[16 & 17] CMSC 173 - User Experience
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Usability
refers to ensuring that interactive products are easy to learn, effective to use, and enjoyable from the person’s perspective
Usability Goals
Effective to Use (effectiveness)
Efficient to Use (efficiency)
Safe to Use (safety)
Having Good Utility (utility)
Easy to Learn (learnability)
Easy to Remember How to Use (memorability)
Enjoyable to Use (satisfaction)
Effectiveness
“Is the product capable of allowing people to carry out their work efficiently, access the information that they need, or buy the goods that they want?”
Efficiency
“How many steps does it take to complete a task?”
How does storing a person’s personal details make it more efficient?”
Safety
“What is the range of errors that are possible using the product, and what measures are there to permit someone to recover easily from them?”
Utility
“Does the product provide an appropriate set of functions that will enable them to carry out all of their tasks in the way they want to do them?”
Learnability
“Is it possible for someone to work out basic use of the product by exploring the interface and trying certain conditions?”
“How hard will it be to master the product in this way? Are additional learning tools needed?”
Memorability
"What types of interface support have been provided to help someone remember to carry out tasks, especially for ones they use infrequently?”
Satisfaction
“What are the mean, median, and mode values on the CSAT (Customer Satisfaction Score) scale?”
“What proportion of users say they are highly satisfied with the product?”
“How many people are still satisfied after using the product for six months?”
User Experience
covers a range of emotions and felt experiences
includes desirable and undesirable aspects
Usability vs. User Experience
objective
concerned with how useful or productive a system is
Usability vs. User Experience
subjective
how a system feels to someone
Seven Design Matters in UX
display design
view (window) management
animation
webpage design
color
nonanthropomorphic design
error messages
Display Design
Ensure that any data that a user needs, at any step in a transaction sequence, are available for display.
Display data to users in directly usable forms; do not require that users convert displayed data.
Maintain a consistent format for any particular type of data display from one display to another.
Use short, simple sentences.
Use affirmative statements rathe than negative statements.
Adopt a logical principle by which to order lists; where no other principle applies, order lists alphabetically.
View (Window)
Important coordinations that might be supported by the interface designers include:
synchronized scrolling
hierarchical browsing
opening/closing of dependent windows
saving/opening of window state
tabbed browsing
tiled or overlapping windows
ribbon interface
design patterns
start menus
Animation
keeping user oriented during transitions
indicating an affordance, inviting interaction
entertaining
indicating background activity (e.g., progress bar)
storytelling
alerting
providing a virtual tour (e.g., for architectural designs)
explaining a process
conveying uncertainty and randomness
Webpage Design
Top 10 Mistakes of Web-based Presentation of Information (from Tullis, 2005):
burying information too deep in a website
overloading pages with too much material
providing awkward or confusing navigation
putting information in unexpected places on the page
not making links obvious and clear
presenting information in bad tables
making text so small that many users cannot read it
using color combinations for test that many users cannot read
using bad forms
hiding (or not providing) features that could help users
Error Messages Guidelines for the End Product
Be as specific and precise as possible. Determine necessary, relevant error messages.
Be constructive. Indicate what the user needs to do.
Use a positive tone. Avoid condemnation. Be courteous.
Choose user-centered phrasing. State the problem, cause, and solution.
Consider multiple levels of messages. State brief, sufficient information to assist with the corrective action.
Maintain consistent grammatical forms, terminology, and abbreviations.
Maintain consistent visual format and placement.
Error Messages Guidelines for the Development Process
Increase attention to message design.
Establish quality control.
Development and enforce guidelines.
Carry out usability tests.
Consider conducting “error handling” reviews.
Record the frequency of occurrence for each message.
Color Theory
the study of how colors work together and how they affect our emotions and perceptions
Primary Colors
yellow
red
blue
Secondary Colors
created by mixing two primary colors:
orange
green
purple
Tertiary Colors
created by mixing both primary and secondary colors:
yellow-orange
red-orange
red-purple
Hue
the attribute of color that distinguishes it as red, blue, green, or any other specific color on the color wheel
Value
represents a color’s relative lightness or darkness or grayscale and it’s crucial for creating contrast and depth in visual art
Saturation
or chroma or intensity
refers to the purity and vividness of a color, ranging from fully saturated (vibrant) to desaturated (grayed)
Color Schemes
monochromatic
analogous
complementary
split-complementary
triadic
tetradic
square
Monochromatic
take one hue and create other elements from difference shades and tints of it
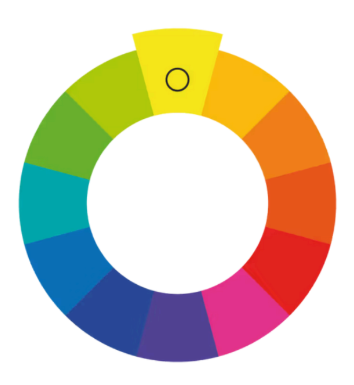
Analogous
use three colors located beside one another on the color wheel
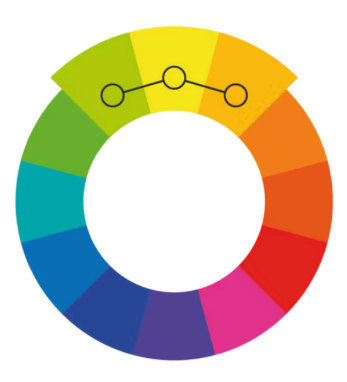
Complementary
use “opposite color” pairs to maximize contrast
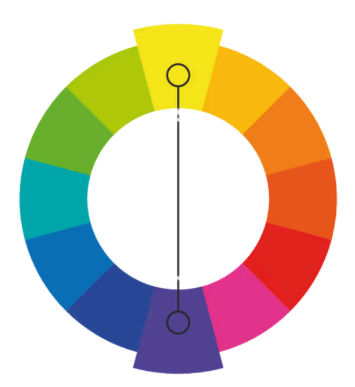
Split-Complementary
or Compound Harmony
add colors from either side of your complementary color pair to soften the contrast
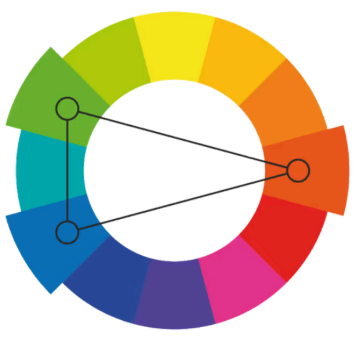
Triadic
take three equally distant colors on the color wheel (i.e., 120° apart)
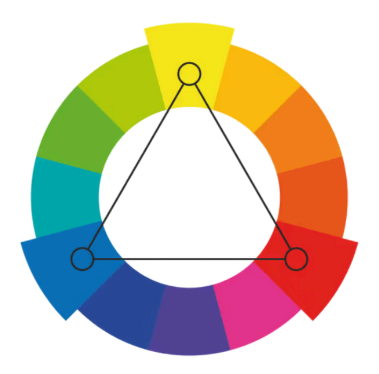
Tetradic
take four colors that are two sets of complementary pairs and choose one dominant color
Square
a variant of tetradic
you find four colors evenly spaced on the color wheel (i.e., 90° apart)
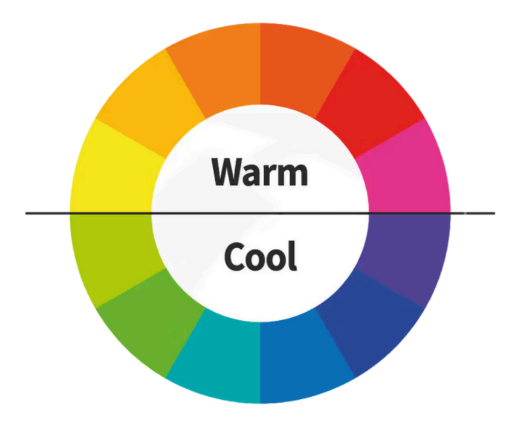
Color Temperature
[The 60-30-10 Rule] neutral
one color—generally something fairly _____ (either literally or psychologically)—makes up 60% of the palette
[The 60-30-10 Rule] complementary
_____ color makes up 30% of the palette
[The 60-30-10 Rule] accent
a third color is used as an _____ for the remaining 10% of the design
Non-anthropomorphic Guidelines
Be cautious is presenting computers as people, either with synthesized or cartoon characters.
Design comprehensible, predictable, and user-controlled interfaces.
Use appropriate humans for audio or video instructions or guides.
Use cartoon characters in games or children’s software, but avoid them elsewhere.
Provide user-centered overviews for orientation and closure.
Do not use pronoun / when the computer responds to human actions.
Use you to guide users, or just state facts.
The 4 Degrees of Anthropomorphism
1st Degree: Courtesy
2nd Degree: Reinforcement
3rd Degree: Roleplay
4th Degree: Companionship
1st Degree: Courtesy
in human-AI interactions, refers to using polite language (“please” or “thank you”) or greetings (“hello” or “good morning”) when interacting with generative AI
Emotional Connection: low—brief and superficial; polite but to the point
Functionality of Behavior: low
2nd Degree: Reinforcement
refers to praising the chatbot when it produces satisfactory responses (or scolding it when it does wrong)
Emotional Connection: low—more than superficial courtesies but still relatively topical
Functionality of Behavior: medium
3rd Degree: Roleplay
occurs when users ask the chatbot to assume the role of a person with specific traits or qualifications
Emotional Connection: medium—there is a deeper human-AI connection, as the user assumes that the bot will be able to correctly play the role indicated in a prompt and behave like a human in that capacity
Functionality of Behavior: highly purpose-driven
4th Degree: Companionship
refers to perceiving and relying on the AI as an emotional being, capable of sustaining a human-like relationship
Emotional Connection: high—the user develops a deep, empathetic connection with AI, that often stimulates or replaces a real-life human; this connection may even supersede the depth of connection that user has in the real world
Functionality of Behavior: high