AP Bio Unit 7 - packet vocab
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Biography
the geographic distribution of species
During Darwin’s studies he proposed..
the idea of descent w modification, which is the modern def of evolution
Evolution
change in the genetic makeup of a population over time; descent of modification
To explain the pattern of descent w modification (evolution) he observed, he proposed the idea of..
natural selection
Natural selection is…
a process in which individuals that have certain traits tend to survive and reproduce at HIGHER rates than other individuals bc of those traits
Natural selection acts on phenotypic variations in populations.. and
some phenotypes increase or decrease an organims’s fitness ( ability to survive and reproduce )
the theory of natural selection is based on 2 reasons…
traits are heritable and more offspring are produced than can survive
adaptations
inherited characteristics of organisms that enhance their survival and reproduction
more offspring are produced than survive means..
competition will occur, traits that lead to survival accumulate in a population as populations evolve NOT INDIVIDUALS
natural and artificial selection leads to..
evolutionary change
population
a group of individuals that of the same species that live in the same area and interbreed to produce fertile offspring
gene pool
a populations genetic makeup that consists of all copies of every allele type
if there is only one allele present for a particular locus in a population then it is..
fixed
many fixed alleles =
less genetic diversity
micro evolution
small scale genetic changes in a population
evolution is driven by random occurrences like
mutations, genetic drift, gene flow, natural selection
mutations can result in genetic variation and can
form new alleles
genetic drift def
chance events that cause a change in allele frequency from one generation to the next
genetic drift!
most significant to SMALL populations
can lead to a loss of genetic variation
can cause harmful alleles to become fixed
does NOT produce adaptations
two types : bottleneck and founder
bottleneck effect
large population is drastically reduced by a natural disaster
some alleles may become overrepresented, underrepresented, or absent
founder effect
few individuals become isolated from a large population and establish a new small population w a gene pool that differs from a large population ( lose genetic diversity)
gene flow
transfer of alleles into or out of a population due to fertile individuals or gametes
alleles can be transferred between populations
reproductive success is measured by
relative fitness
directional selection
selection towards ONE extreme phenotype
stablizing selection
selection towards the mean and against extreme phenotypes
disruptive selection
selection against MEAN ONLY, both extreme phenotypes have the highest relative fitness
sexual selection
species w showy traits (peacocks)
Hardy Weinberg
determines what the genetic makeup of the population would be if it were NOT evolving, then its compared to actual data
if there are no differences, then the population is NOT evolving
Hardy Weinberg principle
frequencies of alleles and genotypes in a population will remain constant w mendelian segregation and recombination of alleles are active
five conditions of Hardy Weinberg equilibrium
no mutations, random mating, no natural selection, extremely large population, no gene flow
if any of that happens the micro evolution occurs
p and q
allele frequencies
p² and q²
individual organisms
primary sources of evidence
fossil record, comparative morphology, biogeography
fossil record
gives a visual of evolutionary change over time ; examined by carbon 14 decay
comparative morphology
analysis of the structure of living and extinct organisms
homology
characteristics in related species that have similarities even if the functions differ
embryonic homology
many species have similar embryonic development
vestigial structures
structures that are conserved even though they are no longer have a use
molecular homology
many species share similar DNA and amino acid sequences
homologous structures
characteristics that are similar in 2 species bc they share a common ancestor
analogous structures
structures that are similar but have separate evolutionary origins (ex. wings in bats and bees)
convergent evolution
similar adaptations that have evolved in distantly related organisms due to similar environments
structural evidence indicates common ancestry of all eukaryotes
many fundamental and cellular features and processes are conserved across organisms
cellular examples: membrane bound organelles, linear chromosomes, INTRONS in genes
biogeography
the distribution of animals and plants geographically
systematics
classification of organisms and determining their evolutionary relationships
taxonomy
naming and classifying species
phylogenetics
hypothesis of evolutionary history
to determine evolutionary relationships, scientists use..
fossil records, DNA, proteins, homologous structures
phylogenytic trees
diagrams that represent the evolutionary history of a group of organisms similar to cladograms, BUT the trees show the amount of change over time measured by fossils
line of cladogram
reps a lineage
branching point on cladogram
is a node
nodes rep…
common ancestors
nodes and all branches
clades
species in a clade have..
shared derived features
root…
common ancestor of the species
unbranched
basal taxon
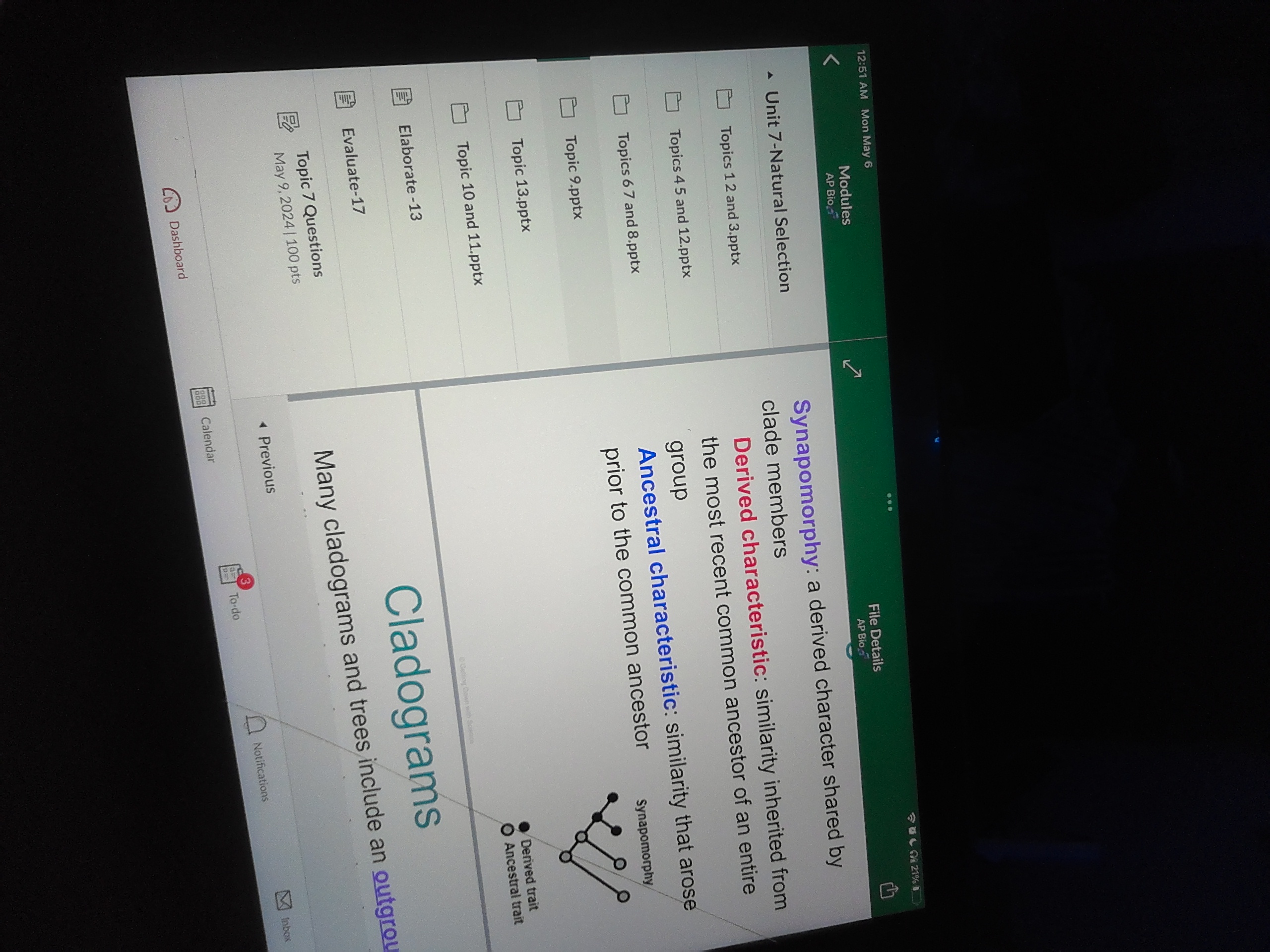
synapomorphy
a derived characteristic shared by clade members
derived characteristic
similarity inherited from the most recent common ancestor of an entire group
ancestral characteristic
similarity that arose prior to the common ancestor
monophyletic group
includes the most common ancestor of the group and all descendants (clade)
paraphyletic group
includes the most common ancestor of the group, BUT NOT ALL THE DESCENDANTS
polyphyletic group
does not include the most common ancestor of all members of the group
if there are conflicts use the principle of parsimony..
uses the hypothesis that requires the fewest assumptions (DNA changes)
species
a group able to interbreed and produce viable fertile offspring
speciation ( occurs due to reproductive isolation )
formation of new species; results in diversity of life forms
geography has an impact on what
…speciation
allopatric
physical barrier that divides population, or small population is separated from main population
populations are geographically isolated, and prevents gene flow
symbatric
a new species evolves while still inhabiting the same geographic region as ancestral species via the exploitation of a new niche
prezygotic barriers (habitat, temporal, behavioral, mechanical, gametic isolation)
prevents mating or hinders fertilization
habitat isolation
species live in diff areas or they occupy different habitats within the same area
temporal isolation
species breed at diff times of day, year, or season
behavioral isolation
unique behavioral patterns and rituals separate species
mechanical isolation
the reproduction anatomy of one species doesn’t fit w the anatomy of another species
gametic isolation
proteins on the surface of gametes don’t allow for the egg and sperm to fuse
postzygotic barriers (reduced hybrid viability, reduced hybrid fertility, hybrid breakdown)
prevent a hybrid zygote from developing into a viable fertile adult
reduced hybrid viability
the genes of different parent species may interact in ways that impair the hybrid’s development or survival
reduced hybrid fertility
a hybrid can develop into a healthy adult, but it is sterile - usually results due to differences in number of chromosomes between parents
hybrid breakdown
the hybrid of the first generation may be fertile, but when they mate w a parent species or one another, their offspring is sterile (f2 )
micro-evolution is the change of…
allele frequencies within a species or population (natural and sexual selection, genetic drift, gene flow)
macro evolution
large evolutionary patterns, extinctions, adaptive radiation
stasis
no change over long periods of time
Adaptive radiation is
if a new habitat or niche becomes available, species can diversify rapidly
punctuated equilibrium
when evolution occurs rapidly after a long period of stasis
gradualism
when evolution occurs slowly over thousands of years
convergent
two different species develop similar traits despite having def ancestors
divergent
groups w the same common ancestor evolve and accumulate differences resulting in the formation of a new species
early earth contained inorganic molecules, that couldve been synthesized….
organic molecules due to free energy and ABUNDANT OXYGEN.. or meteorites
Oparin and Haldane hypothesized that early earth was primarily composed of….
hydrogen
methane
ammonia
water
stanley miller and Harold urey tested the hypothesis in their lab and as a result they
found organic compounds and amino acids formed
stanley miller and Harold urey hypothesized that the organic molecules that formed served as the
buliding blocks for macromolecules
RNA world hypothesis
proposes that RNA could have been the earliest genetic material, and explains the pre-cellular stage of life