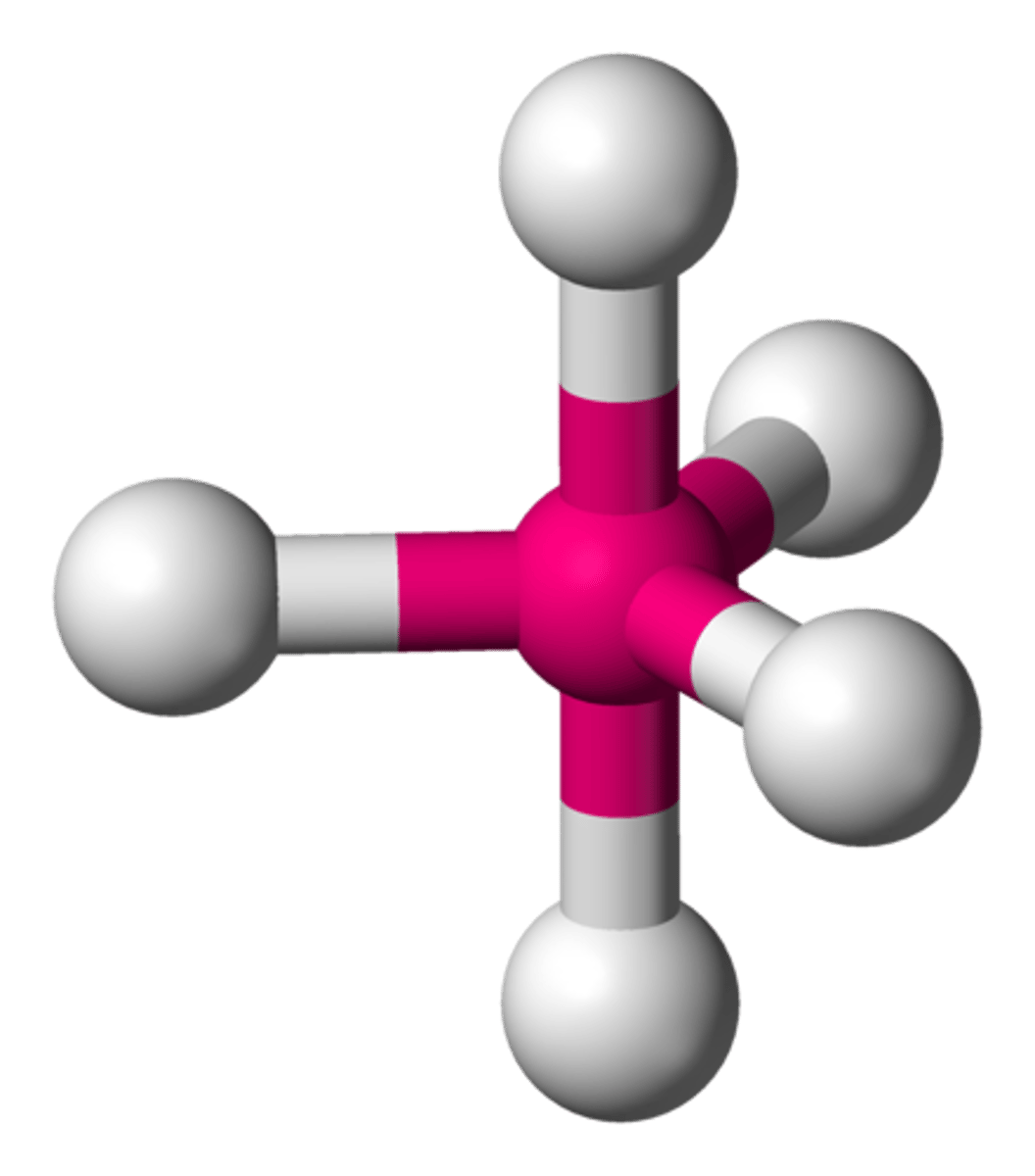
6 groups around central atom
octahedral (90)
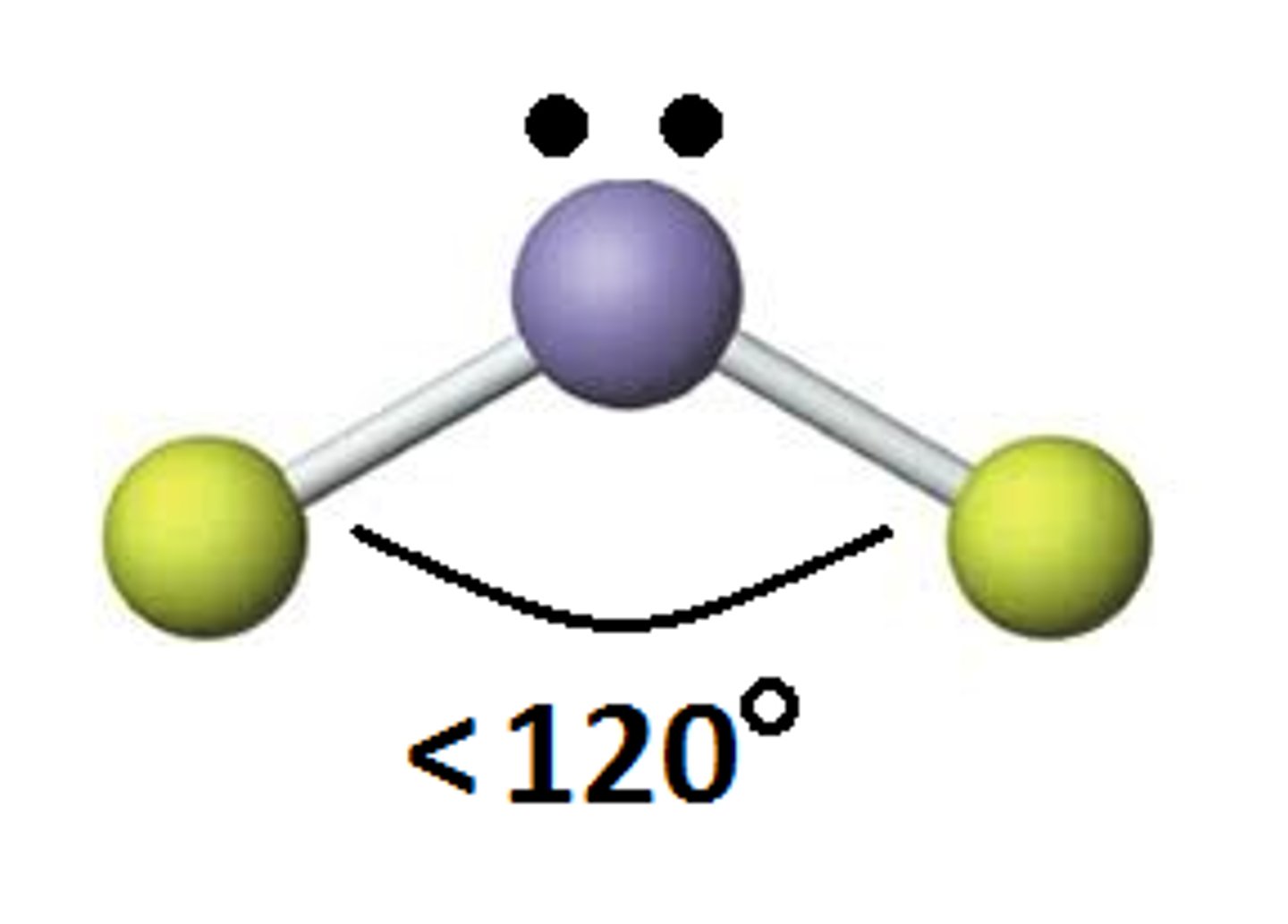
3 electron groups- 1 is lone pair
Trigonal planar, Bent (less than 120)
4 groups- 1 is a lone pair
tetrahedral, Trigonal Pyramidal (107)

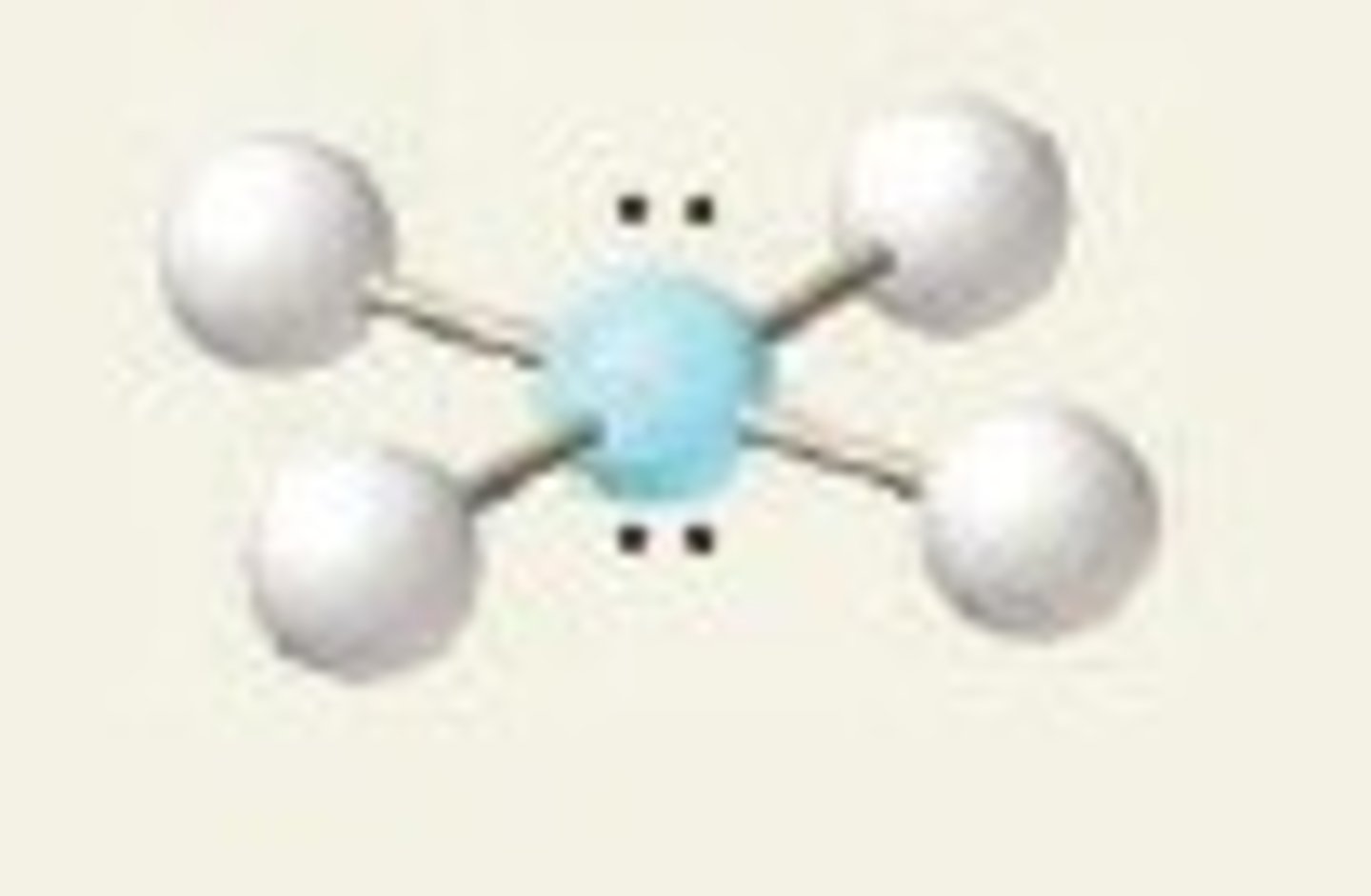
4 groups- 2 groups are lone pairs
Tetrahedral, bent (105)
5 groups- 1 is a lone pair
Trigonal bipyramidal, Seesaw (101.5, 173.1)
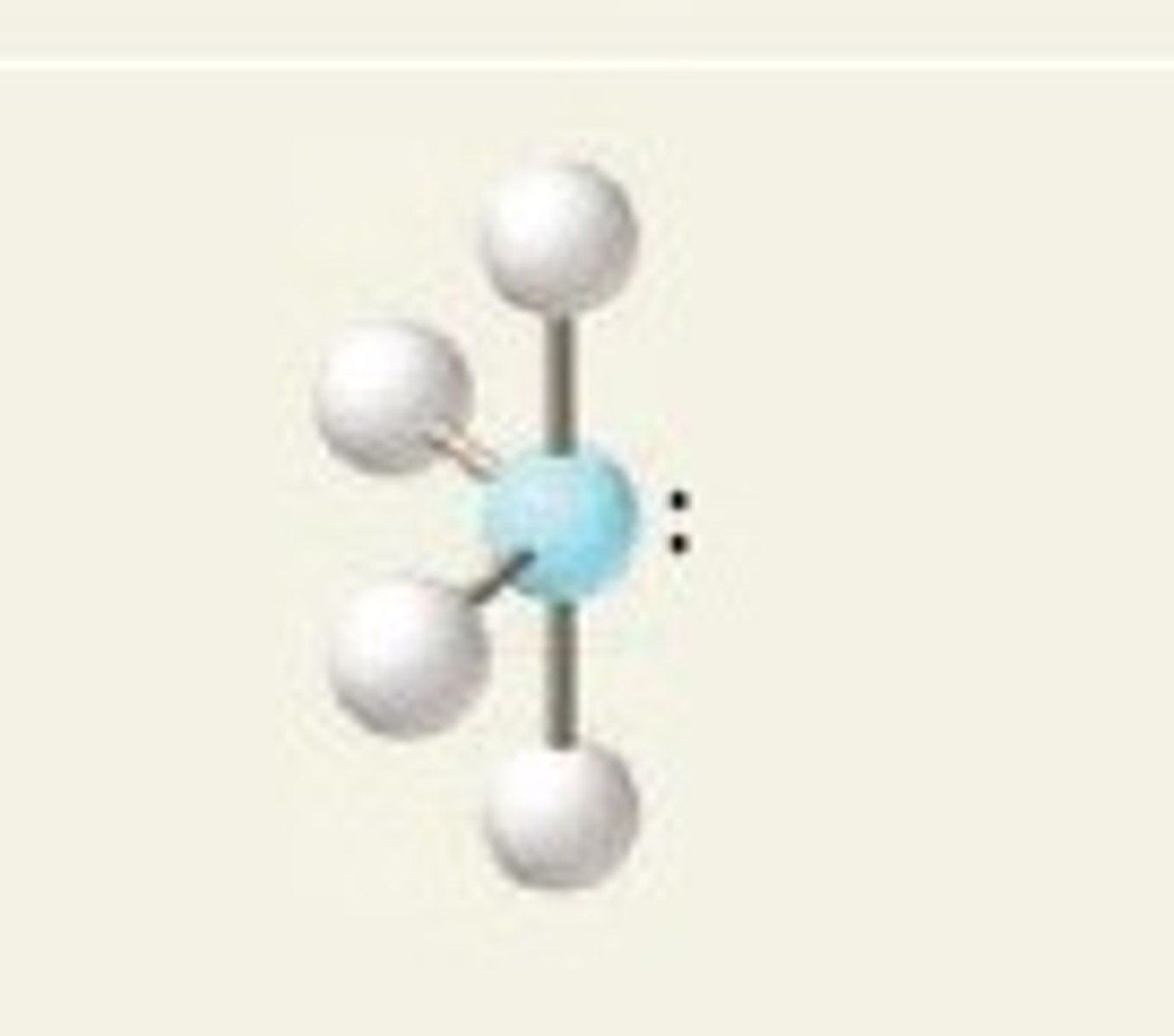
5 groups- 2 groups are lone pairs
Trigonal bipyramidal, T-shaped